Biosorption of Cr(VI) Using Cellulose Nanocrystals Isolated from the Waterless Pulping of Waste Cotton Cloths with Supercritical CO2: Isothermal, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
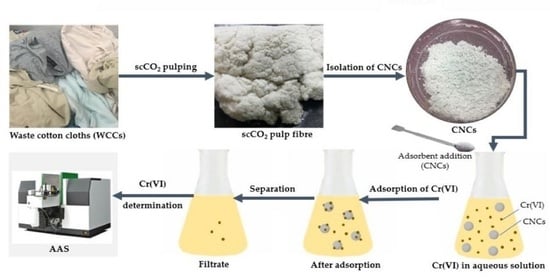
2.1. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Cellulose Nanocrystals Isolation from WCCs
2.3. Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using CNCs
2.4. Adsorption Isotherm
2.5. Kinetics and Thermodynamics Modelling
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Analyses
3.2. ATR-FTIR Analysis
3.3. Zeta Potential Analyses
3.4. BET Analysis
3.5. Adsorption of Cr(VI) Using CNCs
3.6. Adsorption Equilibrium Studies
3.7. Adsorption Kinetics
3.8. Adsorption Thermodynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohamed, S.H.; Hossain, M.S.; Mohamad Kassim, M.H.; Ahmad, M.I.; Omar, F.M.; Balakrishnan, V.; Zulkifli, M.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Recycling WCCs for the Isolation of Cellulose Nanocrystals: A Sustainable Approach. Polymers 2021, 13, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, S.; Tatariants, M.; Tichonovas, M.; Sarwar, Z.; Jonuškienė, I.; Kliucininkas, L. A new strategy for using textile waste as a sustainable source of recovered cotton. Res. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Cicala, G.; Acierno, D. Eco-Sustainability of the Textile Production: Waste Recovery and Current Recycling in the Composites World. Polymers 2021, 13, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Solid waste issue: Sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2018, 27, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Phoungthong, K.; Lü, F.; Shao, L.-M.; He, P.-J. Evaluation of a classification method for biodegradable solid wastes using anaerobic degradation parameters. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y. Extraction and comparison of cellulose nanocrystals from lemon (Citrus limon) seeds using sulfuric acid hydrolysis and oxidation methods. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Chhajed, M.; Gupta, P.; Roy, S.; Maji, P.K. Isolation of cellulose nanocrystals from different waste bio-mass collating their liquid crystal ordering with morphological exploration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Yu, H.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. A comprehensive investigation on cellulose nanocrystals with different crystal structures from cotton via an efficient route. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 276, 118766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, N.M.; Matuana, L.M. Trends in sustainable biobased packaging materials: A mini review. Mater. Today Sustain. 2021, 15, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Amirkhosravi, M.; Ke, K.; Gray, T.G.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Cellulose Nanocrystals: Accelerator and Reinforcing Filler for Epoxy Vitrimerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, G.; Yu, L.; Zhao, B. Cellulose Nanocrystal and Silver Nanobelt Gel: Cooperative Interactions Enabling Dispersion, Colloidal Gels, and Flexible Electronics. Langmuir 2019, 35, 15897–15903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, K.; Patel, D.K.; Dutta, S.D.; Shin, W.-C.; Lim, K.-T. Stimuli-responsive self-assembly of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs): Structures, functions, and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ju, B.; Zhang, S. Preparation of cysteamine-modified cellulose nanocrystal adsorbent for removal of mercury ions from aqueous solutions. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4971–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, M.K.M.; Balakrishnan, V.; Zuknik, M.H.; Al-Gheethi, A.; Ghfar, A.A.; Hossain, M.S. Supercritical CO2 separation of lipids from chicken by-product waste for biodiesel production: Optimization, kinetics, and thermodynamics modeling. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery, 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafi, F.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Shaah, M.; Lalung, J.; Ab Kadir, M.O.; Ahmad, M.I. Waterless sterilization and cleaning of sheep wool fiber using supercritical carbon dioxide. Text. Res. J. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easmin, M.S.; Sarker, M.Z.I.; Ferdosh, S.; Shamsudin, S.H.; Yunus, K.B.; Uddin, M.S.; Sarker, M.M.R.; Akanda, M.J.H.; Hossain, M.S.; Khalil, H.A. Bioactive compounds and advanced processing technology: Phaleria macrocarpa (sheff.) Boerl, a review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustinelli, G.; Eliasson, L.; Svelander, C.; Alminger, M.; Ahrné, L. Supercritical CO2 extraction of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) seed oil: Fatty acid composition and antioxidant activity. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 135, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.K.M.; Tengku Norsalwani, T.L.; Asmah, M.S.; Badrulhisham, Z.Y.; Easa, A.M.; Omar, F.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Zuknik, M.H.; Nik Norulaini, N.A. Implementation of the supercritical carbon dioxide technology in oil palm fresh fruits bunch sterilization: A review. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, D.; Pimenta, M.T.B.; Ferreira, L.H.; Curvelo, A.A.S. Sugar cane bagasse pulping using supercritical CO2 associated with co-solvent 1-butanol/water. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2005, 34, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedoya, C.I.; Vallejos, M.E.; Area, M.C.; Felissia, F.E.; Raffaeli, N.; da Silva Curvelo, A.A. Hydrothermal treatment and organosolv pulping of softwood assisted by carbon dioxide. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 147, 112244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, X.; Chang, C.; Wang, Y. Recent developments and prospective food-related applications of cellulose nanocrystals: A review. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2991–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y. Reuse of waste cotton cloth for the extraction of cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, M.M.Á.D.; Benini, K.C.C.d.C.; Voorwald, H.J.C.; Cioffi, M.O.H. Obtainment and characterization of nanocellulose from an unwoven industrial textile cotton waste: Effect of acid hydrolysis conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jobby, R.; Jha, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Desai, N. Biosorption and biotransformation of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]: A comprehensive review. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiopoulou, E.; Gikas, P. Regulations for chromium emissions to the aquatic environment in Europe and elsewhere. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, B.; Paul, D. Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics of hexavalent chromium removal using biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, R.E.K.; Khan, M.A.; Park, Y.-K.; AM, A.; Majdoubi, H.; Haddaji, Y.; Jeon, B.-H. A Comparative Study on Hexavalent Chromium Adsorption onto Chitosan and Chitosan-Based Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Khan, M.; Govindasamy, R.; Ahmad, A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Alshareef, S.A.; Hakami, A.A.H.; Rafatullah, M. Carbon Based Polymeric Nanocomposites for Dye Adsorption: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jin, R.-N.; Ouyang, X.-K.; Wang, Y.-G. Adsorption behavior of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal—Polyethyleneimine composite for removal of Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surface Sci. 2017, 408, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Nik Ab Rahman, N.N.; Balakrishnan, V.F.M.; Alkarkhi, A.; Ahmad Rajion, Z.; Ab Kadir, M.O. Optimizing supercritical carbon dioxide in the inactivation of bacteria in clinical solid waste by using response surface methodology. Waste Manag. 2015, 38, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hurren, C. Degumming methods for bast fibers—A mini review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 174, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surup, G.R.; Hunt, A.J.; Attard, T.; Budarin, V.L.; Forsberg, F.; Arshadi, M.; Abdelsayed, V.; Shekhawat, D.; Trubetskaya, A. The effect of wood composition and supercritical CO2 extraction on charcoal production in ferroalloy industries. Energy 2020, 193, 116696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatah, I.Y.A.; Khalil, H.P.S.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Aziz, A.A.; Davoudpour, Y.; Dungani, R.; Bhat, A. Exploration of a Chemo-Mechanical Technique for the Isolation of Nanofibrillated Cellulosic Fiber from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch as a Reinforcing Agent in Composites Materials. Polymers 2014, 6, 2611–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razali, N.; Hossain, M.S.; Taiwo, O.