Adsorption of Wormlike Chains onto Partially Permeable Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Perfectly Penetrable Free-Standing Film
2.1. Adsorption Threshold
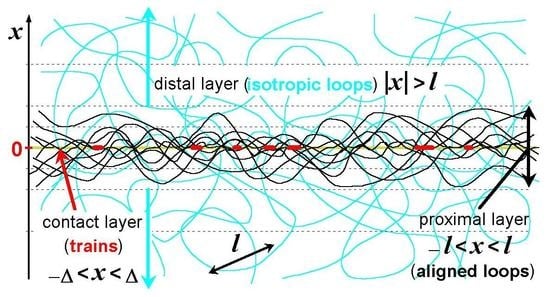
2.2. Adsorbed Layer Structure and Concentration Profile
2.3. Dependencies of Energy, Free Energy and Concentration Profiles on the Attraction Strength u
3. Quantitative Approach
4. Dependence of the Adsorbed Layer Structure on the Attraction Strength
5. Preliminary Discussion
6. Partially Penetrable Membranes
7. Discussion
7.1. Discussion on Two Models of Polymer/Membrane Interactions
7.2. Notes Related to the Model of Solid Film with Holes
7.3. Loop and Tail Distributions
7.4. Non-Ideality Effects
7.5. Estimates of the Layer Thickness
8. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| c | Polymer concentration |
| Monomer concentration profile | |
| Concentration profile of monomers belonging to loops | |
| Concentration profile of monomers belonging to tails | |
| D | Mean hole diameter |
| E | Chain potential energy |
| Chain confinement free energy | |
| Angle-dependent factor of the partition function, Equation (39) | |
| h | The terminal thickness of adsorbed layer |
| L | Chain contour length |
| The total polymer length in the attractive layer | |
| The mean tail length | |
| Persistence length | |
| l | Kuhn segment |
| N | Number of monomer units (or -segments) per chain |
| Number of polymer/membrane contacts | |
| p | Fraction of polymer segments in the attraction layer, Equation (59) |
| R | Coil size |
| T | Temperature in energy units |
| U | Attraction potential (per unit length), Equation (4) |
| u | Membrane attraction strength |
| Critical adsorption threshold | |
| w | Porosity of nano-membrane |
| Distance to the membrane | |
| Crossover length-scales | |
| Partition function of a loop of length s | |
| Partition function of a tail of length s | |
| Partition function of a loop s for porosity w, Equation (70) |
| Critical exponent, Equation (39) | |
| The value of corresponding to a repulsive membrane | |
| The exponent corresponding to critically adsorbing membrane | |
| Critical exponent for proximal concentration profile, Equation (81) | |
| Membrane attraction range | |
| Reduced adsorption energy per unit length, Equation (34) | |
| Reduced tilt angle, | |
| Typical bending angle of a loop at distance x from the film | |
| Crossover length-scale | |
| Characteristic segment length in the contact layer, Equation (7) | |
| Distribution of the reduced tilt angle, Equation (48) | |
| Relative deviation from the critical point, | |
| The crossover critical exponent, Equation (1) | |
| The chain partition function | |
| The Tricomi function, Equation (43) |
References
- Napper, D.H. Polymer Stabilization of Colloidal Dispersions; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Lekkerkerker, H.; Tuiner, R. Colloids and Depletion Interaction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.G. Polymers at an Interface; a Simplified View. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 27, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenriegler, E. Polymers Near Surfaces; World Scientific: Singapore, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Stuart, M.; Cosgrove, T.; Vincent, B. Experimental aspects of polymer adsorption at solid/solution interface. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1985, 24, 143–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, K.; Cosgrove, T.; Crowley, T.; Tadros, J.; Vincent, B. The Effects of Polymers on Dispersion Stability; Tadros, J., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982; p. 183. [Google Scholar]
- Semenov, A.N.; Shvets, A.A. Theory of colloid depletion stabilization by unattached and adsorbed polymers. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8863–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Abel, S.M. Shaping membrane vesicles by adsorption of a semiflexible polymer. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goda, T.; Goto, Y.; Ishihara, K. Cell-penetrating macromolecules: Direct penetration of amphipathic phospholipid polymers across plasma membrane of living cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, B.; Radler, J.O. Conformation and Self-Diffusion of Single DNA Molecules Confined to Two Dimensions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herold, C.; Schwille, P.; Petrov, E.P. DNA Condensation at Freestanding Cationic Lipid Bilayers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 148102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, K. Critical Behaviour at Surfaces. In Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena; Domb, C., Lebowitz, J.L., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983; Volume 8, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, M.E. Walks, walls, wetting, and melting. J. Stat. Phys. 1984, 34, 667–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.H.L.; Plascak, J.A.; Bachmann, M. Adsorption of flexible polymer chains on a surface: Effects of different solvent conditions. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 204901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.P.; Basnet, S.; Luettmer-Strathmann, J. Partition-function-zero analysis of polymer adsorption for a continuum chain model. Phys. Rev. E 2021, 104, 034502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassberger, P. Simulations of grafted polymers in a good solvent. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 2005, 38, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinn-Justin, J. Quantum Field Theory and Critical Phenomena; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Maggs, A.C.; Huse, D.A.; Leibler, S. Unbinding Transitions of Semi-flexible Polymers. Europhys. Lett. 1989, 8, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlov, A.R.; Ternovsky, F.F.; Zheligovskaya, E.A. Statistics of stiff polymer chains near an adsorbing surface. Makromol. Chem. Theory Simul. 1993, 2, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, D.V.; Sung, W. Semiflexible Polymers near Attracting Surfaces. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 2679–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.N. Adsorption of a semiflexible wormlike chain. Eur. Phys. J. E 2002, 9, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odjik, T. The statistics and dynamics of confined or entangled stiff polymers. Macromolecules 1983, 16, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschnagel, J.; Meyer, H.; Wittmer, J.; Kulić, I.; Mohrbach, H.; Ziebert, F.; Nam, G.M.; Lee, N.K.; Johner, A. Semiflexible Chains at Surfaces: Worm-Like Chains and beyond. Polymers 2016, 8, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kratky, O.; Porod, G. Röntgenuntersuchung gelöster Fadenmoleküle. Rec. Trav. Chim. 1949, 68, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezanilla, M.; Drake, B.; Nudler, E.; Kashlev, M.; Hansma, P.K.; Hansma, H.G. Motion and enzymatic degradation of DNA in the atomic force microscope. Biophys. J. 1994, 67, 2454–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bustamante, C.; Rivetti, C. Visualizing Protein-Nucleic Acid Interactions on a Large Scale with the Scanning Force Microscope. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 1996, 25, 395–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milchev, A.; Binder, K. How does stiffness of polymer chains affect their adsorption transition? J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 064901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Statistical Physics; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Grosberg, A.Y. On Some Possible Conformational States of Homogeneous Elastic Polymer Chain. Biofizika 1979, 24, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S.F. The statistical mechanics of polymers with excluded volume. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1965, 85, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosberg, A.; Khokhlov, A. Statistical Physics of Macromolecules; American Institute of Physics: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- De Gennes, P.G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornell Univ. Press: Ithaca, NY, USA; London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Antonietti, M.; Kaul, A.; Thünemann, A. Complexation of lecithin with cationic polyelectrolytes. Langmuir 1995, 11, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, S.A. Electrostatic Potentials at Membrane-Solution Interfaces. Curr. Top. Membr. Transp. 1977, 9, 71–144. [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau, D.A. DNA Uptake in Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1999, 53, 217–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolff, J.A.; Budker, V. The mechanism of naked DNA uptake and expression. Adv. Genet. 2005, 54, 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Howorka, S. Building membrane nanopores. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkhangelsky, E.; Sefi, Y.; Hajaj, B.; Rothenberg, G.; Gitis, V. Kinetics and mechanism of plasmid DNA penetration through nanopores. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, P.; Zuber, K.; Guo, Q.; Gibson, B.C.; Yang, J.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H. Large-area Freestanding Gold Nanomembranes with Nanoholes. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Ekinci, Y.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Turchanin, A. Freestanding carbon nanomembranes and graphene monolayers nanopatterned via EUV interference lithography. 2D Mater. 2019, 6, 021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, C.; Rodler, A.; Tscheliessnig, R.; Jungbauer, A. Freely suspended perforated polymer nanomembranes for protein separations. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manoharan, M.P.; Lee, H.; Rajagopalan, R.; Foley, H.C.; Haque, M.A. Elastic Properties of 4–6 nm thick Glassy Carbon Thin Films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, P.; Gölzhäuser, A. Carbon Nanomembranes. Phys. Sci. Rev. 2017, 2, 20160105. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Vidal, F.J.; Martin-Moreno, L.; Pendry, J.B. Surfaces with holes in them: New plasmonic metamaterials. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2005, 7, S97–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritter, R.; Wilhelm, R.A.; Stöger-Pollach, M.; Heller, R.; Mücklich, A.; Werner, U.; Vieker, H.; Beyer, A.; Facsko, S.; Gölzhäuser, A.; et al. Fabrication of nanopores in 1nm thick carbon nanomembranes with slow highly charged ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 063112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gompper, G.; Seifert, U. Unbinding transition of flexible Gaussian polymers in two dimensions. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1990, 23, L1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierfeld, J.; Lipowsky, R. Unbinding and desorption of semiflexible polymers. Europhys. Lett. 2003, 62, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stepanow, S. Adsorption of a semiflexible polymer onto interfaces and surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, A.N.; Khokhlov, A.R. Statistical physics of liquid-crystalline polymers. Sov. Phys. Uspekhi 1988, 31, 988–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milchev, A.; Binder, K. Semiflexible Polymers Interacting With Planar Surfaces: Weak versus Strong Adsorption. Polymers 2020, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milchev, A.; Binder, K. Linear Dimensions of Adsorbed Semiflexible Polymers: What Can Be Learned about Their Persistence Length? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 128003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semenov, A.N.; Nyrkova, I.A. Statistical Description of Chain Molecules. In Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference; Matyjaszewski, K., Moeller, M., Eds.; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Han, X.; Ji, X.; Chen, Q.; Pasch, H.; Liu, Y. Conformation and persistence length of chitosan in aqueous solutions of different ionic strengths via asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, D.A.; Mullins, R.D. Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton. Nature 2010, 463, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abels, J.A.; Moreno-Herrero, F.; van der Heijden, T.; Dekker, C.; Dekker, N.H. Single-Molecule Measurements of the Persistence Length of Double-Stranded RNA. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semenov, A.; Nyrkova, I. Adsorption of Wormlike Chains onto Partially Permeable Membranes. Polymers 2023, 15, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010035
Semenov A, Nyrkova I. Adsorption of Wormlike Chains onto Partially Permeable Membranes. Polymers. 2023; 15(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemenov, Alexander, and Irina Nyrkova. 2023. "Adsorption of Wormlike Chains onto Partially Permeable Membranes" Polymers 15, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010035
APA StyleSemenov, A., & Nyrkova, I. (2023). Adsorption of Wormlike Chains onto Partially Permeable Membranes. Polymers, 15(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010035