Assessment of Acute Oral Toxicity of Thiolated Gum Ghatti in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Thiolated Gum Ghatti
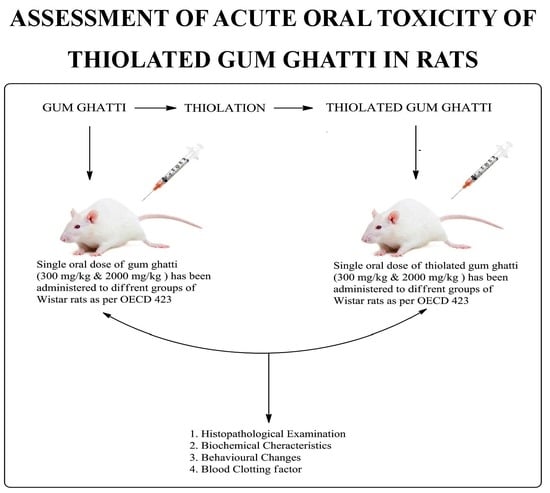
2.4. Experimental Procedure
2.4.1. Hematology and Biochemical Test Parameters
2.4.2. Histopathology
2.4.3. Whole Blood Clotting Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hematology and Biochemical Test Parameters
3.2. Histopathology Findings
3.3. Blood Clotting Factor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Setty, C.M.; Badiger, A.M.; Muralikrishna, K.S. Gum ghatti: A promising polysaccharide for pharmaceutical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, P.; Singh, I. Thiolation of biopolymers for developing drug delivery systems with enhanced mechanical and mucoadhesive properties: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, S.; Mudgil, D.; Taneja, S. Exudate gums: Chemistry, properties and food applications–a review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2828–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JMHLW. Japan’s Specifications and Standards for Food Additives, 8th ed.; The Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare: Tokyo, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Available online: https://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/JECFA_84_Summary_Report.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Hobbs, C.A.; Swartz, C.; Maronpot, R.; Davis, J.; Recio, L.; Hayashi, S.M. Evaluation of the genotoxicity of the food additive, gum ghatti. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, P.; Mundlia, J.; Ahuja, M. Thiol modified Moringa gum–A potential bioadhesive polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, M.P.; Bhamare, M.S.; Bhavsar, C.J.; Patil, P.O.; Deshmukh, P.K. Development of novel thiolated carboxymethyl-gellan gum as potential mucoadhesive polymer: Application of DoE. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Ahuja, M.; Mehta, H. Thiol derivatization of Xanthan gum and its evaluation as a mucoadhesive polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Ahuja, M. Thiol modification of psyllium husk mucilage and evaluation of its mucoadhesive applications. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 284182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Yadav, S.; Ahuja, M.; Dilbaghi, N. Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of thiolated tamarind seed polysaccharide as a mucoadhesive polymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1543–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahulkar, S.S.; Munot, N.M.; Surwase, S.S. Synthesis, characterization of thiolated karaya gum and evaluation of effect of pH on its mucoadhesive and sustained release properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, P.; Singh, I.; Huanbutta, K. Synthesis and Characterization of Thiolated Gum Ghatti as a Novel Excipient: Development of Compression-Coated Mucoadhesive Tablets of Domperidone. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15844–15854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maronpot, R.R.; Davis, J.; Moser, G.; Giri, D.K.; Hayashi, S.M. Evaluation of 90-day oral rat toxicity studies on the food additive, gum ghatti. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, R.; Watanabe, K.; Yamane, R.; Yasui, H.; Kikugawa, N.; Mori, N.; Akiyama, R.; Matsubara, T.; Harada, M.; Kaneda, S. Four-week repeated dose oral toxicity study of gum ghatti in rats. Fundam. Toxicol. Sci. 2020, 7, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Publisher Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, OECD 423. Acute Oral Toxicity-Acute Toxic Class Method, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/iccvam/suppdocs/feddocs/oecd/oecd_gl423.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2022).
