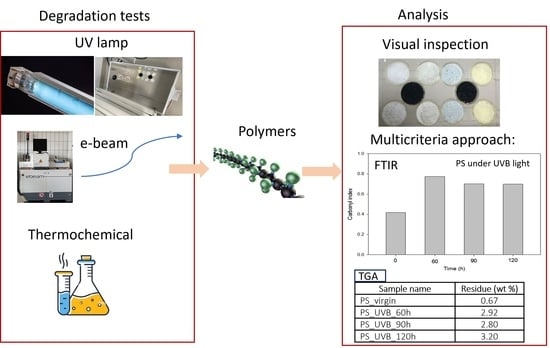
Effect of Abiotic Treatments on Agricultural Plastic Waste: Efficiency of the Degradation Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Thermal/thermomechanical treatments;
- Photo-oxidation treatments;
- Chemical/thermochemical treatments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polymers Used
2.2. Processing Conditions to Enhance Polymer Degradation
2.2.1. Photo-Oxidation: UV Pre-Treatments
2.2.2. E-Beam-Radiation Pre-Treatment
2.2.3. Thermochemical Pre-Treatments
2.3. Analytical Approaches to Evaluating Polymer Degradation
2.3.1. FTIR Determinations
2.3.2. Thermal Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of the Different Pre-Treatments on PS Materials
3.1.1. Effects of the Photo-Oxidation Pre-Treatments
3.1.2. Effects of the Thermochemical Pre-Treatments
3.2. Effects of the Different Pre-Treatments on Polyolefin (LDPE and LLDPE) Materials
3.2.1. Effects of the Photo-Oxidation Pre-Treatments
3.2.2. Effects of the Thermochemical Pre-Treatments
3.3. Effect of the Different Pre-Treatments on PET Materials
3.3.1. Effects of the Photo-Oxidation Pre-Treatments
3.3.2. Effects of the Thermochemical Pre-Treatments
3.4. Selection of the Most Efficient and Highest-Cost–Benefit Pre-Treatment Procedure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scarascia-Mugnozza, G.; Sica, C.; Russo, G. Plastic materials in European agriculture: Actual use and perspectives. J. Agric. Engin. 2011, 42, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular Economy. 2018. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/circular-economy/pdf/plastics-strategy-brochure.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Dorigato, A.; Pegoretti, A.; Fambri, L.; Lonardi, C.; Slouf, M.; Kolarik, J. Linear low-density polyethylene/cycloolefincopolymer blends. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Lettieri, P.; Baeyens, J. Recycling and recovery routes of plastic solid waste (PSW): A review. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2625–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2020. An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data. 2020. Available online: https://www.plasticseurope.org/en/resources/publications/4312-plastics-facts-2020 (accessed on 21 December 2023).
- Mantia, F.P.; Morreale, M.; Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Ceraulo, M.; Scaffaro, R. Degradation of polymer blends: A brief review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 145, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inderthal, H.; Tai, S.L.; Harrison, S.T.L. Non-hydrolyzable plastics—An interdisciplinary look at plastic bio-oxidation. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 39, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiellini, E.; Corti, A.; D’Antone, S.; Baciu, R. Oxo-biodegradable carbon backbone polymers—Oxidative degradation of polyethylene under accelerated test conditions. Polym. Degr. Stab. 2006, 91, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G. Degradable Polymers Principles and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Al-Dousari, N.M.; Joseph Abraham, G.; D’Souza, M.A.; Al-Qabandi, O.A.; Al-Zakri, W. Effect of die head temperature at compounding stage on the degradation of linear low density polyethylene/plastic film waste blends after accelerated weathering. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 5147209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.V.; Duarte, F.M.; Botelho, G.; Moura, I. Photo-chemical aging and processability of life-time-controlled polystyrene/high-impact polystyrene blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 2930–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskolczi, N.; Bartha, L.; Deák, G. Thermal degradation of polyethylene and polystyrene from the packaging industry over different catalysts into fuel-like feed stocks. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.B.; Aglietto, M. Riutilizzo dei Materiali Polimerici; Edizione Nouva Cultura: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Skariyachan, S.; Setlur, A.S.; Naik, S.Y.; Naik, A.A.; Usharani, M.; Vasist, K.S. Enhanced biodegradation of low and high-density polyethylene by novel bacterial consortia formulated from plastic-contaminated cow dung under thermophilic conditions. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2017, 24, 8443–8457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Sharma, N. Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, R.A.; Aristilde, L. Degradation and metabolism of synthetic plastics and associated products by Pseudomonas sp.: Capabilities and challenges. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filiciotto, L.; Rothenberg, G. Biodegradable plastics: Standards, policies, and impacts. Chem. Sus. Chem. 2021, 14, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.X.; Jin, Y.J.; Meng, Q.Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.Z. Biodegradation behavior of poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT), poly (lactic acid) (PLA), and their blend under soil conditions. Polym. Test. 2013, 32, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Yuan, L.M.; Huang, G.; Chen, X.; Shi, W. Degradation degree analysis of environmental microplastics by micro-FTIR imaging technology. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.K.; Devi, D. Characteristics investigation on biofilm formation and biodegradation activities of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain ISJ14 colonizing low density polyethylene (LDPE) surface. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Qin, J.; Tao, Y.; Jie, G.; Wang, J. Natural weathering severity of typical coastal environment on polystyrene: Experiment and modeling. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, J.C.; Reis, V.; Paço, A.; Martins, P.; Cruz, A.; da Costa, J.P.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T. Effects of spatial and seasonal factors on the characteristics and carbonyl index of (micro) plastics in a sandy beach in Aveiro, Portugal. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.O.; Abrantes, N.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Nogueira, H.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Spatial and temporal distribution of microplastics in water and sediments of a freshwater system (Antuã River, Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1549–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salem, S.M.; Bumajdad, A.; Khan, A.R.; Sharma, B.K.; Chandrasekaran, S.R.; Al-Turki, F.A.; Jassem, F.H.; Al-Dhafeeri, A.T. Non-isothermal degradation kinetics of virgin linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) and biodegradable polymer blends. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, S.G.; Barel, B.; Shpasser, D.; Segal, E.; Gazit, O.M. Correlating chemical and physical changes of photo-oxidized low-density polyethylene to the activation energy of water release. Polym. Test. 2017, 64, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, E.; Haddad, R. Photo-degradation and photo-stabilization of polymers, especially polystyrene: Review. SpringerPlus 2013, 2, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewert, B.; Plassmann, M.M.; MacLeod, M. Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2015, 17, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamas, A.; Moon, H.; Zheng, J.; Qiu, Y.; Tabassum, T.; Jang, J.H.; Abu-Omar, M.; Scott, S.L.; Suh, S. Degradation rates of plastics in the environment. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3494–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ojeda, M.E.; Trastoy, B.; López-Arbeloa, Í.; Bañuelos, J.; Costela, Á.; García-Moreno, I.; Chiara, J.L. Click Assembly of Dye-Functionalized Octasilsesquioxanes for Highly Efficient and Photostable Photonic Systems. Chem.–A Eur. J. 2011, 17, 13258–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijsman, P.; Meijers, G.; Vitarelli, G. Comparison of the UV-degradation chemistry of polypropylene, polyethylene, polyamide 6 and polybutylene terephthalate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1999, 65, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, M.N. Degradation of linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) exposed to UV-irradiation. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 52, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.U.; Jung, J.W.; Jo, J.W.; Jo, W.H. Degradation and stability of polymer-based solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24265–24283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecozzi, M.; Nisini, L. The differentiation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable polyethylene terephthalate (PET) samples by FTIR spectroscopy: A potential support for the structural differentiation of PET in environmental analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 101, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Type UV | W × Chamber | Irradiated Surface (m2) | Power Consumption (kW/m2 h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 20 | 0.2479 | 0.161 |
