Experimental Investigation of the Magnetorheological Behavior of PDMS Elastomer Reinforced with Iron Micro/Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Isotropic MREs
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Material Constitutive Model
3. Results
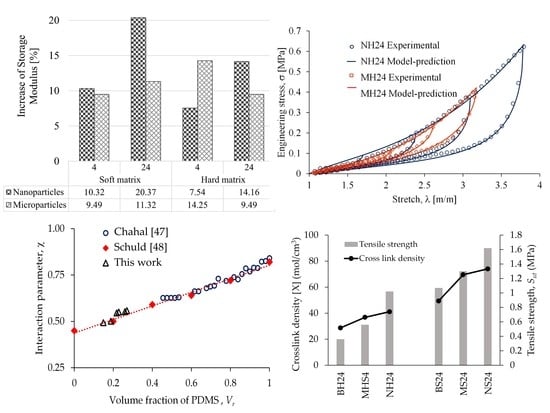
3.1. Mechanical Properties
3.2. Stress Softening
3.3. Rheological Properties
3.4. Magnetic Measurement
3.5. Morphological and Structural Analysis
3.6. FTIR and XPS Characterization
3.7. Thermal Stability
3.8. Relationship between Polymer Swelling and Tension Tests
3.9. Summary
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forster, E.; Mayer, M.; Rabindranath, R.; Böse, H.; Schlunck, G.; Monkman, G.J.; Shamonin, M. Patterning of Ultrasoft, agglutinative magnetorheological elastomers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khimi, S.R.; Pickering, K.L.; Mace, B.R. Dynamic properties of magnetorheological elastomers based on Iron Sand and Natural Rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bica, I.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Magnetic field intensity effect on plane electric capacitor characteristics and viscoelasticity of magnetorheological elastomer. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1115–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gong, X.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z. Effects of rubber/magnetic particle interactions on the performance of magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2006, 25, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suna, T.L.; Gong, X.L.; Jiang, W.Q.; Li, J.F.; Xu, Z.B.; Li, W.H. Study on the damping properties of magnetorheological elastomers based on cis-polybutadiene rubber. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Dong, X.; Ou, J. Magnetostrictive effect of magnetorheological elastomer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, K.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, C.H.; Cho, W.O. A study on the tribological characteristics of a MagnetoRheological Elastomer. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 014501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.F.; Li, W.H.; Alici, G.; Du, H.; Deng, Y.M. Microstructure and magnetorheology of graphite-based MR elastomers. Rheol. Acta 2011, 50, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Qiao, X.; Watanabe, H.; Gong, X.; Yang, T.; Li, W.; Sun, K.; Li, M.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; et al. Mechanical and structural investigation of isotropic and anisotropic thermoplastic magnetorheological elastomer composites based on poly(styrene-b-ethyleneco-butylene-b-styrene) (SEBS). Rheol. Acta 2012, 51, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Gong, X.; Xuan, S.; Guo, C.; Zong, L. Magnetic-field-induced normal force of magnetorheological elastomer under compression status. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 3322–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.E.; Cho, S.K.; Park, S.Y.; Jeong, I.B.; Jeong, M.G.; Kim, Y.D.; Choi, H.J.; Cho, S.M. Ultrathin polydimethylsiloxane-coated carbonyl iron particles and their magnetorheological characteristics. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.A.N.; Mazlan, S.A.; Mohamad, N.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Ubaidillah. An overview of nanoparticles utilization in magnetorheological materials. AIP Conf. Proc. 2016, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.X.; Gong, X.L.; Wang, L.H. Development of an adaptive tuned vibration absorber with magnetorheological elastomer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanov, G.V.; Abramchuk, S.S.; Grishin, D.A.; Nikitin, L.V.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Effect of a homogeneous magnetic field on the viscoelastic behavior of magnetic elastomers. Polymer 2007, 48, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gong, X.L.; Li, W.H. Effect of carbon black on the mechanical performances of magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.L.