Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion by Bio-Inspired Catechol-Functionalized Soy Protein with Versatile Reactivity: Preparation of Fully Utilizable Soy-Based Film
Abstract
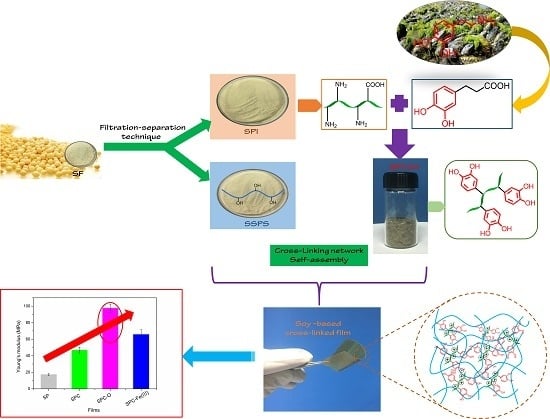
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Catechol-Conjugated SPI (SPI-CH)
2.3. Preparation of Soy-Based Composite Films with SPI-CH
2.4. Chemical Characterization of SPI-CH
2.5. Film Characterization
2.5.1. Preconditioning
2.5.2. Structural Characterization
2.5.3. Surface Contact Angles
2.5.4. Water Vapor Permeability
2.5.5. Water Solubility Testing
2.5.6. Mechanical Behavior Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Catechol-Conjugated SPI
3.2. Structural Analysis of Films Crosslinked under Different Conditions
3.3. Micromorphology of Soy-Based Composite Films
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Soy-Based Composite Films
3.5. Thermal Behavior of Soy-Based Composite Films
3.6. Water Resistance and Surface Hydrophobicity of Soy-Based Composite Films
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coltelli, M.-B.; Wild, F.; Bugnicourt, E.; Cinelli, P.; Lindner, M.; Schmid, M.; Weckel, V.; Müller, K.; Rodriguez, P.; Staebler, A.; et al. State of the art in the development and properties of protein-based films and coatings and their applicability to cellulose based products: An extensive review. Coatings 2015, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, R.R.; Mary, S.K.; Thomas, S.; Pothan, L.A. Environment friendly green composites based on soy protein isolate—A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 50, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-G.; Qi, X.-M.; Guan, Y.; Peng, F.; Yao, C.-L.; Sun, R.-C. High strength hemicellulose-based nanocomposite film for food packaging applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Long, Z.; Chen, J.; An, X.; Cheng, D.; Khan, A.; Ni, Y. Robust guar gum/cellulose nanofibrils multilayer films with good barrier properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5477–5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.K.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Pappu, A. Synthesis and applications of biodegradable soy based graft copolymers: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, J.; Wyrobnik, T.; Prinz, T.; Schmid, M. Physical, chemical and biochemical modifications of protein-based films and coatings: An extensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.R.; Netravali, A.N. Self-healing properties of protein resin with soy protein isolate-loaded poly(d,l-lactide-co-glycolide) microcapsules. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4786–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cai, S.; Sellers, A.; Yang, Y. Intrinsically water-stable electrospun three-dimensional ultrafine fibrous soy protein scaffolds for soft tissue engineering using adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15451–15457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Su, D.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Soy protein-based polyethylenimine hydrogel and its high selectivity for copper ion removal in wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4163–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, C.; Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, S.Q.; Cai, L. Soy protein isolate-based films reinforced by surface modified cellulose nanocrystal. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 80, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpiné, D.; Dagostin, J.L.A.; de Andrade, E.F.; Bertan, L.C.; Mafra, M.R. Effect of the natural surfactant yucca schidigera extract on the properties of biodegradable emulsified films produced from soy protein isolate and coconut oil. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 83, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol) and 1,2,3-propanetriol diglycidyl ether incorporated soy protein isolate-based films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. Physico-chemical properties improvement of soy protein isolate films through caffeic acid incorporation and tri-functional aziridine hybridization. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Yang, Y.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Robust soy protein films obtained by slight chemical modification of polypeptide chains. Polym. Chem. (UK) 2013, 4, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Shukry, N.; El-Gendy, A.; El-Sakhawy, M. Bioactive cellulose grafted soy protein isolate towards biomimetic calcium phosphate mineralization. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 95, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q. Development and application of nanoparticles synthesized with folic acid conjugated soy protein. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2013, 61, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeshin Lee, S.M.D.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.P.; Messersmith, P.B.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Waite, J.H. Mussel-inspired adhesives and coatings. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2011, 41, 99–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Kamperman, M. Jack of all trades: Versatile catechol crosslinking mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 8271–8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, K. Modification of soy protein for wood adhesives using mussel protein as a model: The influence of a mercapto group. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 1835–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Song, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. High-performance and fully renewable soy protein isolate-based film from microcrystalline cellulose via bio-inspired poly(dopamine) surface modification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Improvement of interfacial interactions using natural polyphenol-inspired tannic acid-coated nanoclay enhancement of soy protein isolate biofilms. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 401, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarbashi, D.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Noghabi, M.S.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Sedaghat, N.; Ramezani, M.; Shahabi-Ghahfarrokhi, I. Development of new active packaging film made from a soluble soybean polysaccharide incorporating ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Yao, P. Soy protein/soy polysaccharide complex nanogels: Folic acid loading, protection, and controlled delivery. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8636–8644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh Dastidar, T.; Netravali, A.N. A soy flour based thermoset resin without the use of any external crosslinker. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Reichert, K.; Hammann, F.; Stäbler, A. Storage time-dependent alteration of molecular interaction–property relationships of whey protein isolate-based films and coatings. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4396–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Li, J. Carbon nanoparticles/soy protein isolate bio-films with excellent mechanical and water barrier properties. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 82, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvarec, O.; Purushotham, S.; Masic, A.; Ramanujan, R.V.; Miserez, A. Catechol-functionalized chitosan/iron oxide nanoparticle composite inspired by mussel thread coating and squid beak interfacial chemistry. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10899–10906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Hong, S.; Lee, H. Bio-inspired adhesive catechol-conjugated chitosan for biomedical applications: A mini review. Acta Biomater. 2015, 27, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.; Fu, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, D.A. A mussel-inspired double-crosslinked tissue adhesive intended for internal medical use. Acta Biomater. 2016, 33, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Ni, K.; Wei, D.; Ren, Y. Fe3+-induced oxidation and coordination cross-linking in catechol–chitosan hydrogels under acidic pH conditions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37377–37384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Li, J. Preparation of cross-linked soy protein isolate-based environmentally-friendly films enhanced by PTGE and PAM. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 67, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.T.; Liu, L.L. Structural and functional properties of soy protein isolates modified by soy soluble polysaccharides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7275–7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Cui, S.W.; Gong, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Hua, Y. A soy protein-polysaccharides maillard reaction product enhanced the physical stability of oil-in-water emulsions containing citral. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 48, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammann, F.; Schmid, M. Determination and quantification of molecular interactions in protein films: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 7975–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Q. Bio-inspired hydrogen-bond cross-link strategy toward strong and tough polymeric materials. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3957–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Peng, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, H. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-tannic acid hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties and shape memory behaviors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27199–27206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Mussel-inspired injectable supramolecular and covalent bond crosslinked hydrogels with rapid self-healing and recovery properties via a facile approach under metal-free conditions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6644–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Shen, X.; Zhang, W.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Simultaneously strengthening and toughening soy protein isolate-based films using poly(ethylene glycol)-block-polystyrene (PEG-b-PS) nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83256–83263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Bai, H.; Dong, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, M. Superior performance of polyurethane based on natural melanin nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3782–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Su, C.; Zhang, X.; Yin, W.; Xu, J.; Yang, S. Reversible swelling-shrinking behavior of hydrogen-bonded free-standing thin film stabilized by catechol reaction. Langmuir 2015, 31, 5147–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Codes | SSPS (g) | Glycerol (g) | Water (g) | SPI-CH (g) | NaIO4 (g) | Fe(III) (g, 4%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | 5 | 2.5 | 95 | - | - | - |
| SPC | 5 | 2.5 | 95 | 0.4 | - | - |
| SPC-O | 5 | 2.5 | 95 | 0.4 | 0.005 | - |
| SPC-Fe(III) | 5 | 2.5 | 95 | 0.4 | - | 0.015 |
| Film Code | Thickness | Tensile strength | Elongation at break | Young’s modulus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm) | (MPa) | (%) | (MPa) | |
| SP | 0.233 (0.031) a | 2.80 (0.17) | 47.2 (0.48) | 17.24 (1.41) |
| SPC | 0.245 (0.024) | 3.04 (0.38) | 21.5 (0.93) | 46.60 (3.81) |
| SPC-O | 0.205 (0.009) | 4.04 (0.22) | 13.9 (0.47) | 97.22 (4.89) |
| SPC-Fe(III) | 0.217 (0.010) | 3.93 (0.31) | 21.4 (0.33) | 65.61 (5.71) |
| Curve | SP | SPC | SPC-O | SPC-Fe(III) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti a (°C) | 214.51 | 213.70 | 215.16 | 213.25 |
| Tmax b (°C) | 237.15 | 235.49 | 235.90 | 235.12 |
| Residual mass (wt %) at 550 °C | 27.76 | 27.54 | 28.18 | 28.08 |
| Film code | Total soluble matter | Water vapor permeability | Water contact angles |
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (×10−12 g·(cm·s·Pa)−1) | (°) | |
| SP | 92.35 (0.85) a | 9.83 (0.23) | 25.9 (3.8) |
| SPC | 74.63 (0.97) | 8.10 (0.31) | 44.7 (2.1) |
| SPC-O | 62.14 (1.04) | 6.74 (0.19) | 37.5 (1.3) |
| SPC-Fe(III) | 67.82 (0.65) | 7.32 (0.34) | 55.8 (0.9) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Kang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion by Bio-Inspired Catechol-Functionalized Soy Protein with Versatile Reactivity: Preparation of Fully Utilizable Soy-Based Film. Polymers 2017, 9, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030095
Wang Z, Kang H, Zhang W, Zhang S, Li J. Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion by Bio-Inspired Catechol-Functionalized Soy Protein with Versatile Reactivity: Preparation of Fully Utilizable Soy-Based Film. Polymers. 2017; 9(3):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhong, Haijiao Kang, Wei Zhang, Shifeng Zhang, and Jianzhang Li. 2017. "Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion by Bio-Inspired Catechol-Functionalized Soy Protein with Versatile Reactivity: Preparation of Fully Utilizable Soy-Based Film" Polymers 9, no. 3: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030095
APA StyleWang, Z., Kang, H., Zhang, W., Zhang, S., & Li, J. (2017). Improvement of Interfacial Adhesion by Bio-Inspired Catechol-Functionalized Soy Protein with Versatile Reactivity: Preparation of Fully Utilizable Soy-Based Film. Polymers, 9(3), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9030095