Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silk Degumming with Different Neutral Proteases
2.2. Degumming Ratio
2.3. Morphological Characterization of Degummed Silk Fibers
2.4. Amino Acid Analysis
2.5. Thermal Analysis of Degummed Silk Fibers
2.6. Preparation of Regenerated SF Solution
2.7. Characterization of the Molecular Weight Distribution of Regenerated Silk Fibroin
2.8. Measurement for Shear Viscosity of Regenerated SF Solution
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Degumming Ratio and Morphological Characterization of Degummed Silk Fibers
3.2. Amino Acid Analysis and Sericin Containing Ratio
3.3. Thermal Analysis
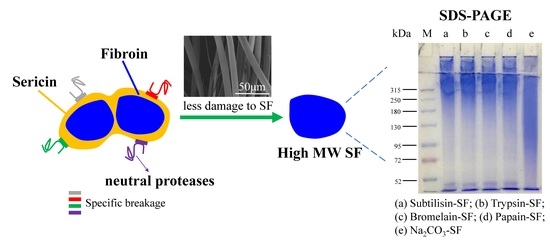
3.4. Characterization of the Molecular Weight Distribution of Regenerated Silk Fibroin
3.5. Viscosity of Regenerated SF Solution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Gregory, D.A.; Tomeh, M.A.; Zhao, X. Silk fibroin as a functional biomaterial for tissue engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.J.; Ki, C.S.; Oh, H.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C. Molecular weight distribution and solution properties of silk fibroins with different dissolution conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partlow, B.P.; Tabatabai, A.P.; Leisk, G.G.; Cebe, P.; Blair, D.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk fibroin degradation related to rheological and mechanical properties. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, K.H.; Nho, S.K.; Han, M.S.; Um, I.C. Effect of degumming methods on structural characteristics and properties of regenerated silk. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allardyce, B.J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Dilley, R.J.; Atlas, M.D.; Kaur, J.; Wang, X. The impact of degumming conditions on the properties of silk films for biomedical applications. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Shao, Z. Effect of various dissolution systems on the molecular weight of regenerated silk fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Lin, J.; Pei, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, D.; Huang, Z. Recent advances in environmentally friendly and green degumming processes of silk for textile and non-textile applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkhowa, R.; Wang, L.; Kanwar, J.R.; Wang, X. Molecular weight and secondary structure change in eri silk during alkali degumming and powdering. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 119, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of regeneration of liquid silk fibroin on its structure and characterization. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, A.; Greco, G.; Corridori, I.; Pugno, N.M.; Motta, A. A design of experiment rational optimization of the degumming process and its impact on the silk fibroin properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1374–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulrajanid, M.L.; Sethi, S.; Gupta, S. Some studies in degumming of silk with organic acids. J. Soc. Dyers. Colour. 1992, 108, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, P.; Capar, G.; Toprak, T.; Yener, E. Sericin removal from silk fibers with eco-friendly alternative methods. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2016, 26, 368–374. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, M.L. Degumming of silk. Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top. 1992, 22, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of strongly alkaline electrolyzed water on silk degumming and the physical properties of the fibroin fiber. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, W.; Li, C. Effect of silk degumming on the structure and properties of silk fibroin. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arami, M.; Mazaheri, F.; Rahimi, S. Degradation of sericin (degumming) of Persian silk by ultrasound and enzymes as a cleaner and environmentally friendly process. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, T.K.H.; Toh, S.L.; Goh, J.C.H. Optimization of the silk scaffold sericin removal process for retention of silk fibroin protein structure and mechanical properties. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5, 035008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Liu, H.; Li, T.; Wang, J. Surface modification and functionalization of silk fibroin fibers/fabric toward high performance applications. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mathummal, S.; Ashoke, R.T.; Shaon, R.C. Degumming of raw silk fabric with help of marine extracellular protease. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 9, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gulrajani, M.L.; Gupta, S.V.; Gupta, A.; Suri, M. Degumming of silk with different protease enzymes. Indian J. Fibre Text. 1996, 21, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Ninpetch, U.; Tsukada, M.; Promboon, A. Mechanical properties of silk fabric degummed with bromelain. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2015, 10, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freddi, G.; Mossotti, R.; Innocenti, R. Degumming of silk fabric with several proteases. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 106, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwannaphan, S.; Fufeungsombut, E.; Promboon, A.; Chim-anage, P. A serine protease from newly isolated Bacillus sp. for efficient silk degumming, sericin degrading and colour bleaching activities. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 2017, 117, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Ong, S.E.; Mann, M. Trypsin cleaves exclusively C-terminal to arginine and lysine residues. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sneha; Pandey, J.P.; Pandey, D.M. Evaluating the role of trypsin in silk degumming: An insilico approach. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 20, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohakunjit, N.; Selamassakul, O.; Kerdchoechuen, O. Seafood-like flavour obtained from the enzymatic hydrolysis of the protein by-products of seaweed (Gracilaria sp.). Food Chem. 2014, 158, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, S.K.; Shukla, S.R. Comparative study of degumming of silk varieties by different techniques. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 107, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, N.V.; Das, B.; Thirumalesh, R.M. Enzyme applications in silk processing. Adv. Silk Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Nakpathom, M.; Somboon, B.; Narumol, N. Papain enzymatic degumming of Thai Bombyx mori silk fibers. J. Microsc. Soc. Thail. 