Plateau-Shaped Flexible Polymer Microelectrode Array for Neural Recording
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
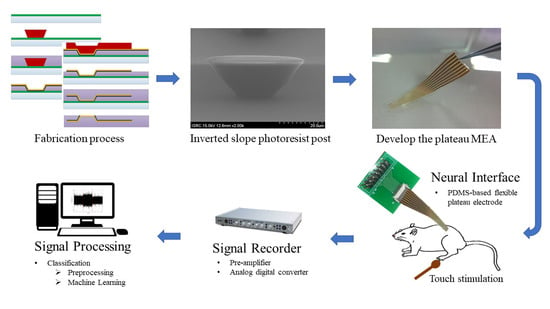
2.1. Electrode Structure and Fabrication
2.2. Device Characterization
2.2.1. Electrode Profile
2.2.2. Surface Treatment
2.2.3. Electrode Impedance Measurement
2.2.4. Surface Contact Performance
2.3. In Vivo Experiments
3. Results and Disscussion
3.1. Electrode Profile
3.2. Surface Treatment
3.3. Electrode Impedance Measurement
3.4. Surface Contact Performance
3.5. In Vivo Experiments
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aravanis, A.M.; Wang, L.P.; Zhang, F.; Meltzer, L.A.; Mogri, M.Z.; Schneider, M.B.; Deisseroth, K. An optical neural interface: In vivo control of rodent motor cortex with integrated fiberoptic and optogenetic technology. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, S143–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, J.P.; Nurmikko, A.; Black, M.; Hochberg, L.R. Assistive technology and robotic control using motor cortex ensemble-based neural interface systems in humans with tetraplegia. J. Physiol. 2007, 579, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoghue, J.P. Bridging the Brain to the World: A Perspective on Neural Interface Systems. Neuron 2008, 60, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disselhorst-Klug, C.; Bahm, J.; Ramaekers, V.; Trachterna, A.; Rau, G. Non-invasive approach of motor unit recording during muscle contractions in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 83, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reucher, H.; Rau, G.; Silny, J. Spatial Filtering of Noninvasive Multielectrode EMG: Part I-Introduction to Measuring Technique and Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1987, BME-34, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubehn, B.; Bosman, C.; Oostenveld, R.; Fries, P.; Stieglitz, T. A MEMS-based flexible multichannel ECoG-electrode array. J. Neural Eng. 2009, 6, 036003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenaar, D.A.; Potter, S.M. Real-time multi-channel stimulus artifact suppression by local curve fitting. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2002, 120, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, K.D.; Angell, J.B. A Low-Capacitance Multielectrode Probe for Use in Extracellular Neurophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1975, BME-22, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, K.D.; Angell, J.B.; Starr, A. An Integrated-Circuit Approach to Extracellular Microelectrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1970, BME-17, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; McConnell, G.C.; Schneider, T.M.; Bellamkonda, R.V. A Novel Anti-inflammatory Surface for Neural Electrodes. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3529–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdondini, L.; Chiappalone, M.; van der Wal, P.D.; Imfeld, K.; de Rooij, N.F.; Koudelka-Hep, M.; Tedesco, M.; Martinoia, S.; van Pelt, J.; Le Masson, G.; et al. A microelectrode array (MEA) integrated with clustering structures for investigating in vitro neurodynamics in confined interconnected sub-populations of neurons. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 114, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppart, S.A.; Wheeler, B.C.; Wallace, C.S. A flexible perforated microelectrode array for extended neural recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 39, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.C.; Renaud, P.; Tanila, H.; Djupsund, K. Flexible polyimide microelectrode array for in vivo recordings and current source density analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodger, D.C.; Fong, A.J.; Li, W.; Ameri, H.; Ahuja, A.K.; Gutierrez, C.; Lavrov, I.; Zhong, H.; Menon, P.R.; Meng, E.; et al. Flexible parylene-based multielectrode array technology for high-density neural stimulation and recording. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 132, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Viventi, J.; Amsden, J.J.; Xiao, J.; Vigeland, L.; Kim, Y.-S.; Blanco, J.A.; Panilaitis, B.; Frechette, E.S.; Contreras, D.; et al. Dissolvable films of silk fibroin for ultrathin conformal bio-integrated electronics. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, N.; Yoo, S.; Kim, S. A Largely Deformable Surface Type Neural Electrode Array Based on PDMS. IEEE Trans Neural Syst. Rehabil. 2013, 21, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meacham, K.W.; Giuly, R.J.; Guo, L.; Hochman, S.; DeWeerth, S.P. A lithographically-patterned, elastic multi-electrode array for surface stimulation of the spinal cord. Biomed. Microdevices 2007, 10, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Meacham, K.W.; Hochman, S.; DeWeerth, S.P. A PDMS-Based Conical-Well Microelectrode Array for Surface Stimulation and Recording of Neural Tissues. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McClain, M.A.; Clements, I.P.; Shafer, R.H.; Bellamkonda, R.V.; LaPlaca, M.C.; Allen, M.G. Highly-compliant, microcable neuroelectrodes fabricated from thin-film gold and PDMS. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrega, T.; Lacour, S.P. Stretchable gold conductors embedded in PDMS and patterned by photolithography: Fabrication and electromechanical characterization. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 055025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Oh, D.R.; Sanchez, J.; Kim, S.H.; Seo, J.M. Fabrication of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)—Based multielectrode array for neural interface. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1716–1719. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Seo, J.M. Fabrication of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-Based Flexible Electrode Array for Improving Tissue Contact. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference of the International Federation for Medical and Biological Engineering, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 7–11 September 2014; Lacković, I., Vasic, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Schuettler, M.; Henle, C.; Ordonez, J.; Suaning, G.J.; Lovell, N.H.; Stieglitz, T. Patterning of Silicone Rubber for Micro-Electrode Array Fabrication. In Proceedings of the 3rd International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (CNE ’07), Kohala Coast, HI, USA, 2–5 May 2007; pp. 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Balakrisnan, B.; Patil, S.; Smela, E. Patterning PDMS using a combination of wet and dry etching. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 047002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodas, D.S.; Khan-Malek, C. Fabrication of long-term hydrophilic surfaces of poly(dimethyl siloxane) using 2-hydroxy ethyl methacrylate. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 120, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschwanez, J.H.; Carlson, R.H.; Meldrum, D.R. Thin PDMS Films Using Long Spin Times or Tert-Butyl Alcohol as a Solvent. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, I.; Coleman, A.W.; Kim, B. Transfer of thin Au films to polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) with reliable bonding using (3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane (MPTMS) as a molecular adhesive. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 23, 085016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Jun, S.B.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.W.; Im, C.; Shin, H.C.; Chang, J.W.; Kim, S.J. A Flexible Depth Probe Using Liquid Crystal Polymer. IEEE Trans Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.N.; Park, C.; Whitesides, G.M. Solvent Compatibility of Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-Based Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6544–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franks, W.; Heer, F.; McKay, I.; Taschini, S.; Sunier, R.; Hagleitner, C.; Hierlemann, A.; Baltes, H. CMOS monolithic microelectrode array for stimulation and recording of natural neural networks. In Proceedings of the12th International Conference on Transducers, Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Grahame, D.C. Mathematical theory of the faradaic admittance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1952, 99, 370C–385C. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Hyun Bae, S.; Min, K.S.; Seo, J.-M.; Chung, H.; June Kim, S. A Miniaturized, Eye-Conformable, and Long-Term Reliable Retinal Prosthesis Using Monolithic Fabrication of Liquid Crystal Polymer (LCP). IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Myers, A.; Malhotra, A.; Lin, F.; Bozkurt, A.; Muth, J.; Zhu, Y. Wearable Hydration Sensor with Conformal Nanowire Electrodes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Song, U.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. An ultrathin stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator with coplanar electrode for energy harvesting and gesture sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12361–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.S.; Pan, B.C.; Liou, G.S. Highly transparent AgNW/PDMS stretchable electrodes for elastomeric electrochromic devices. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2633–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| NMP:TBAF (v/v) | 3:1 (25%) | 5:1 (12%) | 10:1 (9%) | 15:1 (6%) |
| Etching rate (μm/min) | 3.7 | 2.8 | 2 | 1.3 |
| Method | Time after treatment (h) | Adhesion test with tape 1 | Adhesion test with tape 2 | Contact angle (degrees) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No treatment | -- | X | X | ~105 |
| Oxygen plasma | 1 | 0% | 0% | ~10 |
| 24 | 60% | 80% | ~92 | |
| HEMA | 1 | 0% | 0% | ~12 |
| 48 | 0% | 0% | ~20 | |
| 120 | 0% | 0% | ~35 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-M.; Im, C.; Lee, W.R. Plateau-Shaped Flexible Polymer Microelectrode Array for Neural Recording. Polymers 2017, 9, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120690
Kim J-M, Im C, Lee WR. Plateau-Shaped Flexible Polymer Microelectrode Array for Neural Recording. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120690
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jun-Min, Changkyun Im, and Woo Ram Lee. 2017. "Plateau-Shaped Flexible Polymer Microelectrode Array for Neural Recording" Polymers 9, no. 12: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120690
APA StyleKim, J.-M., Im, C., & Lee, W. R. (2017). Plateau-Shaped Flexible Polymer Microelectrode Array for Neural Recording. Polymers, 9(12), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120690