Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts
Abstract
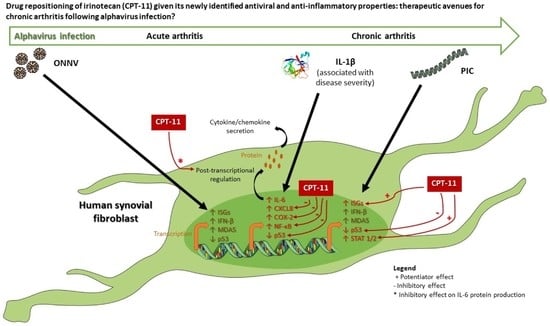
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. MTT Assay
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay (LDH Assay)
2.5. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marks, M.; Marks, J.L. Viral arthritis. Clin. Med. 2016, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, E.A.; Higgs, S. Impact of climate change and other factors on emerging arbovirus diseases. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.C.; Lecuit, M. Chikungunya virus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 93–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kurkela, S.; Manni, T.; Myllynen, J.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Clinical and laboratory manifestations of Sindbis virus infection: Prospective study, Finland, 2002–2003. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgherini, G.; Poubeau, P.; Jossaume, A.; Gouix, A.; Cotte, L.; Michault, A.; Arvin-Berod, C.; Paganin, F. Persistent arthralgia associated with chikungunya virus: A study of 88 adult patients on reunion island. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mostafavi, H.; Abeyratne, E.; Zaid, A.; Taylor, A. Arthritogenic alphavirus-induced immunopathology and targeting host inflammation as a therapeutic strategy for alphaviral disease. Viruses 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaaitanya, I.K.; Muruganandam, N.; Sundaram, S.G.; Kawalekar, O.; Sugunan, A.P.; Manimunda, S.P.; Ghosal, S.R.; Muthumani, K.; Vijayachari, P. Role of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in chronic arthropathy in CHIKV infection. Viral Immunol. 2011, 24, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuklia, W.; Kasisith, J.; Modhiran, N.; Rodpai, E.; Thannagith, M.; Thongsakulprasert, T.; Smith, D.R.; Ubol, S. Osteoclastogenesis induced by CHIKV-infected fibroblast-like synoviocytes: A possible interplay between synoviocytes and monocytes/macrophages in CHIKV-induced arthralgia/arthritis. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troost, B.; Mulder, L.M.; Diosa-Toro, M.; van de Pol, D.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A.; Smit, J.M. Tomatidine, a natural steroidal alkaloid shows antiviral activity towards chikungunya virus in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Liu, T.; Liu, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, S.; Yang, J. Anti-influenza a virus activity of dendrobine and its mechanism of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitby, K.; Pierson, T.C.; Geiss, B.; Lane, K.; Engle, M.; Zhou, Y.; Doms, R.W.; Diamond, M.S. Castanospermine, a potent inhibitor of dengue virus infection in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 8698–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bin Kang, K.; Ming, G.; Kim, G.J.; Ha, T.-K.-Q.; Choi, H.; Oh, W.K.; Sung, S.H. Jubanines F-J, cyclopeptide alkaloids from the roots of Ziziphus jujuba. Phytochemistry 2015, 119, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazis, P.; Han, Z.; Chatterjee, D.; Wyche, J. Water-insoluble camptothecin analogues as potential antiviral drugs. J. Biomed. Sci. 1999, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, D.C.; Avery, R.J.; Dimmock, N.J. Camptothecin: An inhibitor of influenza virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 1974, 25, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, R.P.; Stewart, R.A.; Hogan, P.A.; Ptak, R.G.; Mankowski, M.K.; Hartman, T.L.; Buckheit, R.W.; Snyder, B.A.; Salter, J.D.; Morales, G.A.; et al. An analog of camptothecin inactive against Topoisomerase I is broadly neutralizing of HIV-1 through inhibition of Vif-dependent APOBEC3G degradation. Antivir. Res. 2016, 136, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Veloso, A.; Biewen, B.; Paulsen, M.T.; Berg, N.; Lima, L.C.D.A.; Prasad, J.; Bedi, K.; Magnuson, B.; Wilson, T.E.; Ljungman, M. Genome-wide transcriptional effects of the anti-cancer agent camptothecin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C. Irinotecan: 25 years of cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 148, 104398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanLandingham, D.L.; Higgs, S.; Hong, C.; Klingler, K.A.; McElroy, K.L.; Lehane, M.J.; Tsetsarkin, K. Determinants of vector specificity of o’nyong nyong and chikungunya viruses in Anopheles and Aedes mosquitoes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 74, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idili, A.; Arroyo-Curras, N.; Ploense, K.L.; Csordas, A.T.; Kuwahara, M.; Kippin, T.E.; Plaxco, K.W. Seconds-resolved pharmacokinetic measurements of the chemotherapeutic irinotecan in situ in the living body. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 8164–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chabot, G.G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of irinotecan. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 33, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Gale, M., Jr. Differential recognition of double-stranded RNA by RIG-I-like receptors in antiviral immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polyak, K.; Xia, Y.; Zweier, J.L.