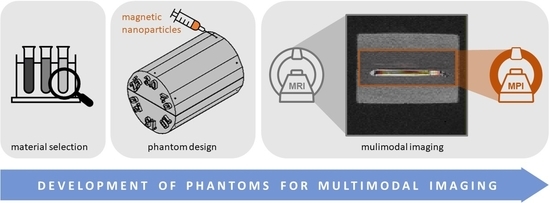
Development of Phantoms for Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. In-Process and Post-Process Procedure
2.3. Examination Methods
2.3.1. Shore A Hardness Test
2.3.2. Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy (MPS)
2.3.3. Time-Domain Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (TD-NMR)
2.3.4. Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI)
2.3.5. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Selection
3.2. Phantom Development
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billings, C.; Langley, M.; Warrington, G.; Mashali, F.; Johnson, J.A. Magnetic Particle Imaging: Current and Future Applications, Magnetic Nanoparticle Synthesis Methods and Safety Measures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, M.G.; Weber, O.; Heinen, U.; Reitmeier, A.; Mummert, T.; Jung, C.; Raabe, N.; Knopp, T.; Ittrich, H.; Adam, G. Combined Preclinical Magnetic Particle Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Initial Results in Mice. Rofo 2015, 187, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, H.; Taupitz, M.; de Schellenberger, A.A.; Kosch, O.; Eberbeck, D.; Wagner, S.; Trahms, L.; Hamm, B.; Schnorr, J. Novel Magnetic Multicore Nanoparticles Designed for MPI and Other Biomedical Applications: From Synthesis to First in Vivo Studies. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, S.; Löwa, N.; Paysen, H.; Fratila, R.M.; Reverte-Salisa, L.; Trakoolwilaiwan, T.; Niu, Z.; Kasparis, G.; Preuss, S.F.; Kosch, O.; et al. Quantification of Lipoprotein Uptake in Vivo Using Magnetic Particle Imaging and Spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Kundu, S.; Nag, A.; Xu, Y. 3D Printed Sensors for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, J.; Heinen, U.; Lehr, H.; Weber, A.; Jaspard, F.; Ruhm, W.; Heidenreich, M.; Schulz, V. System Characterization of a Highly Integrated Preclinical Hybrid MPI-MRI Scanner. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, S.; Vogel, P.; Dietrich, P.; Kampf, T.; Rückert, M.A.; Kickuth, R.; Behr, V.C.; Bley, T.A. Magnetic Particle Imaging Guided Real-Time Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty in a Phantom Model. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol 2018, 41, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöckel, L.; Wells, J.; Kosch, O.; Lyer, S.; Alexiou, C.; Grüttner, C.; Wiekhorst, F.; Dutz, S. Long-Term Stable Measurement Phantoms for Magnetic Particle Imaging. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 471, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exner, M.; Szwargulski, P.; Knopp, T.; Graeser, M.; Ludewig, P. 3D Printed Anatomical Model of a Rat for Medical Imaging. Curr. Dir. Biomed. 2019, 5, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacik, J.; Frölich, A.; Spallek, J.; Forkert, N.D.; Faizy, T.D.; Werner, F.; Knopp, T.; Krause, D.; Fiehler, J.; Buhk, J.-H. Magnetic Particle Imaging for High Temporal Resolution Assessment of Aneurysm Hemodynamics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutz, S.; Stang, A.; Wöckel, L.; Zahn, D.; Grüttner, C.; Löwa, N.; Kosch, O.; Wiekhorst, F. 3D Printed Measurement Phantoms for Evaluation of Magnetic Particle Imaging Scanner. Trans. Addit. Manuf. Meets Med. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, S.; Hirsch, T.; Patterson, W.M.; Scheucher, E.; Mayr, T.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Multicolor Upconversion Nanoparticles for Protein Conjugation. Theranostics 2013, 3, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Pantoja, P.E.; Sánchez-Domínguez, M.; Caballero-Robledo, G.A. Micro–Nanoparticles Magnetic Trap: Toward High Sensitivity and Rapid Microfluidic Continuous Flow Enzyme Immunoassay. Biomicrofluidics 2020, 14, 014111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Su, D.; Saha, R.; Liu, J.; Chugh, V.K.; Wang, J.-P. Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy: A Short Review of Applications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.09577. [Google Scholar]
- Löwa, N.; Hoffmann, R.; Gutkelch, D.; Kosch, O.; Dutz, S.; Wiekhorst, F. A Multi-Purpose Phantom Kit for Magnetic Particle Imaging. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 7, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsouras, D.; Lee, T.C.; Liacouras, P.; Ionita, C.N.; Pietilla, T.; Maier, S.E.; Mulkern, R.V. 3D Printing of MRI-Visible Phantoms and MR Image-Guided Therapy Simulation. Magn Reson. Med. 2017, 77, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, B.E.; Stupic, K.F.; Wagner, J.L.; Huddle, S.; Shandas, R.; Weir, R.F.; Russek, S.E.; Keenan, K.E. Characterization of 3-Dimensional Printing and Casting Materials for Use in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Phantoms at 3 T. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, E.; Walker, E.; Naguib, H.E. Novel Development of 3D Printable UV-Curable Silicone for Multimodal Imaging Phantom. Bioprinting 2017, 7, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wommer, L.; Meiers, P.; Kockler, I.; Ulber, R.; Kampeis, P. Development of a 3D-Printed Single-Use Separation Chamber for Use in MRNA-Based Vaccine Production with Magnetic Microparticles. Eng. Life Sci. 2021, 21, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeltaMed GmbH Safety Data Sheet (e-Shell 600 Clear). Available online: http://envisiontec.asia/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/MSDS-EShell-600.