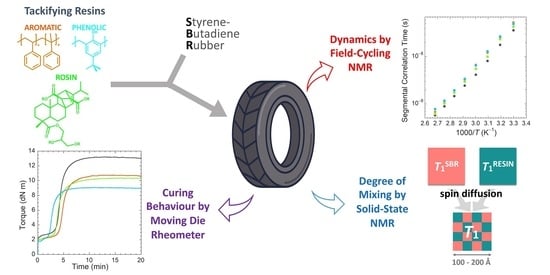
Exploring the Effect of Resins of Different Origin on the Structure, Dynamics and Curing Characteristics of SBR Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. MDR, Equilibrium Swelling, DSC, and DMA Experiments
2.3. SSNMR Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MDR, Equilibrium Swelling, DSC, and DMA Experiments
3.2. SSNMR Study
3.2.1. Structural Characterization
3.2.2. Characterization of Dynamics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gwin, L.E.; Weaver, E.J. A New Dimension in Rubber Compound Tackifiers. J. Elastom. Plast. 1977, 9, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, B.; Waddell, W. The Science of Rubber Compounding. In Science and Technology of Rubber, 3rd ed.; Mark, J.E., Erman, B., Eirich, F.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 401–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, J.; Han, B.; Wang, B.; Mao, L.; Zhang, L. Novel Design of Eco-Friendly Super Elastomer Materials with Optimized Hard Segments Micro-Structure: Toward Next-Generation High-Performance Tires. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, P.; Tang, Z.; Guo, B. Solving “Magic Triangle” of Tread Rubber Composites with Phosphonium-Modified Petroleum Resin. Polymer 2020, 190, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, M.; Grosch, K.A. A Laboratory Method to Comprehensively Evaluate Abrasion, Traction and Rolling Resistance of Tire Tread Compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2007, 80, 580–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, N.; Pille-Wolf, W.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W.M. Understanding the Influence of Oligomeric Resins on Traction and Rolling Resistance of Silica-Reinforced Tire Treads. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2015, 88, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Ortega, P.; Gaillard, E.; van Elburg, F.; Blume, A. Use of Hydrocarbon Resins as an Alternative to TDAE Oil in Tire Tread Compounds. Polym. Test. 2023, 126, 108168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinova, P.; Ilieva, N.; Metodiev, V. Investigation of Elastomers Ratio Influence in the Composites for Truck Tires Treads Production. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2022, 57, 232–240. [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel, S. Sustainable Rubbers and Rubber Additives. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, Z.H.; Teo, Y.Y.; Ang, D.T.-C. Recent Development of Biodegradable Synthetic Rubbers and Bio-Based Rubbers Using Sustainable Materials from Biological Sources. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 34028–34052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, T.; Mussone, P.; Khalil, H.; Bressler, D. Progress in Bio-Based Plastics and Plasticizing Modifications. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2013, 1, 13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Chen, K.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y. Crosslinked Bicontinuous Biobased PLA/NR Blends via Dynamic Vulcanization Using Different Curing Systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 113, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y. Crosslinked Bicontinuous Biobased Polylactide/Natural Rubber Materials: Super Toughness, “Net-like”-Structure of NR Phase and Excellent Interfacial Adhesion. Polym. Test. 2014, 38, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.S.; Cornish, K. Processing and Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber/Waste-Derived Nano Filler Composites Compared to Macro and Micro Filler Composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 107, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.S.; Cornish, K. Novel Mineral and Organic Materials from Agro-Industrial Residues as Fillers for Natural Rubber. J. Polym. Environ. 2015, 23, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.S.; Cornish, K. High Performance Waste-Derived Filler/Carbon Black Reinforced Guayule Natural Rubber Composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 86, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intharapat, P.; Kongnoo, A.; Kateungngan, K. The Potential of Chicken Eggshell Waste as a Bio-Filler Filled Epoxidized Natural Rubber (ENR) Composite and Its Properties. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, D.; de Morais Teixeira, E.; da Silva Curvelo, A.A.; Belgacem, M.N.; Dufresne, A. Extraction of Cellulose Whiskers from Cassava Bagasse and Their Applications as Reinforcing Agent in Natural Rubber. Ind. Crops Prod. 2010, 32, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awais, H.; Nawab, Y.; Amjad, A.; Anjang, A.; Md Akil, H.; Zainol Abidin, M.S. Environmental Benign Natural Fibre Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites: A Review. Compos. C Open Access 2021, 4, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formela, K. Strategies for Compatibilization of Polymer/Waste Tire Rubber Systems Prepared via Melt-Blending. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Parmar, B.S.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Application of the Resin Derived from the Native Euphorbia Caducifolia Haines as Multifunctional Additive in Filled Natural Rubber Compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2017, 90, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Han, J. Effect of Rosin Resin on the Properties of Natural Rubber/Polyester Layered Fibers. J. Macromol. Sci. B 2021, 60, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Gan, S.N.; Hassan, A.; Terakawa, K.; Hattori, T.; Ichikawa, N.; Choong, D.H. Reactions between Epoxidized Natural Rubber and Palm Oil-based Alkyds at Ambient Temperature. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 1503–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünügül, T.; Erenkaya, M.; Karaağaç, B. Use of Liquidambar Orientalis Mills in Natural Rubber Compounds as an Alternative to Synthetic Resins. J. Elastomers Plast. 2022, 54, 778–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Parmar, B.S.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Analysis of Autohesion and Physico-Mechanical Properties (Multifunctional Behavior) of the Coagulum from the Latex of Euphorbia Caducifolia Haines Vis-à-Vis Comparison against Synthetic Resins in Natural Rubber Compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2015, 88, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Class, J.B.; Chu, S.G. The Viscoelastic Properties of Rubber–Resin Blends. I. The Effect of Resin Structure. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Class, J.B.; Chu, S.G. The Viscoelastic Properties of Rubber–Resin Blends. II. The Effect of Resin Molecular Weight. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Class, J.B.; Chu, S.G. The Viscoelastic Properties of Rubber–Resin Blends. III. The Effect of Resin Concentration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chang, S.; Feng, N. Effect of C5 Petroleum Resin Content on Damping Behavior, Morphology, and Mechanical Properties of BIIR/BR Vulcanizates. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J.; Hu, H.; Song, M.; Wu, S. Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study on the Damping Mechanism of C5 Petroleum Resin/Chlorinated Butyl Rubber Composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3960–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, N.; Finger, S.; Karimi-Varzaneh, H.A.; Lacayo-Pineda, J. Rigidity of Plasticizers and Their Miscibility in Silica-Filled Polybutadiene Rubber by Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dae Han, C.; Kim, J.; Man Baek, D.; Gun Chu, S. Viscoelastic Behavior, Order-disorder Transition, and Phase Equilibria in Mixtures of a Block Copolymer and an Endblock-associating Resin. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 1990, 28, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, M.; Tardiff, J.; Haakenson, D.; Joandrea, M.; Knych, M. Tire Tread Performance Modification Utilizing Polymeric Additives. SAE Int. J. Veh. Dyn. Stab. NVH 2017, 1, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Fernandes, J.P.C.; Yan, C.; Dieden, R.; Poorters, L.; Weydert, M.; Verge, P. An Investigation on the Thermally Induced Compatibilization of SBR and α-Methylstyrene/Styrene Resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaijaroen, W. Effect of Tackifiers on Mechanical and Dynamic Properties of Carbon-black-filled NR Vulcanizates. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2011, 51, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Geppi, M. Solid State NMR: Principles, Methods, and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Saalwächter, K. Proton Multiple-Quantum NMR for the Study of Chain Dynamics and Structural Constraints in Polymeric Soft Materials. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2007, 51, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalwächter, K. Microstructure and Molecular Dynamics of Elastomers as Studied by Advanced Low-Resolution Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Methods. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2012, 85, 350–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, F.; Martini, F.; Lee, J.; Lluvears-Tenorio, A.; La Nasa, J.; Duce, C.; Ormsby, B.; Geppi, M.; Bonaduce, I. The Stability of Paintings and the Molecular Structure of the Oil Paint Polymeric Network. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Latta, E.; Sabatini, F.; Micheletti, C.; Carlotti, M.; Martini, F.; Nardelli, F.; Battisti, A.; Degano, I.; Geppi, M.; Pucci, A.; et al. Performant Flexible Luminescent Solar Concentrators of Phenylpolysiloxanes Crosslinked with Perylene Bisimide Fluorophores. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, F.; Carignani, E.; Nardelli, F.; Rossi, E.; Borsacchi, S.; Cettolin, M.; Susanna, A.; Geppi, M.; Calucci, L. Glassy and Polymer Dynamics of Elastomers by 1H Field Cycling NMR Relaxometry: Effects of Cross-Linking. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 10028–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, F.; Martini, F.; Carignani, E.; Rossi, E.; Borsacchi, S.; Cettolin, M.; Susanna, A.; Arimondi, M.; Giannini, L.; Geppi, M.; et al. Glassy and Polymer Dynamics of Elastomers by 1H Field Cycling NMR Relaxometry: Effects of Fillers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 4546–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, F.; Calucci, L.; Carignani, E.; Borsacchi, S.; Cettolin, M.; Arimondi, M.; Giannini, L.; Geppi, M.; Martini, F. Influence of Sulfur-Curing Conditions on the Dynamics and Crosslinking of Rubber Networks: A Time-Domain NMR Study. Polymers 2022, 14, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierigé, M.; Nerli, F.; Nardelli, F.; Calucci, L.; Cettolin, M.; Giannini, L.; Geppi, M.; Martini, F. Influence of Resins on the Structure and Dynamics of SBR Compounds: A Solid-State NMR Study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, F.; Hughes, D.J.; Badolato Bönisch, G.; Zwick, T.; Schäfer, C.; Geppi, M.; Alam, M.A.; Ubbink, J. Antiplasticization and Phase Behavior in Phase-Separated Modified Starch-Sucrose Blends: A Positron Lifetime and Solid-State NMR Study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, F.; Borsacchi, S.; Spera, S.; Carbonera, C.; Cominetti, A.; Geppi, M. P3HT/PCBM Photoactive Materials for Solar Cells: Morphology and Dynamics by Means of Solid-State NMR. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, I.; Sukeksi, L.; Hayeemasae, N. Studies on Cure Index, Swelling Behaviour, Tensile and Thermooxidative Properties of Natural Rubber Compounds in the Presence of Alkanolamide. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 309, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saville, B.; Watson, A.A. Structural Characterization of Sulfur-Vulcanized Rubber Networks. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1967, 40, 100–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 37:2017; Rubber, Vulcanized or Thermoplastic: Determination of Tensile Stress-Strain Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Maus, A.; Hertlein, C.; Saalwächter, K. A Robust Proton NMR Method to Investigate Hard/Soft Ratios, Crystallinity, and Component Mobility in Polymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2006, 207, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathematica; Version 11; Wolfram Research, Inc.: Champaign, IL, USA, 2010.
