Preparation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (MIONs) with Improved Saturation Magnetization Using Multifunctional Polymer Ligand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Polymer Ligand PTMP-PMAA
2.3. Synthesis of MIONs
2.4. Characterization of MIONs
2.5. Cytotoxicity Analysis of MIONs
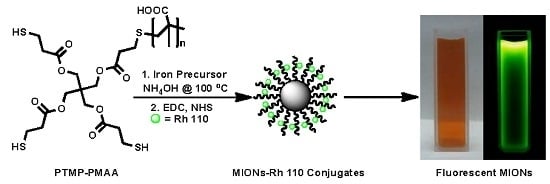
2.6. Conjugation of MIONs@PTMP-PMAA with Rhodamine 110
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of PTMP-PMAA
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Polymer Stabilized MIONs
3.2.1. Effect of Polymer Concentration on Size of MIONs
3.2.2. Characterization of MIONs
3.2.3. Toxicity Analysis of MIONs
3.3. Functionalization of MIONs with Fluorescent Dye
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Dong, W.F.; Sun, H.B. Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Design, synthesis and biomedical photonic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7664–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Carregal-Romero, S.; Casula, M.F.; Gutierrez, L.; Morales, M.P.; Bohm, I.B.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Prosperi, D.; Parak, W.J. Biological applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4306–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhaohui, W.; Taekyung, Y.; Changzhong, J.; Woo-Sik, K. Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 023501. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Zhu, H.; Shen, J.; Yi, C.; Wu, S.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Xu, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. Self-assembled magnetic fluorescent polymeric micelles for magnetic resonance and optical imaging. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yi, P.W.; Sun, Q.; Lei, H.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhu, Z.H.; Smith, S.C.; Lan, M.B.; Lu, G.Q.M. Ultrasmall water-soluble and biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as positive and negative dual contrast agents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2387–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Andujar, C.; Ortega, D.; Southern, P.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Thanh, N.T.K. High performance multi-core iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia: Microwave synthesis, and the role of core-to-core interactions. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1768–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Ponnusamy, S.; Muthamizhchelvan, C. Synthesis, properties and heating characteristics of bovine serum albumin coated Fe3O4 magnetic fluid for magnetic fluid hyperthermia application. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2013, 5, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ling, M.; Jia, M.; Huang, P.; Li, C.; Yan, B. Facile synthesis and characterization of polyethylenimine-coated Fe3O4 superparamagnetic nanoparticles for cancer cell separation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Qu, H.; Duan, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, X.; Ji, T.; Cao, L.; Nie, G.; Sun, S. Dopamine coating as a general and facile route to biofunctionalization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles for magnetic separation of proteins. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6657–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinto, C.A.; Mohindra, P.; Tong, S.; Bao, G. Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined chemotherapy and hyperthermia cancer treatment. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12728–12736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, C.; Ushimaru, K.; Horiishi, N.; Tsuge, T.; Kitamoto, Y. Core–shell composite particles composed of biodegradable polymer particles and magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 381, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Salazar, P.; Villalonga, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarron, J.M.; Gonzalez-Mora, J.L. Preparation of core-shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles for biosensor construction. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, M.; Taylor, A.; Murray, P.; Rosseinsky, M.J.; Adams, D.J. Design considerations for the synthesis of polymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles for stem cell labelling and tracking using MRI. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6733–6748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palui, G.; Aldeek, F.; Wang, W.; Mattoussi, H. Strategies for interfacing inorganic nanocrystals with biological systems based on polymer-coating. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 193–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, A.M.; Mari, M.; Muñoz-Espí, R. Synthetic strategies in the preparation of polymer/inorganic hybrid nanoparticles. Materials 2014, 7, 4057–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Hui, Z.; Liyun, L.; Bien, T. Preparation of nanoparticles with multi-functional water-soluble polymer ligands. Prog. Chem. 2010, 22, 953–961. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, D.; Hackett, M.J.; Hyeon, T. Surface ligands in synthesis, modification, assembly and biomedical applications of nanoparticles. Nano Today 2014, 9, 457–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ji, X.; Na, H.B.; Safi, M.; Smith, A.; Palui, G.; Perez, J.M.; Mattoussi, H. Design of a multi-dopamine-modified polymer ligand optimally suited for interfacing magnetic nanoparticles with biological systems. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6197–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernia Leal, M.; Rivera-Fernandez, S.; Franco, J.M.; Pozo, D.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Garcia-Martin, M.L. Long-circulating pegylated manganese ferrite nanoparticles for mri-based molecular imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Tan, B.; Allix, M.; Cooper, A.I.; Rosseinsky, M.J. Direct coprecipitation route to monodisperse dual-functionalized magnetic iron oxide nanocrystals without size selection. Small 2008, 4, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.T.; Tung, L.D.; Robinson, I.; Ung, D.; Tan, B.; Long, J.; Cooper, A.I.; Fernig, D.G.; Thanh, N.T.K. Size and shape control for water-soluble magnetic cobalt nanoparticles using polymer ligands. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2453–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaque, S.; Hussain, S.; Hussain, I.; Tan, B. Design and utility of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles mediated by thioether end-functionalized polymeric ligands. Polymers 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oanh, V.T.K.; Lam, T.D.; Thu, V.T.; Lu, L.T.; Nam, P.H.; Tam, L.T.; Manh, D.H.; Phuc, N.X. A novel route for preparing highly stable Fe3O4 fluid with poly(acrylic acid) as phase transfer ligand. J. Electron. Mater. 2016, 45, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Qi, B.; Witmer, M.; Kitchens, C.L.; Powell, B.A.; Mefford, O.T. Quantitative measurement of ligand exchange on iron oxides via radiolabeled oleic acid. Langmuir 2014, 30, 10918–10925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, M.I.; Lu, Q.; Yan, W.; Li, Z.; Hussain, I.; Tahir, M.N.; Tremel, W.; Tan, B. Highly water-soluble magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles for drug delivery: Enhanced in vitro therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin and mion conjugates. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2874–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Li, Y.; Wei, Z.; Cao, G.; Gai, Z.; Hong, K.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S. Magnetic iron oxide-fluorescent carbon dots integrated nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging, near-infrared light-responsive drug carrier and photothermal therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2014, 2, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Sadat, M.E.; Dunn, A.W.; Mast, D.B. Photo-fluorescent and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8209–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, I.; Graham, S.; Wang, Z.X.; Tan, B.; Sherrington, D.C.; Rannard, S.P.; Cooper, A.I.; Brust, M. Size-controlled synthesis of near-monodisperse gold nanoparticles in the 1–4 nm range using polymeric stabilizers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16398–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, B.; Hussain, I.; Schaeffer, N.; Wyatt, M.F.; Brust, M.; Cooper, A.I. Design of polymeric stabilizers for size-controlled synthesis of monodisperse gold nanoparticles in water. Langmuir 2007, 23, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Majeed, I.; Zou, P.; Tan, B. Biolabeling hematopoietic system cells using near-infrared fluorescent gold nanoclusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 16753–16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, N.; Tan, B.; Dickinson, C.; Rosseinsky, M.J.; Laromaine, A.; McComb, D.W.; Stevens, M.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Petit, L.; Barentin, C.; et al. Fluorescent or not? Size-dependent fluorescence switching for polymer-stabilized gold clusters in the 1.1–1.7 nm size range. Chem. Commun. 2008, 34, 3986–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Zhu, J.H.; Hou, Y.L.; Gao, S. Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanocrystals: Recent progress. Chin. Phys. B 2013, 22, 107503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Yokoyama, S.; Zaikova, T.; Masuko, K.; Hutchison, J.E. Synthesis of ligand-stabilized metal oxide nanocrystals and epitaxial core/shell nanocrystals via a lower-temperature esterification process. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, Y.-P.; Liang, B.; Hu, F.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.-F.; Yin, P.-H.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gu, H. Ultra-large-scale production of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for t1-weighted mri. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22575–22585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, W.; Shen, Y. Magnetic targeted drug delivery carriers encapsulated with pH-sensitive polymer: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro doxorubicin release studies. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2016, 27, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J.; Shen, H. Hydrophilic magnetochromatic nanoparticles with controllable sizes and super-high magnetization for visualization of magnetic field intensity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, J.; Mohapatra, J.; Bhargava, P.; Bahadur, D. A pH-responsive folate conjugated magnetic nanoparticle for targeted chemo-thermal therapy and mri diagnosis. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 2454–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, A.M.; Sotiriou, G.A.; Kidambi, P.R.; Teleki, A. Effect of size, composition, and morphology on magnetic performance: First-order reversal curves evaluation of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 044314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Gao, J.; Ai, H.; Chen, X. Applications and potential toxicity of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Small 2013, 9, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]













| Sample | MAA/PTMP (mol/mol) | Molecular weights (g/mol) | Yield (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | Mw | PDI | |||
| 2% PTMP-PMAA | 100/2 | 5,850 | 7,420 | 1.2 | 82 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majeed, M.I.; Guo, J.; Yan, W.; Tan, B. Preparation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (MIONs) with Improved Saturation Magnetization Using Multifunctional Polymer Ligand. Polymers 2016, 8, 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8110392
Majeed MI, Guo J, Yan W, Tan B. Preparation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (MIONs) with Improved Saturation Magnetization Using Multifunctional Polymer Ligand. Polymers. 2016; 8(11):392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8110392
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajeed, Muhammad Irfan, Jiaojiao Guo, Wei Yan, and Bien Tan. 2016. "Preparation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (MIONs) with Improved Saturation Magnetization Using Multifunctional Polymer Ligand" Polymers 8, no. 11: 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8110392
APA StyleMajeed, M. I., Guo, J., Yan, W., & Tan, B. (2016). Preparation of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (MIONs) with Improved Saturation Magnetization Using Multifunctional Polymer Ligand. Polymers, 8(11), 392. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8110392