Amino Acid-Modified Polyethylenimines with Enhanced Gene Delivery Efficiency and Biocompatibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymers
2.3. Polymer Characterization
- Ser-PEI: 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O, TMS): δ = 2.64–3.50 ppm (m, PEI–H and –CH(NH2)CH2OH), 3.76 ppm (s, –CH2OH).
- Ga-PEI: 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O, TMS): δ = 2.52–3.25 ppm (m, PEI–H), 3.94 ppm (s, –CH2OH).
- Gly-PEI: 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O, TMS): δ = 2.64–3.51 ppm (m, PEI–H), 3.67 ppm (m, –CH2NH2).
- Deta-PEI: 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O, TMS): δ = 2.64–3.13 ppm (m, –CH2CH2NH2, –CONCH2CH2), 3.25 ppm (m, –COCH2, –CONCH2).
- Leu-PEI: 1H NMR (400 MHz, D2O, TMS): δ = 0.86 ppm (d, –CH3), 1.58–1.64 ppm (m, –CHCH3), 2.68–3.60 ppm (m, PEI–H), 3.9 ppm (m, –CHNH2).
2.4. Amplification and Purification of Plasmid DNA
2.5. Agarose Gel Retardation Assay
2.6. Particle Size and ζ-Potential Measurement in Water
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Transfection Procedure
2.9. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.10. Protein Adsorption Assay
2.11. Cellular Uptake of Plasmid DNA
2.12. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Acylated Polymers


| Polymer | DS (%) | Mw (kDa) | PDI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ser-PEI1 | 6.8 | 31.9 | 1.67 |
| Ser-PEI2 | 9.3 | 32.6 | 1.66 |
| Ser-PEI3 | 14.8 | 35.8 | 1.80 |
| Ser-PEI4 | 19.0 | 37.0 | 1.71 |
| Ga-PEI1 | 8.0 | 29.4 | 1.55 |
| Ga-PEI2 | 10.0 | 31.0 | 1.63 |
| Ga-PEI3 | 15.9 | 32.6 | 1.68 |
| Ga-PEI4 | 18.2 | 33.3 | 1.68 |
| Gly-PEI1 | 4.0 | 28.5 | 1.54 |
| Gly-PEI2 | 8.7 | 30.5 | 1.58 |
| Gly-PEI3 | 13.3 | 32.7 | 1.60 |
| Gly-PEI4 | 25.0 | 35.2 | 1.70 |
| Deta-PEI1 | 6.5 | 33.2 | 1.88 |
| Deta-PEI2 | 10.5 | 36.0 | 1.77 |
| Deta-PEI3 | 12.5 | 37.3 | 1.96 |
| Deta-PEI4 | 15.4 | 42.1 | 1.90 |
| Leu-PEI1 | 7.0 | 32.3 | 1.56 |
| Leu-PEI2 | 10.3 | 34.6 | 1.71 |
| Leu-PEI3 | 13.3 | 36.6 | 1.78 |
| Leu-PEI4 | 21.1 | 46.4 | 2.37 |
3.2. Formation of Polymer/DNA Complexes (Polyplexes)


