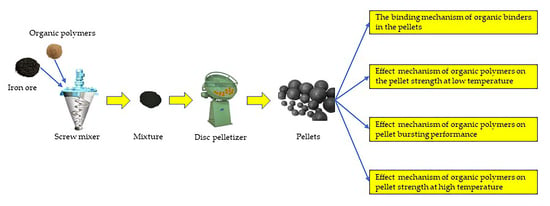
A Review on the Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Properties for Iron Ore Beneficiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Process of Producing Iron Ore Pellet
3. The Binding Mechanism of Organic Binders in the Pellets
4. Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on the Pellet Strength at Low Temperature
5. Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Bursting Performance
6. Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Strength at High Temperature
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmes, R.J.; Lu, Y.; Lu, L. Introduction: Overview of the global iron ore industry. Iron Ore 2015, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawatra, S.K.; Claremboux, V. Iron ore pelletization: Part II. Inorganic binders. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2021, 43, 813–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savel’Ev, S.G.; Gubin, G.V.; Stoikova, Y.A. Prospects for the production of iron-ore pellets. Steel Transl. 2013, 43, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.-R.; Zhang, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-R.; Liu, Z.-J.; Liu, X.-L.; Li, N.-Y. Effects of an inorganic binder on the strength property of cold-bonded pellets. Met. Res. Technol. 2017, 114, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsmo, S.; Apelqvist, A.; Björkman, B.; Samskog, P.-O. Binding mechanisms in wet iron ore green pellets with a bentonite binder. Powder Technol. 2006, 169, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-H.; Gan, M.; Jiang, T.; Chen, X.-L.; Yuan, L.-S. Decreasing bentonite dosage during iron ore pelletising. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2011, 38, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, R.P.; De Mendonca, C.F.; Kater, T. Production of acid iron ore pellet for direct reduction, using an organic binder. Min. Eng. 1984, 36, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar]
- Kater, T.; Steeghs, R. Organic Binders for Iron Ore Pelletizing; U.S. Department of Energy: Duluth, MN, USA, 1984; pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zhou, F.S.; Ma, C.F.; Wei, Z.J.; Long, W.J. Bonding mechanism and process characteristics of special polymers applied in pelletizing binders. Coatings 2022, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claremboux, V.; Kawatra, S.K. Iron ore pelletization: Part III. organic binders. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhou, F.; Bao, X.; Zhou, S.; Wei, Z.; Long, W.J.; Yi, Z. A review on the humic substances in pelletizing binders: Preparation, interaction mechanism, and process characteristics. ISIJ Int. 2022, 36, ISIJINT-2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusti, P.; Barik, K. Effect of additives concentration on pelletization of high grade hematite. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 5373–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zhou, F.S.; Evelina, L.M.A.; Liu, J.L.; Zhou, Y. A review on the industrial solid waste application in pelletizing additives: Composition, mechanism and process characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Duan, D.; Li, Y. Binders and the Bonding Mechanism of Fly Ash and Coke Pelletization. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2017, 39, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, S.L.D.; Lima, J.R.B.D.; Ribeiro, T.R. Iron ore pelletizing process: An overview. In Iron Ores and Iron Oxide Materials; Volodymyr, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, M.; Alnouri, S.Y.; Abu Tarboush, B.J.; Ahmad, M.N. Renewable biofuel production from biomass: A review for biomass pelletization, characterization, and thermal conversion techniques. Int. J. Green Energy 2018, 15, 837–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graça, L.M.; da Silva, G.; Machado, M.M.; da Silva, J.B.S.; Ávila, C.F.; Scholz, R.; Lagoeiro, L. Toward the influence of iron oxide morphology on the grinding and filtration processes and on the cold crushing strength (CCS) of heat-treated iron ore pellets. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2018, 41, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, C.; Alvarenga, T.; Pessanha, S. Study of Iron Ore Mixtures Behavior in the Grinding Pelletizing Process. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2017, 38, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Wu, W.H.; Chen, T.J.; Song, S.X. A case study on large-scale production for iron oxide pellets: Ezhou pelletization plant of the BAOWU. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 39, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K. Pelleting of Iron Ores; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1980; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- Barik, K.; Prusti, P.; Meikap, B.C.; Soren, S.; Venugopal, R.; Biswal, S.K. Investigation on Loss on Ignition to Study the Effect of Iron Ore Mineralogy in Green Pellet Growth Kinetics. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 75, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, H.J.; Kappl, M. Normal capillary forces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 146, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, W. Size enlargement by agglomeration. In Handbook of Powder Science & Technology; Fayed, M.E., Otten, L., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 202–377. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.J. Preparation of MgO Bearing Additive for Pellet and Mechanisem Investigation of it on the Effect to Quality of Pellets. Ph.D. Thesis, Northeastern University, Shenyang, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, H. Capillary forces—modeling and application in particulate technology. Powder Technol. 