Protein Phosphatase 4 Is Required for Centrobin Function in DNA Damage Repair
Abstract
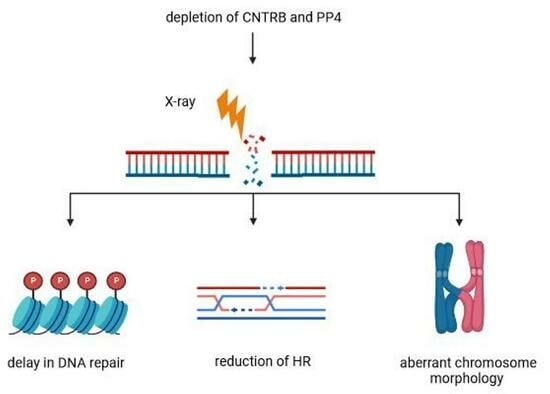
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DNA Constructs
2.2. Recombinant Protein Expression and Purification
2.3. In Vitro Pull-Down Assay
2.4. Cell Culture Maintenance
2.5. Co-Immunoprecipitation
2.6. Gene Silencing, Western Blotting, and qPCR
2.7. γH2AX Foci Quantitation Assay
2.8. EdU Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis of Data
2.10. DR-GFP Reporter Assay
2.11. Chromosome Preparation
2.12. Double Transfection of siRNAs and Transgenic Constructs
2.13. Immunofluorescence and Microscopy
2.14. Antibodies
2.15. Apoptosis Assay
3. Results
3.1. The R3 Subunit of PP4 Directly Binds to CNTRB through Its FRVP Motif
3.2. CNTRB and PP4 Co-Operate in DNA Damage Repair
3.3. Role of SQ and FRVP Motifs of CNTRB and Their Associated Phenotypes in the DNA Damage Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waterman, D.P.; Haber, J.E.; Smolka, M.B. Checkpoint Responses to DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 103–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Vugt, M.A.; Bràs, A.; Medema, R.H. Restarting the Cell Cycle When the Checkpoint Comes to a Halt. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7037–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, V.A.J.; Vega, I.A.-D.; Warmerdam, D.O. Chromatin regulators and their impact on DNA repair and G2 checkpoint recovery. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 2083–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítor, A.C.; Huertas, P.; Legube, G.; de Almeida, S.F. Studying DNA Double-Strand Break Repair: An Ever-Growing Toolbox. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, T.; Newman, S.; West, S.C. Aberrant chromosome morphology in human cells defective for Holliday junction resolution. Nature 2011, 471, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeggo, P.A.; Pearl, L.H.; Carr, A.M. DNA repair, genome stability and cancer: A historical perspective. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 16, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, M.; Conde, C. Phosphatases in Mitosis: Roles and Regulation. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar, A.; Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Ünsal-Kaçmaz, K.; Linn, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Mammalian DNA Repair and the DNA Damage Checkpoints. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlam-Babayov, S.; Ziv, Y.; Shiloh, Y. It takes three to the DNA damage response tango. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 8, 1881395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.L.; Southgate, H.; Tweddle, D.A.; Curtin, N.J. DNA damage checkpoint kinases in cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2020, 22, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, F.; Villoria, M.T.; Alonso-Rodríguez, E.; Clemente-Blanco, A. Role of protein phosphatases PP1, PP2A, PP4 and Cdc14 in the DNA damage response. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; Clemente-Blanco, A. Cell Cycle and DNA Repair Regulation in the Damage Response: Protein Phosphatases Take Over the Reins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.T.; Philp, A.; Vázquez-Martin, C. Protein phosphatase 4—From obscurity to vital functions. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 3278–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, D.-H. Functional roles of protein phosphatase 4 in multiple aspects of cellular physiology: A friend and a foe. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Pan, Y.; Kanner, S.; Sung, P.; Borowiec, J.A.; Chowdhury, D. A PP4 phosphatase complex dephosphorylates RPA2 to facilitate DNA repair via homologous recombination. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Adelmant, G.O.; Pan, Y.; Jeggo, P.A.; Marto, J.A.; Chowdhury, D. Phosphoproteomic analysis reveals that PP4 dephosphorylates KAP-1 impacting the DNA damage response. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Adelmant, G.; Marto, J.A.; Lee, D.-H. Dephosphorylation of DBC1 by Protein Phosphatase 4 Is Important for p53-Mediated Cellular Functions. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Acharya, S.S.; Kwon, M.; Drane, P.; Guan, Y.; Adelmant, G.; Kalev, P.; Shah, J.; Pellman, D.; Marto, J.A.; et al. Dephosphorylation Enables the Recruitment of 53BP1 to Double-Strand DNA Breaks. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, D.; Xu, X.; Zhong, X.; Ahmed, F.; Zhong, J.; Liao, J.; Dykxhoorn, D.M.; Weinstock, D.M.; Pfeifer, G.P.; Lieberman, J. Faculty Opinions recommendation of A PP4-phosphatase complex dephosphorylates gamma-H2AX generated during DNA replication. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villoria, M.T.; Gutiérrez-Escribano, P.; Alonso-Rodríguez, E.; Ramos, F.; Merino, E.; Campos, A.; Montoya, A.; Kramer, H.; Aragón, L.; Clemente-Blanco, A. PP4 phosphatase cooperates in recombinational DNA repair by enhancing double-strand break end resection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10706–10727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hustedt, N.; Seeber, A.; Sack, R.; Tsai-Pflugfelder, M.; Bhullar, B.; Vlaming, H.; van Leeuwen, F.; Guénolé, A.; van Attikum, H.; Srivas, R.; et al. Yeast PP4 Interacts with ATR Homolog ddc2-Mec1 and Regulates Checkpoint Signaling. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingras, A.-C.; Caballero, M.; Zarske, M.; Sanchez, A.; Hazbun, T.R.; Fields, S.; Sonenberg, N.; Hafen, E.; Raught, B.; Aebersold, R. A Novel, Evolutionarily Conserved Protein Phosphatase Complex Involved in Cisplatin Sensitivity. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinszki, Z.; Lefevre, S.; Savoian, M.S.; Singleton, M.R.; Glover, D.M.; Przewloka, M.R. Centromeric binding and activity of Protein Phosphatase 4. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa-Nunes, R.; Chia, W.; Somers, W.G. Protein phosphatase 4 mediates localization of the miranda complex during dro-sophila neuroblast asymmetric divisions. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Kim, H.-R.; Yamamoto, V.; Choi, S.H.; Wei, Z.; Joo, C.-K.; Lu, W. Protein Phosphatase 4 and Smek Complex Negatively Regulate Par3 and Promote Neuronal Differentiation of Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Han, B.K.; Guaderrama, M.; Aslanian, A.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Hunter, T.; Wittenberg, C. Psy2 targets the pp4 family phosphatase pph3 to dephosphorylate mth1 and repress glucose transporter gene expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, S.; Ma, H.; Burch, D.; Maciel, G.A.; Hunter, T.; Dillin, A. SMK-1, an Essential Regulator of DAF-16-Mediated Longevity. Cell 2006, 124, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, Y.; Kruse, T.; Weisser, M.B.; Sundell, G.N.; Larsen, M.S.Y.; Mendez, B.L.; Jenkins, N.P.; Garvanska, D.H.; Cressey, L.; Zhang, G.; et al. A Consensus Binding Motif for the PP4 Protein Phosphatase. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 953–964.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karman, Z.; Rethi-Nagy, Z.; Abraham, E.; Fabri-Ordogh, L.; Csonka, A.; Vilmos, P.; Debski, J.; Dadlez, M.; Glover, D.M.; Lipinszki, Z. Novel perspectives of target-binding by the evolutionarily conserved pp4 phosphatase. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras-Llort, M.; Medina-Giró, S.; Escudero-Ferruz, P.; Lipinszki, Z.; Moreno-Moreno, O.; Karman, Z.; Przewloka, M.R.; Azorín, F. A fraction of barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF) associates with centromeres and controls mitosis progression. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Li, J.; Bai, Y.; Gunning, W.T.; Wazer, D.E.; Band, V.; Gao, Q. Centrobin: A novel daughter centriole-associated protein that is required for centriole duplication. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 171, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudi, R.; Zou, C.; Li, J.; Gao, Q. Centrobin–tubulin interaction is required for centriole elongation and stability. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 193, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, J.M.; Urquhart, A.J.; Subramaniam, V.N.; Parton, R.G.; Khanna, K.K. Centrobin regulates the assembly of functional mitotic spindles. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Yoo, J.C.; Rhee, K. Characterization of NIP2/centrobin, a novel substrate of Nek2, and its potential role in microtubule stabilization. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 2106–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, Y.; Jeong, S.; Rhee, K. Centrobin/nip2 is a microtubule stabilizer whose activity is enhanced by plk1 phos-phorylation during mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 25476–25484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Rhee, K. NEK2 phosphorylation antagonizes the microtubule stabilizing activity of centrobin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 431, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Yu, N.K.; Kaang, B.K.; Rhee, K. The microtubule nucleation activity of centrobin in both the centrosome and cyto-plasm. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, S.; Ballif, B.A.; Smogorzewska, A.; McDonald, E.R., 3rd; Hurov, K.E.; Luo, J.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Zhao, Z.; Solimini, N.; Lerenthal, Y.; et al. Atm and atr substrate analysis reveals extensive protein networks responsive to DNA damage. Science 2007, 316, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, N.M.; Kim, J.M. Centrobin plays a role in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2660–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y. The small molecule CS1 inhibits mitosis and sister chromatid resolution in HeLa cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhard, D.S.; Wagner, L.; Feingold, E.A.; Shenmen, C.M.; Grouse, L.H.; Schuler, G.; Klein, S.L.; Old, S.; Rasooly, R.; Good, P.; et al. The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC). Genome Res. 2004, 14, 2121–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rethi-Nagy, Z.; Abraham, E.; Lipinszki, Z. Gst-ivtt pull-down: A fast and versatile in vitro method for validating and mapping protein-protein interactions. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinszki, Z.; Vernyik, V.; Farago, N.; Sari, T.; Puskas, L.G.; Blattner, F.R.; Posfai, G.; Gyorfy, Z. Enhancing the translational capacity of e. Coli by resolving the codon bias. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 2656–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, A.; Stark, J.M. I-scei-based assays to examine distinct repair outcomes of mammalian chromosomal double strand breaks. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 920, 379–391. [Google Scholar]
- Juhász, S.; Smith, R.; Schauer, T.; Spekhardt, D.; Mamar, H.; Zentout, S.; Chapuis, C.; Huet, S.; Timinszky, G. The chromatin remodeler ALC1 underlies resistance to PARP inhibitor treatment. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb8626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L. t-Test and ANOVA for data with ceiling and/or floor effects. Behav. Res. Methods 2021, 53, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogakou, E.P.; Pilch, D.R.; Orr, A.H.; Ivanova, V.S.; Bonner, W.M. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone h2ax phos-phorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 5858–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burma, S.; Chen, B.P.; Murphy, M.; Kurimasa, A.; Chen, D.J. Atm phosphorylates histone h2ax in response to DNA dou-ble-strand breaks. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42462–42467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeste, A.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O.; Kruhlak, M.J.; Pilch, D.R.; Staudt, D.W.; Lee, A.; Bonner, R.F.; Bonner, W.M.; Nussenzweig, A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation is dispensable for the initial recognition of DNA breaks. Nature 2003, 5, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C.R.; Ramnarain, D.; Horikoshi, N.; Iyengar, P.; Pandita, R.K.; Shay, J.W.; Pandita, T.K. Histone Modifications and DNA Double-Strand Break Repair after Exposure to Ionizing Radiations. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, A.E.; Jones, T.R.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Clarke, C.; Kang, I.H.; Friman, O.; Guertin, D.A.; Chang, J.H.; Lindquist, R.A.; Moffat, J.; et al. CellProfiler: Image analysis software for identifying and quantifying cell phenotypes. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M. Molecular Link between DNA Damage Response and Microtubule Dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, F.A.; Elliott, P.R.; Gruneberg, U. Protein phosphatases and the regulation of mitosis. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2323–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Archambault, V.; Kar, A.; Lio’, P.; D’Avino, P.P.; Sinka, R.; Lilley, K.; Laue, E.D.; Deak, P.; Capalbo, L.; et al. Multiple Protein Phosphatases Are Required for Mitosis in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helps, N.R.; Brewis, N.D.; Lineruth, K.; Davis, T.; Kaiser, K.; Cohen, P.T.W. Protein phosphatase 4 is an essential enzyme required for organisation of microtubules at centrosomes in Drosophila embryos. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Semenova, E.; Maric, D.; Craigie, R. Dephosphorylation of barrier-to-autointegration factor by protein phos-phatase 4 and its role in cell mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyo-oka, K.; Mori, D.; Yano, Y.; Shiota, M.; Iwao, H.; Goto, H.; Inagaki, M.; Hiraiwa, N.; Muramatsu, M.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; et al. Protein phosphatase 4 catalytic subunit regulates cdk1 activity and microtubule organization via ndel1 dephosphory-lation. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, H.; Simões, P.A.; Budrewicz, J.; Lara-Gonzalez, P.; Carvalho, A.X.; Dumont, J.; Desai, A.; Gassmann, R. Nuclear-enriched protein phosphatase 4 ensures outer kinetochore assembly prior to nuclear dissolution. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 222, e202208154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, V.; Li, J.; Emond-Fraser, V.; Larouche, M. Dephosphorylation in nuclear reassembly after mitosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1012768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.M.; Szyjka, S.J.; Lis, E.T.; Bailey, A.O.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Aparicio, O.M.; Romesberg, F.E. Pph3-psy2 is a phosphatase complex required for rad53 dephosphorylation and replication fork restart during recovery from DNA damage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9290–9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.C.; Kim, J.A.; Downey, M.; Fillingham, J.; Chowdhury, D.; Harrison, J.C.; Onishi, M.; Datta, N.; Galicia, S.; Emili, A.; et al. A phosphatase complex that dephosphorylates gammah2ax regulates DNA damage checkpoint recovery. Nature 2006, 439, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaltiel, I.A.; Aprelia, M.; Saurin, A.T.; Chowdhury, D.; Kops, G.J.P.L.; Voest, E.E.; Medema, R.H. Distinct phosphatases antagonize the p53 response in different phases of the cell cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7313–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Stamper, E.L.; Sato-Carlton, A.; Shimazoe, M.A.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Stevens, L.; Tam, K.C.J.; Dernburg, A.F.; Carlton, P.M. Phosphoregulation of dsb-1 mediates control of meiotic double-strand break activity. eLife 2022, 11, e77956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liang, L.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Li, D.; Cai, S. High expression of protein phosphatase 4 is associated with the aggressive malignant behavior of colorectal carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Maller, J.L. Serine/threonine phosphatases in the DNA damage response and cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5977–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, A.; Sun, L.; Zhong, X.; Zhong, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, M.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Liao, J.; et al. Protein phosphatase PP4 is overexpressed in human breast and lung tumors. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.M.; Byun, H.-J.; Kim, B.-R.; Lee, S.-H.; Trink, B.; Rho, S.B. Tumor suppressor BLU enhances pro-apoptotic activity of sMEK1 through physical interaction. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerit, D.A.; Poulton, J.S. Centrosomes are multifunctional regulators of genome stability. Chromosome Res. 2016, 24, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q. Centrosome, microtubule and DNA damage response. Genome Instab. Dis. 2022, 3, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Réthi-Nagy, Z.; Ábrahám, E.; Sinka, R.; Juhász, S.; Lipinszki, Z. Protein Phosphatase 4 Is Required for Centrobin Function in DNA Damage Repair. Cells 2023, 12, 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182219
Réthi-Nagy Z, Ábrahám E, Sinka R, Juhász S, Lipinszki Z. Protein Phosphatase 4 Is Required for Centrobin Function in DNA Damage Repair. Cells. 2023; 12(18):2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182219
Chicago/Turabian StyleRéthi-Nagy, Zsuzsánna, Edit Ábrahám, Rita Sinka, Szilvia Juhász, and Zoltán Lipinszki. 2023. "Protein Phosphatase 4 Is Required for Centrobin Function in DNA Damage Repair" Cells 12, no. 18: 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182219
APA StyleRéthi-Nagy, Z., Ábrahám, E., Sinka, R., Juhász, S., & Lipinszki, Z. (2023). Protein Phosphatase 4 Is Required for Centrobin Function in DNA Damage Repair. Cells, 12(18), 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12182219