- Xiao, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, M.; Fei, C.; Zhang, L.; Xue, F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, K. Acute and 30-day oral toxicity studies of a novel coccidiostat–ethanamizuril. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, A.L.; Quixabeira, C.M.; de Lima, L.M.; Paz, S.T.; Gomes, A.N.; de Souza Araújo, T.A.; de Albuquerque, U.P.; Gomes, D.A.; Silva, T.M.; Lira, E.C. Safety assessment of Bauhinia cheilantha Bong. Steud leaves extract: Acute, sub-acute toxicity, antioxidant, and antihemolytic evaluations. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.; Tran, N.; Riefler, S.; Jacoby, J.; Merkel, D.; Marone, P.; Naouli, N. Toxicologic evaluation of modified gum acacia: Mutagenicity, acute and subchronic toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, L.; Raj, R.; Thakur, A.K.; Singh, I. Development of chitosan-catechol conjugates as mucoadhesive polymer: Assessment of acute oral toxicity in mice. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2020, 35, 2020014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, K. Acute toxicity of benzalkonium chloride in Balb/c mice following intratracheal instillation and oral administration. Environ. Anal. Health Toxicol. 2019, 34, e2019009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, M.; Jestoi, M.; Nathanail, A.V.; Kokkonen, U.M.; Anttila, M.; Koivisto, P.; Karhunen, P.; Peltonen, K. Application of OECD Guideline 423 in assessing the acute oral toxicity of moniliformin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, O.; Krishan, P. Investigations on acute oral toxicity studies of purpurin by application of OECD guideline 423 in rodents. NaunynSchmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, L.; Wu, J.; Li, P.; Wu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Xu, H. Toxicological evaluation of aqueous extract of the traditional Chinese formula Qing Hao Gan Cao. Toxicol. Res. 2021, 10, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, S.Y.; Wu, J.; Moochhala, S.M.; Tan, M.H.; Lu, J. Development of a chitosan-based wound dressing with improved hemostatic and antimicrobial properties. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4323–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, M.F.; Shau, M.D.; Chang, M.Y.; Chiou, S.K.; Chang, J.K.; Cherng, J.Y. Platelet adsorption and hemolytic properties of liquid crystal/composite polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 327, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ngece, K.; Aderibigbe, B.A.; Ndinteh, D.T.; Fonkui, Y.T.; Kumar, P. Alginate-gum acacia based sponges as potential wound dressings for exuding and bleeding wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample No. | Treatment Schedule |
|---|---|
| 1 | Group-I (Pure gum ghatti 300 mg/kg, p.o.; n = 3) |