2009, 23, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Pan, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Hu, C.; Li, M. A high molecular weight silk fibroin scaffold that resists degradation and promotes cell proliferation. Biopolymers 2023, 114, e23554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpay, P.; Uygun, D.A. Usage of immobilized papain for enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2015, 111, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lin, J.; Niu, L.; Pan, P.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, M. A novel method for the quantitative detection of sericin content in silk fiber based on the ratio of aspartate to alanine. J. Renew. Mater. 2023, 11, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lin, J.; Niu, L.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, M. High molecular weight silk fibroin prepared by papain degumming. Polymers 2020, 12, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.E.; Kim, H.H.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, K.H.; Park, Y.H.; Um, I.C. Effects of different Bombyx mori silkworm varieties on the structural characteristics and properties of silk. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nultsch, K.; Bast, L.K.; Näf, M.; Yakhlifi, S.E.; Bruns, N.; Germershaus, O. Effects of silk degumming process on physicochemical, tensile, and optical properties of regenerated silk fibroin. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wray, L.S.; Hu, X.; Gallego, J.; Georgakoudi, I.; Omenetto, F.G.; Schmidt, D.; David, L.K. Effect of processing on silk-based biomaterials: Reproducibility and biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2011, 99B, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Inoue, S.; Mizuno, S. Hydrophobic interaction of P25, containing Asn-linked oligosaccharide Chains, with the H-L complex of silk fibroin produced by Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Dai, F.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Zhou, W.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y. Preparation and characterization of silk fibroin as a biomaterial with potential for drug delivery. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, H.; Nakao, H.; Takasu, Y.; Tsubouchi, K. Preparation of undegraded native molecular fibroin solution from silkworm cocoons. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2001, 14, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Tang, X.; Lu, Q.; Huang, J.; You, X.; Zhang, F. In vitro and in vivo degradation of silk fibers degummed with various sodium carbonate concentrations. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 27, 102369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, H.; Zuo, B. Effect of sodium carbonate concentrations on the degumming and regeneration process of silk fibroin. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kwon, M.; Kim, S. Biological degumming of silk fabrics with proteolytic enzymes. J. Nat. Fibers 2016, 13, 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Rossle, M.; Panine, P.; Urban, V.; Riekel, C. Structural evolution of regenerated silk fibroin under shear: Combined wide- and small-angle X-ray scattering experiments using synchrotron radiation. Biopolymers 2004, 74, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Enzyme | Concentration (g/L) | pH | Temperature (°C) | Each Time (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subtilisin | 4 | 7 | 50 | 60 |
| Trypsin | 4 | 6.8 | 38 | 60 |
| Bromelain | 4 | 6.4 | 40 | 60 |
| Papain | 2 | 6.6 | 55 | 60 |
| Na2CO3 | 0.5 | / | 100 | 30 |
| Amino Acids | Subtilisin | Trypsin | Bromelain | Papain | Na2CO3 | Raw Silk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 1.75 ± 0.04 | 1.76 ± 0.03 | 1.78 ± 0.01 | 1.73 ± 0.01 | 1.69 ± 0.01 | 3.94 ± 0.03 |
| Thr | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 0.91 ± 0.07 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.89 ± 0.14 | 0.93 ± 0.01 | 2.36 ± 0.04 |
| Ser | 10.08 ± 0.18 | 11.91 ± 1.38 | 10.78 ± 0.15 | 10.92 ± 0.02 | 10.85 ± 0.08 | 14.67 ± 0.21 |
| Glu | 1.86 ± 0.06 | 1.01 ± 1.17 | 1.93 ± 0.17 | 2.03 ± 0.18 | 1.57 ± 0.01 | 2.36 ± 0.21 |
| Gly | 42.21 ± 0.08 | 41.33 ± 0.45 | 41.70 ± 0.76 | 41.78 ± 0.48 | 43.30 ± 0.52 | 37.89 ± 0.16 |
| Ala | 31.41 ± 0.47 | 31.73 ± 0.32 | 31.84 ± 0.15 | 31.13 ± 0.07 | 31.12 ± 0.27 | 27.19 ± 0.10 |
| Val | 2.29 ± 0.04 | 2.32 ± 0.10 | 2.36 ± 0.07 | 2.43 ± 0.23 | 2.22 ± 0.00 | 2.46 ± 0.03 |
| Ile | 0.56 ± 0.03 | 0.55 ± 0.04 | 0.60 ± 0.03 | 0.6 ± 0.08 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.58 ± 0.02 |
| Leu | 0.54 ± 0.00 | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 0.54 ± 0.00 | 0.60 ± 0.08 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 0.62 ± 0.04 |
| Tyr | 5.04 ± 0.16 | 4.91 ± 0.20 | 4.92 ± 0.01 | 5.17 ± 0.02 | 5.04 ± 0.12 | 4.63 ± 0.08 |
| Phe | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 0.80 ± 0.05 | 0.85 ± 0.06 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.74 ± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.05 |
| Lys | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.02 |
| His | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 0.36 ± 0.02 |
| Arg | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 0.46 ± 0.01 | 0.44 ± 0.01 | 0.45 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.05 |
| Pro | 0.70 ± 0.16 | 0.64 ± 0.17 | 0.71 ± 0.13 | 0.79 ± 0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.01 | 0.67 ± 0.06 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Huang, Q.; Pan, P.; Fang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases. Polymers 2023, 15, 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163383
Liu X, Huang Q, Pan P, Fang M, Zhang Y, Yang S, Li M, Liu Y. Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases. Polymers. 2023; 15(16):3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163383
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xueping, Qian Huang, Peng Pan, Mengqi Fang, Yadong Zhang, Shanlong Yang, Mingzhong Li, and Yu Liu. 2023. "Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases" Polymers 15, no. 16: 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163383
APA StyleLiu, X., Huang, Q., Pan, P., Fang, M., Zhang, Y., Yang, S., Li, M., & Liu, Y. (2023). Comparative Study of the Preparation of High-Molecular-Weight Fibroin by Degumming Silk with Several Neutral Proteases. Polymers, 15(16), 3383. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15163383