Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of CSP
2.3. Preparation of Epoxy/ATHBP/CSP Thermosets
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of CSPs
3.2. Mechanical Properties of the Epoxy Thermosets Modified with CSPs
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Epoxy/ATHBP Thermosets Modified with CSPs
3.4. Fracture Surface Morphologies
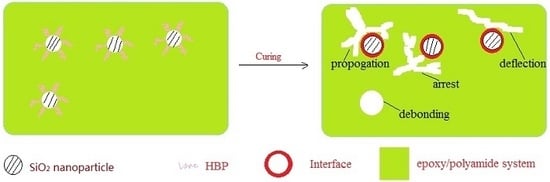
3.5. Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, X.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Jensen, R.E.; Li, W.; Haque, B.Z.; McKnight, S.H. Effect of fiber surface texture on the mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. A 2015, 74, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, L.; Pornwannchai, W.; Hu, Y.; Kandola, B. The effect of graphene presence in flame retarded epoxy resin matrix on the mechanical and flammability properties of glass fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. A 2013, 53, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Alagirusamy, R.; Joshi, M. Development of carbon nanofibre incorporated three phase carbon/epoxy composites with enhanced mechanical, electrical and thermal properties. Compos. A 2011, 42, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaioncz, S.; Silva, A.A.; Sirqueira, A.S.; Soares, B.G. Toughening of Epoxy Resin by Methyl Methacrylate/2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate Copolymers: The Effect of Copolymer Composition. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2007, 292, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; You, S.; Baier, H. Effect of organosilane coupling agents on microstructure and properties of nanosilica/epoxy composites. Polym. Compos. 2012, 33, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Wang, G. A comparative study on the properties of the different amino-functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes reinforced epoxy resin composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 403–411. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Benicewicz, B.C.; Hillborg, H.; Schadler, L.S. Effect of graft density and molecular weight on mechanical properties of rubbery block copolymer grafted SiO2 nanoparticle toughened epoxy. Polymer 2013, 54, 3961–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, M.; Gan, W.; Tao, Q.; Li, S. Polymerization-Induced Viscoelastic Phase Separation in Polyethersulfone-Modified Epoxy Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6208–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannotti, M.; Bernal, C.R.; Oyanguren, P.A.; Galante, M.J. Morphology and fracture properties relationship of epoxy-diamine systems simultaneously modified with polysulfone and poly(ether imide). Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chen, Y.; Su, Z.; Quan, C.; Tan, V.B.C. Effects of clay structural parameters and gallery strength on the damage behavior of epoxy/clay nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 85, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara-Morales, A.; Taylor, A.C. Mechanical and dielectric properties of epoxy-clay nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, F.N.; Berg, J.C. Novel core-shell (dendrimer) epoxy tougheners: Processing and hot-wet performance. Compos. A 2008, 39, 1007–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Yu, D.; He, J.; Xie, Y.; Huang, L.; Guo, X. Simultaneously improved toughness and dielectric properties of epoxy/core-shell particle blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakopoulos, G.; Masania, K.; Taylor, A.C. Toughening of epoxy using core-shell particles. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kinloch, A.J.; Sprenger, S.; Taylor, A.C. The mechanical properties and toughening mechanisms of an epoxy polymer modified with polysiloxane-based core-shell particles. Polymer 2013, 54, 4276–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naguib, M.; Grassini, S.; Sangermano, M. Core/Shell PBA/PMMA-PGMA Nanoparticles to Enhance the Impact Resistance of UV-Cured Epoxy Systems. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Iqbal, N.; Kumar, D.; Rajagopal, C. Polysiloxane-based core-shell microspheres for toughening of epoxy resins. J. Polym. Res. 2014, 21, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, R.A.; Laftah, W.A.; Hashim, S. Core-shell polymers: A review. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 15543–15565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.-W.; Park, I.J.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, D.-K. Preparation and Characterization of Core-Shell Particles Containing Perfluoroalkyl Acrylate in the Shell. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 6811–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitsartarn, W.; Fan, X.; Sun, Y.; Yeo, J.C.C.; Yuan, D.; He, C. Simultaneous enhancement of strength and toughness of epoxy using POSS-Rubber core-shell nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, D.; Ivankovic, A. Effect of core-shell rubber (CSR) nano-particles on mechanical properties and fracture toughness of an epoxy polymer. Polymer 2015, 66, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Thuc, B.H.; Maazouz, A. Morphology and rheology relationships of epoxy/core-shell particle blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z. Preparation of epoxy-functionalized polystyrene/silica core-shell composite nanoparticles. J. Polym. Sci. A 2004, 42, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jing, X. Preparation of polystyrene/polyaniline core/shell structured particles and their epoxy-based conductive composites. Polym. Int. 2007, 56, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Du, B.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, X.; Qi, G. Thermosets with core-shell nanodomain by incorporation of core crosslinked star polymer into epoxy resin. Polymer 2011, 52, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, J. Investigation of the tribological properties: Core-shell structured magnetic Ni@NiO nanoparticles reinforced epoxy nanocomposites. Tribol. Int. 2015, 83, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Joshi, S.C. Environmental durability of glass fiber epoxy composites filled with core-shell polymer particles. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 866–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, S.; Sun, R.; Xu, J. Mechanical reinforcement while remaining electrical insulation of glass fibre/polymer composites using core-shell CNT@SiO2 hybrids as fillers. Compos. A 2015, 73, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Nie, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, X. Hyperbranched polyether as an all-purpose epoxy modifier: Controlled synthesis and toughening mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, C.; Hou, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, S. The effect of hyperbranched polyester and zirconium slag nanoparticles on the impact resistance of epoxy resin thermosets. Compos. B 2015, 79, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, C.; Hou, H. Synthesis and characterization of amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer and as modifier for epoxy resin thermosets. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015, 293, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, C.; Hou, H. Synthesis of Core-shell Particles Based on Hyperbranced Polyester and Zirconium Slag Nanoparticles and Its Influence on the Impact Resistance of Epoxy Resin Thermosets. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Meng, Y.; Qiu, T.; Li, X. An epoxy-ended hyperbranched polymer as a new modifier for toughening and reinforcing in epoxy resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foix, D.; Yu, Y.; Serra, A.; Ramis, X.; Salla, J.M. Study on the chemical modification of epoxy/anhydride thermosets using a hydroxyl terminated hyperbranched polymer. Eur. Polym. J. 2009, 45, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morell, M.; Ramis, X.; Ferrando, F.; Yu, Y.; Serra, A. New improved thermosets obtained from DGEBA and a hyperbranched poly(ester-amide). Polymer 2009, 50, 5374–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Francos, X.; Foix, D.; Serra, À.; Salla, J.M.; Ramis, X. Novel thermosets based on DGEBA and hyperbranched polymers modified with vinyl and epoxy end groups. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Tang, B.; Chen, M.; Zhao, X. Hyperbranched polyurethane as a highly efficient toughener in epoxy thermosets with reaction-induced microphase separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18060–18070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Wei, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, X. Simultaneous enhancements in toughness, tensile strength, and thermal properties of epoxy-anhydride thermosets with a carboxyl-terminated hyperbranched polyester. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 90, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misasi, J.M.; Jin, Q.; Knauer, K.M.; Morgan, S.E.; Wiggins, J.S. Hybrid POSS-Hyperbranched polymer additives for simultaneous reinforcement and toughness improvements in epoxy networks. Polymer 2017, 117, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, Z.; Song, X.; Cui, X.; Cao, P.; Liu, H.; Cheng, F.; Chen, Y. Core-shell type multiarm star poly(ε-caprolactone) with high molecular weight hyperbranched polyethylenimine as core: Synthesis, characterization and encapsulation properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Shen, H.; Wu, D. Controlled Formation of Microgels/Nanogels from a Disulfide-Linked Core/Shell Hyperbranched Polymer. ACS Macro Lett. 2012, 1, 1295–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, Y. Amphiphilic Unimolecular Nanoparticles Based on a Hyperbranched Polyacrylate Core and a PNIPAm Shell: Synthesis via ATRP and Properties. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Yu, B.; Jiang, X.; Yin, J. Hybrid Core-Shell Microspheres from Coassembly of Anthracene-Containing POSS (POSS-AN) and Anthracene-Ended Hyperbranched Poly(ether amine) (hPEA-AN) and Their Responsive Polymeric Hollow Microspheres. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 3519–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, K.; Jiang, P. Core-shell Structured Hyperbranched Aromatic Polyamide/BaTiO3 Hybrid Filler for Poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene-chlorofluoroethylene) Nanocomposites with the Dielectric Constant Comparable to that of Percolative Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, H.; Lv, T.; Lin, Q.; Hou, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Cui, C. The effect of amino-terminated hyperbranched polymers on the impact resistance of epoxy resins. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2016, 294, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Cui, C. Enhancing the mechanical properties of epoxy resin by addition of an amino-terminated hyperbranched polymer grown on glass-fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Zhang, Q.; Bannister, M.; Mai, Y. Investigation of the mechanical properties of DGEBA-based epoxy resin with nanoclay additives. Compos. Struct. 2006, 75, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.P.; Schuman, T.; Vuppalapati, R.R.; Chandrashekhara, K. Fabrication of bio-based epoxy-clay nanocomposites. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonocore, G.G.; Schiavo, L.; Attianese, I.; Borriello, A. Hyperbranched polymers as modifiers of epoxy adhesives. Compos. B 2013, 53, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Yu, J.; Xie, L.; Li, Y.; Jiang, P. Efficient thermal properties enhancement to hyperbranched aromatic polyamide grafted aluminum nitride in epoxy composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogh, L.; Pettersson, B.; Månson, J.-A.E. Dendritic hyperbranched polymers as tougheners for epoxy resins. Polymer 1999, 40, 2249–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, R.; Meng, Y.; Li, X. Dependence of epoxy toughness on the backbone structure of hyperbranched polyether modifiers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 3408–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, G.; Fu, S.; Ye, L. Simultaneous improvements in the cryogenic tensile strength, ductility and impact strength of epoxy resins by a hyperbranched polymer. Polymer 2008, 49, 3168–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Lin, Q.; Wang, C. Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer. Polymers 2017, 9, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120684
Li S, Wu Q, Zhu H, Lin Q, Wang C. Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120684
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuiping, Qisheng Wu, Huajun Zhu, Qing Lin, and Chengshuang Wang. 2017. "Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer" Polymers 9, no. 12: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120684
APA StyleLi, S., Wu, Q., Zhu, H., Lin, Q., & Wang, C. (2017). Impact Resistance Enhancement by Adding Core-Shell Particle to Epoxy Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polymer. Polymers, 9(12), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120684