Biosynthesis and Characterization of Recombinant Silk-Like Polypeptides Derived from the Heavy Chain of Silk Fibrion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
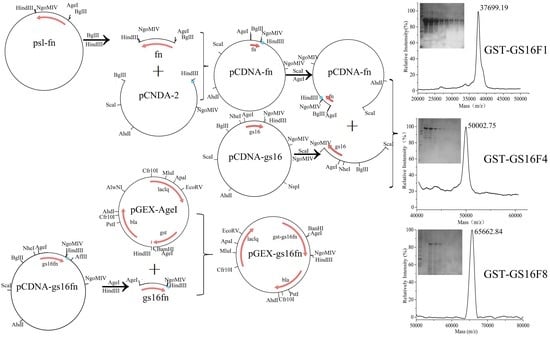
2.2. Vector Construction
2.3. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
2.4. Protein Expression and Purification
2.5. SDS-PAGE
2.6. Mass Spectrometry
2.7. Determination of Expression Yield
2.8. Determining the Amino Acid Composition
2.9. Isoelectric Point Measurement
2.10. Circular Dichroism (CD) Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Vectors
3.2. Fusion Protein Expression and Optimisation
3.3. Purification of Fusion Proteins and MS Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Expression Levels
3.5. Amino Acid Analysis of GST-GS16Fn Proteins
3.6. Charge Analysis of GST-GS16Fn
3.7. CD Analysis of Released Polypeptides GS16Fn
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPTG | isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulphate |
| PAGE | polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| GST | glutathione S-transferase |
| gst | genes encoding GST |
| GST-GS16F1 | recombinant GST and GS16F1 fusion protein |
| GST-GS16F4 | recombinant GST and GS16F4 fusion protein |
| GST-GS16F8 | recombinant GST and GS16F8 fusion protein |
| pI | isoelectric point |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
Amino Acids
| G | Gly |
| S | Ser |
| V | Val |
| A | Ala |
| P | Pro |
| F | Phe |
| N | Asn |
| E | Glu |
| D | Asp |
References
- Hofmann, S.; Hagenmüller, H.; Koch, A.M.; Müller, R.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Kaplan, D.L.; Merkle, H.P.; Meinel, L. Control of in vitro tissue-engineered bone-like structures using human mesenchymal stem cells and porous silk scaffolds. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Chen, E.; Porter, D.; Shao, Z. Enhancing the toughness of regenerated silk fibroin film through uniaxial extension. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Gu, X. Biocompatibility evaluation of silk fibroin with peripheral nerve tissues and cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.N.; Wei, Y.L.; Yi, H.G.; Liu, Z.W.; Sun, D.; Zhao, H.R. Cytocompatibility of a silk fibroin tubular scaffold. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 34, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.L.; Sun, D.; Yi, H.G.; Wang, J.N. Characterization of a PEG-DE cross-linked tubular silk scaffold. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Egaña, A.; Scheibel, T. Interactions of cells with silk surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14330–14336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Jacquet, M.; Perasso, R.; Li, Z.G.; Janin, J. Silk fibroin: Structural implications of a remarkable amino acid sequence. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2001, 44, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, T.; Umemura, K.; Asakura, T. The structural characteristics of Bombyx mori silk fibroin before spinning as studied with molecular dynamics simulation. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8831–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, T.; Yamane, T.; Nakazawa, Y.; Kameda, T.; Ando, K. Structure of Bombyx mori silk fibroin before spinning in solid state studied with wide angle x-ray scattering and 13C cross-polarization/magic angle spinning NMR. Biopolymers 2001, 58, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluzzi, R.; Gido, S.P.; Mulle, W.; Kaplan, D.L. Orientation of silk III at the air-water interface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluzzi, R.; He, S.J.; Gido, S.P.; Kaplan, D.L. Bombyx mori silk fibroin liquid crystallinity and crystallization at aqueous fibroin–organic solvent interfaces. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo, N.D.; Downing, D.T. Crystalline regions of Bombyx mori silk fibroin may exhibit β-turn and β-helix conformations. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4700–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, K.; Somashekar, R.; Noguchi, K.; Ichimura, S. Refined molecular and crystal structure of silk I based on Ala-Gly and (Ala-Gly)2-Ser-Gly peptide sequence. Biopolymers 2001, 59, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Xiao, D.; Chen, X.; Zhou, P.; Yu, T.; Shao, Z. Synthesis and solid-state secondary structure investigation of silk-proteinlike multiblock polymers. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 7508–7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.N.; Lu, C.D.; Bai, L. Study on β-sheet structure formed by self-assembly of fibroin Crystalline typical peptides using thioflavine T fluorescence probe. Acta Chim. Sin. 2007, 65, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z. Two distinct β-sheet fibrils from silk protein. Chem. Commun. 2009, 48, 7506–7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, S.; Santos, A.; Ishii, O.; Ishikawa, K.; Kunieda, S.; Kimura, H.; Shoji, A. Synthesis and conformational study of silk model polypeptides [Ala-Gly]12 by solid-state NMR. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 649, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.X.; Qian, Z.G.; Ki, C.S.; Park, Y.H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Lee, S.Y. Native-sized recombinant spider silk protein produced in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli results in a strong fiber. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14059–14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarsekar, A.; Crissman, J.; Crissman, M.; Ferrari, F.; Cappello, J.; Ghandehari, H. Genetic engineering of stimuli-sensitive silkelastin-like protein block copolymers. Biomacromolecules 2003, 4, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, Y.; Sutherland, T.D.; Kameda, T. Recombinant production and film properties of full-length hornet silk proteins. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3590–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, M.; Ackerschott, C.B.; Scheibel, T. Characterization of recombinantly produced spider flagelliform silk domains. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 170, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.; Azevedo-Silva, J.; Correia, C.; Collins, T.; Arias, F.J.; Rodríguez-Cabello, J.C.; Casal, M. High level expression and facile purification of recombinant silk-elastin-like polymers in auto induction shake flask cultures. AMB Express 2013, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhe, M.; Johansson, U.; Hillerdahl, C.-O.; Hedhammar, M. Recombinant spider silk with cell binding motifs for specific adherence of cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8223–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.N.; Yan, S.Q.; Bai, L. Structure characterization of silk fibroin crystalline domain polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli. J. Donghua Univ. Eng. Ed. 2011, 28, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.N.; Yan, S.Q.; Lu, C.D.; Bai, L. Biosynthesis and characterization of typical fibroin crystalline polypeptides of silkworm Bombyx mori. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Tian, Z.F.; Yi, H.G.; Yang, Y.X.; Wang, J.N. Designing and cloning of the gene sequence encoding silk fibroin amorphous domain. J. Donghua Univ. Eng. Ed. 2012, 29, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.Q.; Wu, M.Y.; Yi, H.G.; Wang, J.N. Biosynthesis and characterization of a non-repetitive polypeptide derived from silk fibroin heavy chain. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.F.; Zhao, H.R.; Yi, H.G.; Wang, J.N. Recombinant Cloning of Gene Sequence Encoding Silk Fibroin Heavy Chain. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 796, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Amino Acid | GST-GS16F1 (mol%) | GST-GS16F4 (mol%) | GST-GS16F8 (mol%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Experimental | Theoretical | Experimental | Theoretical | Experimental | |
| Asp | 5.60 | 5.64 | 5.38 | 5.45 | 5.22 | 5.11 |
| Thr | 1.96 | 1.96 | 1.45 | 1.42 | 1.08 | 0.99 |
| Ser | 11.20 | 10.97 | 15.73 | 15.48 | 19.05 | 19.35 |
| Glu | 5.60 | 5.62 | 6.63 | 6.32 | 7.37 | 7.48 |
| Gly | 20.73 | 20.56 | 21.53 | 20.17 | 22.12 | 22.73 |
| Ala | 13.45 | 13.62 | 13.66 | 12.73 | 13.82 | 13.96 |
| Cys | 1.12 | 1.17 | 0.83 | 7.09 | 0.61 | 1.60 |
| Val | 3.36 | 3.25 | 3.73 | 3.55 | 3.99 | 4.02 |
| Met | 2.52 | 2.69 | 1.86 | 0.00 | 1.38 | 0.00 |
| Ile | 3.64 | 3.72 | 2.69 | 2.47 | 2.00 | 1.99 |
| Leu | 8.12 | 8.20 | 6.00 | 5.75 | 4.45 | 4.29 |
| Tyr | 3.92 | 3.87 | 2.90 | 2.88 | 2.15 | 2.23 |
| Phe | 3.64 | 3.57 | 5.18 | 5.08 | 6.30 | 6.46 |
| Lys | 6.16 | 6.29 | 4.55 | 4.00 | 3.38 | 3.33 |
| His | 1.68 | 1.73 | 1.24 | 1.18 | 0.92 | 0.92 |
| Arg | 2.80 | 2.56 | 2.07 | 1.90 | 1.54 | 1.74 |
| Pro | 4.48 | 4.50 | 4.55 | 4.34 | 4.61 | 4.23 |
| Total | ≈100 | ≈100 | ≈100 | |||
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Kang, Z.; Tian, Z.; Wu, M.; Wang, J. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Recombinant Silk-Like Polypeptides Derived from the Heavy Chain of Silk Fibrion. Polymers 2017, 9, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120669
Wu Y, Kang Z, Tian Z, Wu M, Wang J. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Recombinant Silk-Like Polypeptides Derived from the Heavy Chain of Silk Fibrion. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120669
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yue, Zhao Kang, Zhifang Tian, Mingyang Wu, and Jiannan Wang. 2017. "Biosynthesis and Characterization of Recombinant Silk-Like Polypeptides Derived from the Heavy Chain of Silk Fibrion" Polymers 9, no. 12: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120669
APA StyleWu, Y., Kang, Z., Tian, Z., Wu, M., & Wang, J. (2017). Biosynthesis and Characterization of Recombinant Silk-Like Polypeptides Derived from the Heavy Chain of Silk Fibrion. Polymers, 9(12), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120669