Synthesis of Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (hBMP-2) in E. coli Periplasmic Space: Its Characterization and Preclinical Testing
Abstract
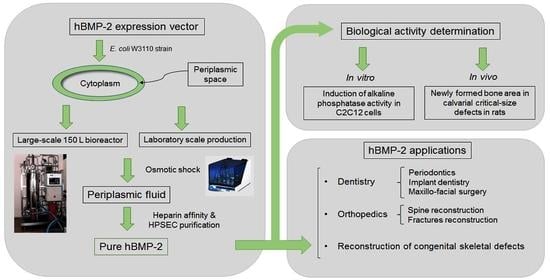
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Construction and Testing of the Expression Vector
2.2. Heparin Affinity and HPSEC Purification
2.3. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.4. Analytical Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
2.5. High-Performance Size-Exclusion Chromatography (HPSEC)
2.6. In Vitro hBMP-2 Bioassay in C2C12 Cells
2.7. Large-Scale Fermentation under Controlled Bioreactor Conditions
2.8. In Vivo Bioassay for the Determination of the Osteoinductive Potential by Treating Calvarial Critical-Size Defects in Rats
2.8.1. Surgical Procedure
2.8.2. Histological and Histometric Analyses
2.8.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression of hBMP-2 in the Periplasm
3.2. In Vitro Bioassay in C2C12 Cells
- (A)
- Y = 0.533X + 0.024 (n =4; r = 0.991; p < 0.01)
- (B)
- Y = 0.637X − 0.011 (n = 5; r = 0.997; p < 0.001)
- (C)
- Y = 0.659X + 0.038 (n = 5; r = 0.947; p < 0.02)
3.3. Fermentation of hBMP-2 in a Bioreactor
3.4. In Vivo Bioassay Based on Rat Calvarias Critical-Size Defect Treatment
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urist, M.R. Bone: Formation by autoinduction. Science 1965, 150, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urist, M.R.; Strates, B.S. The classic: Bone morphogenetic protein. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 3051–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strates, B.S.; Kirkpatrick, S.J.; Heffner, J.E.; Urist, M.R. Effect of chemical modification of tyrosine residues on bone morphogenesis. Biochem. J. 1971, 125, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddi, A.H.; Huggins, C.B. Citrate and alkaline phosphatase during transformation of fibroblasts by the matrix and minerals of bone. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1972, 140, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, T.K.; Reddi, A.H. Dissociative extraction and reconstitution of extracellular matrix components involved in local bone differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 7599–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sampath, T.K.; Muthukumaran, N.; Reddi, A.H. Isolation of osteogenin, an extracellular matrix-associated, bone-inductive protein, by heparin affinity chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7109–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheufler, C.; Sebald, W.; Hulsmeyer, M. Crystal structure of human bone morphogenetic protein-2 at 2.7 A resolution. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 287, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaas, B.; Burmeister, L.; Li, Z.P.; Nimtz, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Rinas, U. Properties of dimeric, disulfide-linked rhBMP-2 recovered from E. coli derived inclusion bodies by mild extraction or chaotropic solubilization and subsequent refolding. Process. Biochem. 2018, 67, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozney, J.M.; Rosen, V.; Celeste, A.J.; Mitsock, L.M.; Whitters, M.J.; Kriz, R.W.; Hewick, R.M.; Wang, E.A. Novel regulators of bone formation: Molecular clones and activities. Science 1988, 242, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, D.I.; Nove, J.; Kerns, K.M.; Moutsatsos, I.K.; Kaufman, R.J. Expression and characterization of bone morphogenetic protein-2 in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Growth Factors 1992, 7, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, S.D. Biology of lumbar spine fusion and use of bone graft substitutes: Present, future, and next generation. Tissue Eng. 2000, 6, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirker-Head, C.A. Potential applications and delivery strategies for bone morphogenetic proteins. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2000, 43, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, L.F.; Brokelmann, M.; Marten, S.; Trappe, S.; Cabrera-Crespo, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Gross, G.; Weich, H.A.; Rinas, U. Renaturation and purification of bone morphogenetic protein-2 produced as inclusion bodies in high-cell-density cultures of recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 94, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikesjo, U.M.; Qahash, M.; Huang, Y.H.; Xiropaidis, A.; Polimeni, G.; Susin, C. Bone morphogenetic proteins for periodontal and alveolar indications; biological observations—clinical implications. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2009, 12, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, R.M.; Susin, C.; Tamshiro, W.M.S.C.; de Souza, J.A.C.; Marcantonio, C.; Wilkesiö, U.M.; Pereira, L.A.V.D.; Marcantonio, E., Jr. Histological analysis and gene expression profile following augmentation of the anterior maxilla using rhBMP-2/ACS versus autogenous bone graft. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herford, A.S.; Boyne, P.J. Reconstruction of mandibular continuity defects with bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). J. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008, 66, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, B.P.; Ashley, R.K.; Wasson, K.L.; O’Hara, C.; Gabbay, J.; Heller, J.B.; Bradley, J.P. Reduced morbidity and improved healing with bone morphogenic protein-2 in older patients with alveolar cleft defects. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 121, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, F.R.; Bouazza-Marouf, K. Evaluation of bone strength: Correlation between measurements of bone mineral density and drilling force. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H J. Eng. Med. 2000, 214, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Even, J.; Eskander, M.; Kang, J. Bone morphogenetic protein in spine surgery: Current and future uses. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2012, 20, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, R.; Hoffmann, E.; Sebald, W. Human bone morphogenetic protein 2 contains a heparin-binding site which modifies its biological activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 237, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, K.; Konishi, Y.; Kaihara, S.; Fujimura, K.; Okubo, Y.; Iizuka, T. Bone induction by Escherichia coli -derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 compared with Chinese hamster ovary cell-derived recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 38, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Truong, L.; Bennett, K.; Phillips, A.; Wong-Staal, F.; Ma, H. Expression, purification, and renaturation of bone morphogenetic protein-2 from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 46, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Musgrave, D.; Pelinkovic, D.; Fukushima, K.; Cummins, J.; Usas, A.; Robbins, P.; Fu, F.H.; Huard, J. Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-2-expressing muscle-derived cells on healing of critical-sized bone defects in mice. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2001, 83, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, K.; Hoshino, M.; Ohta, Y.; Manaka, T.; Naka, Y.; Imai, Y.; Sebald, W.; Takaoka, K. Osteoinductive capacity and heat stability of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 produced by Escherichia coli and dimerized by biochemical processing. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2009, 27, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, Y.; Itoi, T.; Wakitani, S.; Irie, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Zhao, D.; Nezu, Y.; Yogo, T.; Hara, Y.; Tagawa, M. Effect of Escherichia coli-produced recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 on the regeneration of canine segmental ulnar defects. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2012, 30, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, E.M.; Yoon, J.; Chung, S.M.; Prasad, H.; Susin, C.; Wikesjö, U.M.E. Comparative study of Chinese hamster ovary cell versus Escherichia coli-derived Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 using the critical size supraalveolar peri-implant defect model. J. Periodont. 2013, 84, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.Z.; Zheng, G.B.; Lee, J.H. Escherichia coli BMP-2 showed comparable osteoinductivity with Chinese hamster ovary derived BMP-2 with demineralized bone matrix as carrier. Growth Factors. 2019, 37, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.F.; Arthuso, F.S.; Oliveira, J.E.; Oliveira, N.A.; Goulart, H.R.; Capone, M.V.; Ribela, M.T.; Bartolini, P.; Soares, C.R. Expression, purification, and characterization of authentic mouse prolactin obtained in Escherichia coli periplasmic space. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2012, 59, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids. Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, C.R.J.; Ueda, E.K.M.; Oliveira, T.L.; Gomide, F.I.C.; Heller, S.R.; Bartolini, P. Distinct human prolactin (hPRL) and growth hormone (hGH) behavior under bacteriophage lambda PL promoter control: Temperature plays a major role in protein yields. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 133, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.F.; Oliveira, J.E.; Damiani, R.; Lima, E.R.; Amaral, K.C.; Santos, A.M.S.; Magalhães, G.S.; Faverani, L.P.; Pereira, L.A.V.D.; Silva, F.M.; et al. Human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (hBMP-2) characterization by physical-chemical, immunological and biological assays. AMB Express 2020, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirsch, T.; Nickel, J.; Sebald, W. Isolation of recombinant BMP receptor IA ectodomain and its 2:1 complex with BMP-2. FEBS Lett. 2000, 468, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, E.B.; Carlsen, S. Production of recombinant human growth hormone in Escherichia coli: Expression of different precursors and physiological effects of glucose, acetate and salts. Biotech. Bioengin. 