| 2 | Group-II (Thiolated gum ghatti 300 mg/kg, p.o.; n = 3) |
| 3 | Group-III (Pure gum ghatti 2000 mg/kg, p.o.; n = 3) |
| 4 | Group-IV (Thiolated gum ghatti 2000 mg/kg, p.o.; n = 3) |
| 5 | Group-V (control 0.9% w/v saline; n = 6) |
| S. No. | Parameters | Normal Range | Control (0.9% w/v Saline) | Pure Gum Ghatti (300 mg/kg) | ThiolatedGum Ghatti (300 mg/kg) | Pure Gum Ghatti (2000 mg/kg) | ThiolatedGum Ghatti (2000 mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haematological Test | |||||||
| 1. | Hb (g/dL) | 12.1–15.1 | 12.50 ± 0.10 | 13.20 ± 0.20 * | 12.90 ± 0.20 * | 13.00 ± 0.17 * | 12.83 ± 0.21 * |
| 2. | TLC (Total leucocyte count) (cell/cum) | 4000–11,000 | 5877.00 ± 398.14 | 6105.70 ± 257.99 * | 6164.72 ± 181.59 * | 6449.57 ± 407.02 * | 6217.21 ± 241.35 * |
| 3. | DLC (Differential leucocyte count) (%) | ||||||
| Neutrophil | 40–60 | 49.53 ± 1.03 | 49.26 ± 0.84 * | 49.92 ± 0.25 * | 48.82 ± 0.11 * | 49.95 ± 0.16 * | |
| Lymphocyte | 20–40 | 33.00 ± 2.00 | 35.50 ± 2.10 * | 32.20 ± 1.97 * | 33.50 ± 1.70 * | 33.80 ± 1.42 * | |
| Monocyte | 2–8 | 3.00 ± 0.10 | 3.20 ± 0.17 * | 3.40 ± 0.17 * | 3.80 ± 0.17 * | 3.20 ± 0.30 * | |
| Epsinophil | 1–4 | 1.90 ± 0.10 | 2.00 ± 0.26 * | 1.80 ± 0.10 * | 1.77 ± 0.11 * | 2.09 ± 0.18 * | |
| Basophil | 0.5–1.0 | 0.80 ± 0.11 | 0.90 ± 0.26 * | 0.90 ± 0.26 * | 1.00 ± 0.17 * | 0.90 ± 0.26 * | |
| 4. | PCV (packed cell volume) (%) | 35.5–44.9 | 43.80 ± 0.10 | 44.70 ± 0.35 * | 44.80 ± 0.10 * | 44.20 ± 0.10 * | 44.80 ± 0.17 * |
| 5. | MCV (mean corpuscular volume) (fL) | 80–100 | 80.80 ± 0.92 | 78.80 ± 0.26 * | 78.70 ± 0.13 * | 78.99 ± 0.31 * | 79.53 ± 0.59 * |
| 6. | MCH (mean corpuscular hemoglobin) (pg/cell) | 27–31 | 29.10 ± 0.20 | 28.40 ± 0.26 * | 28.90 ± 0.10 * | 27.10 ± 0.45 * | 28.70 ± 0.10 * |
| 7. | MCHC (mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration) (g/dL) | 32–36 | 33.20 ± 1.60 | 33.00 ± 1.32 * | 32.80 ± 1.18 * | 33.50 ± 0.90 * | 32.90 ± 0.95 * |
| 8. | Platelet count (million/cm2) | 150,000–450,000 | 1.94 ± 0.06 | 2.11 ± 0.15 * | 1.91 ± 0.06 * | 1.99 ± 0.10 * | 190 ± 0.08 * |
| 9. | RBC count (million/cm2) | 4.2–5.4 | 4.40 ± 0.10 | 4.60 ± 0.20 * | 4.50 ± 0.10 * | 4.20 ± 0.10 * | 4.60 ± 0.10 * |
| Liver function test | |||||||
| 10. | Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | <1.0–0.4 | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 0.55 ± 0.06 * | 0.63 ± 0.06 * | 0.59 ± 0.15 * | 0.56 ± 0.13 * |
| 11. | Total protein (g/dL) | 6.3–8.0 | 6.50 ± 0.20 | 6.40 ± 0.10 * | 6.60 ± 0.20 * | 6.50 ± 0.26 * | 6.50 ± 0.26 * |
| 12. | Albumin (g/dL) | 3.5–5.5 | 4.30 ± 0.10 | 4.40 ± 0.20 * | 4.50 ± 0.20 * | 4.60 ± 0.10 * | 4.60 ± 0.10 * |
| 13. | SGOT (serum glutamic–oxaloacetic transaminase) (IU/L) | 0–120 | 102.00 ± 1.00 | 118.00 ± 1.00 * | 110.00 ± 1.73 * | 105.00 ± 2.65 * | 105.00 ± 2.65 * |