- Wu, J.; Xing, W.; Huang, G.; Li, H.; Tang, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y. Vulcanization Kinetics of Graphene/Natural Rubber Nanocomposites. Polymer 2013, 54, 3314–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Razzaghi-Kashani, M. Catalytic and Networking Effects of Carbon Black on the Kinetics and Conversion of Sulfur Vulcanization in Styrene Butadiene Rubber. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9194–9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.D.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, B.B.; Tsou, A.H.; Bhowmick, A.K. Probing the Viscoelastic Properties of Brominated Isobutylene-co-p-Methylstyrene Rubber/Tackifier Blends Using a Rubber Process Analyzer. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, R.; Wemyss, A.M.; Du, A.; Bao, X.; Geng, X.; Wan, C. Damping and Electromechanical Behavior of Ionic-Modified Brominated Poly(Isobutylene-Co-Isoprene) Rubber Containing Petroleum Resin C5. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 3063–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Rabjohn, N.; Shaffer, M.C. Dependence of Tensile Strength of Vulcanized Rubber on Degree of Cross-Linking. J. Polym. Sci. 1949, 4, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, S.; Nishioka, H.; Yamano, M.; Yamamoto, Y. Synthetic Rubber with the Tensile Strength of Natural Rubber. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2323–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Hoag, S.W. Plasticizer Effects on Physical–Mechanical Properties of Solvent Cast Soluplus® Films. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, M.I.B. 13C NMR Study PP/Rosin Blends. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2000, 46, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, D.O.; Bras, J.; Gandini, A.; Belgacem, N. Surface Grafting of Cellulose Nanocrystals with Natural Antimicrobial Rosin Mixture Using a Green Process. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 137, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.B.; Botto, R.E. The Nature and Fate of Natural Resins in the Geosphere-III. Re-Evaluation of the Structure and Composition of Highgate Copalite and Glessite. Org. Geochem. 1993, 20, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmich, R.; Anoardo, E. Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2004, 44, 257–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoardo, E.; Galli, G.; Ferrante, G. Fast-Field-Cycling NMR: Applications and Instrumentation. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2001, 20, 365–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmich, R. Chapter 1: Principle, Purpose and Pitfalls of Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry. In Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry: Instrumentation, Model Theories and Applications; Kimmich, R., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich, R.; Fatkullin, N. Polymer Chain Dynamics and NMR. In NMR 3D Analysis Photopolymerization; Advances in Polymer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; Volume 170, pp. 1–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapf, S.; Lozovoi, A. Chapter 13. Field-Cycling Relaxometry of Polymers. In Field-Cycling NMR Relaxometry: Instrumentation, Model Theories and Applications; Kimmich, R., Ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 322–357. [Google Scholar]
- de Gennes, P.G. Reptation of a Polymer Chain in the Presence of Fixed Obstacles. J. Chem. Phys. 1971, 55, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, M.; Edwards, S.F. The Theory of Polymer Dynamics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Sokolov, A.P. Breakdown of Time-Temperature Superposition Principle and Universality of Chain Dynamics in Polymers. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 3322–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelasticity Properties of Polymers; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, A.; Kariyo, S.; Abou Elfadl, A.; Meier, R.; Gmeiner, J.; Novikov, V.N.; Rössler, E.A. Universal Polymer Dynamics Revealed by Field Cycling 1H NMR. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 5236–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Herrmann, A.; Abou Elfadl, A.; Kruk, D.; Wohlfahrt, M.; Rössler, E.A. Glassy, Rouse, and Entanglement Dynamics as Revealed by Field Cycling 1H NMR Relaxometry. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 2390–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyo, S.; Brodin, A.; Gainaru, C.; Herrmann, A.; Hintermeyer, J.; Schick, H.; Novikov, V.N.; Rössler, E.A. From Simple Liquid to Polymer Melt. Glassy and Polymer Dynamics Studied by Fast Field Cycling NMR Relaxometry: Rouse Regime. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5322–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, C.J.F.; Bordewijk, P. Theory of Electric Polarization; Elsevier Scientific: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Blochowicz, T.; Gainaru, C.; Medick, P.; Tschirwitz, C.; Rössler, E.A. The Dynamic Susceptibility in Glass Forming Molecular Liquids: The Search for Universal Relaxation Patterns II. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 134503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, F.; Schonhals, A. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy; Kremer, F., Schonhals, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]









| Ingredients | SBR_ref | SBR_k | SBR_s | SBR_d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBR–TDAE | 137.5 | 137.5 | 137.5 | 137.5 |
| CB | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| Zinc oxide | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Stearic acid | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Kristalex | / | 15 | / | / |
| SMD | / | / | 15 | / |
| Dertoline | / | / | / | 15 |
| CBS | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Sulfur | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Total | 194 | 209 | 209 | 209 |
| Sample | MH (dN m) | ML (dN m) | M (dN m) | tS2 (s) | tC90 (s) | CRI (s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBR_ref | 13.2 | 2.3 | 10.9 | 226 | 380 | 0.65 |
| SBR_k | 10.7 | 1.9 | 8.8 | 263 | 424 | 0.62 |
| SBR_s | 9.1 | 1.7 | 7.3 | 148 | 269 | 0.83 |
| SBR_d | 10.3 | 1.9 | 8.4 | 216 | 385 | 0.59 |
| Sample | TgDSC | TgDMA | Mc−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kristalex | 368 | - | - |
| SMD | 362 | - | - |
| Dertoline | 349 | - | - |
| SBR_ref | 246 | - | - |
| SBR_k | 249 | - | - |
| SBR_s | 249 | - | - |
| SBR_d | 247 | - | - |
| vSBR_ref | 253 | 263 | 1.80 |
| vSBR_k | 257 | 270 | 1.38 |
| vSBR_s | 256 | 268 | 0.96 |
| vSBR_d | 253 | 264 | 0.94 |
| Sample | Wg (%) | We1 (%) | We2 (%) | T2,g (μs) | T2,e1 (μs) | T2,e2 (μs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBR_ref | 8 | 65 | 27 | 22 | 296 | 773 |
| SBR_k | 13 | 56 | 31 | 25 | 216 | 607 |
| SBR_s | 15 | 56 | 29 | 29 | 207 | 632 |
| SBR_d | 14 | 44 | 42 | 21 | 231 | 584 |
| vSBR_ref | 11 | 59 | 30 | 27 | 183 | 615 |
| vSBR_k | 19 | 57 | 24 | 26 | 139 | 535 |
| vSBR_s | 18 | 55 | 26 | 28 | 121 | 461 |
| vSBR_d | 18 | 55 | 27 | 23 | 164 | 601 |
| Sample | T1 |
|---|---|
| Kristalex | 114 |
| SMD | 381 |
| Dertoline | 315 |
| vSBR_ref | 66 |
| vSBR_k | 74 |
| vSBR_s | 76 |
| vSBR_d | 70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pierigé, M.; Nardelli, F.; Calucci, L.; Cettolin, M.; Giannini, L.; Causa, A.; Martini, F.; Geppi, M. Exploring the Effect of Resins of Different Origin on the Structure, Dynamics and Curing Characteristics of SBR Compounds. Polymers 2024, 16, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060834
Pierigé M, Nardelli F, Calucci L, Cettolin M, Giannini L, Causa A, Martini F, Geppi M. Exploring the Effect of Resins of Different Origin on the Structure, Dynamics and Curing Characteristics of SBR Compounds. Polymers. 2024; 16(6):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060834
Chicago/Turabian StylePierigé, Michele, Francesca Nardelli, Lucia Calucci, Mattia Cettolin, Luca Giannini, Andrea Causa, Francesca Martini, and Marco Geppi. 2024. "Exploring the Effect of Resins of Different Origin on the Structure, Dynamics and Curing Characteristics of SBR Compounds" Polymers 16, no. 6: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060834
APA StylePierigé, M., Nardelli, F., Calucci, L., Cettolin, M., Giannini, L., Causa, A., Martini, F., & Geppi, M. (2024). Exploring the Effect of Resins of Different Origin on the Structure, Dynamics and Curing Characteristics of SBR Compounds. Polymers, 16(6), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16060834