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Mohd Nadzri, N.W.; Razak, N.; Mohammad Rawi, N.F.; Mohd Mahadar, M.; Mohamad Kassim, M.H. Influence of Acid Hydrolysis Reaction Time on the Isolation of Cellulose Nanowhiskers from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch Microcrystalline Cellulose. BioResources 2017, 12, 6773–6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohiuddin, G.; Ghosh, S.; Begum, N.; Debnath, S.; Turlapati, S.; Rao, D.S.S.; Nandiraju, R.V.S. Amide linkage in novel three-ring bent-core molecular assemblies: Polar mesophases and importance of H-bonding. Liq. Cryst. 2018, 45, 1549–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambiraj, S.; Ravi Shankaran, D. Preparation and physicochemical characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from industrial waste cotton. Appl. Surface Sci. 2017, 412, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkani, M.H.; Fletcher, A.J.; Fedorov, M.; Abdallah, W.; Sauerer, B.; Anderson, J.; Zhang, Z.J. Mechanisms of surface charge modification of carbonates in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Colloids Interfaces 2019, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhali, K.; Ghasemlou, M.; Daver, F.; Cass, P.; Adhikari, B. A review of nanocellulose as a new material towards environmental sustainability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, C.; Auber, D.; Dahnhardt-Pfeiffer, S.; Briesen, H. Agglomeration of cellulose nanocrystals: The effect of secondary sulfates and their use in product separation. Cellulose 2020, 27, 9839–9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, R.; Hashmet, M.R.; Pourafshary, P. Fine migration control in sandstones: Surface force analysis and application of DLVO theory. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 31624–31639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, J.H.; Easson, M.W.; Condon, B.D. Cellulose hydrolysis using ionic liquids and inorganic acids under dilute conditions: Morphological comparison of nanocellulose. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 39413–39424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, E.; Singhvi, G. Multifunctional nanaocrystals for cancer therapy: A potential nanocarrier. Nanomater. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 2, 91–116. [Google Scholar]
- Morantes, D.; Munoz, E.; Kam, D.; Shoseyov, O. Highly charged cellulose nanocrystals applied as a water treatment flocculant. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Hsieh, Y.-L. Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: Rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Danso, E.; Srivastava, V.; Sillanpää, M.; Bhatnagar, A. Pretreatment assisted synthesis and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibers from absorbent cotton. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobar, E.L.N.; da Silva, T.A.; Pirich, C.L.; Corazza, M.L.; Pereira Ramos, L. Supercritical Fluids: A Promising Technique for Biomass Pretreatment and Fractionation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wabaidur, S.M.; Khan, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.R.; Otero, M.; Jeon, B.-H.; Alothman, Z.A.; Hakami, A.A.H. Oxygenated functionalities enriched MWCNTs decorated with silica coated spinel ferrite—A nanocomposite for potentially rapid and efficient de-colorization of aquatic environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 317, 113916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, B.; Tiwary, R.K.; Yadav, M. Non linear regression analysis and response surface modeling for Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution using poly-aniline coated sugarcane bagasse (PANI@SB) composites as an adsorbent. Surfaces Interfaces 2022, 29, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesaoana, M.; Mlaba, R.P.V.; Mtunzi, F.M.; Klink, M.J.; Ejidike, P.; Pakade, V.E. Influence of inorganic acid modification on Cr(VI) adsorption performance and the physicochemical properties of activated carbon. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 28, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaime, M.Z.A.; Sarjadi, M.S.; Rahman, M.L. Heavy metals removal from water by efficient adsorbents. Water 2021, 13, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ayuso, E.; Garcia-Sanchez, A.; Querol, X. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from synthetic solutions and electroplating wastewaters on amorphous aluminium oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 1, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Ismail, N.; Khalil, N.A.; Balakrishnan, V.; Zulkifli, M.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Isolation and Characterization of Magnetic Oil Palm Empty Fruits Bunch Cellulose Nanofiber Composite as a Bio-Sorbent for Cu(II) and Cr(VI) Removal. Polymers 2021, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mat Yasin, N.M.F.; Hossain, M.S.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Zulkifli, M.; Al-Geethi, A.; Asis, A.J.; Ahmad Yahaya, A.N. Treatment of palm oil refinery effluent using tannin as a polymeric coagulant: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamics analyses. Polymers 2020, 12, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Xiao, R.; Li, R.; Ali, A.; Chen, A.; Zhang, Z. Enhanced aqueous Cr(VI) removal using chitosan-modified magnetic biochars derived from bamboo residues. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Shin, S.S.; Park, C.H.; Jeon, S.; Gwon, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Poly(acryloyl hydrazide)-grafted cellulose nanocrystal adsorbents with an excellent Cr(VI) adsorption capacity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Waste Cotton Cloths | scCO2 Pulped Fibre | CNCs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 104.50 ± 2.54 µm | 85.60 ± 1.73 µm | 100.03 ± 1.15 nm |
| Width | 30 ± 2.56 µm | 13.60 ± 1.91 µm | 7.92 ± 0.53 nm |
| Aspect ratio | 4 | 6 | 13 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | a (L/mg) | b (mg/mg) | R2 | kf (L/mg) | n |
| 0.931 | 0.422 | 0.082 | 0.954 | 0.248 | 5.862 |
| Temperature (°C) | qe (exp.) (mg/mg) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetics | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/mg) | k1 (1/min) | R2 | qe (mg/mg) | k2 (mg/mg.min) | R2 | ||
| 28 | 0.0613 | 0.2018 | 0.1409 | 0.9615 | 0.0785 | 0.898 | 0.9751 |
| 40 | 0.0627 | 0.1250 | 0.1344 | 0.9916 | 0.0730 | 1.649 | 0.9910 |
| 60 | 0.0655 | 0.0546 | 0.1177 | 0.9784 | 0.0709 | 3.391 | 0.9977 |
| 80 | 0.0648 | 0.0354 | 0.1232 | 0.9899 | 0.0674 | 7.297 | 0.9960 |
| Temperature (°C) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/mol.K) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | −0.395 | 27.407 | 0.092 |
| 40 | −1.201 | ||
| 60 | −3.434 | ||
| 80 | −5.033 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, S.H.; Hossain, M.S.; Kassim, M.H.M.; Balakrishnan, V.; Habila, M.A.; Zulkharnain, A.; Zulkifli, M.; Yahaya, A.N.A. Biosorption of Cr(VI) Using Cellulose Nanocrystals Isolated from the Waterless Pulping of Waste Cotton Cloths with Supercritical CO2: Isothermal, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies. Polymers 2022, 14, 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050887
Mohamed SH, Hossain MS, Kassim MHM, Balakrishnan V, Habila MA, Zulkharnain A, Zulkifli M, Yahaya ANA. Biosorption of Cr(VI) Using Cellulose Nanocrystals Isolated from the Waterless Pulping of Waste Cotton Cloths with Supercritical CO2: Isothermal, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies. Polymers. 2022; 14(5):887. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050887
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Siti Hajar, Md. Sohrab Hossain, Mohamad Haafiz Mohamad Kassim, Venugopal Balakrishnan, Mohamed A. Habila, Azham Zulkharnain, Muzafar Zulkifli, and Ahmad Naim Ahmad Yahaya. 2022. "Biosorption of Cr(VI) Using Cellulose Nanocrystals Isolated from the Waterless Pulping of Waste Cotton Cloths with Supercritical CO2: Isothermal, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies" Polymers 14, no. 5: 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050887
APA StyleMohamed, S. H., Hossain, M. S., Kassim, M. H. M., Balakrishnan, V., Habila, M. A., Zulkharnain, A., Zulkifli, M., & Yahaya, A. N. A. (2022). Biosorption of Cr(VI) Using Cellulose Nanocrystals Isolated from the Waterless Pulping of Waste Cotton Cloths with Supercritical CO2: Isothermal, Kinetics, and Thermodynamics Studies. Polymers, 14(5), 887. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050887