A Straightforward Method to Produce Multi-Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Transdermal/Tympanic Patches Using Electrospinning and Electrospray
Abstract
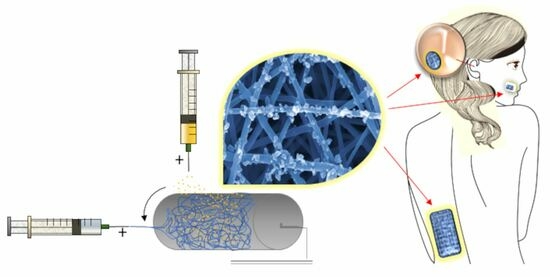
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Production of RHO-Loaded PLGA NPs
2.3. Production of DEX-PHBHV Electrospun Fiber Meshes with RHO-PLGA NPs
2.4. Morphological, Chemical and Mechanical Characterization
2.5. Drug Loading and Entrapment Efficiency
2.6. DEX and RHO Release from PHBHV Meshes and NPs
2.7. Ethical Statement
2.8. HDF Isolation and Culture
2.9. Cytocompatibility
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Dimensional Characterization of NPs
3.2. Morphological and Dimensional Characterization of the Fiber Meshes
3.3. Chemical Characterization
3.4. Mechanical Characterization of the Fiber Meshes
3.5. DEX and RHO In Vitro Releases
3.6. Cytocompatibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danti, S.; D’Alessandro, D.; Mota, C.; Bruschini, L.; Berrettini, S. Applications of bioresorbable polymers in skin and eardrum. In Bioresorbable Polymers for Biomedical Applications: From Fundamentals to Translational Medicine; Perale, G., Hilborn, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 423–444. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, T.; Ishii, D.; Mahara Murakami, S.; Yamaok, T.; Kumar, S.; Samian, R.; Fujita, M.; Maeda, M.; Iwata, T. Scaffolds from electrospun polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers: Fabrication, characterization, bioabsorption and tissue response. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sombatmankhong, K.; Sanchavanakit, N.; Pavasant, P.; Supaphol, P. Bone scaffolds from electrospun fiber mats of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate), poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and their blend. Polymers 2007, 48, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinjaski, N.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, M.; Selvam, S.; Parra-Ruiz, F.J.; Lehman, S.M.; San Román, J.; García, E.; García, J.L.; García, A.J.; Prieto, M.A. PHACOS, a functionalized bacterial polyester with bactericidal activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarali, S.; Marlinghaus, L.; Viebahn, R.; Lewis, H.; Ryadnov, M.J.; Groll, J.; Salber, J.; Roy, I. Activated Polyhydroxyalkanoate Meshes Prevent Bacterial Adhesion and Biofilm Development in Regenerative Medicine Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotech. 2020, 8, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sombatmankhong, K.; Suwantong, O.; Waleetorncheepsawat, S.; Supaphol, P. Electrospun fiber mats of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate), and their blends. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Kim, S.; Yuan, J.; Kim, J.C.; Kwon, O.H.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G.; Ito, Y.; Kang, I.K. Electrospun PHBV/collagen composite nanofibrous scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2007, 18, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Milazzo, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Berrettini, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Qin, Z.; Buehler, M.J.; Danti, S. Electrospinning Piezoelectric Fibers for Biocompatible Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 9, 1901287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Sorayani Bafqi, M.S.; Fusco, A.; Ricci, C.; Gallone, G.; Bagherzadeh, R.; Donnarumma, G.; Uddin, M.J.; Latifi, M.; Lazzeri, A.; et al. Electrospun ZnO/Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride-Trifluoroethylene) Scaffolds for Lung Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2020, 26, 1312–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sun, X.-F.; Li, W.; He, J.; Sun, R.; Hu, S.; Wu, Y. Fabrication of Electrospun Xylan-g-PMMA/TiO2 Nanofibers and Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue. Polymers 2022, 14, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.; Arbabi Bidgoli, S.; Rezayat, S.M. Electrospun polymeric nanofibers for transdermal drug delivery. Nanomed. J. 2017, 4, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Nagiah, N.; Murdock1, C.J.; Bhattacharjee, M.; Nair, L.; Laurencin, C.T. Development of Tripolymeric Triaxial Electrospun Fibrous Matrices for Dual Drug Delivery Applications. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, m.; Yu, D.; Li, X.; Williams, G.R. Review. The Development and Bio-applications of Multifluid Electrospinning. Mater. Highlights 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwantong, O.; Ruktanonchai, U.; Supaphol, P. Electrospun cellulose acetate fiber mats containing asiaticoside or Centella asiatica crude extract and the release characteristics of asiaticoside. Polymers 2008, 49, 4239–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Panayiotou, C.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Electrospun fiber mats containing shikonin and derivatives with potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, E.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, C.M.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.; Shim, I.K. Synergistic effect of a drug loaded electrospun patch and systemic chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer xenograft. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, K.; Dumont, M.; Del Rio, L.; Orsat, V. Producing PHAs in the bioeconomy—Towards a sustainable bioplastic. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2017, 9, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaoglu-Altan, O.I.; Baskan, H.; Meireman, T.; Basnett, P.; Azimi, B.; Fusco, A.; Funel, N.; Donnarumma, G.; Lazzeri, A.; Roy, I.; et al. Silver Nanoparticle-Coated Polyhydroxyalkanoate Based Electrospun Fibers for Wound Dressing Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavadiya, S.; Biswas, P. Electrospray deposition of biomolecules: Applications, challenges, and recommendations. J. Aerosol Sci. 2018, 125, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Clasen, C.; Van den Mooter, G. Pharmaceutical Applications of Electrospraying. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2601–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, D.H.; Choi, S.W. Entrapment of Protein Using Electrosprayed Poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) Microspheres with a Porous Structure for Sustained Release. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Thian, E.S.; Ramakrishna, S. Protein encapsulated core–shell structured particles prepared by coaxial electrospraying: Investigation on material and processing variables. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Dube, N.; Katti, D.S. Electrospraying: A facile technique for synthesis of chitosan-based micro/nanospheres for drug delivery applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2009, 88B, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azimi, B.; Thomas, L.; Fusco, A.; Kalaoglu Altan, O.; Basnett, P.; Cinelli, P.; De Clerck, K.; Roy, I.; Donnarumma, G.; Coltelli, M.B.; et al. Electrosprayed Chitin Nanofibril/Electrospun Polyhydroxyalkanoate Fiber Mesh as Functional Nonwoven for Skin Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Ding, J.; Jiang, X. Fluorofenidone-loaded PLGA microspheres for targeted treatment of paraquat-induced acute lung injury in rats. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wokovich, A.; Prodduturi, S.; Doub, W.; Hussain, A.; Buhse, L. Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günday, C.; Anand, S.; Gencer, H.B.; Munafò, S.; Moroni, L.; Fusco, A.; Donnarumma, G.; Ricci, C.; Hatir, P.C.; Türeli, N.G.; et al. Ciprofloxacin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles incorporated electrospun fibers for drug delivery in tissue engineering applications. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Luo, D.; Li, W.; Ding, Y. Multiscale polymeric fibers for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomedical Technology 2024, 5, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillay, V.; Dott, C.; Choonara, Y.E.; Tyagi, C.; Tomar, L.; Kumar, P. A Review of the Effect of Processing Variables on the Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Nanomat. 2013, 2013, 789289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Ricci, C.; Fusco, A.; Zavagna, L.; Linari, S.; Don-narumma, G.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Danti, S.; Lazzeri, A. Electro-sprayed nanochitins on cellulose tissue for skin contact application. Molecules 2021, 26, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeaux, D.; Ghigo, J.M.; Beloin, C. Biofilm-related infections: Bridging the gap between clinical management and fundamental aspects of recalcitrance toward antibiotics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 510–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, J.; Loh, X.J. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Opening doors for a sustainable future. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallini, C.; Danti, S.; Azimi, B.; Tempesti, V.; Ricci, C.; Ventrelli, L.; Cinelli, P.; Barbani, N.; Lazzeri, A. Multifunctional Coatings for Robotic Implanted Device. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundrat, V.; Cernekova, N.; Kovalcik, A.; Enev, V.; Marova, I. Drug Release Kinetics of Electrospun PHB Meshes. Materials 2019, 12, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasouli, M.; Pirsalami, s.; Zebarjad, S.M. Skin-compatible biobased beauty masks prepared by extrusion. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 23. [Google Scholar]
- De la Ossa, J.G.; Danti, S.; Esposito Salsano, J.; Azimi, B.; Tempesti, V.; Barbani, N.; Digiacomo, M.; Macchia, M.; Uddin, M.J.; Cristallini, C.; et al. Electrospun Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3- Hydroxyvalerate)/Olive Leaf Extract Fiber Mesh as Prospective Bio-Based Scaffold for Wound Healing. Molecules 2022, 27, 6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Mihaila, S.M.; Kulkarni, A.A.; Patel, A.; Di Luca, A.; Reis, R.L.; Gomes, M.E.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Moroni, L.; Khademhosseini, A. Amphiphilic beads as depots for sustained drug release integrated into fibrillar scaffolds. J. Control. Release 2014, 187, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, L.; Licht, R.; de Boer, J.; de Wijn, J.R.; van Blitterswijk, C.A. Fiber diameter and texture of electrospun PEOT/PBT scaffolds influence human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and morphology, and the release of incorporated compounds. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 4911–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Lou, D. Dual drug release from core-shell nanoparticles with distinct release profiles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 3205–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almería, B.; Fahmy, T.M.; Gomez, A. A multiplexed electrospray process for single-step synthesis of stabilized polymer particles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2011, 154, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Jaiswal, N.; Hens, A.; Mahat, N.; Chanda, N. Development of 6-Thioguanine conjugated PLGA nanoparticles through thioester bond formation: Benefits of electrospray mediated drug encapsulation and sustained release in cancer therapeutic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtmann, B.; Tang, J.; Kramer, S.; Eickner, T.; Luderer, F.; Fricker, G.; Gomez, A.; Heemskerk, B.; Jähn, P.S. Electrospray Synthesis of Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) Nanoparticles Encapsulating Peptides to Enhance Proliferation of Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 10, 3316–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodnár, E. Electrospraying of Polymer Solutions for the Generation of Micro-Particles, Nano-Structures, and Granular Films. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitat Rovira i Virgili, Tarragona, Spain, 2016. Available online: https://www.tdx.cat/bitstream/handle/10803/379820/Eszter%20Bodnar_TDX.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 13 August 2023).