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- DeltaMed GmbH Safety Data Sheet (e-Shell 200). Available online: http://envisiontec.asia/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/MSDS-EShell-200.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Envisiontec Safety Data Sheet (R5 Series). Available online: https://etec.desktopmetal.com/wp-content/uploads/safety-data-sheets/MK-SDS-R5Series-20211124-FN-EU.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Dreve Safety Data Sheet (BioTec). Available online: https://otoplastikshop.dreve.de/daten/deu_sds_biotec_813_clp_us.pdf?expired=1658662901 (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Formlabs Safatey Data Sheet (Elastic 50A). Available online: https://formlabs-media.formlabs.com/datasheets/2001417-SDS-ENCA-0.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Radon, P.; Löwa, N.; Gutkelch, D.; Wiekhorst, F. Design and Characterization of a Device to Quantify the Magnetic Drug Targeting Efficiency of Magnetic Nanoparticles in a Tube Flow Phantom by Magnetic Particle Spectroscopy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgo, T.A.L.; Batista, B.C.; Galembeck, F. Electricity on Rubber Surfaces: A New Energy Conversion Effect. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8940–8947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Pahwa, S.; Ma, D.; Lu, L.; Twieg, M.D.; Wright, K.L.; Seiberlich, N.; Griswold, M.A.; Gulani, V. MR Fingerprinting for Rapid Quantitative Abdominal Imaging. Radiology 2016, 279, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, W.; Brühl, R.; Abdulhadi, Y.; Ittermann, B. En Route to Multiphasic Anthropomorphic MR Phantoms: An Additive Manufacturing Approach Applying Silicone 3D-Printing Techniques. In Proceedings of the ISMRM & SMRT Virtual Conference, virtual conference, 15 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kreve, S.; Dos Reis, A.C. Denture Liners: A Systematic Review Relative to Adhesion and Mechanical Properties. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 6913080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyzois, G.L.; Frangou, M.J. Influence of Curing Method, Sealer, and Water Storage on the Hardness of a Soft Lining Material over Time. J. Prosthodont. 2001, 10, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, G.R.; Rueggeberg, F.A. Physical-Property Comparison of a Chairside- or Laboratory-Polymerized Permanent Soft-Liner During 1 Year. J. Prosthodont. 1999, 8, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, D.N.; Goiato, M.C.; Zuccolotti, B.C.R.; Moreno, A.; dos Santos, D.M.; Pesqueira, A.A. Effect of Thermocycling on Hardness, Absorption, Solubility and Colour Change of Soft Liners. Gerodontology 2012, 29, e215–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.L.; Breeding, L.C.; Vergani, C.E.; da Cruz Perez, L.E. Hardness and Surface Roughness of Reline and Denture Base Acrylic Resins after Repeated Disinfection Procedures. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2009, 102, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, C.-D.; Pearson, M.; Trottier-Cournoyer, F.; Dafoe, A.; Kwok, T.H. Automated Storage and Active Cleaning for Multi-Material Digital-Light-Processing Printer. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2019, 25, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Material | Magnetic Impurity | MNP Absorption | TD-NMR Signal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A3 | Ranking | m/A | Ranking | T2 | Ranking | |
| pAm2 | µg/m2 | ms | ||||
| BioTec | 79(8) | II | 0.9(2) | I | 36.6(5) | I |
| Elastic 50A | 38(1) | I | 2.0(2) | II | 3.62(3) | III |
| E-Shell 200 | 23(6) | I | 4.11(8) | III | 0.09(1) | III |
| E-Shell 600 | 11(9) | I | 2.71(1) | II | 0.27(3) | III |
| R5 Red | 6(2) | I | 3.10(2) | II | 0.15(1) | III |
| R5 Gray | 28(2) | I | 3.1(2) | II | 0.15(1) | III |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arenas, M.A.A.; Gutkelch, D.; Kosch, O.; Brühl, R.; Wiekhorst, F.; Löwa, N. Development of Phantoms for Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging. Polymers 2022, 14, 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193925
Arenas MAA, Gutkelch D, Kosch O, Brühl R, Wiekhorst F, Löwa N. Development of Phantoms for Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193925
Chicago/Turabian StyleArenas, Maria Alejandra Ardila, Dirk Gutkelch, Olaf Kosch, Rüdiger Brühl, Frank Wiekhorst, and Norbert Löwa. 2022. "Development of Phantoms for Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging" Polymers 14, no. 19: 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193925
APA StyleArenas, M. A. A., Gutkelch, D., Kosch, O., Brühl, R., Wiekhorst, F., & Löwa, N. (2022). Development of Phantoms for Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Particle Imaging. Polymers, 14(19), 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193925