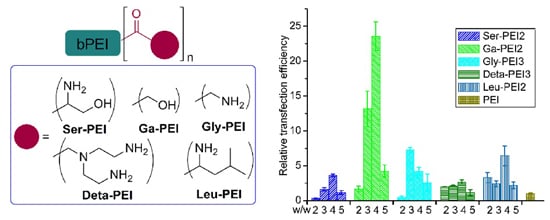
3.3. In Vitro Gene Transfection



3.4. Biocompatibility Studies


3.5. Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Distribution


4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunt, K.K.; Vorburger, S.A. Gene therapy: Hurdles and hopes for cancer treatment. Science 2002, 297, 415–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niidome, T.; Huang, L. Gene therapy progress and prospects: Nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.J.; Yang, W.T. Polymer vectors via controlled/living radical polymerization for gene delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1099–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, H.S.; Manickam, D.S.; You, Y.; Oupicky, D. Temperature-controlled properties of DNA complexes with poly(ethylenimine)-graft-poly(N-iso-propylacrylamide). Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.; Ogris, M.; Zauner, W. Polylysine-based transfection systems utilizing receptor-mediated delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1998, 30, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kukowska-Latallo, J.F.; Bielinska, A.U.; Johnson, J.; Spindler, R.; Tomalia, D.A.; Baker, J.R., Jr. Efficient transfer of genetic material into mammalian cells using starburst polyamidoamine dendrimers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4897–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintzer, M.A.; Simanek, E.E. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 259–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.; Saltik, M.; Lehrmann, H.; Killisch, I.; Mautner, V.; Lamm, G.; Christofori, G.; Cotton, M. Polyethylenimine (PEI) is a simple, inexpensive and effective reagent for condensing and linking plasmid DNA to adenovirus for gene delivery. Gene Ther. 1997, 4, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussif, O.; Lezoualch, F.; Zanta, M.A.; Mergny, M.D.; Scherman, D.; Demeneix, B.; Behr, J.P. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: Polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7297–7301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.S.; Park, T.G.; Maruyama, A. RGD targeting hyaluronic acid coating system for PEI-PBLG polycation gene carriers. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.H.; Huang, F.W.; Qin, S.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhuo, R.X. A strategy to improve serum-tolerant transfection activity of polycation vectors by surface hydroxylation. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9925–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, P.G.; Chua, X.; Wang, X. Amphiphilic polyethylenimine (PEI) as highly efficient non-viral gene carrier. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehshahri, A.; Oskuee, R.K.; Shier, W.T.; Hatefi, A.; Ramezani, M. Gene transfer efficiency of high primary amine content, hydrophobic, alkyl-oligoamine derivatives of polyethylenimine. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4187–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, B.A.; Bai, J.; Kucharski, C.; Farrell, L.L.; Lavasanifar, A.; Ritchie, B.; Ghahary, A.; Uludag, H. RGD conjugation to polyethyleneimine does not improve DNA delivery to bone marrow stromal cells. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Tian, H.Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.S. Biodegradable mPEG-b-P(MCC-g-OEI) copolymers for efficient gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2011, 152, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Ong, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ee, P.L.; Hedrick, J.L. Novel biodegradable block copolymers of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and cationic polycarbonate: Effects of PEG configuration on gene delivery. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2011, 32, 1826–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, H.; Merdan, T.; Kunath, K.; Fischer, D.; Kissel, T. Poly(ethylenimine-co-l-lactamide-co-succinamide): A biodegradable polyethylenimine derivative with an advantageous pH-dependent hydrolytic degradation for gene delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, A.; Hara, E.; Hara, I.; Ozeki, E.; Kimura, S. Size control of core-shell-type polymeric micelle with a nanometer precision. Langmuir 2014, 30, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, S.K.; Yadav, S.; Gupta, K.C.; Kumar, P. Synthesis and evaluation of N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-PEIs as efficient vectors for nucleic acids. Mol. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layek, B.; Haldar, M.K.; Sharma, G.; Lipp, L.; Mallik, S.; Singh, J. Hexanoic acid and polyethylene glycol double grafted amphiphilic chitosan for enhanced gene delivery: Influence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic substitution degree. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, M.-M.; Xiao, Y.-P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Peng, Q.; Guo, Q.; Wu, W.-X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Low molecular weight PEI-based polycationic gene vectors via Michael addition polymerization with improved serum-tolerance. Polymer 2015, 65, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Reineke, T.M. Hydroxyl stereo chemistry and amine number within poly(glycoamidoamine)s affect intracellular DNA delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3004–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, H.; Fechner, P.M.; Martin, A.L.; Kunath, K.; Stolnik, S.; Roberts, C.J.; Fischer, D.; Davies, M.C.; Kissel, T. Polyethylenimine-graft-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers: Influence of copolymer block structure on DNA complexation and biological activities as gene delivery system. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 13, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, K.M.; Yang, J.J.; Zhao, N.N.; Li, J.S.; Xu, F.J. Multiarm cationic star polymers by atom transfer radical polymerization from β-cyclodextrin cores: Influence of arm number and length on gene delivery. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4726–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, F.; Liu, W. Enhanced gene transfection and serum stability of polyplexes by PDMAEMA-polysulfobetaine diblock copolymers. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Cheng, G.; Xie, L.; Nie, Y.; He, B.; Gu, Z. Polyethyleneimine/DNA polyplexes with reduction-sensitive hyaluronic acid derivatives shielding for targeted gene delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Quick, G.K.; Yeo, Y. Gene delivery through the use of a hyaluronate-associated intracellularly degradable crosslinked polyethyleneimine. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 5834–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-F.; Yi, W.-J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Chen, Q.-M.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.-Q. Linear polycations by ring-opening polymerization as non-viral gene delivery vectors. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5391–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-K.; Jones, C.H.; Mistriotis, P.; Yu, Y.; Ma, X.; Ravikrishnan, A.; Jiang, M.; Andreadis, S.T.; Pfeifer, B.A.; Cheng, C. Poly(ethylene glycol)-block-cationic polylactide nanocomplexes of differing charge density for gene delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 9688–9699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Guo, Z.; Lin, L.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, J.; Gao, S.; Zhu, X.; Chen, X. pH-responsive zwitterionic copolypeptides as charge conversional shielding system for gene carriers. J. Control. Release 2014, 174, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Li, Y.X.; Ahlemeyer, B.; Krieglstein, J.; Kissel, T. In vitro cytotoxicity testing of polycations: Influence of polymer structure on cell viability and hemolysis. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wu, R.; Xia, Y.; Huang, H.; Chai, W.; Feng, T.; Gan, Y.; Zhang, W. Biotemplated fabrication of Sn@C anode materials based on the unique metal biosorption behavior of microalgae. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3969–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Wang, H.; Shao, N.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Y. Surface-engineered dendrimers with a diaminododecane core achieve efficient gene transfection and low cytotoxicity. Bioconjugate Chem. 2014, 25, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-F.; Wang, B.; Yin, D.-X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.-X.; Yu, Q.-Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Linear TACN-based cationic polymers as non-viral gene vectors. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 59164–59174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.-J.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Ren, L.; Chen, Q.-M.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.-Q. Cyclen-based lipidic oligomers as potential gene delivery vehicles. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funhoff, A.M.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Lok, M.C.; Fretz, M.M.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Hennink, W.E. Poly(3-guanidinopropyl methacrylate): A novel cationic polymer for gene delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, S.; Kim, W.J. Biodegradable nanoparticles modified by branched polyethylenimine for plasmid DNA delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.H.; Chen, C.-K.; Jiang, M.; Fang, L.; Cheng, C.; Pfeife, B.A. Synthesis of cationic polylactides with tunable charge densities as nanocarriers for effective gene delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1138–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Janzena, J.; Brooks, D.E. Adsorption of amphiphilic hyperbranched polyglycerol derivatives onto human red blood cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3364–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielson, N.P.; Pack, D.W. Acetylation of polyethylenimine enhances gene delivery via weakened polymer/DNA interactions. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Q.-F.; Luan, C.-R.; Yin, D.-X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Peng, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.-Q. Amino Acid-Modified Polyethylenimines with Enhanced Gene Delivery Efficiency and Biocompatibility. Polymers 2015, 7, 2316-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7111516
Zhang Q-F, Luan C-R, Yin D-X, Zhang J, Liu Y-H, Peng Q, Xu Y, Yu X-Q. Amino Acid-Modified Polyethylenimines with Enhanced Gene Delivery Efficiency and Biocompatibility. Polymers. 2015; 7(11):2316-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7111516
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Qin-Fang, Chao-Ran Luan, Dong-Xiao Yin, Ji Zhang, Yan-Hong Liu, Qi Peng, Yong Xu, and Xiao-Qi Yu. 2015. "Amino Acid-Modified Polyethylenimines with Enhanced Gene Delivery Efficiency and Biocompatibility" Polymers 7, no. 11: 2316-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7111516
APA StyleZhang, Q. -F., Luan, C. -R., Yin, D. -X., Zhang, J., Liu, Y. -H., Peng, Q., Xu, Y., & Yu, X. -Q. (2015). Amino Acid-Modified Polyethylenimines with Enhanced Gene Delivery Efficiency and Biocompatibility. Polymers, 7(11), 2316-2331. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7111516