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 1997, 389, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assuncão-Miranda, I.; Cruz-Oliveira, C.; Da Poian, A.T. Molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of alphavirus-induced arthritis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 973516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaral, J.K.; Taylor, P.C.; Teixeira, M.M.; Morrison, T.E.T.; Schoen, R.T. The clinical features, pathogenesis and methotrexate therapy of chronic chikungunya arthritis. Viruses 2019, 11, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georganas, C.; Liu, H.; Perlman, H.; Hoffmann, A.; Thimmapaya, B.; Pope, R.M. Regulation of IL-6 and IL-8 expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts: The dominant role for NF-kappa B but not C/EBP beta or c-Jun. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapoor, M.; Kojima, F.; Crofford, L. Arachidonic acid-derived eicosanoids in rheumatoid arthritis: Implications and future targets. Future Rheumatol. 2006, 1, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninla-Aesong, P.; Mitarnun, W.; Noipha, K. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines as biomarkers of persistent arthralgia and severe disease after chikungunya virus infection: A 5-year follow-up study in Southern Thailand. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Shi, J.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, D.; Tang, F.; Zhang, X.; et al. p53 predominantly regulates IL-6 production and suppresses synovial inflammation in fibroblast-like synoviocytes and adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suhrbier, A.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Gasque, P. Arthritogenic alphaviruses-an overview. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.; Gérardin, P.; Taylor, A.; Mostafavi, H.; Malvy, D.; Mahalingam, S. Review: Chikungunya arthritis: Implications of acute and chronic inflammation mechanisms on disease management. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoarau, J.J.; Jaffar Bandjee, M.C.; Krejbich Trotot, P.; Das, T.; Li-Pat-Yuen, G.; Dassa, B.; Denizot, M.; Guichard, E.; Ribera, A.; Henni, T.; et al. Persistent chronic inflammation and infection by Chikungunya arthritogenic alphavirus in spite of a robust host immune response. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5914–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bokarewa, M.; Tarkowski, A.; Lind, M.; Dahlberg, L.; Magnusson, M. Arthritogenic dsRNA is present in synovial fluid from rheumatoid arthritis patients with an erosive disease course. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoui, Y.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Selambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Gasque, P. Immunomodulatory drug methotrexate used to treat patients with chronic inflammatory rheumatisms post-chikungunya does not impair the synovial antiviral and bone repair responses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fros, J.J.; Pijlman, G.P. Alphavirus infection: Host cell shut-off and inhibition of antiviral responses. Viruses 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hummer, B.T.; Li, X.; Hassel, B.A. Camptothecin induces the ubiquitin-like protein, ISG15, and enhances ISG15 conjugation in response to interferon. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2004, 24, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferies, C.A. Regulating IRFs in IFN driven disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Type I interferon gene induction by the interferon regulatory factor family of transcription factors. Immunity 2006, 25, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dornan, D.; Eckert, M.; Wallace, M.; Shimizu, H.; Ramsay, E.; Hupp, T.R.; Ball, K.L. Interferon regulatory factor 1 binding to p300 stimulates DNA-dependent acetylation of p53. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 10083–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Chung, C.H. Interferon-stimulated gene 15 in the control of cellular responses to genotoxic stress. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Verma, U.N.; Gaynor, R.B.; Frenkel, E.P.; Becerra, C.R. Enhanced chemosensitivity to irinotecan by RNA interference-mediated down-regulation of the nuclear factor-kappaB p65 subunit. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3333–3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seo, S.H.; Kim, S.G.; Shin, J.H.; Ham, D.W.; Shin, E.H. Toxoplasma GRA16 inhibits NF-kappaB activation through PP2A-B55 upregulation in non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Gales, D.; Valenzuela, P.; Miller, S.; Yehualaeshet, T.; Manne, U.; Francia, G.; Samuel, T. Bromoethylindole (BEI-9) redirects NF-kB signaling induced by camptothecin and TNFα to promote cell death in colon cancer cells. Apoptosis 2017, 22, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Lou, W.-H.; Xu, X.-F.; Wu, W.; Rong, Y.-F.; Jin, D.