Unlocking the Genetic Diversity within A Middle-East Panel of Durum Wheat Landraces for Adaptation to Semi-arid Climate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Core-Collection Genotyping
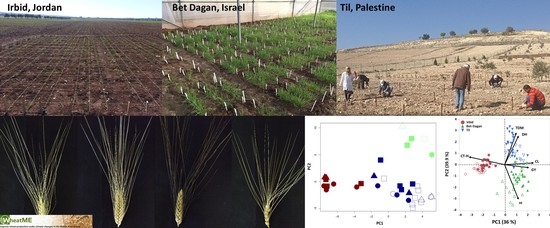
2.3. Experimental Design and Growth Conditions
2.4. Plant Characterization
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Characterization of the WheatME Core Collection
3.2. Genotypic Characterization of the WheatME Core-Collection
3.3. Multi-Site Agronomic Performance of the WheatME Core-Collection
3.4. Dissection of Genotype × Environment Interactions
3.5. Phenotypic Variation between Genetic Clusters
4. Discussion
4.1. Characterizing the Genetic Space of the WheatME Core-Collection
4.2. Multi-Site Agronomic Setup Results in a Stress Gradient and Expose Landraces Agronomic Variability
5. Conclusions and Application for Breeding
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cantrell, R.G. Breeding and genetics of durum wheat. Plant Breed. Rev. 1987, 5, 11–40. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, J.M.; Villegas, D.; Sorrells, M.E.; Royo, C. Durum wheat landraces from east and west regions of the Mediterranean basin are genetically distinct for yield components and phenology. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peleg, Z.; Fahima, T.; Krugman, T.; Abbo, S.; Yakir, D.; Korol, A.B.; Saranga, Y. Genomic dissection of drought resistance in durum wheat x wild emmer wheat recombinant inbreed line population. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 758–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecetti, L.; Annicchiarico, P.; Damania, A.B. Biodiversity in a germplasm collection of durum wheat. Euphytica 1992, 60, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, M.D.; Youssefien, S. Dwarfing genes in wheat. In Progress in Plant Breeding; Russell, G.E., Ed.; Butterworths and Co.: London, UK, 1985; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Flintham, J.E.; Börner, A.; Worland, A.J.; Gale, M.D. Optimizing wheat grain yield: Effects of Rht (gibberellin-insensitive) dwarfing genes. J. Agric. Sci. 1997, 128, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.; Dreccer, F.; Trethowan, R. Drought-adaptive traits derived from wheat wild relatives and landraces. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeven, A.C. Landraces: A review of definitions and classifications. Euphytica 1998, 104, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, K.L.; Perales, H.R. Evolutionary response of landraces to climate change in centers of crop diversity. Evol. Appl. 2010, 3, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nazco, R.; Villegas, D.; Ammar, K.; Peña, R.J.; Moragues, M.; Royo, C. Can Mediterranean durum wheat landraces contribute to improved grain quality attributes in modern cultivars? Euphytica 2012, 185, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbaj, H.; Sall, A.T.; Al-Abdallat, A.; Geleta, M.; Amri, A.; Filali-Maltouf, A.; Belkadi, B.; Ortiz, R.; Bassi, F.M. Genetic diversity within a global panel of durum wheat (Triticum durum) landraces and modern germplasm reveals the history of alleles exchange. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WheatME: Improve Wheat Production under Climate Changes in the Middle East Region. Available online: http://wheatme.wixsite.com/wheatme (accessed on 19 October 2018).
- The Durum Wheat Reference Collection KASP Markers (DWRC). Available online: http://www.cerealsdb.uk.net/cerealgenomics/CerealsDB/wheat_durum_ref.php (accessed on 19 October 2018).
