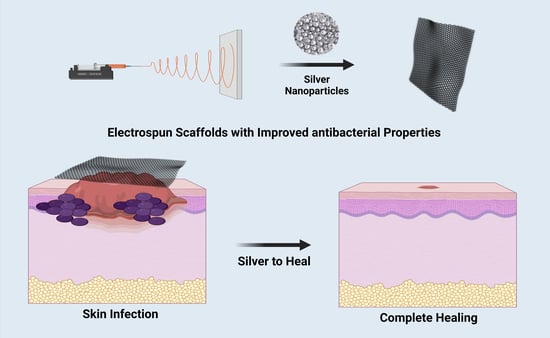
Recent Advances in Silver Nanoparticles Containing Nanofibers for Chronic Wound Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure of the Skin
3. Brief Medical History of Silver Nanoparticles
4. Wound Healing Properties of Silver Nanoparticles
5. Mechanistic Understanding of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
6. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Synthesis
7. Electrospinning
8. Cytoprotective Effect of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Nanofibers
| S. No. | Wound Dressing Materials | Fabrication Techniques and Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Polyurethane/keratin/AgNP biocomposite mats | Electrospinning method The material’s keratin content increased fibroblast cell proliferation while also having strong antibacterial properties. A histological analysis showed that the created biocomposite mat could promote wound healing. | [115] |
| 2 | Hyaluronan and PVA embedded-AgNP Hydrogel | Freeze-thawing method The hydrogel’s semi-interpenetrating network aided in the AgNPs’ uniform dispersion. The hydrogel may be used as a wound dressing since it had strong antibacterial activity, was biocompatible, had a low swelling index, and was nontoxic. | [116] |
| 3 | Genipin-crosslinked chitosan/poly(ethylene glycol)ZnO/Ag | Film casting method The created nanocomposites showed improved mechanical characteristics and pH-sensitive swelling behaviour, and they were successfully used as a material for wound dressings. | [117] |
| 4 | AgNP-Calcium alginate beads in gelatin scaffolds | Freeze-drying method Due to their favourable swelling qualities and non-toxic behaviour against human dermal fibroblasts, they are recommended as acceptable wound dressings. | [118] |
| 5 | Chitosan-hyaluronan nano composite sponges | Ionic cross-linking followed by freeze drying The material had adequate porosity for applications involving wound healing, good biodegradation, and improved swelling properties. | [119] |
| 6 | Methoxy poly (ethylene glycol)-graft-chitosan composite film | Casting/solvent evaporation method The substance that was manufactured showed that the medication curcumin had been loaded successfully. The film had an uneven surface without any pores. The produced film has a significant deal of potential for use in wound healing applications, according to an in vitro cytotoxicity research, antioxidant effectiveness assessments, and animal trials (histological study). | [120] |
| 7 | Tannic acid/chitosan/pullulan composite nanofibers | Force spinning method It has the potential to be used in the treatment of intricate and deep wounds since it replicates a 3D environment, exhibits good water absorption, and encourages fibroblast cell adhesion. | [121] |
| 8 | Ag/ZnO nanocomposites | Deposition precipitation method The porosity of composites, which ranged from 81 to 88%, the swelling ratios, which ranged from 21 to 24, and the moisture retention period, which ranged from 13 to 14 days, all demonstrated good results in various experiments. These characteristics are all crucial for expediting wound healing. | [122] |
| 9 | Silver/hyaluronan bio-nanocomposite fabrics | Wet-dry-spinning technique According to in vivo research, fabrics improved the material’s mechanical qualities and increased wound healing effectiveness. | [123] |
| 10 | Chitosan-Ag/ZnO composite dressing | Lyophilisation and immersion method In many tests, composites performed well in terms of porosity (81–88%), swelling ratios (21–24%), and moisture retention period (13–14 days), all of which are critical elements in improving wound healing. | [124] |
| 11 | Starch-AgNPs | Nanoprecipitation method By using an ecologically friendly process, alkali-dissolved starch served as a reducing and stabilising agent to create AgNPs, and this strategy may be used for applications in the treatment of wounds. | [125] |
| 12 | Cellulose/Polypyrrole/AgNPs/ Ionic liquid composite films | Simple chemical polymerization method Composite films demonstrated effective antibacterial action and may be applied as patches to help heal wounds. | [126] |
| 13 | Fibrin nanoconstructs | Water-in-oil emulsification diffusion technique It served as a reliable carrier molecule for tacrolimus, an immunosuppressant. | [127] |
9. Advantages of Silver and Fibre Platforms
10. Silver Nanoparticles Containing Nanofibers for Wound Healing
| S. No. | AgNPs with Polymers | Solvents | Voltage, Distance, Flow Rate | Diameter (nm) | Antibacterial Efficiency (ZOI (mm), MIC or %) | Bio- Compatability | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kV) | (cm) | (mL/h) | |||||||
| 1 | PLA | Methylene chloride, DMF | 14 | 10 | 3 | 1.44 ± 0.32 μm | S. aureus—6.5 mm P. aeruginosa—9.3 mm | CjECs CECs | [85] |
| 2 | PCL-Gelatin | Acetone | 15 | 15 | 1 | 830–920 | E. coli—1.53 ± 0.32 mm | HDF | [168] |
| 3 | Polyurethane | THF | 15 | 15 | 0.5 | 200–2000 | E. coli—16.2 ± 0.8 mm S. aureus—8.7 ± 1.2 mm | CEFs | [172] |
| 4 | Gum Arabic-PVA-PCL | DMF DI-water | 18 | 15 | 0.5 | 150–250 | E. coli—2.5 mm S. aureus—2.9 mm | MEF | [173] |
| 5 | PCL-PVA | CHCl3, CH3OH, H2O | 27 | - | 3 | - | S. aureus—90 mm | HDF | [176] |
| 6 | Polystyrene | DMF | 2–3 | - | 1–3 | 96–471 | E. coli—11 mm S. aureus—4.0 mm | - | [178] |
| 7 | Polyurethane | HFP | 17 | 20 | 1.5 | 500 | S. aureus—20.41 mm MRSA—18.24 mm | HaCaT | [181] |
| 8 | PVA-PCL | CHCl3, CH3OH, Water | 23 | 15 | 0.02 | 70 nm | E. coli—14 mm S. aureus—18 mm | NIH3T3 | [182] |
| 9 | PCL | water | 18 | 16 | 1 | 0.38 μm | S. aureus—79.2 ± 4.5 % E. coli—80.1 ± 4.9% | HFB4 | [186] |
| 10 | PVA-TPU | Water: DMF | 25 | 10 | 1 | 230–280 | S. aureus—50 μg/mL E. coli—25 μg/ml | - | [188] |
| 11 | Chitosan- PEO | Acetone | 20 | 14 | - | 100–300 | E. coli—20 ± 2 nm | HDF | [123] |
| 12 | PCL-Cellulose acetate | Acetone: DCM | 22 | 16 | 1 | 2–6.3 μm | S. aureus—18 mm P. aeruginosa—10 mm | HOB, HFB4 | [190] |
| 13 | Collagen | HFIP | 18 | 10 | 25 mL/min | 300–700 | S. aureus—3.2 cm P. aeruginosa—2.3 cm | No toxic on rat skin | [194] |
| 14 | PLA-PVP | DCM | 20–30 | 15 | 2 | 500–650 | E. coli—96.7 % S. aureus—96.9 % | – | [195] |
| 15 | Cellulose acetate-PVAc | Acetone water | 25 | 10 | 0.8 | 1.33 ± 0.63µm | S. aureus—9.2 ± 1.6 mm E. coli—8.2 ± 0.9 mm | CEFs | [196] |
| S. No. | Study Title (ClinicalTrial Identifier ID) | Status of Clinical Trails |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Topical Application of Silver Nanoparticles and Oral Pathogens in Ill Patients (NCT02761525) | Completed |
| 2 | Topical Silver Nanoparticles for Microbial Activity (NCT03752424) | Unknown |
| 3 | Silver Nanoparticles in Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria (NCT04431440) | Completed |
| 4 | Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticle Gel Versus a Common Antibacterial Hand Gel (NCT00659204) | Unknown |
| 5 | P11-4 and Nanosilver Fluoride Varnish in Treatment of White Spot Carious Lesions (NCT04929509) | Recruiting |
| 6 | Evaluation of Diabetic Foot Wound Healing Using Hydrogel/ Nano Silver-based Dressing vs. Traditional Dressing (NCT04834245) | Completed |
