Separation of Coiled-Coil Structures in Lamin A/C Is Required for the Elongation of the Filament
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Construction
2.2. Purification of Recombinant Proteins
2.3. Pull-Down Assays
2.4. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
2.5. Circular Dichroism
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
3. Results
3.1. Mutations of Laminopathies Altered the eA22 Interaction
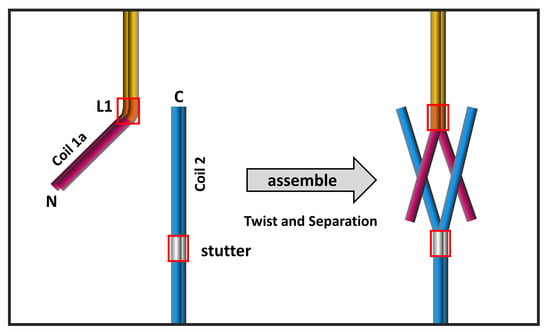
3.2. The eA22 Interaction Requires Separation of the Coiled-Coil Dimer in the Coil 1a Region
3.3. Leu38 and Leu42 at the N-Terminal End Region of Coil 1a Are Vital in the Interaction with the Coil 2 Region
3.4. The eA22 Interaction Requires Separation of Coiled-Coil Dimers in the C-Terminal Region of Coil 2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holaska, J.M.; Wilson, K.L.; Mansharamani, M. The nuclear envelope, lamins and nuclear assembly. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2002, 14, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Soler, R.I.; Moir, R.D.; Spann, T.P.; Stick, R.; Goldman, R.D. A role for nuclear lamins in nuclear envelope assembly. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuurman, N.; Heins, S.; Aebi, U. Nuclear Lamins: Their Structure, Assembly, and Interactions. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 122, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Troncoso, J.C.; Wade, J.B.; Monteiro, M.J. In vitro assembly properties of mutant and chimeric intermediate filament proteins: Insight into the function of sequences in the rod and end domains of IF. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 298, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, H.; Bär, H.; Kreplak, L.; Strelkovand, S.V.; Aebi, U. Intermediate filaments: From cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Häner, M.; Brettel, M.; Ku, N.-O.; Aebi, U. Characterization of distinct early assembly units of different intermediate filament proteins 1 1Edited by W. Baumeister. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 286, 1403–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.A.D.; Steinert, P.M. Intermediate filaments: Molecular architecture, assembly, dynamics and polymorphism. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1999, 32, 99–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.H.; Cohen, C.; Parry, D.A. Heptad Breaks in Alpha-Helical Coiled Coils: Stutters and Stammers. Proteins 1996, 26, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupas, A. Coiled coils: New structures and new functions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, P.; Stetefeld, J.; Strelkov, S.V. Coiled coils: A highly versatile protein folding motif. Trends Cell Biol. 2001, 11, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Strelkov, S.V. History and phylogeny of intermediate filaments: Now in insects. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, H.; Strelkov, S.V.; Feja, B.; Rogers, K.R.; Brettel, M.; Lustig, A.; Häner, M.; Parry, D.A.; Steinert, P.M.; Burkhard, P.; et al. The intermediate filament protein consensus motif of helix 2B: Its atomic structure and contribution to assembly. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 298, 817–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaffeld, M.; Herrmann, H.; Schultess, J.; Markl, J. Vimentin and desmin of a cartilaginous fish, the shark Scyliorhinus stellaris: Sequence, expression patterns and in vitro assembly. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 80, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouklis, P.D.; Traub, P.; Georgatos, S.D. Involvement of the consensus sequence motif at coil 2b in the assembly and stability of vimentin filaments. J. Cell Sci. 1992, 102, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldman, R.D.; Gruenbaum, Y.; Moir, R.D.; Shumaker, D.K.; Spann, T.P. Nuclear lamins: Building blocks of nuclear architecture. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hess, J.F.; Voss, J.C.; Fitzgerald, P.G. Real-time Observation of Coiled-coil Domains and Subunit Assembly in Intermediate Filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35516–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turgay, Y.; Eibauer, M.; Goldman, A.E.G.T.S.R.D.; Shimi, T.; Khayat, M.; Ben-Harush, K.; Dubrovsky-Gaupp, A.; Sapra, K.T.; Goldman, R.D.; Medalia, O. The molecular architecture of lamins in somatic cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 543, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahn, J.; Jo, I.; Kang, S.