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, P.Q. Fabrication and characterization of isotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, I.; Anitas, E.M.; Bunoiu, M.; Vatzulik, B.; Juganaru, I. Hybrid magnetorheological elastomer: Influence of magnetic field and compression pressure on its electrical conductivity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 3994–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ju, B.; Fu, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q. Influence of composition of carbonyl iron particles on dynamic mechanical properties of magnetorheological elastomers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gong, X.L.; Jiang, W.Q.; Fan, Y.C. Investigation of the durability of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers based on mixed rubber. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gong, X.L.; Jiang, W.Q.; Yao, J.J.; Deng, H.X.; Li, W.H. Investigation on magnetorheological elastomers based on natural rubber. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 5483–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Song, K.H.; Choi, H.J. Magnetic carbonyl iron nanoparticle based magnetorheological suspension and its characteristics. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, M.; Hashemabadi, S.H.; Ghaffari, A. A review on the magnetorheological fluid preparation and stabilization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 374, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.F.; Liu, Y.D.; Choi, H.J. Electrorheological and magnetorheological response of polypyrrole/magnetite nanocomposite particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1781–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shin, K.Y.; Jang, J. Enhanced magnetorheological performance of highly uniform magnetic carbon nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9646–9654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rwei, S.P.; Lee, H.Y.; Yoo, S.D.; Wang, L.Y.; Lin, J.G. Magnetorheological characteristics of aqueous suspensions that contain Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2005, 283, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonel, P.S.; Jorge, G.; Perez, O.E.; Butera, A.; Leyva, A.G.; Negri, R.M. Magnetic and elastic properties of CoFe2O4-polydimethylsiloxane magnetically oriented elastomer nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, X.; Yang, J.; Xuan, S. Improving the Dynamic Properties of MRE under Cyclic Loading by Incorporating Silicon Carbide Nanoparticles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denver, H.; Heiman, T.; Martin, E.; Gupta, A.; Borca, D.A. Fabrication of polydimethylsiloxane composites with nickel nanoparticle and nanowire fillers and study of their mechanical and magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Setua, D.K.; Sharma, A.; Mordina, B. Magnetorheology of Polydimethylsiloxane Elastomer/FeCo3 Nanocomposite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 25684–25703. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan, M.P.; Sudeep, P.M.; Al-omari, I.A.; Kurian, P.; Ajayan, P.M.; Narayanan, T.N.; Anantharaman, M.R. Enhanced microactuation with magnetic field curing of magnetorheological elastomers based on iron-natural rubber nanocomposites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2015, 38, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Y.; Feng, X.Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate-polymer composites. Compos. Part B 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales, I.A.; Palacios, L.M.; Lozano, L.M.; Martínez, O.; Puente, J.G.; Elías, A. Enhancement of a magnetorheological PDMS elastomer with carbonyl iron particles. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, K.L.; Khimi, S.R.; Ilanko, S. The effect of silane coupling agent on iron sand for use in magnetorheological elastomers Part 1: Surface chemical modification and characterization. Compos. Part A 2015, 68, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treloar, L.R.G. The elasticity and related properties of rubbers. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1973, 36, 755–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J.; Rehner, J. Statistical mechanics of cross-linked polymer networks II Swelling. J. Chem. Phys. 1943, 11, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.; Beatty, M.F. Constitutive equations for amended non-Gaussian network models of rubber elasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2002, 40, 2265–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, A.; Montoya, B.; Ortega, W.; Flores, E.; Rodríguez, C.A.; Siller, H.R.; Díaz-Elizondo, J.A.; Martínez, O. Stress-softening and residual strain effects in suture materials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elías, A.; Baylon, K.; Ferrer, I.; Sereno, L.; García, M.L.; Bagudanch, I.; Grabalosa, J.; Perez, T.; Martínez, O.; Ortega, W.; et al. On the rule of mixtures for predicting stress-softening and residual strain effects in biological tissues and biocompatible materials. Materials 2014, 7, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zi, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Y.; Dail, J. Size effects on magnetic properties of Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 prepared by Sol-Gel Method. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- DeAntonio, D.A. Soft magnetic ferritic stainless steels. Adv. Mater. Process. 2003, 161, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Wen, W. Applications of micro/nanoparticles in microfluidic sensors: A Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 6952–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Vatani, A.; Mohammadi, T. Synergistic interaction between POSS and fumed silica on the properties of crosslinked PDMS nanocomposite membranes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 82460–82470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.C.M. Polymer Data Handbook; Oxford University Press, Inc.: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Whang, C.M.; Yeo, C.S.; Kim, Y.H. Preparation and Characterization of Sol-Gel Derived SiO2-TiO2-PDMS Composite Films. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2001, 22, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Hanoosh, W.S.; Abdelrazaq, E.M. Polydimethyl siloxane toughened epoxy resins: Tensile strength and dynamic mechanical analysis. Malays. Polym. J. 2009, 4, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Schmucker, A.; Dyke, J.; Hall, S.M.; Retrum, J.; Stein, B.; Remmes, N.; Baxter, D.V.; Dragneaa, B.; Bronstein, L.M. Magnetic nanoparticles with functional silanes: Evolution of well-defined shells from anhydride containing silane. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 4231–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahal, R.S.; Kao, W.P.; Patterson, D. Thermodynamics of polydimethylsiloxane solutions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1973, 69, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuld, N.; Wolf, B. Polymer-solvent interaction parameters. In Wiley Database of Polymer Properties; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
















| Nomenclature | Filler | Shore A hardness | Silicone oil volume (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BS04 | Bare | 14 (Soft) | 4 |
| BS24 | Bare | 14 (Soft) | 24 |
| BH04 | Bare | 20 (Hard) | 4 |
| BH24 | Bare | 20 (Hard) | 24 |
| NS04 | Nanoparticles | 14 (Soft) | 4 |
| NS24 | Nanoparticles | 14 (Soft) | 24 |
| NH04 | Nanoparticles | 20 (Hard) | 4 |
| NH24 | Nanoparticles | 20 (Hard) | 24 |
| MS04 | Microparticles | 14 (Soft) | 4 |
| MS24 | Microparticles | 14 (Soft) | 24 |
| MH04 | Microparticles | 20 (Hard) | 4 |
| MH24 | Microparticles | 20 (Hard) | 24 |
| Material sample identification | µ (MPa) | Sut (MPa) | λL (-) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BS04 | 0.28 | 2.08 | 3.75 |
| BS24 | 0.12 | 1.07 | 3.91 |
| BH04 | 0.20 | 1.25 | 3.35 |
| BH24 | 0.07 | 0.36 | 3.15 |
