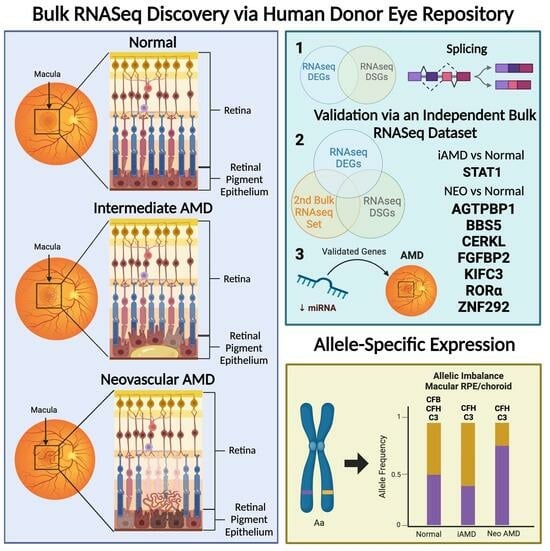
Patterns of Gene Expression, Splicing, and Allele-Specific Expression Vary among Macular Tissues and Clinical Stages of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Resource Availability
2.1. Lead Contact
2.2. Materials Availability
2.3. Data Availability
2.3.1. Processed Data
2.3.2. Donor Eye Tissue Repository
2.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction and RNA-Sequencing
2.5. Primary Processing of RNA Sequencing Data
2.6. Differential Gene Expression of Poly A Tail Sequencing and Splicing Analysis of Poly A Tail
2.7. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.8. Allele-Specific Expression (ASE)
2.9. Differential Expression Validation with Real-Time PCR
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression Differences
3.2. Gene Splicing Differences
3.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Using Our Normalized Expression Dataset
3.4. Analysis of DEGs and DSGs for Overlap with Genes Previously Associated with AMD
DEGs and DSGs: Normal Macular RPE/Choroid vs. Normal Macular Retina
3.5. DEGs: Macular RPE/Choroid Disease State Comparisons
3.6. DEGs: Macular Retina Disease State Comparisons
3.7. DSGs: Macular RPE/Choroid Disease State Comparisons
3.8. DSGs: Macular Retina Disease State Comparisons
4. Overlap of Differentially Expressed Genes and Differentially Spliced Genes
5. Validation of Overlapping DEGs and DSGs through Bulk RNAseq
6. Allele-Specific Expression (ASE) of Known AMD-Associated SNPs
7. Validation and Replication of RNAseq Findings
8. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Ung, C.; Lains, I.; Miller, J.W.; Kim, I.K. Current Management of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. In Age-Related Macular Degeneration; Chew, E.Y., Swaroop, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 295–314. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri, M.; Hassan, Y.; Vemana, P.P.S.B.; Pattanashetty, M.S.B.; Abdin, Z.U.; Siddiqui, H.F. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An Exponentially Emerging Imminent Threat of Visual Impairment and Irreversible Blindness. Cureus 2023, 15, e39624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachigian, L.M.; Liew, G.; Teo, K.Y.C.; Wong, T.Y.; Mitchell, P. Emerging therapeutic strategies for unmet need in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Ngo, W.K.; Chay, I.W.; Ting, D.S.; Sadda, S.R. Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration (nAMD): A Review of Emerging Treatment Options. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, G.S.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Quantitative assessment of retinal fluid in neovascular age-related macular degeneration under anti-VEGF therapy. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 14, 25158414221083363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. A randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of high-dose supplementation with vitamins C and E, beta carotene, and zinc for age-related macular degeneration and vision loss: AREDS report no. 8. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2001, 119, 1417–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, L.G.; Igl, W.; Bailey, J.N.C.; Grassmann, F.; Sengupta, S.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Burdon, K.P.; Hebbring, S.J.; Wen, C.; Gorski, M.; et al. A large genome-wide association study of age-related macular degeneration highlights contributions of rare and common variants. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnapriya, R.; Sosina, O.A.; Starostik, M.R.; Kwicklis, M.; Kapphahn, R.J.; Fritsche, L.G.; Walton, A.; Arvanitis, M.; Gieser, L.; Pietraszkiewicz, A.; et al. Retinal transcriptome and eQTL analyses identify genes associated with age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Grant, G.R.; Bowman, A.S.; Haider, N.; Gudiseva, H.V.; Chavali, V.R.M. Complete Transcriptome Profiling of Normal and Age-Related Macular Degeneration Eye Tissues Reveals Dysregulation of Anti-Sense Transcription. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.P.; Mulfaul, K.; Mullin, N.K.; Flamme-Wiese, M.J.; Giacalone, J.C.; Stone, E.M.; Tucker, B.A.; Scheetz, T.E.; Mullins, R.F. Single-cell transcriptomics of the human retinal pigment epithelium and choroid in health and macular degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24100–24107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.P.; Mullin, N.K.; Mulfaul, K.; Lozano, L.P.; Wiley, L.A.; Flamme-Wiese, M.J.; Boese, E.A.; Han, I.C.; Scheetz, T.E.; Stone, E.M.; et al. Choroidal endothelial and macrophage gene expression in atrophic and neovascular macular degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 31, 2406–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddala, M.S.; Lennikov, A.; Mukwaya, A.; Fan, L.; Hu, Z.; Huang, H. Transcriptome-wide analysis of differentially expressed chemokine receptors, SNPs, and SSRs in the age-related macular degeneration. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, L.; Owen, L.A.; Hofmann, J.; Stockwell, A.D.; Tao, J.; Haller, S.; Mukundan, V.T.; Clarke, C.; Lund, J.; Sridhar, A.; et al. A systems biology approach uncovers novel disease mechanisms in age-related macular degeneration. Cell Genom. 