-M.; Hong, S.; Kim, S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, B.-J.; Ha, N.-C. Structural basis for lamin assembly at the molecular level. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyatina, A.A.; Guzenko, D.; Strelkov, S.V. Intermediate filament structure: The bottom-up approach. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.A. Hendecad repeat in segment 2A and linker L2 of intermediate filament chains implies the possibility of a right-handed coiled-coil structure. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 155, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, B.; Stewart, C.L. The nuclear lamins: Flexibility in function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chojnowski, A.; Ong, P.F.; Dreesen, O. Nuclear lamina remodelling and its implications for human disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2015, 360, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köster, S.; Weitz, D.A.; Goldman, R.D.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H. Intermediate filament mechanics in vitro and in the cell: From coiled coils to filaments, fibers and networks. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 32, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parry, D.A.; Strelkov, S.V.; Burkhard, P.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H. Towards a molecular description of intermediate filament structure and assembly. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2204–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilina, A.V.; Chernyatina, A.A.; Guzenko, D.; Strelkov, S.V. Lateral A11 type tetramerization in lamins. J. Struct. Biol. 2020, 209, 107404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalmans, G.; Lilina, A.V.; Vermeire, P.-J.; Fiala, J.; Novák, P.; Strelkov, S.V. Addressing the Molecular Mechanism of Longitudinal Lamin Assembly Using Chimeric Fusions. Cells 2020, 9, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarov, A.A.; Zou, J.; Houston, D.R.; Spanos, C.; Solovyova, A.S.; Cardenal-Peralta, C.; Rappsilber, J.; Schirmer, E.C. Lamin A molecular compression and sliding as mechanisms behind nucleoskeleton elasticity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butin-Israeli, V.; Adam, S.A.; Goldman, A.E.; Goldman, R.D. Nuclear lamin functions and disease. Trends Genet. 2012, 28, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmer, T.A.; Misteli, T. The lamin protein family. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Zhou, Z. Lamin A/C, laminopathies and premature ageing. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 747–763. [Google Scholar]
- Muchir, A.; Medioni, J.; Laluc, M.; Massart, C.; Arimura, T.; Van Der Kooi, A.J.; Desguerre, I.; Mayer, M.; Ferrer, X.; Briault, S.; et al. Nuclear envelope alterations in fibroblasts from patients with muscular dystrophy, cardiomyopathy, and partial lipodystrophy carrying lamin A/C gene mutations. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelot, A.; Worman, H.J.; Zinn-Justin, S. Protein structural and mechanistic basis of progeroid laminopathies. FEBS J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonne, G.; Mercuri, E.; Muchir, A.; Urtizberea, A.; Becane, H.M.; Recan, D.; Merlini, L.; Wehnert, M.; Boor, R.; Reuner, U.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Genetic Spectrum of Autosomal Dominant Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Due to Mutations of the Lamin a/C Gene. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, E.; Turner, L.; Zador, I.; Reynolds, K.; MacGregor, D.; Giampietro, P.F. Ovarian failure and dilated cardiomyopathy due to a novel lamin mutation. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part. A 2009, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vytopil, M.; Benedetti, S.; Ricci, E.; Galluzzi, G.; Russo, A.D.; Merlini, L.; Boriani, G.; Gallina, M.; Morandi, L.; Politano, L.; et al. Mutation analysis of the lamin A/C gene (LMNA) among patients with different cardiomuscular phenotypes. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 132e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanna, T.; Russo, A.D.; Toniolo, D.; Vytopil, M.; Pelargonio, G.; De Martino, G.; Ricci, E.; Silvestri, G.; Giglio, V.; Messano, L.; et al. Cardiac features of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy caused by lamin A/C gene mutations. Eur. Hear. J. 2003, 24, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.M.; Yoon, M.H.; Park, B.J. Laminopathies; Mutations on Single Gene and Various Human Genetic Diseases. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maraldi, N.; Squarzoni, S.; Sabatelli, P.; Capanni, C.; Mattioli, E.; Ognibene, A.; Lattanzi, G. Laminopathies: Involvement of structural nuclear proteins in the pathogenesis of an increasing number of human diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 203, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strelkov, S.V.; Schumacher, J.; Burkhard, P.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H. Crystal Structure of the Human Lamin A Coil 2B Dimer: Implications for the Head-to-tail Association of Nuclear Lamins. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.; Padilla, G.P.; Herrmann, H.; Wedig, T.; Hergt, M.; Patel, T.R.; Stetefeld, J.; Aebi, U.; Burkhard, P. Vimentin Coil 1A—A Molecular Switch Involved in the Initiation of Filament Elongation. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 390, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripet, B.; Wagschal, K.; Lavigne, P.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Effects of Side-Chain Characteristics on Stability and Oligomerization State of a De Novo-Designed Model Coiled-Coil: 20 Amino Acid Substitutions in Position “D”. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 300, 377–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.A.; Strelkov, S.V.; Burkhard, P.; Aebi, U.; Parry, D.A. Sequence Comparisons of Intermediate Filament Chains: Evidence of a Unique Functional/Structural Role for Coiled-Coil Segment 1A and Linker L1. J. Struct. Biol. 2002, 137, 128–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolet, S.; Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U.; Strelkov, S.V. Atomic structure of vimentin coil 2. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 170, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapinos, L.E.; Burkhard, P.; Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U.; Strelkov, S.V. Simultaneous Formation of Right- and Left-handed Anti-parallel Coiled-coil Interfaces by a Coil2 Fragment of Human Lamin A. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapinos, L.E.; Schumacher, J.; Mücke, N.; Machaidze, G.; Burkhard, P.; Aebi, U.; Strelkov, S.V.; Herrmann, H. Characterization of the Head-to-Tail Overlap Complexes Formed by Human Lamin A, B1 and B2 “Half-minilamin” Dimers. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 396, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePianto, D.; Coulombe, P.A. Intermediate filaments and tissue repair. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 301, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldie, K.N.; Wedig, T.; Mitra, A.K.; Aebi, U.; Herrmann, H.; Hoenger, A. Dissecting the 3-D structure of vimentin intermediate filaments by cryo-electron tomography. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 158, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, H.; Aebi, U. Intermediate Filaments: Molecular Structure, Assembly Mechanism, and Integration Into Functionally Distinct Intracellular Scaffolds. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 749–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.; Jeong, S.; Kang, S.-M.; Jo, I.; Park, B.-J.; Ha, N.-C. Separation of Coiled-Coil Structures in Lamin A/C Is Required for the Elongation of the Filament. Cells 2021, 10, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010055
Ahn J, Jeong S, Kang S-M, Jo I, Park B-J, Ha N-C. Separation of Coiled-Coil Structures in Lamin A/C Is Required for the Elongation of the Filament. Cells. 2021; 10(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Jinsook, Soyeon Jeong, So-Mi Kang, Inseong Jo, Bum-Joon Park, and Nam-Chul Ha. 2021. "Separation of Coiled-Coil Structures in Lamin A/C Is Required for the Elongation of the Filament" Cells 10, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010055
APA StyleAhn, J., Jeong, S., Kang, S. -M., Jo, I., Park, B. -J., & Ha, N. -C. (2021). Separation of Coiled-Coil Structures in Lamin A/C Is Required for the Elongation of the Filament. Cells, 10(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010055