1990, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Improving bioscience research reporting: The ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Shirakata, Y.; Shinohara, Y.; Miron, R.J.; Hasegawa-Nakamura, K.; Fujioka-Kobayashi, M.; Noguchi, K. Comparison of the effects of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -9 on bone formation in rat calvarial critical-size defects. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 2671–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokovic, T.; Ivanjko, N.; Maticic, D.; Luyten, F.P.; Vukicevik, S. Bone morphogenetic proteins, carriers, and animal models in the development of novel bone regenerative therapies. Materials 2021, 14, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donos, N.; Lang, N.P.; Karoussis, I.K.; Bosshardt, D.; Tonetti, M.; Kostopoulos, L. Effect of GBR in combination with deproteinized bovine bone mineral and/or enamel matrix proteins on the healing of critical-size defects. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luvizuto, E.R.; Tangl, S.; Zanoni, G.; Okamoto, T.; Sonoda, C.K.; Gruber, R.; Okamoto, R. The effect of BMP-2 on the osteoconductive properties of β-tricalcium phosphate in rat calvaria defects. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3855–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Shirakata, Y.; Noguchi, K. Bone healing capabilities of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-9 (rhBMP-9) with a chitosan or collagen carrier in rat calvarial defects. Dent. Mater. J. 2016, 35, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vajgel, A.; Mardas, N.; Farias, B.C.; Petrie, A.; Cimões, R.; Donos, N. A systematic review on the critical size defect model. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaas, B.; Burmeister, L.; Li, Z.; Satalov, A.; Behrens, P.; Hoffmann, A.; Rinas, U. Stability and biological activity of E. coli-derived soluble and precipitated bone morphogenetic protein-2. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Purification Step | Total Protein * (µg/mL) | hBMP-2 (µg/mL) ** | Mass Fraction (%) | ALP Activity *** (A405) | ALP Specific Activity (A405/µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periplasmic fluid | 2196 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 1.149 | 0.5 × 10−3 |
| Heparin affinity | 220 | 14.13 | 6.42 | 2.792 | 12.7 × 10−3 |
| HPSEC | 1.6 | 1.29 | 80.62 | 1.006 | 629 × 10−3 |
| GenScript hBMP-2 | 5.00 | 3.70 | 74.00 | 3.2 | 640 × 10−3 |
| Specific Expression (µg/mL/A600) | Specific Expression MEAN ± SD | Final Biomass (A600) | Final Biomass MEAN ± SD | Volumetric Expression (mg/L) | Volumetric Expression MEAN ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.20 | 4.46 | 0.89 | |||
| 0.16 | 2.68 | 0.42 | |||
| 0.19 | 0.16 ± 0.05 | 6.08 | 4.25 ± 1.43 | 1.14 | 0.71 ± 0.37 |
| 0.10 | 3.76 | 0.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliveira, J.E.; Suzuki, M.F.; Damiani, R.; Lima, E.R.; Amaral, K.C.; Santos, A.M.S.; Magalhães, G.S.; Faverani, L.P.; Pereira, L.A.V.D.; Bartolini, P. Synthesis of Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (hBMP-2) in E. coli Periplasmic Space: Its Characterization and Preclinical Testing. Cells 2021, 10, 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123525
Oliveira JE, Suzuki MF, Damiani R, Lima ER, Amaral KC, Santos AMS, Magalhães GS, Faverani LP, Pereira LAVD, Bartolini P. Synthesis of Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (hBMP-2) in E. coli Periplasmic Space: Its Characterization and Preclinical Testing. Cells. 2021; 10(12):3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123525
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliveira, João E., Miriam F. Suzuki, Renata Damiani, Eliana R. Lima, Kleicy C. Amaral, Anderson M. S. Santos, Geraldo S. Magalhães, Leonardo P. Faverani, Luís A. V. D. Pereira, and Paolo Bartolini. 2021. "Synthesis of Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (hBMP-2) in E. coli Periplasmic Space: Its Characterization and Preclinical Testing" Cells 10, no. 12: 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123525
APA StyleOliveira, J. E., Suzuki, M. F., Damiani, R., Lima, E. R., Amaral, K. C., Santos, A. M. S., Magalhães, G. S., Faverani, L. P., Pereira, L. A. V. D., & Bartolini, P. (2021). Synthesis of Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (hBMP-2) in E. coli Periplasmic Space: Its Characterization and Preclinical Testing. Cells, 10(12), 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10123525