- Venugopal, J.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Low, S.; Choon, A.T.; Zhang, Y.; Deepika, G.; Ramakrishna, S. Nanotechnology for nanomedicine and delivery of drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 2184–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adepu, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Controlled Drug Delivery Systems: Current Status and Future Directions. Molecules 2021, 26, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsalehi, M.; Ghajarzadeh, M.; Farhadi, M.; Akbarnejad, Z.; Ahmadi, S.; Salem, M.M. Intratympanic corticosteroid injection as a first-line treatment of the patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss compared to systemic steroid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukaszewska-Kuska, M.; Ślebioda, Z.; Dorocka-Bobkowska, B. The effectiveness of topical forms of dexamethasone in the treatment of oral lichen planus—A systematic review. Oral Diseases 2022, 28, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Vora, L.K.; Peng, K.; Donnelly, R.F. Trilayer microneedle array assisted transdermal and intradermal delivery of dexamethasone. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 612, 121295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, D.S.; O’Malley, M.; Cohen, S.; Watford, K.; Labadie, R.F. Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Mawal-Dewan, M.; Cristofalo, V.J.; Sell, C. Enhanced proliferation of human fibroblasts, in the presence of dexamethasone, is accompanied by changes in p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1 and the insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 177, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, L.; Cascone, M.G.; Danti, S.; Serino, L.P.; Moscato, S.; Bernardini, N. Gelatine/PLLA sponge-like scaffolds: Morphological and biological characterization. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaji, T.; Kawashima, T.; Yamamoto, C.; Sakamoto, M. Rhodamine B inhibits collagen synthesis by human lip fibroblasts in culture. Toxicol Lett. 1992, 61, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Danti, S.; Moroni, L.; Mota, C. Regenerative therapies for tympanic membrane. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 127, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| # | Sample | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Strain Range (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PHBHV fibers | 0.65 ± 0.08 | 0.05–0.20 | <0.05 (#1 vs. #2, #3, #4) |
| 2 | DEX-loaded PHBHV fibers | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.00–0.20 | n.s. (vs. #3, #4) |
| 3 | PHBHV fibers + RHO-loaded PLGA NPs | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.50–1.00 | n.s. (vs. #2, #4) |
| 4 | DEX-loaded PHBHV fibers + RHO-loaded PLGA NPs | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.45–0.80 | n.s. (vs. #2, #3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azimi, B.; Ricci, C.; Macchi, T.; Günday, C.; Munafò, S.; Maleki, H.; Pratesi, F.; Tempesti, V.; Cristallini, C.; Bruschini, L.; et al. A Straightforward Method to Produce Multi-Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Transdermal/Tympanic Patches Using Electrospinning and Electrospray. Polymers 2023, 15, 3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173494
Azimi B, Ricci C, Macchi T, Günday C, Munafò S, Maleki H, Pratesi F, Tempesti V, Cristallini C, Bruschini L, et al. A Straightforward Method to Produce Multi-Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Transdermal/Tympanic Patches Using Electrospinning and Electrospray. Polymers. 2023; 15(17):3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173494
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzimi, Bahareh, Claudio Ricci, Teresa Macchi, Cemre Günday, Sara Munafò, Homa Maleki, Federico Pratesi, Veronika Tempesti, Caterina Cristallini, Luca Bruschini, and et al. 2023. "A Straightforward Method to Produce Multi-Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Transdermal/Tympanic Patches Using Electrospinning and Electrospray" Polymers 15, no. 17: 3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173494
APA StyleAzimi, B., Ricci, C., Macchi, T., Günday, C., Munafò, S., Maleki, H., Pratesi, F., Tempesti, V., Cristallini, C., Bruschini, L., Lazzeri, A., Danti, S., & Günday-Türeli, N. (2023). A Straightforward Method to Produce Multi-Nanodrug Delivery Systems for Transdermal/Tympanic Patches Using Electrospinning and Electrospray. Polymers, 15(17), 3494. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15173494