Robust Electrospinning-Constructed Cellulose Acetate@Anthocyanin Ultrafine Fibers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Controlled Release Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
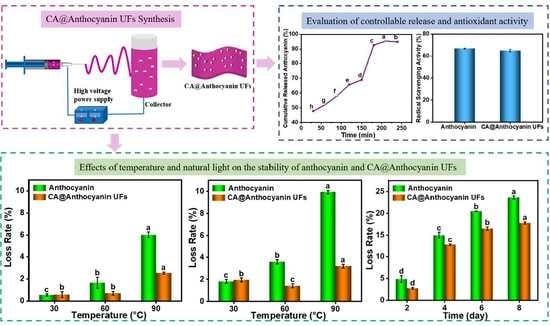
2.2. Synthesis of CA@Anthocyanin UFs
2.3. Characterizations
2.4. The Degree of Swelling of CA UFs and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
2.5. Determination of Anthocyanin Loading Efficiency
M = (M1 + M2 + M3 + … + Mn)/0.2
Loading efficiency (%) = (M/N) × 100
2.6. Effects of Temperature, Natural Light, and pH on the Stability of Anthocyanin and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
2.7. Determination of Controlled Release Properties of CA@Anthocyanin UFs In Vitro
2.8. Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanin and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Morphology and Loading Efficiency of CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.2. FTIR of Pure Anthocyanin, CA UFs, and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.3. Thermal Properties of CA UFs and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.4. Crystallinity and Mechanical Properties of CA UFs and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.5. Swelling Properties of CA UFs and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.6. Effects of Temperature on the Stability of Anthocyanin and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.7. Effects of Natural Light on the Stability of Anthocyanin and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.8. Effects of pH on the Stability of Anthocyanin and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
3.9. Determination of Controlled Release Properties of CA@Anthocyanin UFs In Vitro
3.10. Antioxidant Activity of Anthocyanin and CA@Anthocyanin UFs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castañeda-Ovando, A.; Pacheco-Hernández, M.d.L.; Páez-Hernández, M.E.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Galán-Vidal, C.A. Chemical studies of anthocyanins: A review. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belwal, T.; Singh, G.; Jeandet, P.; Pandey, A.; Giri, L.; Ramola, S.; Bhatt, I.D.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Georgiev, M.I.; Clément, C.; et al. Anthocyanins, multi-functional natural products of industrial relevance: Recent biotechnological advances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesso, C.N. Dietary anthocyanins and human health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yang, K.; Chiang, P. Roselle anthocyanins: Antioxidant properties and stability to heat and pH. Molecules 2018, 23, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Sotero, M.Y.; Cruz-Hernández, C.D.; Oliart-Ros, R.M.; Chávez-Servia, J.L.; Guzmán-Gerónimo, R.I.; González-Covarrubias, V.; Cruz-Burgos, M.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M. Anthocyanins of blue corn and tortilla arrest cell cycle and induce apoptosis on breast and prostate cancer cells. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 72, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Yi, J.; Yang, B.; Li, M.; He, D.; Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, H. Anti-tumor properties of anthocyanins from Lonicera caerulea ‘Beilei’ fruit on human hepatocellular carcinoma: In vitro and in vivo study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Ding, Y.; Ran, L.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of anthocyanins from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murray in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 136, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowd, V.; Jia, Z.; Chen, W. Anthocyanins as promising molecules and dietary bioactive components against diabetes—A review of recent advances. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L.; Saldaña, M.D.A.; Dong, T.; Jin, Y.; Sun, W. A smart nanofibre sensor based on anthocyanin/Poly-L-Lactic acid for mutton freshness monitoring. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakolpakçıl, A.; Osman, B.; Göktalay, G.; Özer, E.T.; Şahan, Y.; Becerir, B.; Karaca, E. Design and in vivo evaluation of alginate-based pH-sensing electrospun wound dressing containing anthocyanins. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconeasa, Z.; Știrbu, I.; Xiao, J.; Leopold, N.; Ayvaz, Z.; Danciu, C.; Ayvaz, H.; Stǎnilǎ, A.; Nistor, M.; Socaciu, C. Anthocyanins, vibrant color pigments, and their role in skin cancer prevention. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, P.M.; Cantrill, V.; Benohoud, M.; Tidder, A.; Rayner, C.M.; Blackburn, R.S. Application of anthocyanins from blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum L.) fruit waste as renewable hair dyes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6790–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, A.K.; Karim, N.; Xu, Y.; Xie, J.; Cui, H.; Mozafari, M.R.; Chen, W. Potential micro-/nano-encapsulation systems for improving stability and bioavailability of anthocyanins: An updated review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, A.; Gashti, M.P.; Mirjalili, M.; Parsania, M. Argon and argon-oxygen plasma surface modification of gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasian, A.; Fard, G.C.; Mirjalili, M.; Gashti, M.P. Fluorinated-PAN nanofibers: Preparation, optimization, characterization and fog harvesting property. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 62, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, A.; Gashti, M.P. Air plasma functionalization of electrospun nanofibers for skin tissue engineering. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.; Mondal, J.; Hasan, M.; Revuri, V.; Lee, D.; Lee, Y.-K. Electrospinning nanofibers for therapeutics delivery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wsoo, M.A.; Razak, S.I.A.; Shahir, S.; Al-Moalemi, H.A.A.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Nayan, N.H.M. Development of prolonged drug delivery system using electrospun cellulose acetate/polycaprolactone nanofibers: Future subcutaneous implantation. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 3664–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Huo, P.; Ding, Z.; Kumar, P.; Liu, B. Preparation of lutein-loaded PVA/sodium alginate nanofibers and investigation of its release behavior. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnevisan, K.; Maleki, H.; Samadian, H.; Shahsavari, S.; Sarrafzadeh, M.H.; Larijani, B.; Dorkoosh, F.A.; Haghpanah, V.; Khorramizadeh, M.R. Cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibers for drug delivery systems: Applications and recent advances. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wsoo, M.A.; Shahir, S.; Bohari, S.P.M.