| NS04 | 0.32 | 1.76 | 3.74 |
| NS24 | 0.18 | 1.61 | 4.85 |
| NH04 | 0.22 | 1.48 | 3.95 |
| NH24 | 0.10 | 1.03 | 4.8 |
| MS04 | 0.32 | 1.97 | 4.09 |
| MS24 | 0.17 | 1.30 | 3.99 |
| MH04 | 0.19 | 1.29 | 3.79 |
| MH24 | 0.09 | 0.56 | 3.62 |
| Sample | μ (MPa) | N (-) | A1 (MPa) | A2 (MPa) | b (-) | c (MPa) | f (-) | Permanent set |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS04 | 0.32 | 7.5 | −2.410 | 0 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.033 | 1.11 |
| NS04 | 0.32 | 10.0 | 0.745 | 0 | 0.7 | 7 | 0.033 | 1.06 |
| MS24 | 0.17 | 6.3 | −0.428 | 0 | 0.5 | 10 | 0.033 | 1.07 |
| NS24 | 0.18 | 5.0 | 0.645 | 0 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.033 | 1.08 |
| MH04 | 0.19 | 5.8 | −0.473 | 0 | 0.5 | 8 | 0.033 | 1.03 |
| NH04 | 0.22 | 5.5 | −0.481 | 0 | 0.65 | 8 | 0.033 | 1.04 |
| MH24 | 0.09 | 5.4 | −0.622 | 0 | 0.4 | 10 | 0.033 | 1.04 |
| NH24 | 0.1 | 7.6 | −0.048 | 0 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.033 | 1.08 |
| Sample | T10% (°C) | Tp (°C) | Rp (%/°C) | Residue (%) | Magnetization (A·m2·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticles | N/A | N/A | N/A | 102.2 | 184.7 |
| Microparticles | N/A | N/A | N/A | 104.1 | 214.2 |
| BS00 | 372.7 | 574.6 | 0.437 | 25.6 | N/A |
| BH00 | 371.2 | 585.5 | 0.484 | 23.1 | N/A |
| BS04 | 374.5 | 577.5 | 0.466 | 24.1 | N/A |
| BS24 | 392.8 | 579.0 | 0.556 | 21.3 | N/A |
| BH04 | 379.8 | 583.5 | 0.483 | 21.9 | N/A |
| BH24 | 383.3 | 575.2 | 0.487 | 18.3 | N/A |
| NS04 | 394.0 | 552.5 | 0.292 | 42.0 | 38.2 |
| NS24 | 404.8 | 571.3 | 0.315 | 39.0 | 39.7 |
| NH04 | 401.5 | 564.8 | 0.324 | 39.6 | 39.8 |
| NH24 | 409.3 | 547.3 | 0.346 | 36.7 | 38.2 |
| MS04 | 398.7 | 556.9 | 0.402 | 39.9 | 42.1 |
| MS24 | 407.9 | 563.6 | 0.464 | 36.7 | 42.2 |
| MH04 | 396.0 | 568.6 | 0.409 | 38.4 | 42.8 |
| MH24 | 405.5 | 567.3 | 0.484 | 36.8 | 42.7 |
| Sample ratio properties | Strength (%) | Elongation at break (%) | Stiffness (%) | Thermal stability (T10%) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS04/BS04 | −16 | −0.4 | 14 | 5 |
| NS24/BS24 | 50 | 32 | 50 | 3 |
| NH04/BH04 | 17 | 26 | 10 | 6 |
| NH24/BH24 | 186 | 77 | 42 | 7 |
| Sample ratio properties | Strength (%) | Elongation at break (%) | Stiffness (%) | Magnetic field sensitivity (%) | Thermal stability (T10%) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NS04/MS04 | −11 | −11 | 0 | 9 | −1.2 |
| NS24/MS24 | 24 | 29 | 6 | 80 | −0.8 |
| NH04/MH04 | 15 | 6 | 16 | −47 | 1.4 |
| NH24/MH24 | 84 | 45 | 11 | 49 | 0.9 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palacios-Pineda, L.M.; Perales-Martinez, I.A.; Lozano-Sanchez, L.M.; Martínez-Romero, O.; Puente-Córdova, J.; Segura-Cárdenas, E.; Elías-Zúñiga, A. Experimental Investigation of the Magnetorheological Behavior of PDMS Elastomer Reinforced with Iron Micro/Nanoparticles. Polymers 2017, 9, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120696
Palacios-Pineda LM, Perales-Martinez IA, Lozano-Sanchez LM, Martínez-Romero O, Puente-Córdova J, Segura-Cárdenas E, Elías-Zúñiga A. Experimental Investigation of the Magnetorheological Behavior of PDMS Elastomer Reinforced with Iron Micro/Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2017; 9(12):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120696
Chicago/Turabian StylePalacios-Pineda, Luis Manuel, Imperio Anel Perales-Martinez, Luis M. Lozano-Sanchez, Oscar Martínez-Romero, Jesús Puente-Córdova, Emmanuel Segura-Cárdenas, and Alex Elías-Zúñiga. 2017. "Experimental Investigation of the Magnetorheological Behavior of PDMS Elastomer Reinforced with Iron Micro/Nanoparticles" Polymers 9, no. 12: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120696
APA StylePalacios-Pineda, L. M., Perales-Martinez, I. A., Lozano-Sanchez, L. M., Martínez-Romero, O., Puente-Córdova, J., Segura-Cárdenas, E., & Elías-Zúñiga, A. (2017). Experimental Investigation of the Magnetorheological Behavior of PDMS Elastomer Reinforced with Iron Micro/Nanoparticles. Polymers, 9(12), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9120696