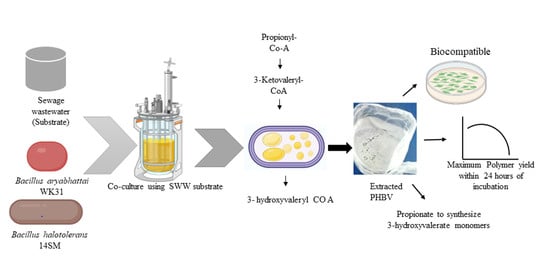
Co-Culture of Halotolerant Bacteria to Produce Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Using Sewage Wastewater Substrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Sewage Wastewater
2.2. Growth Kinetics of the Monocultures in Glucose and SWW
2.3. Co-Culture of WK31 and 14SM for PHA Production
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy of the PHA-Producing Bacterial Cells
2.5. Biomass Collection and PHA Extraction
2.6. Chemical Characterization of the Extracted Polymer
2.7. Cytotoxic Effect of PHA Synthesized Using Wastewater
2.8. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assay
3. Results
3.1. Monoculture of Selected Bacteria Sewage Wastewater as Substrates
3.2. Co-Culture of WK31 and 14SM Using Sewage WW as a Substrate
3.3. Structural Analysis of Intracellular PHA
3.4. Structural Elucidation of the Extracted PHA
3.5. Biocompatibility of PHA Produced Using Wastewater and Open Mixed Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, M.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wen, X.; Tang, W. Are biodegradable plastics a promising solution to solve the global plastic pollution? Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendrossek, D.; Handrick, R. Microbial Degradation of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 403–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, E.; Kaur, R.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E. Prospects of biopolymer technology as an alternative option for non-degradable plastics and sustainable management of plastic wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rathour, R.; Singh, R.; Sun, Y.; Pandey, A.; Gnansounou, E.; Lin, K.Y.; Tsang, D.C.; Thakur, I.S. Bacterial poly-hydroxyalkanoates: Opportunities, challenges, and prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmowafy, E.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Skouras, A.; Tiboni, M.; Casettari, L.; Guarino, V. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, F.; Rasul, I.; Azeem, F.; Siddique, M.H.; Zubair, M.; Nadeem, H. Microbial polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs): Efficient re-placement of synthetic polymers. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 2301–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.-C.; Shen, R.; Yao, H.; Chen, J.-C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.-Q. Engineering the diversity of polyesters. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 29, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, A.B.; Kumar, A.J.; Thulasi, K.; Kumarapillai, H. Evaluation of short-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoate accumulation in Bacillus aryabhattai. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorkoth, D.; Nampoothiri, K.M. Production and characterization of poly(3-hydroxy butyrate-co-3 hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) by a novel halotolerant mangrove isolate. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 201, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, F.I.; Muhammad, N.; Hamid, A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Sharif, F. Recent progress in the utilization of biosynthesized polyhy-droxyalkanoates for biomedical applications–review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1294–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.; Kandasamy, G.P.M.; Kandasamy, S.; Ashokkumar, V.; Nasif, O.; Pugazhendhi, A. Optimization and production of polyhydroxybutyrate from sludge by Bacillus cereus categorized through FT-IR and NMR analyses. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 104908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Kalia, V.C. Microbial Cometabolism and Polyhydroxyalkanoate Co-polymers. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 57, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müller-Santos, M.; Koskimäki, J.J.; Alves, L.P.; de Souza, E.M.; Jendrossek, D.; Pirttilä, A.M. The protective role of PHB and its degra-dation products against stress situations in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuaa058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlacek, P.; Slaninova, E.; Koller, M.; Nebesarova, J.; Marova, I.; Krzyzanek, V.; Obruca, S. PHA granules help bacterial cells to preserve cell integrity when exposed to sudden osmotic imbalances. New Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaninova, E.; Sedlacek, P.; Mravec, F.; Mullerova, L.; Samek, O.; Koller, M.; Hesko, O.; Kucera, D.; Marova, I.; Obruca, S. Light scattering on PHA granules protects bacterial cells against the harmful effects of UV radiation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obruca, S.; Sedlacek, P.; Koller, M.; Kucera, D.; Pernicova, I. Involvement of polyhydroxyalkanoates in stress resistance of microbial cells: Biotechnological consequences and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, R.; Xu, T.; Xiang, H.; Han, J. Current developments on polyhydroxyalkanoates synthesis by using halophiles as a promising cell factory. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Yoon, J.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Hong, J.W.; Hong, Y.G.; Song, H.-S.; Moon, Y.-M.; Jeon, J.-M.; Kim, Y.-G.; Yang, Y.-H. Engineering of artificial microbial consortia of Ralstonia eutropha and Bacillus subtilis for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) copolymer production from sugarcane sugar without precursor feeding. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Jamil, N. Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production in bacterial co-culture using glucose and volatile fatty acids as carbon source. J. Basic Microbiol. 2018, 58, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Jamil, N. Optimized Growth conditions for polyhydroxyalkanoate production by halotolerant bacteria isolated from Karachi mangrove forest. J. Agric. Food 2021, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, T.; Khan, N.; Jamil, N. Synthesis of scl-poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates) by Bacillus cereus found in freshwater, from monosaccharides and disaccharides. Front. Biol. 2018, 13, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Jamil, N. Characterization of Polyhydroxyalkanoates Produced by Contaminated Soil Bacteria using Wastewater and Glucose as Carbon Sources. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2015, 14, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benov, L. Effect of growth media on the MTT colorimetric assay in bacteria. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naik, S.; Nace, R.; Barber, G.N.; Russell, S.J. Potent systemic therapy of multiple myeloma utilizing oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus coding for interferon-β. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouřilová, X.; Schwarzerová, J.; Pernicová, I.; Sedlář, K.; Mrázová, K.; Krzyžánek, V.; Nebesářová, J.; Obruča, S. The first insight into polyhydroxyalkanoates accumulation in multi-extremophilic Rubrobacter xylanophilus and Rubrobacter spartanus. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Sinskey, A.J.; Stubbe, J. Kinetic studies of polyhydroxybutyrate granule formation in Wautersia eutropha H16 by trans-mission electron microscopy. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 3814–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.K.; Munir, R.I.; de Kievit, T.; Levin, D.B. Synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from vegetable oils and free fatty acids by wild-type and mutant strains of Pseudomonas chlororaphis. Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pramanik, N.; DAS, R.; Rath, T.; Kundu, P.P. Microbial Degradation of Linseed Oil-Based Elastomer and Subsequent Accumulation of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) Copolymer. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 1613–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossu, J.; Angellier-Coussy, H.; Totee, C.; Matos, M.; Reis, M.; Guillard, V. Effect of the Molecular Structure of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (P(3HB-3HV)) Produced from Mixed Bacterial Cultures on Its Crystallization and Mechanical Properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 4709–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, G.; Serafim, L.S.; Lemos, P.C.; Ramos, A.M.; Reis, M.A.M.; Cabrita, E.J. Influence of feeding strategies of mixed microbial cultures on the chemical composition and microstructure of copolyesters P(3HB-co-3HV) analyzed by NMR and statistical analysis. Org. Magn. Reson. 2009, 47, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Chujo, R.; Doi, Y. Microstructure of bacterially synthesized poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate). Macromolecules 1989, 22, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadh, P.K.; Duhan, S.; Duhan, J.S. Agro-industrial wastes and their utilization using solid state fermentation: A review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2018, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciesielski, S.; Przybylek, G. Volatile fatty acids influence on the structure of microbial communities producing PHAs. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valentino, F.; Moretto, G.; Lorini, L.; Bolzonella, D.; Pavan, P.; Majone, M. Pilot-scale polyhydroxyalkanoate production from com-bined treatment of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and sewage sludge. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 12149–12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Agyeman, I.; Plaza, E.; Cetecioglu, Z. Production of volatile fatty acids through co-digestion of sewage sludge and external organic waste: Effect of substrate proportions and long-term operation. Waste Manag. 2020, 112, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittmann, T.; Steinmetz, H. Polyhydroxyalkanoate Production on Waste Water Treatment Plants: Process Scheme, Operating Conditions and Potential Analysis for German and European Municipal Waste Water Treatment Plants. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morgan-Sagastume, F.; Valentino, F.; Hjort, M.; Cirne, D.; Karabegovic, L.; Gerardin, F.; Johansson, P.; Karlsson, A.; Magnusson, P.; Alexandersson, T.; et al. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production from sludge and municipal wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 69, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- York, G.M.; Junker, B.H.; Stubbe, J.; Sinskey, A.J. Accumulation of the PhaP Phasin of Ralstonia eutropha Is Dependent on Production of Polyhydroxybutyrate in Cells. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4217–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, S.-W.; Guo, X.-Y.; Shang, G.-G.; Li, J.; Xu, X.-Y.; You, M.-L.; Li, P.; Chen, G.-Q. An assessment of the risks of carcinogenicity associated with polyhydroxyalkanoates through an analysis of DNA aneuploid and telomerase activity. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insomphun, C.; Chuah, J.A.; Kobayashi, S.; Fujiki, T.; Numata, K. Influence of hydroxyl groups on the cell viability of polyhydrox-yalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds for tissue engineering. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3064–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Véronique, A.; Hanik, N.; Pott, J.; Utsunomia, C.; Zinn, M. Tailored Biosynthesis of Polyhydroxyalkanoates in Chemostat Cultures. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, H.S.J.; Bhubalan, K.; Amirul, A.-A.A. A Critical Review on the Economically Feasible and Sustainable Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Production from Alkyl Alcohols. Polymers 2022, 14, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| 1HNMR (ppm) | Integrated Signals | Diad/Triad | Chemical Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.846 | 14.97 | VV (t) | HV5 | CH3 |
| 0.941 | 2.77 | VV | HV5 | CH3 |
| 1.248 | 11 | BV(d) | HB4 | CH3 |
| 1.582 | 12.20 | VV*V | HV4 | CH2 |
| 2.330 | 1.9 | BV | HB2 | CH2 |
| 2.452 | 1.81 | B*V | HB2 | CH2 |
| 2.584 | 1.47 | BV*V | HB2 | CH2 |
| 4.849 | 3.91 | BB | HV3 | CH |
| 5.236 | 1.33 | V*B | HB3 | CH |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, N.; Ali, I.; Mazhar, S.; Munir, S.; Batool, R.; Jamil, N. Co-Culture of Halotolerant Bacteria to Produce Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Using Sewage Wastewater Substrate. Polymers 2022, 14, 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224963
Khan N, Ali I, Mazhar S, Munir S, Batool R, Jamil N. Co-Culture of Halotolerant Bacteria to Produce Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Using Sewage Wastewater Substrate. Polymers. 2022; 14(22):4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224963
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Naima, Iftikhar Ali, Sumaira Mazhar, Sajida Munir, Rida Batool, and Nazia Jamil. 2022. "Co-Culture of Halotolerant Bacteria to Produce Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Using Sewage Wastewater Substrate" Polymers 14, no. 22: 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224963
APA StyleKhan, N., Ali, I., Mazhar, S., Munir, S., Batool, R., & Jamil, N. (2022). Co-Culture of Halotolerant Bacteria to Produce Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Using Sewage Wastewater Substrate. Polymers, 14(22), 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14224963