11. Conclusions Challenges and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharifi, S.; Hajipour, M.J.; Gould, L.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanomedicine in Healing Chronic Wounds: Opportunities and Challenges. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 550–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parani, M.; Lokhande, G.; Singh, A.; Gaharwar, A.K. Engineered Nanomaterials for Infection Control and Healing Acute and Chronic Wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 10049–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ather, S.; Harding, K.G. Wound Management and Dressings. Adv. Text. Wound Care A Vol. Woodhead Publ. Ser. Text. 2009, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J. Providing Cost-Effective Treatment of Hard-to-Heal Wounds in the Community through Use of NPWT. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2015, 20, S14–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The Human Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihai, M.M.; Dima, M.B.; Dima, B.; Holban, A.M. Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control. Materials 2019, 12, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recent Advancements in Biopolymer and Metal Nanoparticle-Based Materials in Diabetic Wound Healing Management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nethi, S.K.; Das, S.; Patra, C.R.; Mukherjee, S. Recent Advances in Inorganic Nanomaterials for Wound-Healing Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2652–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wounds and Its Burden: An Updated Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2019, 8, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, S.; Agabiti, N.; Davoli, M.; Uccioli, L.; Meloni, M.; Giurato, L.; Marino, C.; Bargagli, A.M. Survival and Factors Predicting Mortality after Major and Minor Lower-Extremity Amputations among Patients with Diabetes: A Population-Based Study Using Health Information Systems. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GhavamiNejad, A.; Rajan Unnithan, A.; Ramachandra Kurup Sasikala, A.; Samarikhalaj, M.; Thomas, R.G.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Nasseri, S.; Murugesan, P.; Wu, D.; Hee Park, C.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Electrospun Nanofibers Functionalized with Size-Controlled Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Dressing Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12176–12183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnova, S.A.; Danilushkina, A.A.; Fakhrullina, G.I.; Akhatova, F.S.; Badrutdinov, A.R.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Silver Nanoparticle-Coated “Cyborg” Microorganisms: Rapid Assembly of Polymer-Stabilised Nanoparticles on Microbial Cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13530–13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczkowska, J.; Stetsyshyn, Y.; Awsiuk, K.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Gosiewski, T.; Jany, B.; Lishchynskyi, O.; Shymborska, Y.; Nastyshyn, S.; Bernasik, A.; et al. “Command” Surfaces with Thermo-Switchable Antibacterial Activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schommer, N.N.; Gallo, R.L. Structure and Function of the Human Skin Microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, R.L. Human Skin Is the Largest Epithelial Surface for Interaction with Microbes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1213–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.; Geyer, S.; Weninger, W.; Guimberteau, J.C.; Wong, J.K. The Dynamic Anatomy and Patterning of Skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 25, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.J.; Jones, J.D.; Woessner, A.E.; Quinn, K.P. Skin Structure-Function Relationships and the Wound Healing Response to Intrinsic Aging. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendhi, A.; Prabakar, D.; Jacob, J.M.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saratale, R.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Gelidium Amansii and Its Antimicrobial Property against Various Pathogenic Bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 114, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chiu, H.W.; Tsai, J.C.; Fang, C.Y.; Chen, C.W.; Wang, Y.J. Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis and the Autophagic Effects of Silver Nanoparticles in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4706–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.S.; Stern, J.M.; Vanni, A.J.; Kelley, R.S.; Baumgart, E.; Field, D.; Libertino, J.A.; Summerhayes, I.C. In Vitro Analysis of a Nanocrystalline Silver-Coated Surgical Mesh. Surg. Infect. (Larchmt) 2007, 8, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Reda, M.M.; Klingner, A. Preparation and Characterization of Green Carboxymethylchitosan (CMCS)–Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Electrospun Nanofibers Containing Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) and Its Potential Use as Biomaterials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Mahalingam, S.; Rohn, J.L.; Ren, G.; Edirisinghe, M. Physio-Chemical and Antibacterial Characteristics of Pressure Spun Nylon Nanofibres Embedded with Functional Silver Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, B.S.; Aytac, Z.; Pricope, G.M.; Uyar, T.; Vasile, C. Polylactic Acid (PLA)/Silver-NP/VitaminE Bionanocomposite Electrospun Nanofibers with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.; Nurchi, V.M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Medical Uses of Silver: History, Myths, and Scientific Evidence. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5923–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillo, D.J.; Marx, D.E. Silver in Medicine: A Brief History BC 335 to Present. Burns 2014, 40, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franková, J.; Pivodová, V.; Vágnerová, H.; Juráňová, J.; Ulrichová, J. Effects of Silver Nanoparticles on Primary Cell Cultures of Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes in a Wound-Healing Model. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14, e137–e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Wu, P.; Ho, J.K.; Jin, R.; Zhang, L.; Shao, H.; Han, C. Silver Nanoparticle Loaded Collagen/Chitosan Scaffolds Promote Wound Healing via Regulating Fibroblast Migration and Macrophage Activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiyeh, B.S.; Costagliola, M.; Hayek, S.N.; Dibo, S.A. Effect of Silver on Burn Wound Infection Control and Healing: Review of the Literature. Burns 2007, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosli, N.A.; Teow, Y.H.; Mahmoudi, E. Current Approaches for the Exploration of Antimicrobial Activities of Nanoparticles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2021, 22, 885–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, A.; Gallus, I.; Tegginamath, A.; Maryska, J.; Yalcinkaya, F. Electrospun Antibacterial Nanomaterials for Wound Dressings Applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, L.J.; White, R.J.; Chipman, J.K. Silver and Nanoparticles of Silver in Wound Dressings: A Review of Efficacy and Safety. J. Wound Care 2011, 20, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Birbach, N.L.; Hinestroza, J.P. Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles on Cellulosic Fibers via Stabilization of Carboxymethyl Groups. Cellulose 2012, 19, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.N.; Ho, C.M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.Y.; Yu, W.Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.H.; Chiu, J.F.; Che, C.M. Silver Nanoparticles: Partial Oxidation and Antibacterial Activities. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.Y.; et al. Antimicrobial Effects of Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, H.H.; Garza-Treviño, E.N.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Singh, D.K. Silver Nanoparticles Are Broad-Spectrum Bactericidal and Virucidal Compounds. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galdiero, S.; Falanga, A.; Vitiello, M.; Cantisani, M.; Marra, V.; Galdiero, M. Silver Nanoparticles as Potential Antiviral Agents. Molecules 2011, 16, 8894–8918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorraquín-Peña, I.; Cueva, C.; de Llano, D.G.; Bartolomé, B.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Glutathione-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity against Periodontal Bacteria, and Cytotoxicity and Inflammatory Response in Oral Cells. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Nisi, R.; Stoppa, M.; Licciulli, A. Silver-Functionalized Bacterial Cellulose as Antibacterial Membrane for Wound-Healing Applications. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konop, M.; Damps, T.; Misicka, A.; Rudnicka, L. Certain Aspects of Silver and Silver Nanoparticles in Wound Care: A Minireview. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 7614753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Han, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Hu, X.; Sun, H. The Progress of Silver Nanoparticles in the Antibacterial Mechanism, Clinical Application and Cytotoxicity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 9193–9201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, R.; Karuppusamy, I.; Saravanan, M.; Muthukumar, H.; Ponnuchamy, K.; Ramkumar, V.S.; Pugazhendhi, A. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications-A Comprehensive Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 2650–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikar, S.K.; Giri, D.D.; Pal, D.B.; Mishra, P.K.; Upadhyay, S.N. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: A Review. Green Sustain. Chem. 2016, 6, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.K.; Kumar, S.S.D.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. A Review on Nanoparticle Based Treatment for Wound Healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthet, M.; Gauthier, Y.; Lacroix, C.; Verrier, B.; Monge, C. Nanoparticle-Based Dressing: The Future of Wound Treatment? Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 770–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.; Xia, C.; Ju, M. Bio Fabrication of Silver Nanoparticles as an Effective Wound Healing Agent in the Wound Care after Anorectal Surgery. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, S.; Meinke, M.C.; Werner, L.; Epple, M.; Diendorf, J.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Lademann, J.; Vogt, A.; Rancan, F. Comparison of Silver Nanoparticles Stored under Air or Argon with Respect to the Induction of Intracellular Free Radicals and Toxic Effects toward Keratinocytes. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Shen, W.; Gurunathan, S. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebeish, A.; El-Rafie, M.H.; EL-Sheikh, M.A.; Seleem, A.A.; El-Naggar, M.E. Antimicrobial Wound Dressing and Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Sung, W.S.; Suh, B.K.; Moon, S.K.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, D.G. Antifungal Activity and Mode of Action of Silver Nano-Particles on Candida Albicans. BioMetals 2009, 22, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, M.; Kesharwani, J.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A.; Rai, M. Fungus-Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Activity against Pathogenic Fungi in Combination with Fluconazole. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2009, 5, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.K.; Kim, B.H.; Jung, G. Antifungal Activity of Silver Ions and Nanoparticles on Phytopathogenic Fungi. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speshock, J.L.; Murdock, R.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Schrand, A.M.; Hussain, S.M. Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles with Tacaribe Virus. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimha, G. Antiviral Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Fungal Strain Aspergillus Niger. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 6, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Alshabanah, L.A.; Hagar, M.; Al-Mutabagani, L.A.; Abozaid, G.M.; Abdallah, S.M.; Shehata, N.; Ahmed, H.; Hassanin, A.H. Hybrid Nanofibrous Membranes as a Promising Functional Layer for Personal Protection Equipment: Manufacturing and Antiviral/Antibacterial Assessments. Polymers 2021, 13, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokina, S.; Stephen, A.; Kaviyarasan, V.; Arulvasu, C.; Narayanan, V. Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Activities of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 76, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; Karthik, A.; Prabu, A.; Karthik, S.; Shivashangari, K.S.; Ravikumar, V. Origanum Vulgare Mediated Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Its Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 108, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanth, K.; Ilango, K.; MohanKumar, R.; Agrawal, A.; Dubey, G.P. Anticancer Activity of Moringa Oleifera Mediated Silver Nanoparticles on Human Cervical Carcinoma Cells by Apoptosis Induction. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Dou, D.; Ge, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L.; Gu, N. A Caffeic Acid Mediated Facile Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Powerful Anti-Cancer Activity. Colloids Surf.B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, D.S.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.K.; Shim, M.S.; Kim, D.G. Antimicrobial and Anticancer Activities of Porous Chitosan-Alginate Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, N.; Elbarbary, A.A.; Alkabes, H.A. Antibacterial and Anticancer Activity of Loaded Quinazolinone Polypyrrole/Chitosan Silver Chloride Nanocomposite. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2017, 66, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sherbiny, I.M.; Salih, E.; Yassin, A.M.; Hafez, E.E. Newly Developed Chitosan-Silver Hybrid Nanoparticles: Biosafety and Apoptosis Induction in HepG2 Cells. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Senapati, D.; Wang, S.; Tovmachenko, O.; Singh, A.K.; Yu, H.; Ray, P.C. Effect of Surface Coating on the Toxicity of Silver Nanomaterials on Human Skin Keratinocytes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2010, 487, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanki, R.; Arora, S.; Tyagi, N.; Rusu, L.; Singh, A.P.; Palanki, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. Size Is an Essential Parameter in Governing the UVB-Protective Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles in Human Keratinocytes. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamareddine, L. The Biological Control of the Malaria Vector. Toxins 2012, 4, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Showkot Hossain, A.M.; Qian, K.; Xie, J. In Situ Synthesis of Silver Supported Nanoporous Iron Oxide Microbox Hybrids from Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Catalytic Application in p-Nitrophenol Reduction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 2550–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, B.; Ashok Kumar Reddy, Y.; Shameer, S.; Rajesh, K.M.; Suneetha, Y.; Sreedhara Reddy, P. Lantana Camara Leaf Extract Mediated Silver Nanoparticles: Antibacterial, Green Catalyst. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 149, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, S.; Wraight, P. Silver Based Wound Dressings and Topical Agents for Treating Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, CD005082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lee, P.Y.; Ho, C.M.; Lui, V.C.H.; Chen, Y.; Che, C.M.; Tam, P.K.H.; Wong, K.K.Y. Silver Nanoparticles Mediate Differential Responses in Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts during Skin Wound Healing. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.; Rangasamy, S.; Purushothaman, B.; Song, J.M. The Application of Bactericidal Silver Nanoparticles in Wound Treatment. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 5–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai , J.; Biazar, E.; Jafarpour, M.; Montazeri, M.; Majdi, A.; Aminifard, S.; Zafari, M.; Akbari, H.R.; Rad, H.G. Nanotoxicology and Nanoparticle Safety in Biomedical Designs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Islam, J.; Ray, S.; Raju, P.S.; Mazumder, B. Aspects of Nanomaterials in Wound Healing. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2018, 16, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyavambiza, C.; Elbagory, A.M.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M.; Meyer, S. The Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesised from Cotyledon Orbiculata Aqueous Extract. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jura, J.; Szmyd, R.; Goralczyk, A.G.; Skalniak, L.; Cierniak, A.; Lipert, B.; Filon, F.L.; Crosera, M.; Borowczyk, J.; Laczna, E.; et al. Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Human Primary Keratinocytes. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.L.; Paladini, F.; Romano, A.; Verri, T.; Quattrini, A.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Efficacy of Silver Coated Surgical Sutures on Bacterial Contamination, Cellular Response and Wound Healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Picca, R.A.; Sportelli, M.C.; Cioffi, N.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Surface Chemical and Biological Characterization of Flax Fabrics Modified with Silver Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; De Simone, S.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. Antibacterial and Antifungal Dressings Obtained by Photochemical Deposition of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Ho, C.M.; Lok, C.N.; Yu, W.Y.; Che, C.M.; Chiu, J.F.; Tam, P.K.H. Topical Delivery of Silver Nanoparticles Promotes Wound Healing. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, B.; Radeke, H.H.; Selle, S.; Younes, M.; Sies, H.; Resch, K.; Habermehl, G.G. Human Fibroblasts Release Reactive Oxygen Species in Response to Interleukin-1 or Tumour Necrosis Factor-α. Biochem. J. 1989, 263, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, T.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; El-Aassar, M.R.; El-Hamshary, H.; El-Newehy, M.; Mo, X. Fabrication of Poly(Ester-Urethane)Urea Elastomer/Gelatin Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes for Potential Applications in Skin Tissue Engineering. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73636–73644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdușel, A.C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An up-to-Date Overview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygar, T.; Sarac, N.; Ugur, A.; Karaca, I.R. Antimicrobial Characteristics and Biocompatibility of the Surgical Sutures Coated with Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.; Poulose, E.K. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action, Synthesis, Medical Applications, and Toxicity Effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2012, 2, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamak, S.; Aksoy, E.A.; Ertas, N.; Erdogdu, C.; Sagıroglu, M.; Ulubayram, K. Ag/Silk Fibroin Nanofibers: Effect of Fibroin Morphology on Ag+ Release and Antibacterial Activity. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 67, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillet, S.; Rouanet, J.M. Silver Nanoparticles: Their Potential Toxic Effects after Oral Exposure and Underlying Mechanisms-A Review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 77, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdown, A.B.G. A Pharmacological and Toxicological Profile of Silver as an Antimicrobial Agent in Medical Devices. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 2010, 910686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano Based Drug Delivery Systems: Recent Developments and Future Prospects 10 Technology 1007 Nanotechnology 03 Chemical Sciences 0306 Physical Chemistry (Incl. Structural) 03 Chemical Sciences 0303 Macromolecular and Materials Chemistry 11 Medical and He. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, I.X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, I.S.; Mei, M.L.; Li, Q.; Chu, C.H. The Antibacterial Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Dentistry. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2555–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, C. Functional Silver Nanoparticle as a Benign Antimicrobial Agent That Eradicates Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Promotes Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 25798–25807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; McShan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sinha, S.S.; Arslan, Z.; Ray, P.C.; Yu, H. Mechanistic Study of the Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Combined Silver Nanoparticles and Common Antibiotics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8840–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.; Bulut, O.; Some, S.; Mandal, A.K.; Yilmaz, M.D. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles: Biomolecule-Nanoparticle Organizations Targeting Antimicrobial Activity. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2673–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salleh, A.; Naomi, R.; Utami, N.D.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mustafa, N.; Fauzi, M.B. The Potential of Silver Nanoparticles for Antiviral and Antibacterial Applications: A Mechanism of Action. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, P.d.F.; Cirqueira, S.S.R.; Aguiar, M.L.; Bernardo, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Forum 2014, 802, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, G.; Palem, V.V.; Sundaram, T.; Sundaram, V.; Kishore, S.C.; Bellucci, S. Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications in Theranostics. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafiuddin, A.; Salmiati; Salim, M.R.; Beng Hong Kueh, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Nur, H. A Review of Silver Nanoparticles: Research Trends, Global Consumption, Synthesis, Properties, and Future Challenges. J. Chinese Chem. Soc. 2017, 64, 732–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Servos, M.R.; Liu, J. Ultrahigh Nanoparticle Stability against Salt, PH, and Solvent with Retained Surface Accessibility via Depletion Stabilization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9910–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S. A Review on Nanoparticles : Their Synthesis and Types. Res. J. Recent Sci. Res. J. Recent. Sci. Uttar Pradesh (Lucknow Campus) 2014, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.U.; Malik, N.; Khan, M.; Cho, M.H.; Khan, M.M. Fungi-Assisted Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis and Their Applications. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintubin, L.; Verstraete, W.; Boon, N. Biologically Produced Nanosilver: Current State and Future Perspectives. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2422–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.C. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, S.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Fadaka, A.O.; Meyer, M.; Madiehe, A.M.; du Preez, M.G. The Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized from Extracts of Red and Green European Pear Cultivars. Artif. Cells 2021, 49, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, R.; Chandran, K.; Harper, S.L.; Yun, S.-I.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Plant Extract Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles: An Ongoing Source of Novel Biocompatible Materials. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A Review on Plants Extract Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications: A Green Expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Basumatary, I.B.; Sudhani, H.P.K.; Bajpai, V.K.; Chen, L.; Shukla, S.; Mukherjee, A. Plant Extract Mediated Silver Nanoparticles and Their Applications as Antimicrobials and in Sustainable Food Packaging: A State-of-the-Art Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 112, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Agarwal, P.; Kanawaria, S.; Kachhwaha, S.; Kothari, S.L. Plant-Based Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Characterization. Nanotechnol. Plant Sci. Nanoparticles Their Impact Plants 2015, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, Y.; Rajinikanth, P.S.; Ranjan, S.; Tiwari, U.; Balasubramnaiam, J.; Pandey, P.; Arya, D.K.; Anand, S.; Deepak, P. Curcumin Loaded Polycaprolactone-/Polyvinyl Alcohol-Silk Fibroin Based Electrospun Nanofibrous Mat for Rapid Healing of Diabetic Wound: An in-Vitro and in-Vivo Studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Method for the Preparation of Ultrathin Fibers. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadavil, H.; Zagho, M.; Elzatahry, A.; Altahtamouni, T. Sputtering of Electrospun Polymer-Based Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications: A Perspective. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porrelli, D.; Mardirossian, M.; Musciacchio, L.; Pacor, M.; Berton, F.; Crosera, M.; Turco, G. Antibacterial Electrospun Polycaprolactone Membranes Coated with Polysaccharides and Silver Nanoparticles for Guided Bone and Tissue Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 17255–17267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Majhi, R.K.; Singh, A.; Mishra, M.; Tiwari, A.; Chawla, S.; Guha, P.; Satpati, B.; Mohapatra, H.; Goswami, L.; et al. Carbohydrate-Coated Gold-Silver Nanoparticles for Efficient Elimination of Multidrug Resistant Bacteria and in Vivo Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 42998–43017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, S.P.; Sequeira, R.S.; Moreira, A.F.; Cabral, C.S.D.; Mendonça, A.G.; Ferreira, P.; Correia, I.J. An Overview of Electrospun Membranes Loaded with Bioactive Molecules for Improving the Wound Healing Process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alven, S.; Buyana, B.; Feketshane, Z.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Electrospun Nanofibers/Nanofibrous Scaffolds Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles as Effective Antibacterial Wound Dressing Materials. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Xiang, P.; Lu, J.; Yuan, J.; Shen, J. Electrospun Polyurethane/Keratin/AgNP Biocomposite Mats for Biocompatible and Antibacterial Wound Dressings. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, J.; Kang, D.; Zhang, H. Development of a Complex Hydrogel of Hyaluronan and PVA Embedded with Silver Nanoparticles and Its Facile Studies on Escherichia Coli. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2013, 24, 1410–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kim, H. Il Characterization and Antibacterial Properties of Genipin-Crosslinked Chitosan/Poly(Ethylene Glycol)/ZnO/Ag Nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankongadisak, P.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Supaphol, P.; Suwantong, O. Preparation and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles-Loaded Calcium Alginate Beads Embedded in Gelatin Scaffolds. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisha, B.S.; Sankar, D.; Mohandas, A.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Chitosan-Hyaluronan/Nano Chondroitin Sulfate Ternary Composite Sponges for Medical Use. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Kong, X.Y.; Shi, S.; Gu, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Guo, G.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. Biodegradable MPEG-g-Chitosan and Methoxy Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-b-Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Composite Films: Part 1. Preparation and Characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Weng, B.; Gilkerson, R.; Materon, L.A.; Lozano, K. Development of Tannic Acid/Chitosan/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers from Aqueous Solution for Potential Applications as Wound Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; Lu, Z. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanism of Ag/ZnO Nanocomposite against Anaerobic Oral Pathogen Streptococcus Mutans. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2017, 28, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Mohsen, A.M.; Jancar, J.; Abdel-Rahman, R.M.; Vojtek, L.; Hyršl, P.; Dušková, M.; Nejezchlebová, H. A Novel in Situ Silver/Hyaluronan Bio-Nanocomposite Fabrics for Wound and Chronic Ulcer Dressing: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluations. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 520, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Gao, J.; He, Q.; Wu, J.; Liang, D.; Yang, H.; Chen, R. Enhanced Antibacterial and Wound Healing Activities of Microporous Chitosan-Ag/ZnO Composite Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.D.; Rajendran, N.K.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. Recent Advances on Silver Nanoparticle and Biopolymer-Based Biomaterials for Wound Healing Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.A.; Al-Jumaily, A.M. Regenerated Cellulose/Polypyrrole/Silver Nanoparticles/Ionic Liquid Composite Films for Potential Wound Healing Applications. Wound Med. 2016, 14, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveen, G.; Sreerekha, P.R.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.V.; Chennazhi, K.P. Fibrin Nanoconstructs: A Novel Processing Method and Their Use as Controlled Delivery Agents. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 095102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ji, W.; Kim, J.R.; et al. Engineering of Hollow Polymeric Nanosphere-Supported Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids with Enhanced Antimicrobial Activities. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 5556–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Varyambath, A.; Ding, Y.; Chen, B.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Kim, I.; Song, W. Porous Organic Polymers for Drug Delivery: Hierarchical Pore Structures, Variable Morphologies, and Biological Properties. Biomater. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kim, I.; Lu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Song, W. Intelligent Poly(L-Histidine)-Based Nanovehicles for Controlled Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 963–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenry; Lim, C.T. Nanofiber Technology: Current Status and Emerging Developments. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 70, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, P.I.; Aguiar-Ricardo, A.; Correia, I.J. Asymmetric Membranes as Ideal Wound Dressings: An Overview on Production Methods, Structure, Properties and Performance Relationship. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 490, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Yoshida, C.M.P.; Leonardi, G.R.; Cano, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Zielinska, A.; Viseras, C.; Severino, P.; da Silva, C.F.; Barbosa, R.d.M. Lipid-Polymeric Films: Composition, Production and Applications in Wound Healing and Skin Repair. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumville, J.C.; Deshpande, S.; O’Meara, S.; Speak, K. Hydrocolloid Dressings for Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD009099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; He, J.; Guo, B. Functional Hydrogels as Wound Dressing to Enhance Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 12687–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, L.A.; Hart, M. Regeneration from Injury and Resource Allocation in Sponges and Corals-A Review. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2005, 90, 125–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archana, D.; Singh, B.K.; Dutta, J.; Dutta, P.K. Chitosan-PVP-Nano Silver Oxide Wound Dressing: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 73, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraipandy, N.; Lakra, R.; Vinjimur Srivatsan, K.; Ramamoorthy, U.; Korrapati, P.S.; Kiran, M.S. Plumbagin Caged Silver Nanoparticle Stabilized Collagen Scaffold for Wound Dressing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X. Preparation and Antibacterial Activity of Electrospun Chitosan/ Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Membranes Containing Silver Nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2009, 287, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumathi, K.; Sudheesh Kumar, P.T.; Abhilash, S.; Sreeja, V.; Tamura, H.; Manzoor, K.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Development of Novel Chitin/Nanosilver Composite Scaffolds for Wound Dressing Applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Cho, D.; Kwon, O.H.; Park, W.H. Thermal Fabrication and Characterization of Ag Nanoparticle-Activated Carbon Composites for Functional Wound-Dressing Additives. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2670–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Di Franco, C.; Panico, A.; Scamarcio, G.; Sannino, A.; Pollini, M. In Vitro Assessment of the Antibacterial Potential of Silver Nano-Coatings on Cotton Gauzes for Prevention of Wound Infections. Materials 2016, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Namviriyachote, N.; Lipipun, V.; Akkhawattanangkul, Y.; Charoonrut, P.; Ritthidej, G.C. Development of Polyurethane Foam Dressing Containing Silver and Asiaticoside for Healing of Dermal Wound. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanaruengsrikul, V.; Pimpha, N.; Supaphol, P. In Vitro Efficacy and Toxicology Evaluation of Silver Nanoparticle-Loaded Gelatin Hydrogel Pads as Antibacterial Wound Dressings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 1668–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, N.; Ahmed, R.; Tariq, M.; Ahmed, Z.; Masoud, M.S.; Ali, I.; Asghar, R.; Andleeb, A.; Hasan, A. Silver Nanoparticle Impregnated Chitosan-PEG Hydrogel Enhances Wound Healing in Diabetes Induced Rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; Wu, H.; Pan, X.; Xie, X.; Wu, C. Antimicrobial Activity and the Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticle Thermosensitive Gel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 2873–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Jansen, J.A.; Walboomers, X.F.; Yang, F. Antibacterial Effect and Wound Healing Ability of Silver Nanoparticles Incorporation into Chitosan-Based Nanofibrous Membranes. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Lu, Z.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Chen, R. Novel Asymmetric Wettable AgNPs/Chitosan Wound Dressing: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 3958–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, H.; Chang, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, L. Construction of Cellulose/Nanosilver Sponge Materials and Their Antibacterial Activities for Infected Wounds Healing. Cellulose 2016, 23, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Díaz, M.; Alvarado-Gomez, E.; Magaña-Aquino, M.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Velasquillo, C.; Gonzalez, C.; Ganem-Rondero, A.; Martínez-Castañon, G.; Zavala-Alonso, N.; Martinez-Gutierrez, F. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Chitosan Gels Formulated with Silver Nanoparticles and Their Cytotoxic Effect on Human Fibroblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 60, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Sun, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, P. Preparation and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles on Silk Fibroin/Carboxymethy Lchitosan Composite Sponge as Anti-Bacterial Wound Dressing. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26, S111–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, L.; Shan, X.; Zhao, X.; Zha, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Hao, J.; et al. Spongy Bilayer Dressing Composed of Chitosan–Ag Nanoparticles and Chitosan–Bletilla Striata Polysaccharide for Wound Healing Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Song, W.; Luan, J.; Wen, X.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Guo, S. In Situ Synthesis of Silver-Nanoparticles/Bacterial Cellulose Composites for Slow-Released Antimicrobial Wound Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wen, X.; Lin, Q.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z. Silver Nanoparticle/Bacterial Cellulose Gel Membranes for Antibacterial Wound Dressing: Investigation in Vitro and in Vivo. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 9, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.T.S.; Abhilash, S.; Manzoor, K.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Preparation and Characterization of Novel β-Chitin/Nanosilver Composite Scaffolds for Wound Dressing Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaser, A.S.; Abdel-Mohsen, A.M.; Ramadan, M.A.; Sleem, A.A.; Sahffie, N.M.; Jancar, J.; Hebeish, A. Preparation and Characterization of Alginate/Silver/Nicotinamide Nanocomposites for Treating Diabetic Wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mohsen, A.M.; Hrdina, R.; Burgert, L.; Abdel-Rahman, R.M.; Hašová, M.; Šmejkalová, D.; Kolář, M.; Pekar, M.; Aly, A.S. Antibacterial Activity and Cell Viability of Hyaluronan Fiber with Silver Nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Kanoujia, J.; Parashar, P.; Tripathi, C.B.; Saraf, S.A. Wound Healing Applications of Sericin/Chitosan-Capped Silver Nanoparticles Incorporated Hydrogel. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.S.; Mahdavi, H.; Elbahri, M. Extraordinarily Water Permeable Sol-Gel Formed Nanocomposite Nanofibrous Membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 366, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahri, M.; Homaeigohar, S.; Abdelaziz, R.; Dai, T.; Khalil, R.; Zillohu, A.U. Smart Metal-Polymer Bionanocomposites as Omnidirectional Plasmonic Black Absorber Formed by Nanofluid Filtration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4771–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Botcha, N.K.; Zarie, E.S.; Elbahri, M. Ups and Downs of Water Photodecolorization by Nanocomposite Polymer Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Davoudpour, Y.; Habibi, Y.; Elbahri, M. The Electrospun Ceramic Hollow Nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-l.; Li, B.-c.; Li, Z.-j.; Ren, K.-f.; Jin, L.j.; Zhang, S.-m.; Chang, H.; Sun, Y.-x.; Ji, J. Electropolymerization of Dopamine for Surface Modification of Complex-Shaped Cardiovascular Stents. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7679–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Luo, G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, Y.; He, W.; Tan, J.; Xing, M.; Wu, J. Nano-Silver-Decorated Microfibrous Eggshell Membrane: Processing, Cytotoxicity Assessment and Optimization, Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.; Soni, S.; Patial, V.; Kulurkar, P.M.; Kumari, A.; Mahesh, S.; Padwad, Y.S.; Yadav, S.K. Cytocompatible Anti-Microbial Dressings of Syzygium Cumini Cellulose Nanocrystals Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles Accelerate Acute and Diabetic Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Lu, F.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Lu, B.