| 14. | SGPT (serum glutamic–pyruvic transaminase) (IU/L) | 0–60 | 43.67 ± 1.15 | 45.00 ± 0.26 * | 40.00 ± 0.95 * | 38.00 ± 0.36 * | 38.00 ± 0.36 * |
| 15. | ALP (alkaline phosphatase) (IU/L) | 44–147 | 110.00 ± 1.30 | 110.00 ± 1.30 * | 140.00 ± 0.78 * | 105.31 ± 1.74 * | 115.00 ± 0.91 * |
| 16. | Total globulin (g/dL) | 1.5–3.5 | 2.20 ± 0.10 | 2.00 ± 0.08 * | 2.10 ± 0.10 * | 1.90 ± 0.11 * | 1.90 ± 0.11 * |
| Kidney function test | |||||||
| 17. | Blood urea (mg/dL) | 10–50 | 32.00 ± 2.00 | 30.00 ± 1.00 * | 30.00 ± 1.00 * | 31.00 ± 1.00 * | 31.00 ± 1.00 * |
| 18. | Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.6–1.4 | 1.00 ± 0.13 | 1.20 ± 0.20 * | 1.10 ± 0.10 * | 1.10 ± 0.10 * | 1.10 ± 0.10 * |
| 19. | Serum uric acid (mg/dL) | 2.4–7.0 | 2.50 ± 0.20 | 2.00 ± 0.09 * | 2.40 ± 0.17 * | 2.60 ± 0.10 * | 2.60 ± 0.10 * |
| 20. | Serum potassium (mEq/dL) | 3.6–5.5 | 4.50 ± 0.10 | 5.00 ± 0.20 * | 4.90 ± 0.10 * | 4.40 ± 0.30 * | 4.40 ± 0.30 * |
| 21. | Serum sodium (mEq/dL) | 135–155 | 148.00 ± 1.85 | 155.00 ± 0.36 * | 155.00 ± 0.36 * | 154.71 ± 1.49 * | 154.56 ± 0.90 * |
| 22. | Serum calcium (mEq/dL) | 8.5–11.0 | 10.00 ± 0.79 | 9.80 ± 0.10 * | 10.20 ± 0.43 * | 9.81 ± 0.52 * | 9.90 ± 0.35 * |
| 23. | Serum phosphorous (mEq/dL) | 1.5–6.8 | 3.80 ± 0.10 | 3.00 ± 0.26 * | 3.20 ± 0.10 * | 3.65 ± 0.28 * | 3.60 ± 0.26 * |
| Physiological and feeding behavior parameters | |||||||
| 24. | Body weight 0th day (g) 14th day (g) | - | 210.20 ± 0.20 210.90 ± 0.30 | 212.00 ± 0.26 * 212.00 ± 0.20 * | 212.20 ± 0.61 * 212.90 ± 0.36 * | 211.80 ± 0.17 * 212.50 ± 0.26 * | 212.20 ± 0.08 * 212.80 ± 0.10 * |
| 25. | Feed intake 0th day (g/day) 14th day (g/day) | - | 12.70 ± 0.17 13.80 ± 0.07 | 13.21 ± 1.65 * 13.45 ± 0.08 * | 13.00 ± 0.20 * 13.90 ± 0.10 * | 12.90 ± 0.10 * 13.93 ± 0.58 * | 12.70 ± 0.36 * 13.40 ± 0.36 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puri, V.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, P.; Dua, K.; Huanbutta, K.; Singh, I.; Sangnim, T. Assessment of Acute Oral Toxicity of Thiolated Gum Ghatti in Rats. Polymers 2022, 14, 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183836
Puri V, Sharma A, Kumar P, Dua K, Huanbutta K, Singh I, Sangnim T. Assessment of Acute Oral Toxicity of Thiolated Gum Ghatti in Rats. Polymers. 2022; 14(18):3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183836
Chicago/Turabian StylePuri, Vivek, Ameya Sharma, Pradeep Kumar, Kamal Dua, Kampanart Huanbutta, Inderbir Singh, and Tanikan Sangnim. 2022. "Assessment of Acute Oral Toxicity of Thiolated Gum Ghatti in Rats" Polymers 14, no. 18: 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183836
APA StylePuri, V., Sharma, A., Kumar, P., Dua, K., Huanbutta, K., Singh, I., & Sangnim, T. (2022). Assessment of Acute Oral Toxicity of Thiolated Gum Ghatti in Rats. Polymers, 14(18), 3836. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14183836