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pask, A.J.D.; Pietragalla, J.; Mullan, D.M.; Reynolds, M.P. Physiological Breeding II: A Field Guide to Wheat Phenotyping; Cimmyt: Edo Mex, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: An R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. Ape: Analyses of phylogenetics and evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.S.; Binns, M.R. A superiority measure of cultivar performance for cultivar × location data. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1988, 68, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, R.; Amram, A.; Nashef, K. Genetic improvement of durum wheat establishment under fluctuating environmental conditions. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Genetics and Breeding of Durum Wheat; Porceddu, E., Qualset, C.O., Damania, A.B., Eds.; CIHEAM: Bari, Italy, 2014; Volume 110, pp. 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, A.; Golan, G.; Mayer, J.; Sinmena, B.; Shpiler, L.; Burra, J. The drought response of landraces of wheat from the northern Negev desert in Israel. Euphytica 1989, 43, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotlačil, L.; Hermuth, J.; Stehno, Z.; Dvořáček, V.; Bradová, J.; Leišová, L. How can wheat landraces contribute to present breeding? Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2010, 46, S70–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, S. Landraces: Importance and use in breeding and environmentally friendly agronomic system. In Agrobiodiversity Conservation: Securing the Diversity of Crop Wild Relatives and Landraces; Maxted, N., Ehsan Dulloo, M., Ford-Lloyd, B.V., Frese, L., Iriondo, J.M., Pinheiro de Carvalho, M.A.A., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, R.B.; Bingham, J.; Blackwell, R.D.; Evans, L.T.; Ford, M.A.; Morgan, C.L.; Taylor, M. Genetic improvements in winter wheat yields since 1900 and associated physiological changes. J. Agric. Sci. 1980, 94, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franking, S.; Srinivas, K.; Sela, S.; Goldberg, B.Z.; Mayzlish-Gati, E.; Ben-David, R. What’s in a landrace? A case study on the impact of conservation on intra-accession diversity and retention of genetic and phenotypic traits. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Wheat Landraces for Healthy Food Systems, Bologna, Italy, 13–15 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, G.C.; Rosegrant, M.W.; Koo, J.; Robertson, R.; Sulser, T.; Zhu, T.; Ringler, C.; Msangi, S.; Palazzo, A.; Batka, M.; et al. Climate Change: Impact on Agriculture and Costs of Adaptation; International Food Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- IPPC. Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC; IPPC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, S. Middle East faces a thirstier future. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenoweth, J.; Hadjinicolaou, P.; Bruggeman, A.; Lelieveld, J.; Levin, Z.; Lange, M.A.; Xoplaki, E.; Hadjikakou, M. Impact of climate change on the water resources of the eastern Mediterranean and Middle East region: Modeled 21st century changes and implications. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W06506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Trait | Type | Irbid | Bet-Dagan | Til | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SE | Range | CV | Mean ± SE | Range | CV | Mean ± SE | Range | CV | ||
| Chl (SPAD units) | MDC | 52.6 ± 0.4 | 9.1 | 4.9 | 48.6 ± 1.0 | 24.9 | 12.5 | 53.1 ± 0.8 | 21.9 | 9.8 |
| Landraces | 49.8 ± 0.6 | 20.2 | 9.6 | 46.3 ± 0.8 | 28.7 | 14.0 | 49.5 ± 0.8 | 31.4 | 13.0 | |
| CT-H (°C) | MDC | 29.3 ± 0.2 | 5.1 | 4.3 | 17.7 ± 0.2 | 4.8 | 8.2 | 20.8 ± 0.2 | 5.9 | 6.7 |
