Advanced Maternal Age Deteriorates the Developmental Competence of Vitrified Oocytes in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Oocyte Collection
2.3. Vitrification and Warming
2.4. Immunofluorescence Staining of Oocytes and Blastocysts
2.5. Oocyte Live Imaging Using a Confocal Microscope
2.6. Ultrastructural Observation of Oocytes Using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.7. Quantitative Analysis of Autophagosome Formation in Oocytes
2.8. IVF
2.9. Time-Lapse Monitoring of Embryo Morphokinetics
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. AMA Decreases the Total Number of Ovulated Oocytes and Accelerates Morphologic Abnormalities in Oocytes
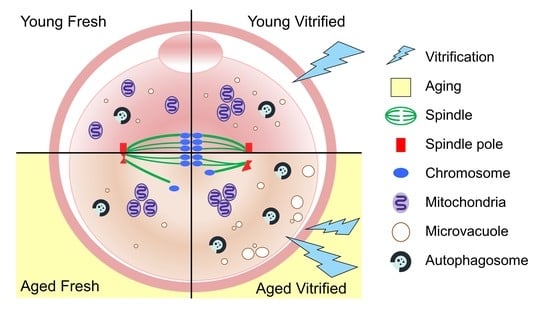
3.2. AMA, but Not Vitrification, Deteriorates the Spindle Structures of Metaphase Chromosomes in Oocytes
3.3. AMA and Vitrification Cause Abnormal Mitochondrial Aggregation in the Central Area of Oocytes
3.4. AMA Significantly Increased the Size of the Microvacuoles in VW Oocytes
3.5. AMA Deteriorates the Developmental Potential of VW Oocytes
3.6. Embryo Morphokinetics of AV Oocytes Were Significantly Retarded
3.7. AMA Was Associated with a Significant Reduction in the Cell Number of the Blastocysts from VW Oocytes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cobo, A.; García-Velasco, J.A.; Remohí, J.; Pellicer, A. Oocyte vitrification for fertility preservation for both medical and nonmedical reasons. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 115, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantazis, A.; Clark, S.J. A parsimonious characterization of change in global age-specific and total fertility rates. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ubaldi, F.M.; Cimadomo, D.; Vaiarelli, A.; Fabozzi, G.; Venturella, R.; Maggiulli, R.; Mazzilli, R.; Ferrero, S.; Palagiano, A.; Rienzi, L. Advanced maternal age in IVF: Still a challenge? The present and the future of its treatment. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimadomo, D.; Fabozzi, G.; Vaiarelli, A.; Ubaldi, N.; Ubaldi, F.M.; Rienzi, L. Impact of maternal age on oocyte and embryo competence. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnston, M.; Richings, N.M.; Leung, A.; Sakkas, D.; Catt, S. A major increase in oocyte cryopreservation cycles in the USA, Australia and New Zealand since 2010 is highlighted by younger women but a need for standardized data collection. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 36, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Nagi, J.; Kasaven, L.S.; Jones, B.P.; Saso, S.; Norris, G.; Green, J.; Petrie, A.; Odia, R.; Serhal, P.; Yasmin, E. Oocyte yield in social, medical and donor oocyte cryopreservation cycles. Hum. Fertil. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaven, L.; Jones, B.; Heath, C.; Odia, R.; Green, J.; Petrie, A.; Saso, S.; Serhal, P.; Ben-Nagi, J. Analysis of ten years of social oocyte cryopreservation: A research article. Authorea Prepr. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rall, W.F.; Fahy, G.M. Ice-free cryopreservation of mouse embryos at−196 C by vitrification. Nature 1985, 313, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iussig, B.; Maggiulli, R.; Fabozzi, G.; Bertelle, S.; Vaiarelli, A.; Cimadomo, D.; Ubaldi, F.M.; Rienzi, L. A brief history of oocyte cryopreservation: Arguments and facts. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2019, 98, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.-J.; Wang, D.-H.; Niu, X.-X.; Kong, X.-W.; Li, Y.-J.; Ren, J.; Zhou, H.-X.; Lu, A.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Liang, C.-G. High survival of mouse oocytes using an optimized vitrification protocol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, T.K.; Lee, D.R.; Cha, S.K.; Chung, H.M.; Lee, W.S.; Cha, K.Y. Survival rate of human oocytes and pregnancy outcome after vitrification using slush nitrogen in assisted reproductive technologies. Fertil. Steril. 2007, 88, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, S.; Boulet, S.L.; Kawwass, J.F.; Jamieson, D.J.; Kissin, D.M. Cryopreserved oocyte versus fresh oocyte assisted reproductive technology cycles, United States, 2013. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rienzi, L.; Cobo, A.; Paffoni, A.; Scarduelli, C.; Capalbo, A.; Vajta, G.; Remohi, J.; Ragni, G.; Ubaldi, F.M. Consistent and predictable delivery rates after oocyte vitrification: An observational longitudinal cohort multicentric study. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ubaldi, F.; Anniballo, R.; Romano, S.; Baroni, E.; Albricci, L.; Colamaria, S.; Capalbo, A.; Sapienza, F.; Vajta, G.; Rienzi, L. Cumulative ongoing pregnancy rate achieved with oocyte vitrification and cleavage stage transfer without embryo selection in a standard infertility program. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capalbo, A.; Hoffmann, E.R.; Cimadomo, D.; Maria Ubaldi, F.; Rienzi, L. Human female meiosis revised: New insights into the mechanisms of chromosome segregation and aneuploidies from advanced genomics and time-lapse imaging. Hum. Reprod. Update 2017, 23, 706–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nottola, S.; Coticchio, G.; Sciajno, R.; Gambardella, A.; Maione, M.; Scaravelli, G.; Bianchi, S.; Macchiarelli, G.; Borini, A. Ultrastructural markers of quality in human mature oocytes vitrified using cryoleaf and cryoloop. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2009, 19, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogessie, B.; Scheffler, K.; Schuh, M. Assembly and positioning of the oocyte meiotic spindle. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 34, 381–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Keilty, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chian, R. Mitochondria in oocyte aging: Current understanding. FactsViews Vis. ObGyn 2017, 9, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; ShiYang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, Z.; Xiong, B. Coenzyme Q10 ameliorates the quality of postovulatory aged oocytes by suppressing DNA damage and apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 143, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatone, C.; Di Emidio, G.; Barbaro, R.; Vento, M.; Ciriminna, R.; Artini, P.G. Effects of reproductive aging and postovulatory aging on the maintenance of biological competence after oocyte vitrification: Insights from the mouse model. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Suzuki, J.; Yu, X.; Kan, F.W.; Qiao, J.; Chian, R.-C. Cryo-survival, fertilization and early embryonic development of vitrified oocytes derived from mice of different reproductive age. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2010, 27, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Liang, Y.; Murphy, S.F.; Huang, A.; Shen, H.; Kelly, D.F.; Sobrado, P.; Sheng, Z. A rapid and high content assay that measures cyto-ID-stained autophagic compartments and estimates autophagy flux with potential clinical applications. Autophagy 2015, 11, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flurkey, K.; Currer, J.M.; Harrison, D. Mouse models in aging research. In The mouse in Biomedical Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 637–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saumet, J.; Petropanagos, A.; Buzaglo, K.; McMahon, E.; Warraich, G.; Mahutte, N. No. 356-egg freezing for age-related fertility decline. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2018, 40, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, D.; Goodwin, P.; Klein, N.; Soules, M. Fertilization and early embryology: Influence of maternal age on meiotic spindle assembly oocytes from naturally cycling women. Hum. Reprod. 1996, 11, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, E.; Jiang, Z.; Bondioli, K. 36 Extended culture after vitrification-warming helps in spindle recovery of bovine oocytes. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2020, 32, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.J.; Sohn, I.P.; Kwon, H.C.; Jo, D.H.; Park, Y.D.; Min, C.K. Characteristics of the cell membrane fluidity, actin fibers, and mitochondrial dysfunctions of frozen-thawed two-cell mouse embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2002, 61, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reader, K.L.; Stanton, J.-A.L.; Juengel, J.L. The role of oocyte organelles in determining developmental competence. Biology 2017, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, N.; Fujita, N.; Tsuruo, T. Mitochondrial aggregation precedes cytochrome c release from mitochondria during apoptosis. Oncogene 2003, 22, 5579–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, T.; Guo, N.; Tan, M.-h.; Li, Y.-f. Effect of mouse oocyte vitrification on mitochondrial membrane potential and distribution. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 2014, 34, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May-Panloup, P.; Boguenet, M.; Hachem, H.E.; Bouet, P.-E.; Reynier, P. Embryo and Its Mitochondria. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, A.; García-Velasco, J.A.; Coello, A.; Domingo, J.; Pellicer, A.; Remohí, J. Oocyte vitrification as an efficient option for elective fertility preservation. Fertil. Steril. 2016, 105, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Santis, L.; Nottola, S.A.; Coticchio, G.; Borini, A.; Iussig, B.; Miglietta, S.; Macchiarelli, G. Type of protein supplement in cryopreservation solutions impacts on the degree of ultrastructural damage in frozen-thawed human oocytes. Cryobiology 2020, 95, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, M.A.; Maione, M.; Palmerini, M.G.; Bianchi, S.; Macchiarelli, G.; Nottola, S.A. Ultrastructure of human mature oocytes after vitrification. Eur. J. Histochem. EJH 2012, 56, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuku, E.; Liu, J.; Downey, B.R. In vitro viability and ultrastructural changes in bovine oocytes treated with a vitrification solution. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1995, 40, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochi, S.; Kozawa, M.; Fujimoto, T.; Hondo, E.; Yamada, J.; Oguri, N. In VitroMaturation and Transmission Electron Microscopic Observation of Horse Oocytes after Vitrification. Cryobiology 1996, 33, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nottola, S.A.; Coticchio, G.; De Santis, L.; Macchiarelli, G.; Maione, M.; Bianchi, S.; Iaccarino, M.; Flamigni, C.; Borini, A. Ultrastructure of human mature oocytes after slow cooling cryopreservation with ethylene glycol. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2008, 17, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.E.; Martínez, O.E.; Vázquez-Nin, G. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural visualization of different routes of oocyte elimination in adult rats. Eur. J. Histochem. EJH 2012, 56, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Kuma, A.; Murakami, M.; Kishi, C.; Yamamoto, A.; Mizushima, N. Autophagy is essential for preimplantation development of mouse embryos. Science 2008, 321, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.; Shin, H.; Song, H.; Suh, C.S.; Lim, H.J. Autophagic activation in vitrified-warmed mouse oocytes. Reproduction 2014, 148, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conaghan, J. Time-lapse imaging of preimplantation embryos. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2014, 32, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S.; Saab, W.; Serhal, P. Time lapse imaging of embryos is useful in in vitro fertilisation (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) treatment: FOR: Time-lapse monitoring of embryos. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 126, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobo, A.; Coello, A.; Remohí, J.; Serrano, J.; de los Santos, J.M.; Meseguer, M. Effect of oocyte vitrification on embryo quality: Time-lapse analysis and morphokinetic evaluation. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 108, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, T.; Huang, C.; Huang, L.; Chen, C.; Lee, M.; Liu, J. Evaluation of mouse blastocyst implantation rate by morphology grading. Chin. J. Physiol. 2004, 47, 43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Zhang, L.; Tan, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Liu, G. Melatonin promotes the in vitro development of pronuclear embryos and increases the efficiency of blastocyst implantation in murine. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Richter, K.S.; Heitmann, R.J.; Graham, J.R.; Tucker, M.J.; DeCherney, A.H.; Browne, P.E.; Levens, E.D. Trophectoderm grade predicts outcomes of single-blastocyst transfers. Fertil. Steril. 2013, 99, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamatani, T.; Falco, G.; Carter, M.G.; Akutsu, H.; Stagg, C.A.; Sharov, A.A.; Dudekula, D.B.; VanBuren, V.; Ko, M.S. Age-associated alteration of gene expression patterns in mouse oocytes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarzer, C.; Siatkowski, M.; Pfeiffer, M.J.; Baeumer, N.; Drexler, H.; Wang, B.; Fuellen, G.; Boiani, M. Maternal age effect on mouse oocytes: New biological insight from proteomic analysis. Reproduction 2014, 148, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Park, J.K.; Yoon, S.Y.; Park, E.A.; Jun, J.H.; Lim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Song, H. Advanced Maternal Age Deteriorates the Developmental Competence of Vitrified Oocytes in Mice. Cells 2021, 10, 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061563
Lee JH, Park JK, Yoon SY, Park EA, Jun JH, Lim HJ, Kim J, Song H. Advanced Maternal Age Deteriorates the Developmental Competence of Vitrified Oocytes in Mice. Cells. 2021; 10(6):1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061563
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ju Hee, Jae Kyun Park, Sook Young Yoon, Eun A Park, Jin Hyun Jun, Hyunjung J. Lim, Jayeon Kim, and Haengseok Song. 2021. "Advanced Maternal Age Deteriorates the Developmental Competence of Vitrified Oocytes in Mice" Cells 10, no. 6: 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061563
APA StyleLee, J. H., Park, J. K., Yoon, S. Y., Park, E. A., Jun, J. H., Lim, H. J., Kim, J., & Song, H. (2021). Advanced Maternal Age Deteriorates the Developmental Competence of Vitrified Oocytes in Mice. Cells, 10(6), 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10061563