Tailoring Drug Release Properties by Gradual Changes in the Particle Engineering of Polysaccharide Chitosan Based Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Chitosan
2.3. Preparation of Powder Samples
2.3.1. Spray-Dried Microparticles
2.3.2. Powder Formulations
2.4. Morphology, Particle Size and Surface Area Analysis
2.5. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometry (FT-IR) Studies
2.7. Drug Loading Analysis
2.8. Drug Dissolution Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of Chitosan
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of Particles
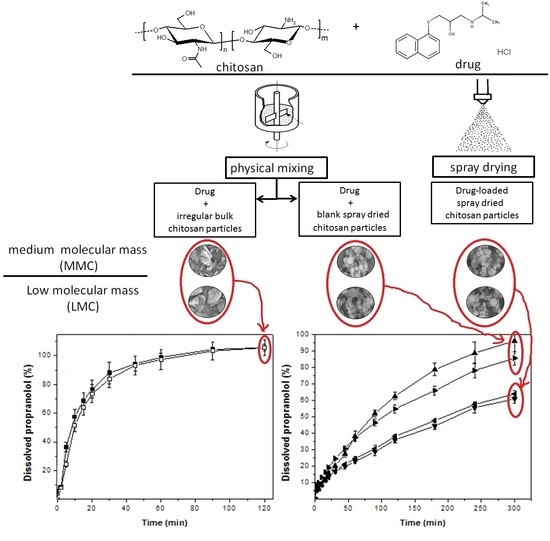
3.3. Drug Dissolution Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aider, M. Chitosan application for active bio-based films production and potential in the food industry: Review. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.-H.; Vo, T.-S.; Ngo, D.-N.; Kang, K.-H.; Je, J.-Y.; Pham, H.N.-D.; Byun, H.-G.; Kim, S.-K. Biological effects of chitosan and its derivatives. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, V.G.; Heinämäki, J.; Antikainen, O.; Revoredo, O.B.; Colarte, A.I.; Nieto, O.M.; Yliruusi, J. Direct compression properties of chitin and chitosan. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, O.; Garcia, M.A.; Villar, M.A.; Gentili, A.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Albertengo, L. Thermo-compression of biodegradable thermoplastic corn starch films containing chitin and chitosan. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hadinoto, K. A highly sustainable and versatile granulation method of nanodrugs via their electrostatic adsorption onto chitosan microparticles as the granulation substrates. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phaechamud, T.; Darunkaisorn, W. Drug release behavior of polymeric matrix filled in capsule. Saudi Pharm. J. 2016, 24, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinoviadou, K.G.; Scholten, E.; Moschakis, T.; Biliaderis, C.G. Engineering interfacial properties by anionic surfactant-chitosan complexes to improve stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, C. Pickering emulsions stabilized by the complex of polystyrene particles and chitosan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 482, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popat, A.; Karmakar, S.; Jambhrunkar, S.; Xu, C.; Yu, C. Curcumin-cyclodextrin encapsulated chitosan nanoconjugates with enhanced solubility and cell cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B. Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwerfalli, A.M.; Al-Kinani, A.; Alany, R.G.; ElShaer, A. Nano-engineering chitosan particles to sustain the release of promethazine from orodispersables. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, M.; Jeon, U.J.; Ubaidulla, U.; Hemalatha, P.; Saravanakumar, A.; Peng, M.M.; Jang, H.T. Chitosan cocrystals embedded alginate beads for enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of aceclofenac. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Nardecchia, S.; Amaral, I.F.; Barbosa, M.A.; Martins, M.C.L. Modulation of stability and mucoadhesive properties of chitosan microspheres for therapeutic gastric application. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, A.M.J.; Indana, V.L.; Kumar, J. Chronotherapeutic drug delivery of Tamarind gum, chitosan and okra gum controlled release colon targeted directly compressed propranolol HCl matrix tablets and in vitro evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, N.; Shahbazi, M.-A.; Araújo, F.; Zhang, H.; Mäkilä, E.M.; Kauppila, J.; Sarmento, B.; Salonen, J.J.; Hirvonen, J.T.; Santos, H.A. Chitosan-modified porous silicon microparticles for enhanced permeability of insulin across intestinal cell monolayers. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7172–7179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapola, N.S.; Lyyra, M.L.; Kolehmainen, R.M.; Sarkkinen, E.S.; Schauss, A.G. Safety aspects and cholesterol-lowering efficacy of chitosan tablets. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2008, 27, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldrick, P. The safety of chitosan as a pharmaceutical excipient. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 56, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomathi, T.; Govindarajan, C.; Rose, H.R.M.H.; Sudha, P.N.; Imran, P.K.M.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K. Studies on drug-polymer interaction, in vitro release and cytotoxicity from chitosan particles excipient. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 468, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diop, M.; Auberval, N.; Viciglio, A.; Langlois, A.; Bietiger, W.; Mura, C.; Peronet, C.; Bekel, A.; Julien David, D.; Zhao, M.; et al. Design, characterisation, and bioefficiency of insulin-chitosan nanoparticles after stabilisation by freeze-drying or cross-linking. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 491, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prata, A.S.; Grosso, C.R.F. Production of microparticles with gelatin and chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 116, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnchanajindanun, J.; Srisa-ard, M.; Baimark, Y. Genipin-cross-linked chitosan microspheres prepared by a water-in-oil emulsion solvent diffusion method for protein delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Jiang, H.; Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Silver/chitosan-based Janus particles: Synthesis, characterization, and assessment of antimicrobial activity in vivo and vitro. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, J.J.; De Sousa, F.B.; Mundim, I.M.; Bonfim, R.R.; Melo, R.; Viana, A.F.; Stolz, E.D.; Borsoi, M.; Rates, S.M.K.; Sinisterra, R.D. Double continuous injection preparation method of cyclodextrin inclusion compounds by spray drying. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Tiwary, A.K.; Rana, V. Spray dried chitosan-EDTA superior microparticles as solid substrate for the oral delivery of amphotericin B. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.D. Potential aspects of chitosan as pharmaceutical excipient. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2011, 68, 619–622. [Google Scholar]
- Szymańska, E.; Winnicka, K. Stability of chitosan—A challenge for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1819–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaai, M.R. Calculation of Mark-Houwink-Sakurada (MHS) equation viscometric constants for chitosan in any solvent-temperature system using experimental reported viscometric constants data. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, L.; Morin, F.G.; Marchessault, R.H. Degree of deacetylation of chitosan using conductometric titration and solid-state NMR. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 246, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, P.C.; Oliveira, A.R.; Pedrosa, M.F.F.; De Oliveira, A.G.; Da Silva-Júnior, A.A. Physicochemical aspects involved in methotrexate release kinetics from biodegradable spray-dried chitosan microparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2015, 81, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmacopeia Brasileira, 5th ed.; ANVISA: Brasília, Brazil, 2010. (In Portuguese)
- Dos Santos, Z.M.; Caroni, A.L.P.F.; Pereira, M.R.; da Silva, D.R.; Fonseca, J.L.C. Determination of deacetylation degree of chitosan: A comparison between conductometric titration and CHN elemental analysis. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2591–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cal, K.; Sollohub, K. Spray drying technique. I: Hardware and process parameters. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvim, I.D.; Stein, M.A.; Koury, I.P.; Dantas, F.B.H.; Cruz, C.L.d.C.V. Comparison between the spray drying and spray chilling microparticles contain ascorbic acid in a baked product application. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, L.; Grimaldi, R.; Sartori, T.; Menegalli, F.C.; Hubinger, M.D. Gallic acid microparticles produced by spray chilling technique: Production and characterization. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, F.; Giovagnoli, S.; Schoubben, A.; Blasi, P.; Rossi, C.; Ricci, M. Development of a spray-drying method for the formulation of respirable microparticles containing ofloxacin-palladium complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 440, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Qadi, S.; Grenha, A.; Carrión-Recio, D.; Seijo, B.; Remuñán-López, C. Microencapsulated chitosan nanoparticles for pulmonary protein delivery: In vivo evaluation of insulin-loaded formulations. J. Control. Release 2012, 157, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kašpar, O.; Jakubec, M.; Štěpánek, F. Characterization of spray dried chitosan—TPP microparticles formed by two- and three-fluid nozzles. Powder Technol. 2013, 240, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kašpar, O.; Tokárová, V.; Nyanhongo, G.S.; Gübitz, G.; Štěpánek, F. Effect of cross-linking method on the activity of spray-dried chitosan microparticles with immobilized laccase. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.V. Otimiza çã o dos par â metros de secagem por aspers ã o de micropart í culas de quitosana como carreadores de insulina. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2003, 22, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.-C.; Hon, M.-H. The effect of the degree of deacetylation of chitosan nanoparticles and its characterization and encapsulation efficiency on drug delivery. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mys, N.; Verberckmoes, A.; Cardon, L. Processing of syndiotactic polystyrene to microspheres for part manufacturing through selective laser sintering. Polymers (Basel) 2016, 8, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mys, N.; Van De Sande, R.; Verberckmoes, A.; Cardon, L. Processing of polysulfone to free flowing powder by mechanical milling and spray drying techniques for use in selective laser sintering. Polymers (Basel) 2016, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Shan, C.