-Y. SN38 increases IL-8 expression through the MAPK pathways in HCT8 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 39, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedlinger, T.; Bartkuhn, M.; Zimmermann, T.; Hake, S.B.; Nist, A.; Stiewe, T.; Kracht, M.; Schmitz, M.L. Chemotherapeutic drugs inhibiting topoisomerase 1 activity impede cytokine-induced and NF-kappaB p65-regulated gene expression. Cancers 2019, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ng, L.F.; Chow, A.; Sun, Y.J.; Kwek, D.J.; Lim, P.L.; Dimatatac, F.; Ng, L.C.; Ooi, E.E.; Choo, K.H.; Her, Z.; et al. IL-1β, IL-6, and RANTES as biomarkers of Chikungunya severity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, W.T.; Nassar, N.N.; Ravindra, D.; Li, X.; Meffert, M.K. Multi-level regulatory interactions between NF-kB and the pluripotency factor Lin28. Cells 2020, 9, 2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; VandenBoom, T.G., II; Kong, D.; Wang, Z.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7 by natural agents leads to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6704–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phuah, N.H.; Nagoor, N.H. Regulation of MicroRNAs by natural agents: New strategies in cancer therapies. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 804510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffet, C.; Catelli, M.-G.; Hecale-Perlemoine, K.; Bricaire, L.; Garcia, C.; Gallet-Dierick, A.; Rodriguez, S.; Cormier, F.; Groussin, L. Dual specificity phosphatase 5, a specific negative regulator of ERK signaling, is induced by serum response factor and Elk-1 transcription factor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kucharska, A.; Rushworth, L.K.; Staples, C.; Morrice, N.A.; Keyse, S.M. Regulation of the inducible nuclear dual-specificity phosphatase DUSP5 by ERK MAPK. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.; Cho, Y.C.; Ju, A.; Lee, S.; Park, B.C.; Park, S.G.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Cho, S. Dual-specificity phosphatase 5 acts as an anti-inflammatory regulator by inhibiting the ERK and NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibian, J.S.; Jefic, M.; Bagchi, R.A.; Lane, R.H.; McKnight, R.A.; McKinsey, T.A.; Morrison, R.F.; Ferguson, B.S. DUSP5 functions as a feedback regulator of TNFα-induced ERK1/2 dephosphorylation and inflammatory gene expression in adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; Kubota, Y.; Ishida, H.; Sasaki, Y. Irinotecan, a key chemotherapeutic drug for metastatic colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12234–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleiberg, H.; Cvitkovic, E. Characterisation and clinical management of CPT-11 (irinotecan)-induced adverse events: The European perspective. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, S18–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, D.; Lu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yao, X. Protective effect of curcumin against irinotecan-induced intestinal mucosal injury via attenuation of NFkappaB activation, oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weingart, J.D.; Thompson, R.C.; Tyler, B.; Colvin, O.M.; Brem, H. Local delivery of the topoisomerase I inhibitor camptothecin sodium prolongs survival in the rat intracranial 9L gliosarcoma model. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 62, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Gene Name | Sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| GAPDH_F (Forward) | TGTTCGTCATGGGTGTGAAC |
| GAPDH_R (Reverse) | GCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG |
| E1_F | CACCGTCCCCGTACGTAAAA |
| E1_R | GGCTCTGTAGGCTGATGCAA |
| nsP2_F | GCGGAGCAGGTAAAAACGTG |
| nsP2_R | TAGAACACGCCCGTCGTATG |
| ISG15_F | AGATCACCCAGAAGATCGGC |
| ISG15_R | GAGGTTCGTCGCATTTGTCC |
| IFN-β_F | GTTCGTGTTGTCAACATGACCAA |
| IFN-β_R | TCAATTGCCACAGGAGCTTCT |
| MDA5_F | CTGTTTACATTGCCAAGGATC |
| MDA5_R | ACACCAGCATCTTCTCCATTT |
| STAT1_F | TGGTGAAATTGCAAGAGCTG |
| STAT1_R | AGAGGTCGTCTCGAGGTCAA |
| p53_F | GAAGAGAATCTCCGCAAGAAAGG |
| p53_R | TCCATCCAGTGGTTTCTTCTTTG |
| ISG54_F | CTGGTCACCTGGGGAAACTA |
| ISG54_R | GAGCCTTCTCAAAGCACACC |
| OAS1_F | CATGCAAATCAACCATGCCA |
| OAS1_R | ACAACCAGGTCAGCGTCAGATC |
| PKR_F | GTGATGCAGCTCACAATGCT |
| PKR_R | GGCACTGTAAAATGGGTGCT |
| CXCL8_F | CAGAGACAGCAGAGCACACA |
| CXCL8_R | GGCAAAACTGCACCTTCACA |
| IL-6_F | TACAGGGAGAGGGAGCGATAA |
| IL-6_R | TGGACCGAAGGCGCTTGT |
| COX-2_F | TGGCTACAAAAGCTGGGAAG |
| COX-2_R | GGGGATCAGGGATGAACTTT |
| NFKB1_F | CCGGCCCGCCTGAATCATTCTC |
| NFKB1_R | CAGGTGGCGACCGTGATACCT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dobi, A.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Selambarom, J. Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2021, 10, 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431
Dobi A, Gasque P, Guiraud P, Selambarom J. Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431
Chicago/Turabian StyleDobi, Anthony, Philippe Gasque, Pascale Guiraud, and Jimmy Selambarom. 2021. "Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts" Cells 10, no. 6: 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431
APA StyleDobi, A., Gasque, P., Guiraud, P., & Selambarom, J. (2021). Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells, 10(6), 1431. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061431