| Landraces | 29.3 ± 0.2 | 7.3 | 5.1 | 17.3 ± 0.1 | 5.0 | 6.3 | 21.5 ± 0.1 | 4.5 | 5.2 | |
| CT-M (°C) | MDC | 21.7 ± 0.3 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 31.0 ± 0.4 | 9.6 | 7.6 | 28.2 ± 0.3 | 7.6 | 5.6 |
| Landraces | 21.0 ± 0.2 | 6.3 | 7.0 | 30.2 ± 0.2 | 7.7 | 6.3 | 28.9 ± 0.2 | 9.3 | 6.3 | |
| DH (days) | MDC | 77.1 ± 0.5 | 13.0 | 3.8 | 79.2 ± 1.6 | 65.0 | 12.4 | 84.8 ± 1.1 | 29.0 | 8.2 |
| Landraces | 81.0 ± 0.5 | 23.0 | 5.4 | 83.5 ± 0.9 | 35.0 | 9.1 | 92.0 ± 0.9 | 21.0 | 8.3 | |
| CL (cm) | MDC | 53.1 ± 1.4 | 44.0 | 16.7 | 87.1 ± 3.2 | 77.0 | 22.7 | 75.4 ± 1.0 | 31.3 | 8.6 |
| Landraces | 69.0 ± 1.4 | 48.0 | 16.6 | 109.8 ± 2.7 | 88.0 | 20.4 | 91.8 ± 1.4 | 67.7 | 13.0 | |
| TDM (g) | MDC | 78.8 ± 3.3 | 111.8 | 26.4 | 57.6 ± 4.2 | 107.0 | 38.3 | 182.9 ± 4.8 | 215.7 | 16.4 |
| Landraces | 96.9 ± 2.2 | 104.2 | 19.1 | 81.2 ± 3.1 | 96.0 | 27.7 | 178.8 ± 1.9 | 107.6 | 8.8 | |
| GY (g) | MDC | 32.6 ± 1.8 | 49.6 | 34.5 | 48.9 ± 3.6 | 112.9 | 45.0 | 82.6 ± 2.9 | 67.9 | 22.1 |
| Landraces | 37.5 ± 1.1 | 48.1 | 24.2 | 52.3 ± 2.6 | 128.3 | 41.0 | 51.9 ± 2.6 | 100.4 | 41.2 | |
| TKW (g) | MDC | 36.2 ± 1.2 | 31.0 | 21.3 | 36.3 ± 1.3 | 53.3 | 22.9 | 40.1 ± 1.1 | 31.8 | 16.2 |
| Landraces | 39.8 ± 0.8 | 32.4 | 15.9 | 39.4 ± 0.8 | 30.6 | 17.2 | 40.1 ± 1.0 | 40.8 | 20.3 | |
| HI | MDC | 0.3 ± 0 | 0.1 | 11.8 | 0.5 ± 0 | 0.5 | 25.5 | 0.3 ± 0 | 0.3 | 17.0 |
| Landraces | 0.3 ± 0 | 0.1 | 10.7 | 0.4 ± 0 | 0.4 | 25.6 | 0.2 ± 0 | 0.4 | 34.2 | |
| Source of Variance | d.f. 1 | Mean Square | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl | CT-H | CT-M | DH | CL | TDM | GY | TKW | HI | ||
| Environment (E) | 2 | 490.5 *** | 3982.4 *** | 2586.1 *** | 2845.2 *** | 40233.1 *** | 33,0092.0 *** | 20,340.5 *** | 96.4 *** | 0.722 *** |
| Genotype (G) | 35 | 103.2 *** | 1.9 | 4.1 | 223.2 *** | 1636.2 *** | 918.9 *** | 1007.3 *** | 128.4 *** | 0.010 *** |
| G × E | 70 | 37.4 *** | 1.5 n.s. | 3.3 n.s. | 75.7 *** | 262.7 *** | 649.6 ** | 742.4 *** | 99.9 *** | 0.008 *** |
| R2 | 0.63 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.82 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Zaitoun, S.Y.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Assili, S.; Shtaya, M.J.; Jamous, R.M.; Mallah, O.B.; Nashef, K.; Sela, H.; Distelfeld, A.; Alhajaj, N.; et al. Unlocking the Genetic Diversity within A Middle-East Panel of Durum Wheat Landraces for Adaptation to Semi-arid Climate. Agronomy 2018, 8, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8100233
Abu-Zaitoun SY, Chandrasekhar K, Assili S, Shtaya MJ, Jamous RM, Mallah OB, Nashef K, Sela H, Distelfeld A, Alhajaj N, et al. Unlocking the Genetic Diversity within A Middle-East Panel of Durum Wheat Landraces for Adaptation to Semi-arid Climate. Agronomy. 2018; 8(10):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8100233
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Zaitoun, Salam Y., Kottakota Chandrasekhar, Siwar Assili, Munqez J. Shtaya, Rana M. Jamous, Omar B. Mallah, Kamal Nashef, Hanan Sela, Assaf Distelfeld, Nawal Alhajaj, and et al. 2018. "Unlocking the Genetic Diversity within A Middle-East Panel of Durum Wheat Landraces for Adaptation to Semi-arid Climate" Agronomy 8, no. 10: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8100233
APA StyleAbu-Zaitoun, S. Y., Chandrasekhar, K., Assili, S., Shtaya, M. J., Jamous, R. M., Mallah, O. B., Nashef, K., Sela, H., Distelfeld, A., Alhajaj, N., Ali-Shtayeh, M. S., Peleg, Z., & Ben-David, R. (2018). Unlocking the Genetic Diversity within A Middle-East Panel of Durum Wheat Landraces for Adaptation to Semi-arid Climate. Agronomy, 8(10), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy8100233