Vertical Alignment of Liquid Crystal on Sustainable 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Substituted Polystyrene Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparations of Poly(4-chloromethylstyrene) (PCMS)
2.3. Preparations of 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Modified Polystyrene (PDtBP#)
2.4. Film Preparation and LC Cell Assembly
2.5. Instrumentation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Modified Polystyrene
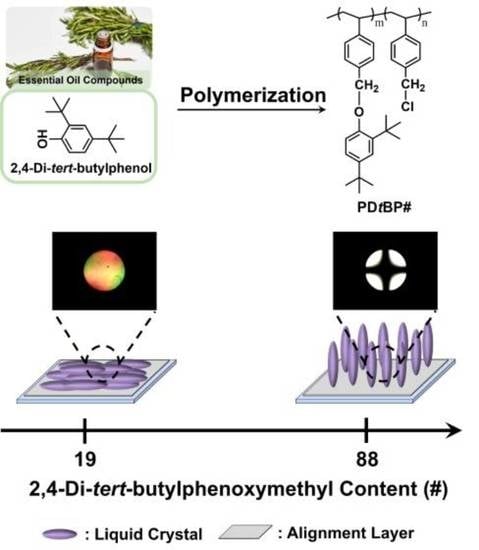
3.2. LC Orientation Behavior of the LC Cell Fabricated with 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Modified Polystyrene Film
3.3. Surface Properties of 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Modified Polystyrene Films
3.4. Reliability and Optical Performance of the LC Cells Fabricated with 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Modified Polystyrene Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMS | 4-Chloromethylstyrene |
| 5CB | 4′-Pentyl-4-biphenylcarbonitrile |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimetry |
| 1H NMR | 1H nuclear magnetic resonance |
| LC | Liquid crystal |
| LCDs | Liquid crystal displays |
| PI | Polyimide |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PCMS | Poly(4-chloromethylstyrene) |
| PDtBP | 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-substituted polystyrene |
| POM | Polarized optical microscopy |
References
- Xu, Z.; Gao, C. Aqueous liquid crystals of graphene oxide. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2908–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajak, P.; Nath, L.K.; Bhuyan, B. Liquid crystals: An approach in drug delivery. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 81, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Hagar, M.; Alhaddad, O.A. Mesomorphic and geometrical orientation study of the relative position of fluorine atom in some thermotropic liquid crystal systems. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schadt, M. Liquid crystal materials and liquid crystal displays. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1997, 27, 305–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alnoman, R.B.; Hagar, M.; Ahmed, H.A.; Naoum, M.M.; Sobaih, H.A.; Almshaly, J.S.; Haddad, M.M.; Alhaisoni, R.A.; Alsobhi, T.A. Binary liquid crystal mixtures based on schiff base derivatives with oriented lateral substituents. Crystals 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, I.; Martins Figueiredo Neto, A. Novel trends in lyotropic liquid crystals. Crystals 2020, 10, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogolla, T.; Paley, R.S.; Collings, P.J. Temperature dependence of the pitch in chiral lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, J.K.; Collings, P.J. A chiral–racemic lyotropic chromonic liquid crystal system. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Kang, H. Vertical orientation of liquid crystal on comb-like 4-(trans-4-alkylcyclohexyl) phenoxymethyl-substituted polystyrene containing liquid crystal precursor. Polymers 2021, 13, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, C.K.; Ramesh, D.R.; Ola, M.M.; Chaudhari, V.A. Liquid crystals: A review. Int. J. All Res. Writ. 2019, 1, 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mahajan, J.T.; Gujarathi, N.; Jadhav, A.; Pathan, V.; Borse, L. Lyotropic liquid crystalline system for effective topical delivery of tolnaftate. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2018, 6, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapalli, V.K.; Waghule, T.; Hans, N.; Mahmood, A.; Gorantla, S.; Dubey, S.K.; Singhvi, G. Insights of lyotropic liquid crystals in topical drug delivery for targeting various skin disorders. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, Y.; Imran, O.Q.; Osuji, C.O.; Foudazi, R. Lyotropic liquid crystals as templates for advanced materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 21607–21658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, I.R.; Immich, M.F.; Lundberg, D.; Poletto, F.; Loh, W. Physiological neutral pH drives a gradual lamellar-to-reverse cubic-to-reverse hexagonal phase transition in phytantriol-based nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 177, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, S.; Huang, J.; Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Chu, X. Characterization of lipid-based lyotropic liquid crystal and effects of guest molecules on its microstructure: A systematic review. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 2023–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe-Zanutto, F.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; McKenna, P.E.; Paredes, A.J.; Dávila, J.L.; McCrudden, M.T.; Tangerina, M.M.P.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Vilegas, W.; Brisibe, A. Novel transdermal bioadhesive surfactant-based system for release and solubility improvement of antimalarial drugs artemether-lumefantrine. