Polyvinylidene Fluoride Surface Polarization Enhancement for Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Treatment of PVDF Film
2.3. Fabrication of PSPE TENG Device
2.4. Characterization and Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
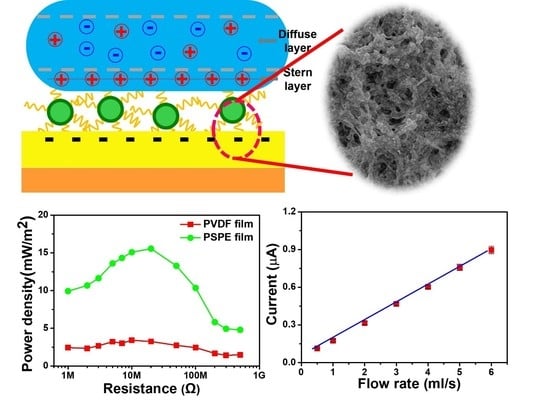
3.1. Characterization of PSPE Film
3.2. Working Principle of TENG
3.3. Electrical Output Characterization of PSPE TENG
3.4. Practicability in Self-Powered Sensing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeon, Y.P.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.W. Highly flexible triboelectric nanogenerators fabricated utilizing active layers with a ZnO nanostructure on polyethylene naphthalate substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Haider, Z.; Ahmad, R.u.S.; Claver, U.P.; Shah, A.; Zhao, G.; He, W.-D. Highly porous and thermally stable tribopositive hybrid bimetallic cryogel to boost up the performance of triboelectric nanogenerators. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 8442–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, I.; Jayababu, N.; Kim, D. Performance-enhanced triboelectric nanogenerator based on the double-layered electrode effect. Polymers 2020, 12, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, C.-D.; Vo, C.-P.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Vu, D.-L.; Ahn, K.K. Liquid-solid contact electrification based on discontinuous-conduction triboelectric nanogenerator induced by radially symmetrical structure. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Burman, S.R.; Khan, I.; Saha, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.H. Recent advancements in solid-liquid triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17663–17697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinchet, R.; Seung, W.; Kim, S.W. Recent progress on flexible triboelectric nanogenerators for selfpowered electronics. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2327–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.; Choi, Y.-M.; Jang, Y.; Jeong, J. A multilayer thin-film screen-printed triboelectric nanogenerator. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 3688–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, C.G.; Nam, G.H.; Ahn, K.K. Unsteady streaming flow based TENG using hydrophobic film tube with different charge affinity. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Guo, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhuo, J.; Mo, J.; Wang, Z.L. Superhydrophobic cellulose paper-based triboelectric nanogenerator for water drop energy harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.L.; Ahn, K.K. High-Performance Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites Film. In Proceedings of the 2021 24th International Conference on Mechatronics Technology (ICMT), Singapore, 18–22 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.J.; Kuang, S.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhu, G. Highly adaptive solid-liquid interfacing triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting diverse water wave energy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 4280–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Xiang, S.; Tao, C.; Yang, S.; Fan, X. Self-powered all-in-one fluid sensor textile with enhanced triboelectric effect on all-immersed dendritic liquid-solid interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30819–30826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, A.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered electrostatic actuation systems for manipulating the movement of both microfluid and solid objects by using triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1606408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Seol, M.-L.; Kim, D.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, Y.-K. Self-powered ion concentration sensor with triboelectricity from liquid-solid contact electrification. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1600006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Lee, C. Self-powered liquid triboelectric microfluidic sensor for pressure sensing and finger motion monitoring applications. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.-D.; Vo, C.-P.; Vu, D.-L.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Ahn, K.K. Water electrification based triboelectric nanogenerator integrated harmonic oscillator for waste mechanical energy harvesting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 251, 115014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, M.; Siddiqui, K. A critical review on advanced velocity measurement techniques in pulsating flows. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbage, N.; Shepherd, J.M. The influence of urban development patterns on streamflow characteristics in the charlanta megaregion. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3728–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.X.; Lee, Y.P.; Lee, D.Y. Effects of the pulsating flow agitation on the heat transfer in a triangular grooved channel. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 3062–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xu, S.; Wei, S.; Chen, P. Experimental investigation of heat transfer for pulsating flow of GOPs-water nanofluid in a microchannel. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 110, 104403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, H.; Wood, D.A.; Choubineh, A.; Tatar, A.; Abarghoyi, P.G.; Madani, M.; Mohamadian, N. Prediction of oil flow rate through an orifice flow meter: Artificial intelligence alternatives compared. Petroleum 2020, 6, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watral, Z.; Jakubowski, J.; Michalski, A. Electromagnetic flow meters for open channels: Current state and development prospects. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2015, 42, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, H.; Oertel, D.; Sandau, R.; Zimmermann, G. Aspects of the determination of ocean wave parameters by means of an optoelectronic satellite sensor. Acta Astronaut. 1989, 19, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Zhou, L.; Yin, X.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered sensor for quantifying ocean surface water waves based on triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 7092–7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Jung, S.; Lee, T.W.; Jo, J.; Chae, H.Y.; Choi, K.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yang, C.; Baik, J.M. High-output triboelectric nanogenerator based on dual inductive and resonance effects-controlled highly transparent polyimide for self-powered sensor network systems. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Cho, H.J.; Chun, J.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, S.; Ahn, C.W.; Kim, I.W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, C.; et al. Robust nanogenerators based on graft copolymers via control of dielectrics for remarkable output power enhancement. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Feng, C.-p.; Deng, B.-w.; Yin, B.; Yang, M.-b. Facile method to enhance output performance of bacterial cellulose nanofiber based triboelectric nanogenerator by controlling micro-nano structure and dielectric constant. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, P.; Sobola, D.; Castkova, K.; Knapek, A.; Burda, D.; Orudzhev, F.; Dallaev, R.; Tofel, P.; Trcka, T.; Grmela, L.; et al. Characterization of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) electrospun fibers doped by carbon flakes. Polymers 2020, 12, 2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; An, X.; Qian, X. Methyl orange-doped polypyrrole promoting growth of ZIF-8 on cellulose fiber with tunable tribopolarity for triboelectric nanogenerator. Polymers 2022, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Shi, Z.; Zheng, R.; Ye, W.; Gao, X.; Zhao, W.; Yang, G. Superhydrophobic liquid–solid contact triboelectric nanogenerator as a droplet sensor for biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40021–40030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.Y.; Khan, U.; Kim, S.-W. Water droplet-driven triboelectric nanogenerator with superhydrophobic surfaces. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; La, M.; Cho, S.; Yun, Y.; Choi, J.H.; Ra, Y.; Park, S.J.; Choi, D. Monocharged electret based liquid-solid interacting triboelectric nanogenerator for its boosted electrical output performance. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.L.; Vo, C.P.; Le, C.D.; Ahn, K.K. Enhancing the output performance of fluid-based triboelectric nanogenerator by using poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene)/ionic liquid nanoporous membrane. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 8960–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Zha, J.-W.; Zhao, C.-L.; Gong, S.-B.; Gao, J.-F.; Li, R.K.Y. Flexible PVDF/nylon-11 electrospun fibrous membranes with aligned ZnO nanowires as potential triboelectric nanogenerators. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Wan, H.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G. High β phase content in PVDF/CoFe2O4 nanocomposites induced by DC magnetic fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 102904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, S.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Pan, Z.; Du, Z.; Cheng, F. Preparation of omniphobic PVDF membranes with silica nanoparticles for treating coking wastewater using direct contact membrane distillation: Electrostatic adsorption vs. chemical bonding. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 574, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Q.; Ma, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-L.; Gu, Z.-Y. Superhydrophobic modification of PVDF–SiO2 electrospun nanofiber membranes for vacuum membrane distillation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 67962–67970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Peng, Y.; Ge, L.; Lin, R.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S. Amphiphobic PVDF composite membranes for anti-fouling direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vu, D.L.; Le, C.D.; Vo, C.P.; Ahn, K.K. Surface polarity tuning through epitaxial growth on polyvinylidene fluoride membranes for enhanced performance of liquid-solid triboelectric nanogenerator. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2021, 223, 109135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffinger, J.C.; Kim, H.W.; DiMagno, S.G. The polar hydrophobicity of fluorinated compounds. Chembiochem 2004, 5, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routray, K.L.; Sahoo, B.; Behera, D. Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of nano-sized CoFe2O4 employing various synthesis techniques for high frequency and magneto recording devices: A comparative analysis. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 085016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh Medina, L.M.; Negri, R.M. Dielectric behavior and electro-magnetic coupling at room temperature in BiFeO3/PVDF and CoFe2O4/PVDF composites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 27683–27692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, M.; Wei, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yan, H. Improving dielectric properties of PVDF composites by employing surface modified strong polarized BaTiO(3) particles derived by molten salt method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24480–24491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozbial, A.; Li, Z.; Conaway, C.; McGinley, R.; Dhingra, S.; Vahdat, V.; Zhou, F.; D’Urso, B.; Liu, H.; Li, L. Study on the surface energy of graphene by contact angle measurements. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8598–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, L.S.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrostatic charging due to separation of ions at interfaces: Contact electrification of ionic electrets. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2188–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhao, X.S. Carbon-based materials as supercapacitor electrodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2520–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamee, C.E. Effect of a liquid flow on the forces between charged solid surfaces and the non-equilibrium electric double layer. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 266, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F. Solid–liquid triboelectrification control and antistatic materials design based on interface wettability control. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, M.; Vo, C.P.; Ahn, K.K. Self-powered flexible PDMS channel assisted discrete liquid column motion based triboelectric nanogenerator (DLC-TENG) as mechanical transducer. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. -Green Technol. 2019, 6, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, C.P.; Shahriar, M.; Le, C.D.; Ahn, K.K. Mechanically active transducing element based on solid–liquid triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered sensing. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. -Green Technol. 2019, 6, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Liquid-FEP-based U-tube triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water-wave energy. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 4062–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Ren, Z.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhan, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.L. Probing contact-electrification-induced electron and ion transfers at a liquid–solid interface. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Tsao, Y.-H.; Chiu, C.-M.; Yoo, D.; Lin, Z.-H.; Kim, D.S. A smart pipet tip: Triboelectricity and thermoelectricity assisted in situ evaluation of electrolyte concentration. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Atom Percent (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1s | O1s | F1s | Si2p | |
| PVDF | 50.70 | 0.45 | 48.85 | 0.00 |
| PSPE | 41.39 | 3.64 | 53.39 | 1.58 |
| Triboelectric Layer | Current (μA) | Voltage (V) | Charge Density (μC/m2) | Power Density (mw/m2) | Sensing Objective | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobic fumed silica film | 0.002 | ~ | 4.0 | ~ | Biomedical sensing | [30] |
| PDMS channel | 0.01 | 0.02 | 2.6 | 0.01 | Pressure fluctuation | [49] |
| Thin PDMS layer | 0.012 | 0.019 | ~ | ~ | Pressure, finger motion | [15] |
| PTFE tube | 0.23 | 2.3 | 1.2 | 0.15 | Velocity transducing | [50] |
| FEP U-shaped tube | 0.26 | 81.7 | 28.9 | ~ | Ion concentration | [51] |
| PVDF film | 0.17 | 3.1 | 12.7 | 3.3 | Velocity, ion concentration | This work |
| PSPE film | 0.47 | 6.5 | 36.1 | 15.6 | Velocity, ion concentration | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vu, D.L.; Le, C.D.; Ahn, K.K. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Surface Polarization Enhancement for Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050960
Vu DL, Le CD, Ahn KK. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Surface Polarization Enhancement for Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application. Polymers. 2022; 14(5):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050960
Chicago/Turabian StyleVu, Duy Linh, Chau Duy Le, and Kyoung Kwan Ahn. 2022. "Polyvinylidene Fluoride Surface Polarization Enhancement for Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application" Polymers 14, no. 5: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050960
APA StyleVu, D. L., Le, C. D., & Ahn, K. K. (2022). Polyvinylidene Fluoride Surface Polarization Enhancement for Liquid-Solid Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Its Application. Polymers, 14(5), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14050960