2023, 3, 100302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, L.D.; Chen, H.-H.; Cox, C.; Katschke, K.J.; Arceo, R.; Espiritu, C.; Caplazi, P.; Nghiem, S.S.; Chen, Y.-J.; Modrusan, Z.; et al. Integration of eQTL and a Single-Cell Atlas in the Human Eye Identifies Causal Genes for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1246–1259.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zauhar, R.; Biber, J.; Jabri, Y.; Kim, M.; Hu, J.; Kaplan, L.; Pfaller, A.M.; Schäfer, N.; Enzmann, V.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; et al. As in Real Estate, Location Matters: Cellular Expression of Complement Varies Between Macular and Peripheral Regions of the Retina and Supporting Tissues. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 895519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Zauhar, R.; Dana, N.; Strang, C.E.; Hu, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, S.; Pan, N.; Gamlin, P.; Kimble, J.A.; et al. Implication of specific retinal cell-type involvement and gene expression changes in AMD progression using integrative analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA-seq profiling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Fung-Leung, W.-P.; Bittner, A.; Ngo, K.; Liu, X. Comparison of RNA-Seq and Microarray in Transcriptome Profiling of Activated T Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e78644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, P.J.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. Long noncoding RNAs: Emerging stars in gene regulation, epigenetics and human disease. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1932–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, P.; Frigerio, C.S.; De Strooper, B. Variance in the identification of microRNAs deregulated in Alzheimer’s disease and possible role of lincRNAs in the pathology: The need of larger datasets. Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 17, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.; Papp, A.C.; Curtis, A.; Newman, L.C.; Pietrzak, M.; Seweryn, M.; Handelman, S.K.; Rempala, G.A.; Wang, D.; Graziosa, E.; et al. RNA sequencing of transcriptomes in human brain regions: Protein-coding and non-coding RNAs, isoforms and alleles. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, E.D.; Fernandez-Godino, R.; Kaczynksi, T.J.; Sousa, M.E.; Farkas, M.H. Characterization of lincRNA expression in the human retinal pigment epithelium and differentiated induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Wu, J.; Sun, H.; Briganti, F.; Meder, B.; Wei, W.; Steinmetz, L.M. Single-molecule, full-length transcript isoform sequencing reveals disease-associated RNA isoforms in cardiomyocytes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-C.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Chen, S.-Y.; Tseng, S.C. Wnt signaling induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition with proliferation in ARPE-19 cells upon loss of contact inhibition. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Manley, J.L. Mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation: Insights from molecular and genomics approaches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval-Castellanos, A.M.; Sandoval-Castellanos, A.; Bhargava, A.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J. Serine and arginine rich splicing factor 1: A potential target for neuroprotection and other diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Pérez, R.; Ramirez, J.M.; Ripoll-Cladellas, A.; Chazarra-Gil, R.; Oliveros, W.; Soldatkina, O.; Bosio, M.; Rognon, P.J.; Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Calvo, M.; et al. The landscape of expression and alternative splicing variation across human traits. Cell Genom. 2023, 3, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, M.A.; Silveira, A.C.; Huynh, N.; Jun, G.; Smith, S.E.; Zacharaki, F.; Sato, H.; Loomis, S.; Andreoli, M.T.; Adams, S.M.; et al. Systems biology-based analysis implicates a novel role for vitamin D metabolism in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Hum. Genom. 2011, 5, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.C.; Morrison, M.A.; Ji, F.; Xu, H.; Reinecke, J.B.; Adams, S.M.; Arneberg, T.M.; Janssian, M.; Lee, J.-E.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Convergence of linkage, gene expression and association data demonstrates the influence of the RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORA) gene on neovascular AMD: A systems biology based approach. Vis. Res. 2010, 50, 698–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, J.T.; Bowes Rickman, C.; Dick, A.D.; Gorin, M.B.; Miller, J.W.; Toth, C.A.; Ueffing, M.; Ueffing, M.; Farrer, L.A. A systems biology approach towards understanding and treating non-neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, U.; Li, K.; Mei, S.; Liu, G. Research progress in allele-specific expression and its regulatory mechanisms. J. Appl. Genet. 