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 065015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Gui, S. Factors affecting the structure of lyotropic liquid crystals and the correlation between structure and drug diffusion. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 6978–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, P.; Gui, S. Cubic and hexagonal liquid crystals as drug delivery systems. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 815981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chountoulesi, M.; Pippa, N.; Pispas, S.; Chrysina, E.D.; Forys, A.; Trzebicka, B.; Demetzos, C. Cubic lyotropic liquid crystals as drug delivery carriers: Physicochemical and morphological studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Mozaffari, A.; de Pablo, J.J. Autonomous materials systems from active liquid crystals. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, R. Analysis of electro-optical behavior in liquid crystal cells with asymmetric anchoring strength. Symmetry 2022, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Lv, J.; Zhu, C.; Qin, L.; Yu, Y. Photodeformable azobenzene-containing liquid crystal polymers and soft actuators. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1904224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Koyama, D.; Fukui, M.; Emoto, A.; Nakamura, K.; Matsukawa, M. Molecular orientation in a variable-focus liquid crystal lens induced by ultrasound vibration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatoh, H.; Ishikawa, M.; Hirata, J.; Hisatake, Y.; Yamamoto, T. Improvement of viewing angle characteristics in a twisted-nematic liquid-crystal display by using a cholesteric liquid-crystal compensation layer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1992, 60, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaki, K.; Uesaka, T.; Nishimura, S.; Mazaki, H. P-137: Comparison of viewing angle performance of TN-LCD and ECB-LCD using hybrid-aligned nematic compensators. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2006, 38, 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Jo, S.I.; Bae, K.; Choi, B.; Kim, J.; Yu, C. Fast vertical alignment mode with continuous multi-domains for a liquid crystal display. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 23417–23422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, M.H. Liquid crystal displays with high image quality and fast response time. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2001, 39, S42–S48. [Google Scholar]
- Mizusaki, M.; Ishihara, S. A novel technique for determination of residual direct-current voltage of liquid crystal cells with vertical and in-plane electric fields. Symmetry 2021, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Sun, Y. Fast-response vertical alignment liquid crystal display driven by in-plane switching. Liq. Cryst. 2011, 38, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung-Yu, W.; Hsin-Min, F.; Jan-Tian, L. Real multi-domain reduced color and gamma shift in fringe-field-switching (FFS) mode LCD with photoalignment method. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2012, 22, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Choi, Y.E.; Lee, B.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kundu, S.; Jin, H.; Yun, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Komitov, L. Surface polymer-stabilised in-plane field driven vertical alignment liquid crystal device. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, K.; Kawanishi, Y.; Seki, T.; Sakuragi, M.; Tamaki, T.; Ichimura, K. Reversible alignment change of liquid crystals induced by photochromic molecular films: Properties of azobenzene chromophores covalently attached to silica surfaces. Liq. Cryst. 1995, 19, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, D.; Manaka, T.; Iwamoto, M. Orientational ordering process of liquid crystalline molecules evaporated on azobenzene monolayer optical polarized absorption measurements and adsorption kinetics. Int. J. Mater. Eng. 2006, 13, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoki, K.; Tamaki, T.; Seki, T.; Kawanishi, Y.; Ichimura, K. Regulation of alignment of cyanobiphenyl liquid crystals by azobenzene molecular films. Langmuir 1992, 8, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, Z.; Peng, B.; Xie, D.; Yao, S.; Jiang, M.; Bai, J. High dielectric permittivity silver/polyimide composite films with excellent thermal stability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 112910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y. Preparation and characterization of a novel polyimide liquid crystal vertical alignment layer. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.; Pang, Y.; Liu, X. Characterization of alignment correlation between LC molecules and chemical groups on/in the surface of polyimide films with biphenyl side chains. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9731–9737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, Z.; Yang, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, H.; Jia, X.; Wang, X. Three-dimensional printing of high-performance polyimide by direct ink writing of hydrogel precursor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W.; Chen, X.; Chi, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, T.; Cao, Z.; Tseng, T.; Hsieh, C. P-146: Fabrication of polyimide-free liquid crystal with reactive self-aligning amphiphile using three times UV curing. SID Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2019, 50, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.P.; Sikarwar, S.; Pandey, K.K.; Manohar, R.; Depriester, M.; Singh, D.P. Carbon nanotubes blended nematic liquid crystal for display and electro-optical applications. Electron. Mater. 2021, 2, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Kang, H. Vertical orientation of liquid crystal on polystyrene substituted with n-alkylbenzoate-p-oxymethyl pendant group as a liquid crystal precursor. Polymers 2021, 13, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishihara, S.; Mizusaki, M. Alignment control technology of liquid crystal molecules. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2020, 28, 44–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Kang, H. Vertical orientation of liquid crystal on 4-n-alkyloxyphenoxymethyl-substituted polystyrene containing liquid crystal precursor. Polymers 2021, 13, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, C.; Kim, T.; Kang, H. Renewable, eugenol-modified polystyrene layer for liquid crystal orientation. Polymers 2018, 10, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, C.; Park, C.; Kim, T.; Kang, H. Vertical alignment of liquid crystals on plant-based vanillin derivative-substituted polystyrene films. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14188–14193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; Seo, K.; Kang, H. Alignment layer of liquid crystal using plant-based isoeugenol-substituted polystyrene. Polymers 2021, 13, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajka, A.; Hazell, G.; Eastoe, J. Surfactants at the design limit. Langmuir 2015, 31, 8205–8217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamalakar, G.; Komura, K.; Sugi, Y. Tert-butylation of phenol over ordered solid acid catalysts in supercritical carbon dioxide: Efficient synthesis of 2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol and 2, 4, 6-tri-tert-butylphenol. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 6118–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, P.; Lucardi, R.D.; Su, Z.; Li, S. Natural sources and bioactivities of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and its analogs. Toxins 2020, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuah, T.S.; Norhafizah, M.Z.; Naimah, A.H.; Ismail, B.S. Phytotoxic activity of the allelochemical, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol on two selected weed species. Sains Malays. 2016, 45, 963–967. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, G. Acaricidal, repellent, and oviposition-deterrent activities of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol and ethyl oleate against the carmine spider mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mabury, S.A. Unexpectedly high concentrations of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol in human urine. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.K.; Harris, K.; Kim, C.; Park, G.G.; Park, C.; Shin, D. 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol from sweet potato protects against oxidative stress in PC12 cells and in mice. J. Med. Food 2013, 16, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dharni, S.; Maurya, A.; Samad, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Sharma, A.; Patra, D.D. Purification, characterization, and in vitro activity of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol from Pseudomonas monteilii PsF84: Conformational and molecular docking studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6138–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahdati, S.N.; Lashkari, A.; Navasatli, S.A.; Ardestani, S.K.; Safavi, M. Butylated hydroxyl-toluene, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, and phytol of Chlorella sp. protect the PC12 cell line against H2O2-induced neurotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viszwapriya, D.; Prithika, U.; Deebika, S.; Balamurugan, K.; Pandian, S.K. In vitro and in vivo antibiofilm potential of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol from seaweed surface associated bacterium Bacillus subtilis against group A streptococcus. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 191, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, A.R.; Periyasamy, M.; Pandian, S.K. Assessment of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol induced modifications in extracellular polymeric substances of Serratia marcescens. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 188, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmavathi, A.R.; Abinaya, B.; Pandian, S.K. Phenol, 2,4-bis (1,1-dimethylethyl) of marine bacterial origin inhibits quorum sensing mediated biofilm formation in the uropathogen Serratia marcescens. Biofouling 2014, 30, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.V.; Jayasree, D.V.; Biju, P.G.; Baby, S. Anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of erythrodiol-3-acetate and 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol isolated from Humboldtia unijuga. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 2319–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaichelvan, S.; Sundaraganesan, N.; Dereli, O.; Sayin, U. Experimental, theoretical calculations of the vibrational spectra and conformational analysis of 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 85, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, N.A.; Razak, S.B.A.; Simbak, N.; Seng, C.T. 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol-induced leaf physiological and ultrastructural changes in chloroplasts of weedy plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 112, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, J.; Heo, H.J.; Cho, H.Y.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, C.; Kim, M.O.; Suh, S.H.; Shin, D. Punica granatum protects against oxidative stress in PC12 cells and oxidative stress-induced alzheimer’s symptoms in mice. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugscheider, E.; Bobzin, K. Wettability of PVD compound materials by lubricants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 165, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, G.J. Conjugation of Phenols; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 247–269. ISBN 0-12-380060-9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, P.; Tian, W.; Zhang, J. Novel thermoplastic cellulose esters containing bulky moieties and soft segments. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4931–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Weisen, A.R.; Lee, Y.; Aplan, M.A.; Fenton, A.M.; Masucci, A.E.; Kempe, F.; Sommer, M.; Pester, C.W.; Colby, R.H. Glass transition temperature from the chemical structure of conjugated polymers. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seslija, S.; Spasojević, P.; Panić, V.; Dobrzyńska-Mizera, M.; Immirzi, B.; Stevanović, J.; Popović, I. Physico-chemical evaluation of hydrophobically modified pectin derivatives: Step toward application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, G.; Ding, Y.; Zheng, J. Construction of a different polymer chain structure to study π-π interaction between polymer and reduced graphene oxide. Polymers 2018, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweep, N.; Hopkinson, A.; Meetsma, A.; Browne, W.R.; Feringa, B.L.; van Esch, J.H. Balancing hydrogen bonding and van der Waals interactions in cyclohexane-based bisamide and bisurea organogelators. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8802–8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, H.J.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, K.C.; Hwang, B.H.; Kim, J.T.; Baik, H.K.; Park, J.S.; Kang, D. Liquid crystal pretilt angle control using adjustable wetting properties of alignment layers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 253505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Polymer Designation | Feed Ratio of 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol (mol%) | Degree of Substitution (mol%) | Tg (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCMS | 0 | 0 | 106.4 |
| PDtBP19 | 40 | 19 | 107.6 |
| PDtBP35 | 60 | 35 | 106.9 |
| PDtBP68 | 80 | 68 | 101.5 |
| PDtBP88 | 100 | 88 | 99.2 |
| Polymer Designation | Contact Angle (°) a | Surface Energy (mJ/m2) b | Vertical LC Aligning Ability | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Diiodo Methane | Polar | Dispersion | Total | ||
| PCMS | 71.1 | 35.2 | 8.7 | 37.0 | 45.7 | No |
| PDtBP19 | 87.5 | 39.2 | 2.1 | 37.4 | 39.5 | No |
| PDtBP35 | 90.9 | 50.9 | 2.2 | 31.1 | 33.3 | No |
| PDtBP68 | 97.3 | 57.9 | 1.2 | 28.2 | 29.4 | Yes |
| PDtBP88 | 96.1 | 67.2 | 2.5 | 21.8 | 24.3 | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Jin, C.; Kang, H. Vertical Alignment of Liquid Crystal on Sustainable 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Substituted Polystyrene Films. Polymers 2022, 14, 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071302
Yang D, Jin C, Kang H. Vertical Alignment of Liquid Crystal on Sustainable 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Substituted Polystyrene Films. Polymers. 2022; 14(7):1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071302
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, DaEun, Chowon Jin, and Hyo Kang. 2022. "Vertical Alignment of Liquid Crystal on Sustainable 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Substituted Polystyrene Films" Polymers 14, no. 7: 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071302
APA StyleYang, D., Jin, C., & Kang, H. (2022). Vertical Alignment of Liquid Crystal on Sustainable 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenoxymethyl-Substituted Polystyrene Films. Polymers, 14(7), 1302. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071302