1984, 37, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iveson, S.M.; Litster, J.D.; Hapgood, K.; Ennis, B.J. Nucleation, growth and breakage phenomena in agitated wet granulation processes: A review. Powder Technol. 2001, 117, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsmo, S.; Samskog, P.-O.; Björkman, B. A study on plasticity and compression strength in wet iron ore green pellets related to real process variations in raw material fineness. Powder Technol. 2008, 181, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holuszko, M.E.; Laskowski, J.S. Use of Pelletization to Assess the Effect of Particle–Particle Interactions on Coal Handleability. Coal Prep. 2004, 24, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawachi, S.; Kasama, S. Effect of Micro-particles in Iron Ore on the Granule Growth and Strength. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, J.; Ghorai, S.; Agarwal, S.; Nandi, B.; Chakraborty, T.; Das, G.; Prakash, S. Effect of Blaine Fineness on the Quality of Hematite Iron Ore Pellets for Blast Furnace. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2014, 36, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Lobo, N.F.; Kumar, P. Optimization of disc parameters producing more suitable size range of green pellets. Int. J. Metall. Eng. 2012, 1, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.Q.; Pan, J.; Lu, L.M.; Holmes, R.J. Iron ore pelletization. Iron Ore 2015, 435–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Jiang, T.; Fan, X.; Zhu, D.; Huang, Z. Effects of binders on balling behaviors of iron ore concentrates. Scand. J. Met. 2004, 33, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasiya, S.K.; Markandeya, R. Utilization of Kimberlite as Binder for Iron Ore Pellet Making. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 1969–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, D. Structural Adhesives-Chemistry and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987; Volume 25, p. 233. [Google Scholar]
- Casey, L. Organic Binders for Iron ore Pelletization. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University, Helsinki, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, G.; Jiang, T.; Li, H.; Wang, D. Functions and molecular structure of organic binders for iron ore pelletization. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 224, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsmo, S.P.E. Influence of Green Pellet Properties on Pelletizing of Magnetite Iron Ore. Ph.D. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Goetzman, H.; Bleifuss, R.; Engesser, J. Investigation of carboxymethyl cellulose binders for taconite pelletizing. In Proceedings of the SME Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25 January 1988; pp. 88–111. [Google Scholar]
- Halt, J.A.; Kawatra, S.K. Review of organic binders for iron ore concentrate agglomeration. Mining, Met. Explor. 2014, 31, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BeMiller, J.N.; Whistler, R.L. Industrial gums: Polysaccharides and Their Derivatives; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pensini, E.; Yip, C.M.; O’Carroll, D.; Sleep, B.E. Carboxymethyl cellulose binding to mineral substrates: Characterization by atomic force microscopy–based Force spectroscopy and quartz-crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 402, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, A. Synthetic organic binders in iron ore pelletisation. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Agglomeration, Nagoya, Japan, 3–7 May 1993; pp. 196–201. [Google Scholar]
- Illés, E.; Tombácz, E. The effect of humic acid adsorption on pH-dependent surface charging and aggregation of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 295, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeer, A.; Koopal, L.K. Adsorption of Humic Acids to Mineral Particles. 2. Polydispersity Effects with Polyelectrolyte Adsorption. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4210–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Schmitt, J.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L.; McCarthy, J.F. Adsorption and desorption of natural organic matter on iron oxide: Mechanisms and models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Lin, D.; Xing, B. Interactions of Humic Acid with Nanosized Inorganic Oxides. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3571–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-B.; Li, P.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Han, G.-H.; Li, G.-H.; Xu, B.; Jiang, T. Adsorption of lignite humic acid onto magnetite particle surface. J. Central South Univ. 2012, 19, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunde, M. Organic Binder as a Substitute for Bentonite in Ilmenite Pelletization. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Potapova, E.; Yang, X.; Grahn, M.; Holmgren, A.; Forsmo, S.P.E.; Fredriksson, A.; Hedlund, J. The effect of calcium ions, sodium silicate and surfactant on charge and wettability of magnetite. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 386, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, M.C.J.; Garbers-Craig, A.M. Influence of a carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) binder on the mechanical properties of iron ore pellets. J. South. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 2017, 117, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Kawatra, S.K. Pelletization using humic substance-based binder. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2016, 38, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, G.; Yu, J. Effects and Mechanisms of Binders on the Properities of Magnesium Oxide Pellets. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2016, 57, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Dishwar, R.K.; Omar, R.J.; Mahobia, G.S. Hardening Behaviour of Pellets Prepared from a Novel Combination of Rare Multimetallic Magnetite Ore and Binder. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2021, 74, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrikaya, O. Use of Boron Based Binders in Pelletization of Iron Ores. Ph.D. Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wattanaphan, P.; Kawatra, S.K. Application of modified humic acid (MHA) binder in the pelletizing of fluxed hematite concentrate. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2016, 31, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Liu, B.-B.; Li, G.-H.; Jiang, T. Effect of modified humic acid binder on pelletisation of specularite concentrates. J. Central South Univ. 2015, 22, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, C. Binding mechanisms of polysaccharides adsorbing onto magnetite concentrate surface. Powder Technol. 2018, 340, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizhikova, V.M.; Vainshtein, R.M.; Zorin, S.N.; Zainetdinov, T.I.; Zinyagin, G.A.; Shevchenko, A.A. Production of Iron-Ore Pellets with an Organic Binder. Metallurgist 2003, 47, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B. Study on the Binding Mechanisms and Experiment of Sodium Lignosulfonate in Pellets. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eisele, T.C.; Kawatra, S.K. A review of binders in iron ore pelletization. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2003, 24, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonova, N.S.; Il’Chenko, L.G.; Gol’Dman, M.M.; Ni, L.P. IR spectroscopic study of the adsorption of polyacrylamide on hematite. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 1975, 23, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.T.; Somasundaran, P. Adsorption of polyacrylamide on oxide minerals. Langmuir 1989, 5, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Dixon, J.B.; White, G.N.; Loeppert, R.H.; Juo, A.S.R. Bonding between polyacrylamide and smectite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 281, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Mishra, V.; Singh, P.; Srivastava, A.; Kumar, R. Comparative study of thermal degradation behavior of graft copolymers of polysaccharides and vinyl monomers. J. Therm. Anal. 2011, 107, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettignano, A.; Charlot, A.; Fleury, E. Carboxyl-functionalized derivatives of carboxymethyl cellulose: Towards advanced biomedical applications. Polym. Rev. 2019, 59, 510–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogendam, C.W.; de Keizer, A.; Stuart, A.M.A.C.; Bijsterbosch, B.H.; Batelaan, J.G.; van der Horst, P.M. Adsorption Mechanisms of Carboxymethyl Cellulose on Mineral Surfaces. Langmuir 1998, 14, 3825–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.-M.; Fan, X.-H.; Chen, X.-L.; Yuan, L.-S.; Huang, X.-X.; Li, X. Interaction mechanism between carboxylmethyl cellulose and iron ore concentrates in iron ore agglomeration. J. Central South Univ. 2015, 22, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.H.; Yang, G.M.; Chen, X.L.; He, X.N.; Huang, X.X.; Gao, L. Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose on the drying dynamics and thermal cracking performance of iron ore green pellets. Powder Technol. 2014, 267, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Patra, A.S.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Paul, I. Interaction and thermal stability of carboxymethyl cellulose on alpha-Fe2O3(001) surface: ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulations study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2021, 102, 107787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinkels, J.J.M. Composition and properties of commercial native starches. Starch 1985, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halt, J.A.; Kawatra, S.K. Can modified starch be used as a binder for iron ore pellets? Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2016, 38, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.J.; Bin, D.; Yi, D.D.; Kai, J.X.; Bo, X.J. Action and behavior of gelatinized starch in iron pellets. Iron Steel 2017, 52, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ripke, S.J. Advances in Iron Ore Pelletization by Understanding Bonding and Strengthening Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, T. Detailed Adsorption Studies of Active Humic Acid Fraction of a New Binder on Iron Ore Particles. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2013, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Su, S.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, X. Research on the Interaction of Humic Acid with Iron Minerals. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Han, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Huang, Y. A further study on the interaction between one of organic active fractions of the MHA binder and iron ore surface. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 100, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.-H.; Jiang, T.; Huang, Y.-F.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Li, G.-H. Characteristics of humin fractions associated with inorganic minerals obtained by NaOH, and NaOH assisted with anthraquinone extraction procedures. J. Central South Univ. 2012, 19, 2286–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.B.; Lu, M.M.; Zhou, Y.L.; Su, Z.J.; Liu, B.B.; Li, G.H.; Jiang, T. Interfacial interaction between humic acid and vanadium, titanium-bearing magnetite (VTM) particles. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2018, 41, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Comparative study on the adsorption interactions of humic acid onto natural magnetite, hematite and quartz: Effect of initial HA concentration. Powder Technol. 2014, 251, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Effects of metal cations on the fulvic acid (FA) adsorption onto natural iron oxide in iron ore pelletizing process. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Kawatra, S.K. Humic Substance-based Binder in Iron Ore Pelletization: A Review. Miner. Process. Extr. Met. Rev. 2017, 38, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holladay, J.E.; White, J.F.; Bozell, J.J.; Johnson, D. Top Value-Added Chemicals from Biomass-Volume II—Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Biorefinery Lignin; Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–79. [Google Scholar]
- Beste, A. ReaxFF Study of the Oxidation of Lignin Model Compounds for the Most Common Linkages in Softwood in View of Carbon Fiber Production. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D. Lignin as a base material for materials applications: Chemistry, application and economics. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2008, 27, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanthakumar, B.; Arinaitwe, E.; Pawlik, M. Adsorption of sodium lignosulfonates on hematite. Adsorption 2010, 16, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S. Concretion mechanism and strengthened pathway of green iron ore pellet. Met. Mater. Metall. Eng. 2013, 41, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Adams, M.; Reynolds, G.; Salman, A.; Hounslow, M. Impact deformation and rebound of wet granules. Powder Technol. 2004, 140, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Wu, E.H.; Li, J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, S.L.; Li, J.H. Analysis of effect of modified organic binder on pelletizing properties. Sinter. Pelletizing 2017, 42, 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xie, B.; Qin, Y.-L. Effect of Bentonite on the Pelleting Properties of Iron Concentrate. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 7639326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, G.; Fan, X.; Gan, M.; Ji, Z.; Chen, X.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Z. Improvement on the thermal cracking performance of pellets prepared from ultrafine iron ore. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.F.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Zhou, X.J. Study on increasing the burst temperature of green ball from Chengchao pellet plant. Min. Eng. 2021, 19, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.L.; Zhou, G.F.; Yang, H. Mechanism of binder’s effect in shock resisting of green balls. Sinter. Pelletizing 1995, 20, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Qin, G.L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.Y.; Yang, T. Experimental research on pellet production with boron-containing concentrate. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Dong, X.; Li, M. Study on Application of Iron Ore Fine in Pelletizing. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 279–285. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.G.; Yang, D.B. Influence of binder on quality of chengchao iron concentrate pellet. Sinter. Pelletizing 2011, 36, 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Roorda, H.J.; Burghardt, O.; Kortmann, H.A.; Jipping, M.J.; Kater, T. Organic binder for iron ore agglomeration. In Proceedings of the 11th International Mineral Processing Congress, Cagliari, Italy, 20–26 April 1975; pp. 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, D.Y. Study on the Behavior and Experiment of Gelatinized Starch in Iron Oxide Pellets. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y. Research on Application of MHA Binder in Oxidized Pellet Preparation from Specularite Concentrates. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J. Advances in alternative binders for iron ore pellets. Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan Technological University, Houghton, MI, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, J.E.D. Effects of starch solubility on the quality of unfired hematite concentrate pellets. Mining, Met. Explor. 2014, 31, 177–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, L.A.; Aldinger, J.A.; Zahl, R.K. Effectiveness of Organic Binders for Iron Ore Pelletization; US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.H.; Zhang, Y.B.; Jiang, T.; Huang, Y.F.; Li, G.H. Effects of binders on oxidized pellets preparation from vanadium/titanium-bearing magnetite. In 2nd International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 279–287. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, T. Optimizing the Mass Ratio of Two Organic Active Fractions in Modified Humic Acid (MHA) Binders for Iron Ore Pelletizing. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsmo, S.; Hägglund, A. Influence of the olivine additive fineness on the oxidation of magnetite pellets. Int. J. Miner. Process 2003, 70, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Li, J. Crystal rule of Fe2O3 in oxidized pellet. J. Cent. South Univ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 38, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.B. Study on crystallization rule of oxidized pellet. Res. Iron Steel 2005, 33, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L. Influence and Mechanism of Al2O3 and SiO2 on Iron Ore Sintering. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, R.; Li, W.; Wang, N.; Fu, G.; Chu, M.; Zhu, M. Influence and Mechanism of CaO on the Oxidation Induration of Hongge Vanadium Titanomagnetite Pellets. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Yan, Z.Z.; Liu, X.J.; Dong, X.X.; Lan, C.C.; Li, J.P. Research status of the effect of chemical composition on the compressive strength of pellets. Sinter. Pelletizing 2017, 42, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, J.F.; Wang, Y.F.; He, Z.J.; Zhan, W.L. Study on influence of iron ore composition on the basic sintering characteristics. Sinter. Pelletizing 2016, 41, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Jiang, X.; Shen, F.; Zheng, H.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, X. Influence of SiO2 on the Compressive Strength and Reduction-Melting of Pellets. Metals 2019, 9, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDonald, J.E.D.; Kawatra, S.K. Agglomeration of hematite concentrate by starches. Miner. Processing Extr. Metall. Rev. 2016, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, C.-Y.; Liu, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Wang, R.-R.; Ma, L.-M. Effect of organic binders on the activation and properties of indurated magnetite pellets. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2021, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.S.; Yuan, Z.T.; Liu, J.T.; Lu, J.W.; Li, L.X.; Hao, H.Q. Binding effects and mechanisms of the carboxymethyl starch modified with nano-CaCO3 in magnetite concentrate pellets. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrikaya, O.; Arol, A.I. Use of organic binders and borates in pelletizing of iron oxides. In Proceedings of the 4th International Boron Symposium, Eskişehir, Turkey, 15–17 October 2009; pp. 251–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sivrikaya, O.; Arol, A.I. The bonding/strengthening mechanism of colemanite added organic binders in iron ore pelletization. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2012, 110-111, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.-W.; Bai, J.-L.; Zhang, J.-L.; Li, H.-G. Mechanism of Strength Improvement of Magnetite Pellet by Adding Boron-bearing Iron Concentrate. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuchkov, V.I.; Zayakin, O.V.; Akberdin, A.A. Prospects for Using Boron in Metallurgy. Report 1. Steel Transl. 2021, 51, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malysheva, T.; Chesnokova, G.; Akberdin, A.; Dolitskaya, O. Effect of boron on the quality of iron ore pellets. J. Russ. Metall. Met. 1996, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Suman, S.K. Compressive Strength of Fired Pellets Using Organic Binder: Response Surface Approach for Analyzing the Performance. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrikaya, O.; Arol, A. Pelletization of magnetite ore with colemanite added organic binders. Powder Technol. 2011, 210, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrikaya, O.; I Arol, A. Method to improve preheated and fired strengths of haematite pellets using boron compounds with organic binders. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M. Study on the Process and Mechanism of Improving the Pelletization of Brazilian Hematite by Adding Boron Bearing Compound Additives. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.P.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhu, J.G. Effect of alkali metals content on roasting of Fe2O3 briquetting. Nonferrous Met. Extr. Metall. 2016, 3, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.D.; Sun, Q.; He, M.Z.; Luo, G.P. Influence of element of F, K, Na on pellet morphology and composition. Nonferrous Met. Extr. Metall. 2019, 2, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.P.; Jia, X.B.; Wu, S.L.; Duan, X.G.; Hao, Z.Z. Effect of K and Na on sinter crystal-intensity of baiyunebo iron ore concentrates. J. Iron Steel Res. 2014, 26, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Luo, G.-P.; Sun, C.-C.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.-G. Effect of K and Na on reduction swelling performance of oxidized roasted briquettes. High Temp. Mater. Process. 2021, 40, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammasi, A.; Pal, J. Replacement of bentonite in hematite ore pelletisation using a combination of sodium lignosulphonate and copper smelting slag. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2016, 43, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, B.; Jana, R. Premchand Characteristics and utilisation of copper slag—a review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 39, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, T.C.; Singh, P.; Nikoloski, A.N. The potential for copper slag waste as a resource for a circular economy: A review—Part II. Miner. Eng. 2021, 172, 107150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, H.; Ma, C.; Zhou, Y. A Review on the Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Properties for Iron Ore Beneficiation. Polymers 2022, 14, 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224874
Zhao H, Zhou F, Zhao H, Ma C, Zhou Y. A Review on the Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Properties for Iron Ore Beneficiation. Polymers. 2022; 14(22):4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224874
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hongxing, Fengshan Zhou, Hongyang Zhao, Cunfa Ma, and Yi Zhou. 2022. "A Review on the Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Properties for Iron Ore Beneficiation" Polymers 14, no. 22: 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224874
APA StyleZhao, H., Zhou, F., Zhao, H., Ma, C., & Zhou, Y. (2022). A Review on the Effect of the Mechanism of Organic Polymers on Pellet Properties for Iron Ore Beneficiation. Polymers, 14(22), 4874. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224874