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Razak, S.I.A. A review on the properties of electrospun cellulose acetate and its application in drug delivery systems: A new perspective. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 491, 107978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wutticharoenmongkol, P.; Hannirojram, P.; Nuthong, P. Gallic acid-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate nanofibers as potential wound dressing materials. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, D.-G.; Wang, G.; Williams, G.R.; Zhang, Z. Tunable drug release from nanofibers coated with blank cellulose acetate layers fabricated using tri-axial electrospinning. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 203, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, S.; Markovic, D.; Aksentijevic, K.; Stojanovic, D.B.; Ivanovic, J.; Zizovic, I. Application of cellulose acetate for controlled release of thymol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Cai, J.; Dong, Q.; Din, Z.-U.; Hu, Z.; Wang, G.; Ding, W.; He, J.; Cheng, S. Starch/tea polyphenols nanofibrous films for food packaging application: From facile construction to enhance mechanical, antioxidant and hydrophobic properties. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Son, B.C.; Jang, S.R.; Aguilar, L.E.; Oh, Y.M.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Analysis of drug release behavior utilizing the swelling characteristics of cellulosic nanofibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddel, R.; Hesari, J.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S.; Hamishehkar, H.; Fathi-Achachlouei, B.; Huang, Q. Use of gelatin and gum Arabic for encapsulation of black raspberry anthocyanins by complex coacervation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 107, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantarodsakun, T.; Vongsetskul, T.; Jangpatarapongsa, K.; Tuchinda, P.; Uamsiri, S.; Bamrungcharoen, C.; Kumkate, S.; Opaprakasit, P.; Tangboriboonrat, P. [6]-Gingerol-loaded cellulose acetate electrospun fibers as a topical carrier for controlled release. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 3163–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, F.D.; Castro-Guerrero, C.F.; León-Silva, U. Thin films of cellulose acetate nanofibers from cigarette butt waste. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2020, 36, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Cho, Y.; Kang, S.W. Porous cellulose acetate membranes prepared by water pressure-assisted process for water-treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 78, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Sousa, A.M.M.; Fan, X.; Jin, T.; Li, X.; Tomasula, P.M.; Liu, L. Electrospun ultra-fine cellulose acetate fibrous mats containing tannic acid-Fe3+ complexes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 157, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaram, S.; Geethakrishnan, T. Vibrational spectroscopic, linear and nonlinear optical characteristics of Anthocyanin extracted from blueberry. Results Opt. 2020, 1, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Liu, J. Recent advances in the preparation, physical and functional properties, and applications of anthocyanins-based active and intelligent packaging films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Bai, R.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J. Preparation of pH-sensitive and antioxidant packaging films based on κ-carrageenan and mulberry polyphenolic extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 134, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tungprapa, S.; Jangchud, I.; Supaphol, P. Release characteristics of four model drugs from drug-loaded electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats. Polymer 2007, 48, 5030–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohany, M.; Tawakkal, I.S.M.A.; Ariffin, S.H.; Shah, N.N.A.K.; Yusof, Y.A. Characterization of anthocyanin associated purple sweet potato starch and peel-based pH indicator films. Foods 2021, 10, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, P.; Martí, N.; García-Viguera, C. Varietal blends as a way of optimizing and preserving the anthocyanin content of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6936–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tao, C.; Liu, M.; Pan, Y.; Lv, Z. Effect of temperature and pH on stability of anthocyanin obtained from blueberry. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdyło, A.; Nowicka, P.; Teleszko, M. Degradation kinetics of anthocyanins in sour cherry cloudy juices at different storage temperature. Processes 2019, 7, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaoglan, H.A.; Keklik, N.M.; Isıklı, N.D. Degradation kinetics of anthocyanin and physicochemical changes in fermented turnip juice exposed to pulsed UV light. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 56, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinopoli, A.; Calogero, G.; Bartolotta, A. Computational aspects of anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: A review. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, N.; Martín, J.; Asuero, A.G. State of the art of anthocyanins: Antioxidant activity, sources, bioavailability, and therapeutic effect in human health. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Zhang, S.; Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; He, J.; Wei, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J. Robust Electrospinning-Constructed Cellulose Acetate@Anthocyanin Ultrafine Fibers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Controlled Release Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 4036. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194036
Liu M, Zhang S, Ye Y, Liu X, He J, Wei L, Zhang D, Zhou J, Cai J. Robust Electrospinning-Constructed Cellulose Acetate@Anthocyanin Ultrafine Fibers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Controlled Release Properties. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):4036. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194036
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Mingzhu, Shilei Zhang, Yuanyuan Ye, Xiaoqing Liu, Jiangling He, Lingfeng Wei, Die Zhang, Jiaojiao Zhou, and Jie Cai. 2022. "Robust Electrospinning-Constructed Cellulose Acetate@Anthocyanin Ultrafine Fibers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Controlled Release Properties" Polymers 14, no. 19: 4036. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194036
APA StyleLiu, M., Zhang, S., Ye, Y., Liu, X., He, J., Wei, L., Zhang, D., Zhou, J., & Cai, J. (2022). Robust Electrospinning-Constructed Cellulose Acetate@Anthocyanin Ultrafine Fibers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Controlled Release Properties. Polymers, 14(19), 4036. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14194036