-L.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Y.-L.; Xu, F.; Han, L.-R.; Ibrahim, M.; Guo, L.-B.; Xie, G.-L.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial activity of cross-linked chitosan-glutaraldehyde. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1534–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Han, Z.; Zeng, X.-A.; Xiong, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-J. Enhancing mechanical properties of chitosan films via modification with vanillin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolomei, M.; Bertocchi, P.; Cotta Ramusino, M.; Santucci, N.; Valvo, L. Physico-chemical characterisation of the modifications I and II of (R,S) propranolol hydrochloride: Solubility and dissolution studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 21, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florey, K. Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Gao, X.; Wu, W.D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, X.D. Aerosol-assisted fast formulating uniform pharmaceutical polymer microparticles with variable properties toward pH-sensitive controlled drug release. Polymers (Basel) 2016, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Burgaz, M.; García-Ochoa, B.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Chitosan-carboxymethylcellulose interpolymer complexes for gastric-specific delivery of clarithromycin. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 359, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragelle, H.; Vandermeulen, G.; Préat, V. Chitosan-based siRNA delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokoumetzidis, A.; Macheras, P. A century of dissolution research: From noyes and whitney to the biopharmaceutics classification system. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 321, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, K.A.; Tran, P.H.L. Modulation of particle size and molecular interactions by sonoprecipitation method for enhancing dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drug. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 24, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Samples | Powder (Composition) | Mass of Diluent (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| LMC | Low molecular mass chitosan | 76 |
| MMC | Medium molecular mass chitosan | 69 |
| CH | Chitin | 76 |
| MCC | Microcystalline celullose | 76 |
| Blank LMC-MPs | Microparticles of LMC | 76 |
| Blank MMC-MPs | Microparticles of MMC | 76 |
| PPHy LMC-MPs | Drug-loaded LMC-MPs | 116 * |
| PPHy MMC- MPs | Drug-loaded MMC-MPs | 116 * |
| Samples | Particle Size Analysis | BET Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D10 (μm) | D50 (μm) | D90 (μm) | Mean (μm) | SPAN | Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (Å) | |
| Blank LMC-MPs | 0.7 | 2.3 | 5.2 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 25.3 | 0.056 | 42.4 |
| Blank MMC-MPs | 1.4 | 3.5 | 5.8 | 3.5 | 1.3 | 25.8 | 0.059 | 39.7 |
| PPHy-LMC-MPs | 0.4 | 1.7 | 5.0 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 19.2 | 0.046 | 48.7 |
| PPHy-MMC-MPs | 1.4 | 3.4 | 5.8 | 3.4 | 1.3 | 43.5 | 0.098 | 37.5 |
| GROUPS | SAMPLES | Molecular Weight | Q30min ± SD (%) | f2 ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immediate release | LMC | 4.61 × 105 | 86.95 | 60.07 |
| MMC | 7.15 × 105 | 87.15 | ||
| CH | ND | 107.60 | - | |
| MCC | 3.6 × 103 * | 107.04 | ||
| Slow release | blank LMC-MPs | ND | 20.27 | 50.35 |
| blank MMC-MPs | ND | 24.58 | ||
| PPHy-LMC-MPs | ND | 16.95 | 77.98 | |
| PPHy-MMC-MPs | ND | 14.15 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Do Nascimento, E.G.; De Caland, L.B.; De Medeiros, A.S.A.; Fernandes-Pedrosa, M.F.; Soares-Sobrinho, J.L.; Dos Santos, K.S.C.R.; Da Silva-Júnior, A.A. Tailoring Drug Release Properties by Gradual Changes in the Particle Engineering of Polysaccharide Chitosan Based Powders. Polymers 2017, 9, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070253
Do Nascimento EG, De Caland LB, De Medeiros ASA, Fernandes-Pedrosa MF, Soares-Sobrinho JL, Dos Santos KSCR, Da Silva-Júnior AA. Tailoring Drug Release Properties by Gradual Changes in the Particle Engineering of Polysaccharide Chitosan Based Powders. Polymers. 2017; 9(7):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070253
Chicago/Turabian StyleDo Nascimento, Ednaldo G., Lilia B. De Caland, Arthur S.A. De Medeiros, Matheus F. Fernandes-Pedrosa, José L. Soares-Sobrinho, Kátia S.C.R. Dos Santos, and Arnóbio Antonio Da Silva-Júnior. 2017. "Tailoring Drug Release Properties by Gradual Changes in the Particle Engineering of Polysaccharide Chitosan Based Powders" Polymers 9, no. 7: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070253
APA StyleDo Nascimento, E. G., De Caland, L. B., De Medeiros, A. S. A., Fernandes-Pedrosa, M. F., Soares-Sobrinho, J. L., Dos Santos, K. S. C. R., & Da Silva-Júnior, A. A. (2017). Tailoring Drug Release Properties by Gradual Changes in the Particle Engineering of Polysaccharide Chitosan Based Powders. Polymers, 9(7), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9070253