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lan, G. In Situ Assembly of Ag Nanoparticles (AgNPs) on Porous Silkworm Cocoon-Based Would Film: Enhanced Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, N.; Ning, X.; Miao, Y.; Long, Y.; Wu, T.; Leng, X. Harnessing Biocompatible Nanofibers and Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing: Sandwich Wound Dressing versus Commercial Silver Sulfadiazine Dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 128, 112342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Dong, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, M. The Preparation of a Recyclable Catalyst of Silver Nanoparticles Dispersed in a Mesoporous Silica Nanofiber Matrix. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65613–65618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; Lei, T.; Ehrenhauser, F.; Song, K.; Li, M.; Sun, X.; Wu, Q. Electrospun Nanofibers Made of Silver Nanoparticles, Cellulose Nanocrystals, and Polyacrylonitrile as Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Materials 2017, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aassar, M.R.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Fouda, M.M.G.; El-Beheri, N.G.; Agwa, M.M. Wound Healing of Nanofiber Comprising Polygalacturonic/Hyaluronic Acid Embedded Silver Nanoparticles: In-Vitro and in-Vivo Studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, H.S.; Akram, T.; Tamboli, A.H.; Majeed, A.; Shabir, N.; Sheikh, F.A. Novel Lavender Oil and Silver Nanoparticles Simultaneously Loaded onto Polyurethane Nanofibers for Wound-Healing Applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 569, 118590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbalifam, N.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Hashemi-Najafabadi, S.; Khorasani, A.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Antimicrobial Wound Dressing Material Based on Silver Nanoparticles Loaded Gum Arabic Nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salesa, B.; Assis, M.; Andrés, J.; Serrano-Aroca, Á. Carbon Nanofibers versus Silver Nanoparticles: Time-Dependent Cytotoxicity, Proliferation, and Gene Expression. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, G.; Miele, D.; Faccendini, A.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Rossi, S.; Grisoli, P.; Taglietti, A.; Ruggeri, M.; Bruni, G.; Vigani, B.; et al. Chitosan/Glycosaminoglycan Scaffolds: The Role of Silver Nanoparticles to Control Microbial Infections in Wound Healing. Polymers 2019, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni, M.; Shamloo, A.; Aghababaie, Z.; Afjoul, H.; Abdi, S.; Moravvej, H.; Vossoughi, M. A Comparative Study of Wound Dressings Loaded with Silver Sulfadiazine and Silver Nanoparticles: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.W.; Li, C.W.; Wang, Q.; Shi, S.J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, H.H.; Sun, J.B.; Zhou, M.; Wu, G.L.; et al. The Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Silver Nanoparticle/Chitosan Oligosaccharide/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofiber-Mediated Wound Healing. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.; Kandile, N.G.; Mahmoud, M.K.; Ibrahim, H.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Polystyrene with Embedded Silver Nanoparticle Nanofibers to Utilize as Antibacterial and Wound Healing Biomaterial. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, E.; Eslami-Arshaghi, T.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Elahirad, E.; Jamalpoor, Z.; Hatamie, S.; Soleimani, M. The Biomedical Potential of Cellulose Acetate/Polyurethane Nanofibrous Mats Containing Reduced Graphene Oxide/Silver Nanocomposites and Curcumin: Antimicrobial Performance and Cutaneous Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardania, H.; Mahmoudi, R.; Bagheri, H.; Salehpour, Z.; Fouani, M.H.; Darabian, B.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; Mousavizadeh, A.; Kowsari, M.; Moosavifard, S.E.; et al. Facile Preparation of a Novel Biogenic Silver-Loaded Nanofilm with Intrinsic Anti-Bacterial and Oxidant Scavenging Activities for Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, J.W.; Knowles, J.C.; Gong, M.S. Facile Preparation of Antibacterial, Highly Elastic Silvered Polyurethane Nanofiber Fabrics Using Silver Carbamate and Their Dermal Wound Healing Properties. J. Biomater. Appl. 2017, 31, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamady Hussein, M.A.; Guler, E.; Rayaman, E.; Cam, M.E.; Sahin, A.; Grinholc, M.; Sezgin Mansuroglu, D.; Sahin, Y.M.; Gunduz, O.; Muhammed, M.; et al. Dual-Drug Delivery of Ag-Chitosan Nanoparticles and Phenytoin via Core-Shell PVA/PCL Electrospun Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 270, 118373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Dai, L.; Si, C.; Zeng, Z. Antibacterial and Hemostatic Hydrogel via Nanocomposite from Cellulose Nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, M.; Sun, J.; Sheng, F.; Shi, S.; Lu, L. Zinc Oxide/Silver Bimetallic Nanoencapsulated in PVP/PCL Nanofibres for Improved Antibacterial Activity. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1248–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.P.; Gong, J.S.; Su, C.; Liu, Y.G.; Jiang, M.; Pan, H.; Li, R.Y.; Geng, Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Shi, J.S. Fabrication and Characterization of High Molecular Keratin Based Nanofibrous Membranes for Wound Healing. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 194, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Zayed, M.A.; El-dek, S.I.; Hady, M.A.; El Sherbiny, D.H.; Uskoković, V. Nanofibrous ε-Polycaprolactone Scaffolds Containing Ag-Doped Magnetite Nanoparticles: Physicochemical Characterization and Biological Testing for Wound Dressing Applications in Vitro and in Vivo. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2070–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonda-Turo, C.; Ruini, F.; Ceresa, C.; Gentile, P.; Varela, P.; Ferreira, A.M.; Fracchia, L.; Ciardelli, G. Nanostructured Scaffold with Biomimetic and Antibacterial Properties for Wound Healing Produced by ‘Green Electrospinning. ’ Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, M.; Validi, M.; Gholipour, A.; Makvandi, P.; Sharifi, E. Chitosan Nanofiber Biocomposites for Potential Wound Healing Applications: Antioxidant Activity with Synergic Antibacterial Effect. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, R.; Sofi, H.S.; Akram, T.; Rather, H.A.; Abdal-hay, A.; Shabir, N.; Vasita, R.; Alrokayan, S.H.; Khan, H.A.; Sheikh, F.A. Fabrication of Multifunctional Cellulose/TiO2/Ag Composite Nanofibers Scaffold with Antibacterial and Bioactivity Properties for Future Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2020, 108, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassiba, A.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Webster, T.J.; Abdullah, A.M.; Nasrallah, G.K.; Khalil, K.A.; Luyt, A.S.; Elzatahry, A.A. Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Properties of Novel Double Layer Nanocomposite Electrospun Fibers for Wound Dressing Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.H.; Nguyen, V.Q.; Le, A.T. Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, Toxicology, Applications and Perspectives. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, S.; Attia, N.; Nouh, S.; El-Kammar, M.; Korittum, A.; Abu-Ahmed, H. Fabrication of Sliver Nanoparticles/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Gelatin Ternary Nanofiber Mats for Wound Healing Application. J. Biomater. Appl. 2020, 35, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Yao, Q.; Yu, F.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Sun, H.; Lin, J.; Fu, Y. Surface Modified Electrospun Poly(Lactic Acid) Fibrous Scaffold with Cellulose Nanofibrils and Ag Nanoparticles for Ocular Cell Proliferation and Antimicrobial Application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, G.; Hussain, T.; Chauhan, G.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K. Collagen Nanofiber Containing Silver Nanoparticles for Improved Wound-Healing Applications. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ye, J.; Sun, Y.; Kang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ning, G. Electrospun Fibrous Mat Based on Silver (I) Metal-Organic Frameworks-Polylactic Acid for Bacterial Killing and Antibiotic-Free Wound Dressing. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Menazea, A.A.; Abdelghany, A.M. Blend Biopolymeric Nanofibrous Scaffolds of Cellulose Acetate/ε-Polycaprolactone Containing Metallic Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation for Wound Disinfection Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| S. No. | Wound Dressing Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fibers |