| C | 16.7 | 0.2479 | 0.135 |
| Treatments | Code | Plastic Type | Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| (NH4)2S2O8 + H2SO4 | AM | LDPE, LLDPE, LLDPE + LDPE, PP, PET, PS | 6 and 12 days, 35 and 70 °C, concentrated and diluted (100% and 33%) reagents |
| K2Cr2O7 + H2SO4 | CM | LDPE, LLDPE, LLDPE + LDPE, PP, PET, PS | 6 and 12 days, 35 and 70 °C, concentrated and diluted (100% and 33%) reagents |
| HCl:HNO3:H2O 3:1:1, Aqua regia | AR | LDPE, LLDPE, LLDPE + LDPE, PP, PET, PS | 6 and 12 days, 35 and 70 °C, concentrated and diluted (100% and 33%) reagents |
| E-Beam Pre-Treatment | Carbonyl Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | LDPE | LLDPE | PET | |
| 0 kGy | 0.309 | 0.039 | 0.070 | 0.999 |
| 100 kGy | 0.277 | 0.063 | 0.087 | 1.002 |
| 200 kGy | 0.331 | 0.065 | 0.094 | 1.002 |
| 500 kGy | 0.373 | 0.097 | 0.125 | 1.004 |
| Time consuming (T) Costs | Code | Assessment |
| Low | T-L | <24 h |
| Medium | T-M | 1–5 days |
| High | T-H | >5 days |
| Energy consuming (E) Costs | Code | Assessment |
| Low | E-L | <15 kW/m2 |
| Medium | E-M | 15–60 kW/m2 |
| High | E-H | >60 kW/m2 |
| Environmental Cost (Env) | Code | Assessment |
| Low | Env-L | 0–1 |
| Medium | Env-M | 2–3 |
| High | Env-H | 3–4 |
| Plastic Type | UV-B | UV-C | E-Beam | Thermochemical |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS | 60 h 2.5 d 9.7 kW | 45 h 1.9 d 6.1 kW | 500 kGy <1 d 3.6 kW | AM ≈ CM > AR Concentrated > diluted 12 d > 6 d 35 °C ≥ 70 °C 8 kW |
| Cost-effectiveness assessment | T-M/E-L/Env-L | T-M/E-L/Env-L | T-L/E-L/Env-L | T-H/E-L/Env-H |
| PET | 90 h 3.7 d 14.5 kW | 30 h 1.3 d 4.0 kW | 100–200 kGy <1 d 2.8 kW | AM ≈ CM > AR Concentrated > diluted 12 d > 6 d 70 °C ≥ 35 °C 16 kW |
| Cost-effectiveness assessment | T-M/E-L/Env-L | T-M/E-L/Env-L | T-L/E-L/Env-L | T-H/E-M/Env-H |
| LDPE | 500–750 h 20–31 d 80–120 kW | 750 h 31 d 101 kW | 1000 kGy <1 d 4.9 kW | AR > CM > AM Concentrated > diluted 12 d > 6 d 70 °C ≥ 35 °C 16 kW |
| Cost-effectiveness assessment | T-H/E-H/Env-L | T-H/E-H/Env-L | T-L/E-L/Env-L | T-H/E-M/Env-H |
| LLDPE | 500–750 h 20–31 d 80–120 kW | 750 h 31 d 101 kW | 1000 kGy <1 d 4.4 kW | CM ≈ AR > AM Concentrated > diluted 12 d > 6 d 70 °C ≥ 35 °C 16 kW |
| Cost-effectiveness assessment | T-H/E-H/Env-L | T-H/E-H/Env-L | T-L/E-L/Env-L | T-H/E-M/Env-H |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blesa Marco, Z.E.; Sáez, J.A.; Andreu-Rodríguez, F.J.; Penalver, R.; Rodríguez, M.; Eissenberger, K.; Cinelli, P.; Bustamante, M.Á.; Moral, R. Effect of Abiotic Treatments on Agricultural Plastic Waste: Efficiency of the Degradation Processes. Polymers 2024, 16, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030359
Blesa Marco ZE, Sáez JA, Andreu-Rodríguez FJ, Penalver R, Rodríguez M, Eissenberger K, Cinelli P, Bustamante MÁ, Moral R. Effect of Abiotic Treatments on Agricultural Plastic Waste: Efficiency of the Degradation Processes. Polymers. 2024; 16(3):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030359
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlesa Marco, Zbigniew Emil, José Antonio Sáez, Francisco Javier Andreu-Rodríguez, Rosa Penalver, Manuel Rodríguez, Kristina Eissenberger, Patrizia Cinelli, María Ángeles Bustamante, and Raúl Moral. 2024. "Effect of Abiotic Treatments on Agricultural Plastic Waste: Efficiency of the Degradation Processes" Polymers 16, no. 3: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030359
APA StyleBlesa Marco, Z. E., Sáez, J. A., Andreu-Rodríguez, F. J., Penalver, R., Rodríguez, M., Eissenberger, K., Cinelli, P., Bustamante, M. Á., & Moral, R. (2024). Effect of Abiotic Treatments on Agricultural Plastic Waste: Efficiency of the Degradation Processes. Polymers, 16(3), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030359