Hybrid Polymer-Network Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Response
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Remarks
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Oscillatory Shear Rheology
2.4. Static Light Scattering
3. Results and Discussion
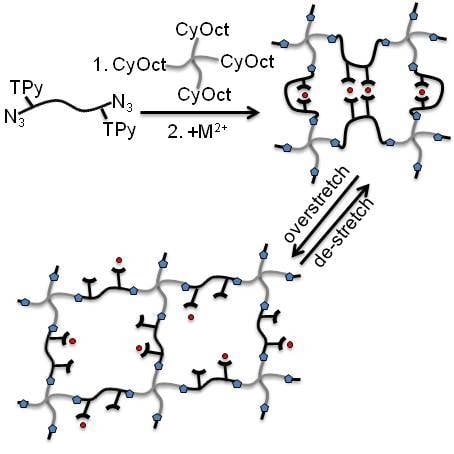
3.1. Polymer Synthesis and Hybrid Network Formation
3.2. Gel-Network Mechanics
3.3. Network Nanostructures
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEG | poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PVA | poly(vinylalcohol) |
| PDMS | poly(dimethylsiloxane) |
References
- Wojtecki, R.J.; Meador, M.A.; Rowan, S.J. Using the dynamic bond to access macroscopically responsive structurally dynamic polymers. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffert, S.; Sprakel, J. Physical chemistry of supramolecular polymer networks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordier, P.; Tournilhac, F.; Soulie-Ziakovic, C.; Leibler, L. Self-healing and thermoreversible rubber from supramolecular assembly. Nature 2008, 451, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.K.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F. Molecularly engineered dual-crosslinked hydrogel with ultrahigh mechanical strength, toughness, and good self-recovery. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, T.; Mayumi, K.; Ducouret, G.; Hébraud, P. Viscoelastic properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels having permanent and transient cross-links studied by microrheology, classical rheometry, and dynamic light scattering. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 4174–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Huang, J.; Guo, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F. Bioinspired engineering of sacrificial metal-ligand bonds into elastomers with supramechanical performance and adaptive recovery. Macromolecules 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Seiffert, S. Nanostructural heterogeneity in polymer networks and gels. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 5515–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayumi, K.; Marcellan, A.; Ducouret, G.; Creton, C.; Narita, T. Stress-strain relationship of highly stretchable dual cross-link gels: Separability of strain and time effect. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Nomura, S. Swelling/shrinking and dynamic light scattering studies on chemically cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) gels in the presence of borate ions. Macromolecules 1994, 27, 5350–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Uesaka, M.; Inamoto, S.; Mihara, H.; Nomura, S. Analogy between swelling of gels and intrinsic viscosity of polymer solutions for ion-complexed poly(vinyl alcohol) in aqueous medium. Macromolecules 1996, 29, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, R.; Mayumi, K.; Creton, C.; Narita, T.; Hui, C.Y. Time dependent behavior of a dual cross-link self-healing gel: Theory and experiments. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 7243–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, T.; Hackelbusch, S.; van Assenbergh, P.; Seiffert, S. A modular construction kit for supramolecular polymer gels. Polym. Chem. 2013, 4, 2515–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackelbusch, S.; Rossow, T.; van Assenbergh, P.; Seiffert, S. Chain dynamics in supramolecular polymer networks. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 6273–6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Hiroi, T.; Han, Y.S.; Kim, T.H.; Shibayama, M.; Chung, U.I.; Sakai, T. Reliable hydrogel with mechanical “fuse link” in an aqueous environment. Adv. Mater. 2015, 7407–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Ito, C.; Yoshida, R.; Suzuki, S.; Sasaki, N.; Shibayama, M.; Chung, U.I. Design and fabrication of a high-strength hydrogel with ideally homogeneous network structure from tetrahedron-like macromonomers. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5379–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Sakai, T.; Akagi, Y.; Chung, U.I.; Shibayama, M. Structure characterization of tetra-PEG gel by small-angle neutron scattering. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Sakai, T.; Akagi, Y.; Chung, U.I.; Shibayama, M. Sans and sls studies on tetra-arm PEG gels in as-prepared and swollen states. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 6245–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, T.; Seiffert, S. Supramolecular polymer gels with potential model-network structure. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 3018–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskin, J.M.; Prescher, J.A.; Laughlin, S.T.; Agard, N.J.; Chang, P.V.; Miller, I.A.; Lo, A.; Codelli, J.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Copper-free click chemistry for dynamic in vivo imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16793–16797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sletten, E.M.; Bertozzi, C.R. Bioorthogonal chemistry: Fishing for selectivity in a sea of functionality. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6974–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, U.S.; Eschbaumer, C. Macromolecules containing bipyridine and terpyridine metal complexes: Towards metallosupramolecular polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2892–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R.; Wilkins, R.G. 57. Exchange studies of certain chelate compounds of the transitional metals. Part VIII. 2,2′,2′′-terpyridine complexes. J. Chem. Soc. 1962, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyer, R.H.; Hubbard, C.D.; Kettle, S.F.A.; Wilkins, R.G. The kinetics of replacement reactions of complexes of the transition metals with 2,2′,2′′-terpyridine. Inorg. Chem. 1966, 5, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-Y.; Nancollas, G.H. Calorimetric studies of complex formation of transition metal ions with 2,2′,2′′-terpyridine. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C. The coordination chemistry of 2,2′:6′,2′′-terpyridine and higher oligopyridines. In Advances in Inorganic Chemistry; Emeléus, H.J., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 1986; Volume 30, pp. 69–121. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, K.J.; Zhou, T.C.; Otim, K.J.; Shull, K.R. Ionically cross-linked triblock copolymer hydrogels with high strength. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6193–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbert, D.L.; Hubbell, J.A. Conjugate addition reactions combined with free-radical cross-linking for the design of materials for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dommerholt, J.; Schmidt, S.; Temming, R.; Hendriks, L.J.A.; Rutjes, F.P.J.T.; van Hest, J.C.M.; Lefeber, D.J.; Friedl, P.; van Delft, F.L. Readily accessible bicyclononynes for bioorthogonal labeling and three-dimensional imaging of living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9422–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debye, P.; Bueche, A.M. Scattering by an inhomogeneous solid. J. Appl. Phys. 1949, 20, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debye, P.P. A photoelectric instrument for light scattering measurements and a differential refractometer. J. Appl. Phys. 1946, 17, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekeris, C.L. Note on the scattering of radiation in an inhomogeneous medium. Phys. Rev. 1947, 71, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Du, B.; Oppermann, W. Influence of formation conditions on spatial inhomogeneities in poly(n-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogels. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 6558–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisgen, R. 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition—Introduction, survey, mechanism. In 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition Chemistry; Padwa, A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984; Volume 1, pp. 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G.; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: Diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armspach, D.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M.; Zehnder, M. Carbaborane-functionalised 2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine ligands for metallosupramolecular chemistry: Syntheses, complex formation, and the crystal and molecular structures of 4′-(ortho-carboranyl)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine and 4′-(ortho-carboranylpropoxy)-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine1. J. Organomet. Chem. 1998, 550, 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Irving, H.; Williams, R.J.P. Order of stability of metal complexes. Nature 1948, 162, 746–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, H.M.; Guth, E. Theory of the elastic properties of rubber. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 455–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilay, M.Y.; Okay, O. Effect of hydrolysis on spatial inhomogeneity in poly(acrylamide) gels of various crosslink densities. Polymer 2003, 44, 5239–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizilay, M.Y.; Okay, O. Effect of initial monomer concentration on spatial inhomogeneity in poly(acrylamide) gels. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 6856–6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakdogen, N.; Kizilay, M.Y.; Okay, O. Suppression of inhomogeneities in hydrogels formed by free-radical crosslinking copolymerization. Polymer 2005, 46, 11407–11415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakdogen, N.; Okay, O. Correlation between crosslinking efficiency and spatial inhomogeneity in poly(acrylamide) hydrogels. Polym. Bull. 2006, 57, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orakdogen, N.; Okay, O. Influence of the initiator system on the spatial inhomogeneity in acrylamide-based hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuru, E.A.; Orakdogen, N.; Okay, O. Preparation of homogeneous polyacrylamide hydrogels by free-radical crosslinking copolymerization. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Metal ion | K (L2·mol−2) | Kdiss. (s−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Zn2+ | 2.2 × 1012 | 0.25 (at 10 °C) |
| Co2+ | 7.2 × 1010 | 1.1 × 10−3 (at 25 °C) |
| Mn2+ | 1.3 × 107 | 1.4 (at 10 °C) |
| Sample | GP (Pa) | GP* (Pa) |
|---|---|---|
| covalent crosslinked gel | 840 | n/a |
| Zn2+-hybrid gel | 1,840 | 850 |
| Co2+-hybrid gel | 1,470 | not accessible |
| Mn2+-hybrid gel | not accessible | not accessible |
| Sample | γyield (%) | γrupture (%) |
|---|---|---|
| covalent crosslinked gel | 180 | 460 |
| Zn2+-hybrid gel | 150 | 535 |
| Co2+-hybrid gel | 100 | 625 |
| Mn2+-hybrid gel | 250 | 460 |
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czarnecki, S.; Rossow, T.; Seiffert, S. Hybrid Polymer-Network Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Response. Polymers 2016, 8, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030082
Czarnecki S, Rossow T, Seiffert S. Hybrid Polymer-Network Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Response. Polymers. 2016; 8(3):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030082
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzarnecki, Sebastian, Torsten Rossow, and Sebastian Seiffert. 2016. "Hybrid Polymer-Network Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Response" Polymers 8, no. 3: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030082
APA StyleCzarnecki, S., Rossow, T., & Seiffert, S. (2016). Hybrid Polymer-Network Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Response. Polymers, 8(3), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym8030082