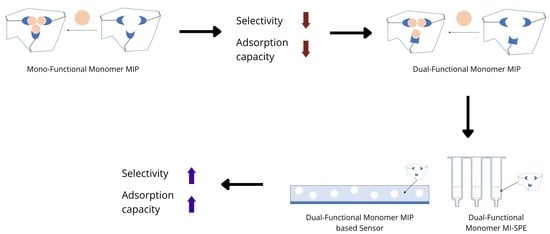
Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs and Their Comparison to Mono-Functional Monomer MIPs for SPE and as Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dual-Functional Monomer Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction (MI-SPE)
2.1. Polymerization Techniques of Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs as an MI-SPE Sorbent
2.2. Dual-Functional Monomer MIP Application as an SPE Sorbent
- Dual-Functional Monomer MIP for Boc-L-tryptophan
- b.
- Dual-Functional Monomer MI-SPE for Ciprofloxacin and Sarafloxacin Antibiotics
- c.
- Dual-Functional Monomer MI-SPE for Natural Compound Myricetin and Glycyrrhizic Acid
- d.
- Dual-Functional Monomer MI-SPE for Starch
- e.
- Dual-Functional Monomer MI-SPE for Environmental Samples
| No | Monomer | Template Molecule | Qmax (mg/g) | IF | % Recovery | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM | DM | SM | DM | |||||
| 1 | MAA and 2VP | Boc-L-Tryptophan | 0.115 (2VP) | 0.058 | 2.35 (2VP) | 4.35 | - | [32] |
| 0.035 (MAA) | 1.9 (MAA) | |||||||
| 2 | MAA and 2VP | Ciprofloxacin | 1.12 (2VP) | 2.4 | 1.51 (2VP) | 1.66 | 105% | [50] |
| 1.6 (MAA) | 0.8 (MAA) | |||||||
| 3 | MAA and 2VP | Ciprofloxacin | 4.66 (MAA) | 10.28 | 0.92 (MAA) | 2.55 | 65.97–119.26% | [10] |
| 4 | MAA and 4VP | Sarafloxacin | 51.64 (4VP) | 52.80 | 4.94 (4VP) | 5.52 | 94.0–101.3% | [76] |
| 48.56 (MAA) | 5.4 (MAA) | |||||||
| 5 | 4VP and GMA | Myricetin | 3.42 (4VP) | 11.8 | - | 4.9 | 79.82–84.32% | [34] |
| 6 | β-CD and MAA | Glycyrrhizic Acid | 75.4 (β-CD) | 69.3 | 1.24 (β-CD) | 3.77 | 71.5–77.5% | [49] |
| 69.1 (MAA) | 1.41 (MAA) | |||||||
| 7 | APBA and AMPA | Polysaccharide (starch) | 8.89 (APBA) | 13.08 | 1.63 (APBA) | 2.22 | - | [33] |
| 4.62 (AMPA) | 1.39 (AMPA) | |||||||
| 8 | MAA and 4VP | Methyl parathion | 1.25 (4VP) | 2 | 4.4 (4VP) | 5 | 81.1–87.0% | [96] |
| 3.5 (MAA) | 1.4 (MAA) | |||||||
3. Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs as Detection Elements in Sensors
3.1. Polymerization Techniques of Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs as Recognition Elements in Sensors
3.2. Dual−Functional Monomer MIP Applications as Recognition Elements in Sensors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-VP | 2-vinylpyridine |
| 4-VP | 4-vinylpiridine |
| AMPA | 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulphonic acid |
| APBA | 3-aminobenzeneboronic acid |
| CIP | Ciprofloxacin |
| CIP-MIP | Ciprofloxacin-based Molecularly Imprinted Polymer |
| CV | Cyclic Voltammetry |
| DM | Double Monomer |
| EGDMA | Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate |
| FluMa | Fluorescein Methacrylate |
| GC | Gas Chromatography |
| GMA | Glycidyl Methacrylate |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| IA | Itaconic Acid |
| IF | Imprinting Factor |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| L-Trp | L-tryptophan |
| MAA | Methacrylic Acid |
| MIP | Molecularly Imprinted Polymer |
| MI-SPE | Molecularly Imprinted Solid-phase extraction |
| MP | Methyl Parathion |
| PAH | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon |
| RAM-MIPs | Restricted Access Media Molecularly Imprinted Polymers |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| SAR | Sarafloxacin |
| SM | Single Monomer |
| SPE | Solid-phase extraction |
| SPR | Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| β-CD | β-cyclodextrin |
References
- Marć, M.; Wieczorek, P.P. Introduction to MIP Synthesis, Characteristics and Analytical Application. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 86, pp. 1–15. ISBN 9780444642660. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular Imprinting: Perspectives and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, L.; Erny, G.L.; Santos, L.; Alves, A. Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers to the Analysis and Removal of Personal Care Products: A Review. Talanta 2016, 146, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulff, G.; Vietmeier, J. Enzyme-Analogue Built Polymers, 26†. Enantioselective Synthesis of Amino Acids Using Polymers Possessing Chiral Cavities Obtained by an Imprinting Procedure with Template Molecules. Die Makromol. Chem. 1989, 190, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagishi, T.; Klotz, I.M. Macromolecule-Small Molecule Interactions; Introduction of Additional Binding Sites in Polyethyleneimine by Disulfide Cross-Linkages. Biopolymers 1972, 11, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, S.; Azar, P.A.; Husain, S.W.; Rajabi, H.R. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Spherical and Uniform Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Nanobeads as Efficient Sorbent for Selective Extraction of Rosmarinic Acid from Plant Matrix. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonipour, F.; Rajabi, H.R. Development of Flow Injection Analysis-Solid Phase Extraction Based on Ion Imprinted Polymeric Nanoparticles as an Efficient and Selective Technique for Preconcentration of Zinc Ions from Aqueous Solution. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 8828–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haginaka, J. Monodispersed, Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Affinity-Based Chromatography Media. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 866, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, L.; Yao, Y.; Ping, J.; Ying, Y. Recent Advances in Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors for Antibiotics Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Vuong Bui, N.T.; Kanhounnon, W.G.; Vu Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, T.V.A.; Nguyen, H.M.; Do, M.H.; Badawi, M.; Thach, U.D. Co-Precipitation Polymerization of Dual Functional Monomers and Polystyrene: Co-Divinylbenzene for Ciprofloxacin Imprinted Polymer Preparation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 34281–34290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, R.; Na, G.; Yan, Q.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z. Preparation and Application of a Molecularly Imprinted Monolith for Specific Recognition of Domoic Acid. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, M.B.; Shamsipur, M.; Dehdashtian, S.; Rajabi, H.R. Development of a Selective and Sensitive Voltammetric Sensor for Propylparaben Based on a Nanosized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer–Carbon Paste Electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 36, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarezadeh, A.; Rajabi, H.R.; Sheydaei, O.; Khajehsharifi, H. Application of a Nano-Structured Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as an Efficient Modifier for the Design of Captopril Drug Selective Sensor: Mechanism Study and Quantitative Determination. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheydaei, O.; Khajehsharifi, H.; Rajabi, H.R. Rapid and Selective Diagnose of Sarcosine in Urine Samples as Prostate Cancer Biomarker by Mesoporous Imprinted Polymeric Nanobeads Modified Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gao, Y.; Ji, Z.; Zhu, L.-B.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, Y.; Jin, D.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, W.-W. Dual Functional Molecular Imprinted Polymer-Modified Organometal Lead Halide Perovskite: Synthesis and Application for Photoelectrochemical Sensing of Salicylic Acid. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 9356–9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, W.J.; Yang, S.H.; Ali, F. Molecular Imprinted Polymers for Separation Science: A Review of Reviews. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Moral, N.; Mayes, A.G. Comparative Study of Imprinted Polymer Particles Prepared by Different Polymerisation Methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 504, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratiwi, R.; Megantara, S.; Rahayu, D.; Pitaloka, I.; Hasanah, A.N. Comparison of Bulk and Precipitation Polymerization Method of Synthesis Molecular Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction for Atenolol Using Methacrylic Acid. J. Young Pharm. 2018, 11, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Dwi Utari, T.N.; Pratiwi, R. Synthesis of Atenolol-Imprinted Polymers with Methyl Methacrylate as Functional Monomer in Propanol Using Bulk and Precipitation Polymerization Method. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Geng, X.; Liu, Y.; Long, H.; Du, J. A Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Determination of Luteolin. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 842, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-Phase Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Li, H. Bioinspired Synthesis of PDA@GO-Based Molecularly Imprinted Nanocomposite Membranes Assembled with Dendrites-like Ag Microspheres for High-Selective Adsorption and Separation of Ibuprofen. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 553, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Nur, Z.; Piletska, E.V.; Yimit, O.; Piletsky, S.A. Rational Design of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer: The Choice of Cross-Linker. Analyst 2012, 137, 2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaran, A.M.; Mohammadi, N.; Javanbakht, M.; Akbari-Adergani, B. Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction for Selective Trace Analysis of Trifluoperazine. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hroboňová, K.; Lomenova, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Stationary Phase for HPLC Separation of Phenylalanine Enantiomers. Mon. Fur Chem. 2018, 149, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, C.; Andac, M.; Bereli, N.; Say, R.; Henden, E.; Denizli, A. Highly Selective Ion-Imprinted Particles for Solid-Phase Extraction of Pb2+ Ions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 2464–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, E.; Marcé, R.M.; Cormack, P.A.G.; Sherrington, D.C.; Borrull, F. Synthesis and Application of an Oxytetracycline Imprinted Polymer for the Solid-Phase Extraction of Tetracycline Antibiotics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 552, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moein, M.M.; Javanbakht, M.; Akbari-adergani, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Cartridges Coupled On-Line with High Performance Liquid Chromatography for Simple and Rapid Analysis of Dextromethorphan in Human Plasma Samples. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Qiao, N.; Liu, H.; Du, J.; Wang, N.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Fast and Efficient Removal of Copper Using Sandwich-like Graphene Oxide Composite Imprinted Materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 326, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Dang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Ye, B.C. A Robust Electrochemical Sensing of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Using Bifunctional Monomer and Its Application in Detection of Cypermethrin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 127, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, M.; Katsuki, H.; Fukutomi, C.; Takahashi, M.; Motomura, M.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Isohama, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Kume, T.; et al. HMGB1 Inhibitor Glycyrrhizin Attenuates Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Injury in Rats. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstrbm, O.; Andersson, L.I.; Mosbach, K. Recognition Sites Incorporating Both Pyridinyl and Carboxy Functionalities Prepared by Molecular Imprinting. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 7562–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Huang, W.; Yang, X.; Yao, L.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Dual Functional Monomer Surface Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres for Polysaccharide Recognition in Aqueous Solution. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2800–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, M.; Fu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, K.; Xia, Z.; Gao, D. Novel Dual Functional Monomers Based Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Extraction of Myricetin from Herbal Medicines. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1097–1098, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimpe, K.M.; Nomngongo, P.N. Current Sample Preparation Methodologies for Analysis of Emerging Pollutants in Different Environmental Matrices. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L. Synthesis of Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Adsorbents for Solid Phase Extraction of Aminoglycosides Antibiotics from Environmental Water Samples. Talanta 2020, 208, 120385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Niu, L.; Yu, W.; Yang, C.; Fang, M.; Lv, H.; et al. Application of Solid-Phase Extraction Based on Magnetic Nanoparticle Adsorbents for the Analysis of Selected Persistent Organic Pollutants in Environmental Water: A Review of Recent Advances. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 44–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierucka, M.; Biziuk, M. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction in Preparing Biological, Environmental and Food Samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpupa, A.; Dinc, M.; Mizaikoff, B.; Nomngongo, P.N. Exploration of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (Mips) as an Adsorbent for the Enrichment of Trenbolone in Water. Processes 2021, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BelBruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Bagheri, A.R.; Guo, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Strategies of Molecular Imprinting-Based Solid-Phase Extraction Prior to Chromatographic Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 128, 115923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinhua, L.; Yingying, W.; Lingxin, C. Advances of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Solid Phase Extraction. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2013, 31, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizkarguenaga, E.; Ros, O.; Iparraguirre, A.; Navarro, P.; Vallejo, A.; Usobiaga, A.; Zuloaga, O. Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with Large Volume Injection-Programmable Temperature Vaporization–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry for the Multiresidue Determination of Priority and Emerging Organic Pollutants in Wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1247, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, M.; Sobek, H.; Mizaikoff, B. Advances in Imprinting Strategies for Selective Virus Recognition a Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Stöver, H.D.H. Synthesis of Monodisperse Poly(Divinylbenzene) Microspheres. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1993, 31, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, X. Precipitation Polymerization. In Encyclopedia of Polymeric Nanomaterials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 2108–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, O. Handbook of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Handbook of Molecularly; Smithers Rapra Technology Ltd.: Shawbury, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Adumitrăchioaie, A.; Tertiş, M.; Cernat, A.; Săndulescu, R.; Cristea, C. Electrochemical Methods Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Drug Detection. A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 2556–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Du, W.; Guo, P.; Wu, N.; Du, K.; Xu, C.; Luo, Z.; Chang, R.; Zeng, A.; Jing, W.; et al. Molecularly Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction Using Bismethacryloyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Methacrylic Acid as Double Functional Monomers for Selective Analysis of Glycyrrhizic Acid in Aqueous Media. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thach, U.D.; Thi, H.H.N.; Pham, T.D.; Mai, H.D.; Nhu-Trang, T.T. Synergetic Effect of Dual Functional Monomers in Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Preparation for Selective Solid Phase Extraction of Ciprofloxacin. Polymers 2021, 13, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Tavengwa, N.T.; Chimuka, L. Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Solid-Phase Extraction of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Analgesics from Environmental Waters and Biological Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Karimi, M. Novel Developments and Trends of Analytical Methods for Drug Analysis in Biological and Environmental Samples by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Su, X.; Wang, T. Advancements of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in the Food Safety Field. Analyst 2016, 141, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; He, C.; Liu, S. Recent Advances and Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Solid-phase Extraction for Real Sample Analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 274–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machyňáková, A.; Lhotská, I.; Hroboňová, K.; Šatínský, D. On-Line Coupling of Molecularly Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction with Liquid Chromatography for the Fast Determination of Coumarins from Complex Samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhotská, I.; Kholová, A.; Machyňáková, A.; Hroboňová, K.; Solich, P.; Švec, F.; Šatínský, D. Preparation of Citrinin-Selective Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Its Use for on-Line Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2395–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Song, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, H.; Li, Y. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Double Templates for Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Melamine and Dicyandiamide in Dairy Products. Talanta 2015, 134, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luliński, P.; Bamburowicz-Klimkowska, M.; Dana, M.; Maciejewska, D. Development of a Validated Strategy for the Determination of Tryptamine in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid in the Presence of Competitors Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luliński, P.; Bamburowicz-Klimkowska, M.; Dana, M.; Szutowski, M.; Maciejewska, D. Efficient Strategy for the Selective Determination of Dopamine in Human Urine by Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Bhatia, T.; Singh, A.; Saxena, P.N.; Kesavchandran, C.; Mudiam, M.K.R. Application of Nano-Sized Multi-Template Imprinted Polymer for Simultaneous Extraction of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Metabolites in Urine Samples Followed by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 985, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicario, A.; Aragón, L.; Wang, C.C.; Bertolino, F.; Gomez, M.R. A Simple and Highly Selective Molecular Imprinting Polymer-Based Methodology for Propylparaben Monitoring in Personal Care Products and Industrial Waste Waters. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Wen, H.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Tang, C.; Yang, J. Preparation and Evaluation of Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as a Potential Sorbent for Solid Phase Extraction of Imidazole Fungicides from River Water. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1586, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.-Q.; He, X.-P.; Wang, J.-T. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer as Efficient Sorbent of Solid-Phase Extraction for Determination of Gonyautoxin 1,4 in Seawater Followed by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 5737–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golker, K.; Karlsson, B.C.G.; Olsson, G.D.; Rosengren, A.M.; Nicholls, I.A. Influence of Composition and Morphology on Template Recognition in Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, D.; Lanni, L.M.; Shimizu, K.D. Importance of Functional Monomer Dimerization in the Molecular Imprinting Process. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6284–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Cheng, G.; Wang, P.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J. Water Compatible Imprinted Polymer Prepared in Water for Selective Solid Phase Extraction and Determination of Ciprofloxacin in Real Samples. Talanta 2019, 200, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, E.; Marcé, R.M.; Cormack, P.A.G.; Sherrington, D.C.; Borrull, F. Direct Determination of Ciprofloxacin by Mass Spectrometry after a Two-Step Solid-Phase Extraction Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turiel, E.; Martín-Esteban, A.; Tadeo, J.L. Molecular Imprinting-Based Separation Methods for Selective Analysis of Fluoroquinolones in Soils. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1172, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zeng, G.; Ma, X. Multi-Templates Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Rapid Separation and Analysis of Quinolones in Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7177–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Row, K.H. Simultaneous Determination of Levofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin in Human Urine by Ionic-Liquid-Based, Dual-Template Molecularly Imprinted Coated Graphene Oxide Monolithic Solid-Phase Extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marestoni, L.D.; Wong, A.; Feliciano, G.T.; Marchi, M.R.R.; Tarley, C.R.T.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T. Semi-Empirical Quantum Chemistry Method for Pre-Polymerization Rational Design of Ciprofloxacin Imprinted Polymer and Adsorption Studies. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2015, 27, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Ma, X.; Xie, X.; Huang, R.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zeng, G.; Fan, Y. Preparation of Dual-Dummy-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Coated Magnetic Graphene Oxide for Separation and Enrichment of Phthalate Esters in Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y. Water-Compatible Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers with Synergy of Bi-Functional Monomers for Enhanced Selective Adsorption of Bisphenol A from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Nano 2016, 3, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Lv, J.; Wang, X.; Zhu, B.; Lou, D. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction of Fluoroquinolones from Water Samples Using Titanium-Based Metal-Organic Framework Functionalized Magnetic Microspheres. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1579, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, L.; Visciano, P.; Stramenga, A.; Colagrande, M.N.; Campana, G.; Scortichini, G.; Migliorati, G.; Compagnone, D. Development and Validation of a Method for the Determination of Quinolones in Muscle and Eggs by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2308–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Gong, B. Preparation of Monodisperse, Restricted-Access, Media-Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using Bi-Functional Monomers for Solid-Phase Extraction of Sarafloxacin from Complex Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1642, 462009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Ma, M.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Hou, J.; Gong, B. Preparation of Monodisperse Magnetic Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Recognition of Lincomycin Hydrochloride in Milk. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2019, 42, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J. Recent Advances in Molecular Imprinting Technology: Current Status, Challenges and Highlighted Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Du, L.; Tao, J.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.; Duan, J. Dynamic Changes of Flavonoids in Abelmoschus Manihot Different Organs at Different Growth Periods by UPLC–MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1059, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survay, N. New Genera of Flavonols and Flavonol Derivatives as Therapeutic Molecules. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zang, W.; Zhao, G. Myricetin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Gastric Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 408, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.-Y.; Chen, X.-Q.; Kang, B.-J.; Qin, Z.-X.; Chen, J.-H.; Hu, R.-D.; Wu, L.-C. Myricetin Protects against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation by Anti-Inflammatory and Anticoagulation Effect. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Efficient Conversion of Myricetin from Ampelopsis Grossedentata Extracts and Its Purification by MIP-SPE. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 945–946, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Peng, J.; Peng, H.; Bu, L.; Pan, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Gong, C.; Tang, Q. Preparation and Evaluation of Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Stationary Phase Columns for High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7951–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganewatta, N.; El Rassi, Z. Monolithic Capillary Columns Consisting of Poly(Glycidyl Methacrylate- Co -Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate) and Their Diol Derivatives with Incorporated Hydroxyl Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes for Reversed-Phase Capillary Electrochromatography. Analyst 2018, 143, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feczkó, T.; Trif, L.; Németh, B.; Horák, D. Silica-Coated Poly(Glycidyl Methacrylate-Ethylene Dimethacrylate) Beads Containing Organic Phase Change Materials. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 641, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H. Ambient Temperature Synthesis of Narrow or Monodisperse, Highly Cross-Linked, and “Living” Polymer Microspheres by Atom Transfer Radical Precipitation Polymerization. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. The Antiviral and Antimicrobial Activities of Licorice, a Widely-Used Chinese Herb. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S.; Hu, C.; Gong, Z.; Jia, L. Antihyperlipidaemic and Hepatoprotective Activities of Acidic and Enzymatic Hydrolysis Exopolysaccharides from Pleurotus Eryngii SI-04. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Jiang, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y. Anti-Tumor and Anti-Virus Activity of Polysaccharides Extracted from Sipunculus Nudus(SNP) on Hepg2.2.15. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Joseph, M.M.; Aravind, S.R.; Unnikrishnan, B.S.; Sreelekha, T.T. The Inhibitory Effect of Anti- Tumor Polysaccharide from Punica Granatum on Metastasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, A.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Qu, X.; Cao, J.; et al. Anti-Metastatic and Anti-Angiogenic Activities of Sulfated Polysaccharide of Sepiella Maindroni Ink. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Row, K.H. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Recognition and Enrichment of Polysaccharides from Seaweed. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 4765–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcheumi, H.L.; Tonle, I.K.; Ngameni, E.; Walcarius, A. Electrochemical Analysis of Methylparathion Pesticide by a Gemini Surfactant-Intercalated Clay-Modified Electrode. Talanta 2010, 81, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Bai, H.; Xie, G.; Xiao, J. Trace Determination of Organophosphorus Pesticides in Environmental Samples by Temperature-Controlled Ionic Liquid Dispersive Liquid-Phase Microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1188, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wei, C.; Tang, Y. Methyl Parathion Imprinted Polymer Nanoshell Coated on the Magnetic Nanocore for Selective Recognition and Fast Adsorption and Separation in Soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebelo, P.; Costa-Rama, E.; Seguro, I.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Natália, M.; Cordeiro, D.S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Environmental Analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 172, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; Nie, J.; Cheng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, J.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Mushtaq, A.; Zhang, H. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers’ Application in Pesticide Residue Detection. Analyst 2018, 143, 3971–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-M.; Du, L.; Ma, Y.-L.; Zhao, Q.-H. A Dual-Functional Cadmium(II) Coordination Polymer as a Luminescent Sensor for Selective Sensing of Iron(III) Ions and Detecting the Temperature. Transit. Met. Chem. 2016, 41, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. A Molecularly Imprinted Copolymer Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Highly Sensitive Detection of L-Tryptophan. Talanta 2020, 206, 120245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, T.; Ahmad, M.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Wei, T. A Recyclable Tetracycline Imprinted Polymeric SPR Sensor: In Synergy with Itaconic Acid and Methacrylic Acid. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 3102–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, A.D.; Jamieson, O.; Crapnell, R.D.; Rurack, K.; Soares, T.C.C.; Mecozzi, F.; Laude, A.; Gruber, J.; Novakovic, K.; Peeters, M. Dual Detection of Nafcillin Using a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Platform Coupled to Thermal and Fluorescence Read-Out. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 5105–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Kan, X. Aptamer and Molecularly Imprinted Polymer: Synergistic Recognition and Sensing of Dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 367, 137433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elaine, A.A.; Krisyanto, S.I.; Hasanah, A.N. Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs and Their Comparison to Mono-Functional Monomer MIPs for SPE and as Sensors. Polymers 2022, 14, 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173498
Elaine AA, Krisyanto SI, Hasanah AN. Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs and Their Comparison to Mono-Functional Monomer MIPs for SPE and as Sensors. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173498
Chicago/Turabian StyleElaine, Angela Alysia, Steven Imanuel Krisyanto, and Aliya Nur Hasanah. 2022. "Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs and Their Comparison to Mono-Functional Monomer MIPs for SPE and as Sensors" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173498
APA StyleElaine, A. A., Krisyanto, S. I., & Hasanah, A. N. (2022). Dual-Functional Monomer MIPs and Their Comparison to Mono-Functional Monomer MIPs for SPE and as Sensors. Polymers, 14(17), 3498. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173498