|
| [131] |
| 2 | Membranes |
|
| [132] |
| 3 | Films |
|
| [133] |
| 4 | Hydrocolloids |
|
| [134] |
| 5 | Hydrogels |
|
| [135] |
| 6 | Sponges |
|
| [136] |
| S. No. | Wound Dressing Materials | Size of AgNPs (nm) | Target Microbe | In Vivo/In Vitro Model | Advantage of Nanocoating | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chitosan-Poly Vinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP) composite | 10–30 | E. coli and S. aureus | L929 cell line | Compared to the control sample, silver nanocomposite reduced the amount of inflammatory cells by 99. | [137] |
| 2 | Plumbagin caged AgNP-collagen scaffolds | 60 nm | E. coli and B. subtilis | wistar rat/Swiss 3T6 | The antibacterial and wound-healing capabilities of silver and plumbagin in the PCSN cross-linked collagen scaffold showed the importance of nano-biotechnology. | [138] |
| 3 | Chitosan/Poly (Ethylene Oxide) matrix | 5 | E. coli | - | AgNPs, because of their size and structure, were found to increase antibacterial activity when introduced. | [139] |
| 4 | Chitin/nanosilver composite scaffolds | 5 nm | E. coli and S. aureus | L929 | The scaffolds are antibacterial and have excellent blood clotting capabilities, which will help with wound healing. These scaffolds were hazardous to mouse fibroblasts in vitro. Whether in vitro cytotoxicity affects in vivo wound healing is unknown. | [140] |
| 5 | Activated Carbon coated silver nanocomposite | 50–400 | S. aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae and P. aeruginosa | - | When compared to plain activated carbon, the Ag composites’ antibacterial activity was significantly higher. | [141] |
| 6 | Silver nano-coatings on cotton gauzes | 100–300 nm | S. aureus | HaCaT/3T3 | The developed textile materials show promise as an alternative to traditional wound dressings due to their antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility. | [142] |
| 7 | Polyurethane Foam mixed Ag-NPs Dressing | 100 | E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus | Human fibroblast | Wound healing was enhanced by the use of the foam dressing. | [143] |
| 8 | AgNP gelatin hydrogel pads | 7.7–10.8 nm | E. coli, S. aureus P. aeruginosa | Human’s normal skin fibroblasts | Gelatin hydrogel pads infused with silver nanoparticles have shown promise as antibacterial wound dressings. | [144] |
| 9 | Chitosan-PEG hydrogel | 75 | E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus | Rabbit | On day 14, the dermal layer of skin and the collagen pattern were both healthy in the Ag-NPs impregnated chitosan-PEG hydrogel group. | [145] |
| 10 | AgNPs incorporated Pluronic F127 and Pluronic F68 thermosensitive gel | - | E. coli, S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | - | Gel may disrupt the structure of bacterial cell membranes, allowing the substance to enter the cell, where it can condense DNA, combine and coagulate with the cytoplasm, and ultimately kill the bacteria by causing the cytoplasmic component to leak out. | [146] |
| 11 | Chitosan nanofiber | 25 | S. aureus | Wistar Hannover rats | Biological media had a substantial impact on the release of silver; proteins blocked the release of the metal, whereas inorganic ions slowed it down. As a result, to elicit in vivo antibacterial activities, a high concentration of AgNPs was required. | [147] |
| 12 | Asymmetric Wettable Chitosan nanocomposite | 25 | E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus | HEK293 cell line | The dressing has been shown to encourage cell growth in an in vitro cytocompatibility study. | [148] |
| 13 | Cellulose hydrogel | 5–50 | E. coli and S. aureus | New Zealand rabbit | Three days faster wound healing was seen using nanohydrogel compared to the control group. | [149] |
| 14 | Chitosan gels | 15 | P. aeruginosa | Human dermal fibroblasts | Chitosan gels containing AgNPs showed improvement in biocompatibility tests on primary fibroblasts. | [150] |
| 15 | Silk fibroin/ carboxymethyl chitosan composite sponge | 4.9 ± 1.9 nm | S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | - | This AgNP-loaded SF/CMC sponge shows promise as a potential antimicrobial wound dressing. | [151] |
| 16 | Chitosan cross-linked bilayer nanocomposite | 45 | E. coli, P. aeruginosa and S. aureus | L929 cell line | The treated group’s organized and developed epithelium was a marked improvement over that of the control group. | [152] |
| 17 | AgNPs/Bacterial cellulose composites | 10–30 nm | E. coli, S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | Epidermal cells | In vitro studies show that a nanostructured AgNP-BC gel-membrane has the potential to be an effective antimicrobial wound dressing with good biocompatibility for the expedited healing of scald wounds. | [153] |
| 18 | Silver NPs embedded bacterial cellulose gel membranes | 30 | S. aureus | Westar rats | A significant amount of healing (85.92%) occurred after 14 days of treatment. | [154] |
| 19 | β-chitin-based hydrogels | 5 | E. coli and S. aureus | ERO cell line | Manufactured scaffolds showed improved whole-blood clotting ability. | [155] |
| 20 | Silver Alginate/Nicotinamide Nanocomposites | 20–80 | E. coli and S. aureus | Mice | Significant wound healing had occurred by the fourth day of treatment. | [156] |
| 21 | Hyaluronan Nanofiber | 25 | E. coli and S. aureus | Cell line (NIH 3T3) | Since nanoparticles are so much smaller than typical particles, they are able to exert a far stronger effect on microbes. | [157] |
| 22 | Chitosan-Ag/ZnO composite dressing | 10–30 nm | Drug sensitive E. coli, S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | BALB/c mice /L02 cells | These findings support the feasibility of using the prepared chitosan-Ag/ZnO composite dressing in wound care. | [124] |
| 23 | Chitosan-based multifunctional hydrogel | 250 | E. coli and S. aureus | Rat model | Following 14 days of therapy, the test organism showed the slowest rate of re-epithelialization. | [158] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabarees, G.; Velmurugan, V.; Tamilarasi, G.P.; Alagarsamy, V.; Raja Solomon, V. Recent Advances in Silver Nanoparticles Containing Nanofibers for Chronic Wound Management. Polymers 2022, 14, 3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193994
Sabarees G, Velmurugan V, Tamilarasi GP, Alagarsamy V, Raja Solomon V. Recent Advances in Silver Nanoparticles Containing Nanofibers for Chronic Wound Management. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193994
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabarees, Govindaraj, Vadivel Velmurugan, Ganesan Padmini Tamilarasi, Veerachamy Alagarsamy, and Viswas Raja Solomon. 2022. "Recent Advances in Silver Nanoparticles Containing Nanofibers for Chronic Wound Management" Polymers 14, no. 19: 3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193994
APA StyleSabarees, G., Velmurugan, V., Tamilarasi, G. P., Alagarsamy, V., & Raja Solomon, V. (2022). Recent Advances in Silver Nanoparticles Containing Nanofibers for Chronic Wound Management. Polymers, 14(19), 3994. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193994