2013, 54, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.C.; Fan, J.-B.; Karikari, C.; Bibikova, M.; Garcia, E.W.; Zhou, L.; Barker, D.; Serre, D.; Feldmann, G.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Allele-specific expression in the germline of patients with familial pancreatic cancer: An unbiased approach to cancer gene discovery. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, E.; Shohat, S.; Shifman, S. Allelic expression analysis in the brain suggests a role for heterogeneous insults affecting epigenetic processes in autism spectrum disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4111–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Grupe, A.; Rowland, C.; Nowotny, P.; Kauwe, J.S.; Smemo, S.; Hinrichs, A.; Tacey, K.; Toombs, T.A.; Kwok, S.; et al. DAPK1 variants are associated with Alzheimer’s disease and allele-specific expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guda, K.; Natale, L.; Lutterbaugh, J.; Wiesner, G.L.; Lewis, S.; Tanner, S.M.; Tomsic, J.; Valle, L.; de la Chapelle, A.; Elston, R.C.; et al. Infrequent detection of germline allele-specific expression of TGFBR1 in lymphoblasts and tissues of colon cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4959–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle, L.; Serena-Acedo, T.; Liyanarachchi, S.; Hampel, H.; Comeras, I.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, H.-T.; Pennison, M.J.; Sadim, M.; et al. Germline allele-specific expression of TGFBR1 confers an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Science 2008, 321, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.-C.; Pérez-Tur, J.; Dupire, M.J.; Galasko, D.; Mann, D.; Amouyel, P.; Hardy, J.; Delacourte, A.; Chartier-Harlin, M.-C. Distortion of Allelic Expression of Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1997, 6, 2151–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, L.A.; Shakoor, A.; Morgan, D.J.; Hejazi, A.A.; McEntire, M.W.; Brown, J.J.; Farrer, L.A.; Kim, I.; Vitale, A.; DeAngelis, M.M. The Utah Protocol for Postmortem Eye Phenotyping and Molecular Biochemical Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Owen, L.; Shakoor, A.; Lillvis, J.L.; Zhang, C.; Farkas, M.; Kim, I.K.; Li, Y.; et al. A multi-omics atlas of the human retina at single-cell resolution. Cell Genom. 2023, 3, 100298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Dharmat, R.; Owen, L.; Shakoor, A.; Li, Y.; Kim, S.; Vitale, A.; Kim, I.; Morgan, D.; Liang, S.; et al. Single-nuclei RNA-seq on human retinal tissue provides improved transcriptome profiling. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lowe, A.; Dharmat, R.; Lee, S.; Owen, L.A.; Wang, J.; Shakoor, A.; Li, Y.; Morgan, D.J.; Hejazi, A.A.; et al. Generation, transcriptome profiling, and functional validation of cone-rich human retinal organoids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 10824–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Age-Related Eye Disease Study Research Group. The Age-Related Eye Disease Study system for classifying age-related macular degeneration from stereoscopic color fundus photographs: The Age-Related Eye Disease Study Report Number 6. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 132, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadley, W. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Goedhart, J.; Luijsterburg, M.S. VolcaNoseR is a web app for creating, exploring, labeling and sharing volcano plots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, C.W.; Chen, Y.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Voom: Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, E.; Bonneux, S.; Corneveaux, J.J.; Schrauwen, I.; Di Berardino, F.; White, C.H.; Ohmen, J.D.; Van de Heyning, P.; Ambrosetti, U.; Huentelman, M.J.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis demonstrates the highly polygenic character of age-related hearing impairment. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 23, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, B.R.; Voloudakis, G.; Igo Jr, R.P.; Kinzy, T.; Halladay, C.W.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Zeng, B.; Venkatesh, S.; Bailey, J.N.C.; Crawford, D.C.; et al. Distinctive cross-ancestry genetic architecture for age-related macular degeneration. medRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Schu, M.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Farrell, J.; Lunetta, K.L.; Jun, G.; Baldwin, C.T.; DeAngelis, M.M.; Farrer, L.A. Search for age-related macular degeneration risk variants in Alzheimer disease genes and pathways. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1510.e7–1510.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaumberg, D.A.; Chasman, D.; Morrison, M.A.; Adams, S.M.; Guo, Q.; Hunter, D.J.; Hankinson, S.E.; DeAngelis, M.M. Prospective study of common variants in the retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor α gene and risk of neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, G.; Nicolaou, M.; Morrison, M.A.; Buros, J.; Morgan, D.J.; Radeke, M.J.; Yonekawa, Y.; Tsironi, E.E.; Kotoula, M.G.; Zacharaki, F.; et al. Influence of ROBO1 and RORA on Risk of Age-Related Macular Degeneration Reveals Genetically Distinct Phenotypes in Disease Pathophysiology. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, I.E.; Willems, E.; Kersten, E.; Keizer-Garritsen, J.; Kragt, E.; Bakker, B.; Galesloot, T.E.; Hoyng, C.B.; Fauser, S.; van Gool, A.J.; et al. Semi-Quantitative Multiplex Profiling of the Complement System Identifies Associations of Complement Proteins with Genetic Variants and Metabolites in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasella, F.; Plössl, K.; Karl, C.; Weber, B.H.F.; Friedrich, U. Altered Protein Function Caused by AMD-associated Variant rs704 Links Vitronectin to Disease Pathology. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naj, A.C.; Scott, W.K.; Courtenay, M.D.; Cade, W.H.; Schwartz, S.G.; Kovach, J.L.; Agarwal, A.; Wang, G.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. Genetic factors in nonsmokers with age-related macular degeneration revealed through genome-wide gene-environment interaction analysis. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2013, 77, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, L.R.; Barber, G.P.; Benet-Pagès, A.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Cline, M.S.; Diekhans, M.; Fischer, C.; Gonzalez, J.N.; Hickey, G.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser database: 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1188–D1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.L.; Feehan, M.; Tak, C.; Owen, L.A.; Finley, R.C.; Cromwell, P.A.; Lillvis, J.H.; Hicks, P.M.; Au, E.; Farkas, M.H.; et al. Heritable Risk and Protective Genetic Components of Glaucoma Medication Non-Adherence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; Da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A web-based tool for the analysis of sets through Venn diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, S.E.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Banks, E.; Lappalainen, T. Tools and best practices for data processing in allelic expression analysis. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curcio, C.A.; Johnson, M.; Rudolf, M.; Huang, J.-D. The oil spill in ageing Bruch membrane. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, D.; Blackshaw, S.; Cepko, C.L.; Dryja, T.P. Profile of the genes expressed in the human peripheral retina, macula, and retinal pigment epithelium determined through serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Ishikawa, K.; Spee, C.; Mehta, H.H.; Wan, J.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. The Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide Humanin Protects RPE Cells from Oxidative Stress, Senescence, and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1238–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, L.A.; Morrison, M.A.; Ahn, J.; Woo, S.J.; Sato, H.; Robinson, R.; Morgan, D.J.; Zacharaki, F.; Simeonova, M.; Uehara, H.; et al. FLT1 genetic variation predisposes to neovascular AMD in ethnically diverse populations and alters systemic FLT1 expression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 3543–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutto, I.; Lutty, G. Understanding age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Relationships between the photoreceptor/retinal pigment epithelium/Bruch’s membrane/choriocapillaris complex. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Clark, M.E.; Crossman, D.K.; Kojima, K.; Messinger, J.D.; Mobley, J.A.; Curcio, C.A. Abundant Lipid and Protein Components of Drusen. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzottera, E.C.; Messinger, J.D.; Ach, T.; Smith, R.T.; Curcio, C.A. Subducted and melanotic cells in advanced age-related macular degeneration are derived from retinal pigment epithelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Lytvynchuk, L.; Ardan, T.; Studenovska, H.; Sharma, R.; Faura, G.; Eide, L.; Verma, R.S.; Znaor, L.; Erceg, S.; et al. Progress in Stem Cells-Based Replacement Therapy for Retinal Pigment Epithelium: In Vitro Differentiation to In Vivo Delivery. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2023, 12, 536–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.W.; Kondo, M.; Terasaki, H.; Lin, Y.; McCall, M.; Marc, R.E. Retinal remodeling. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 56, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Davila-Velderrain, J.; Goods, B.A.; Cadwell, T.D.; Xing, Y.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Shalek, A.K.; Love, J.C.; Kellis, M.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomic atlas of the human retina identifies cell types associated with age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, A.P.; Mullin, N.K.; Stone, E.M.; Tucker, B.A.; Scheetz, T.E.; Mullins, R.F. Single-cell RNA sequencing in vision research: Insights into human retinal health and disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 83, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, T.; Li, Y.I.; Wong, G.; Humphrey, J.; Wang, M.; Ramdhani, S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Ng, B.; Gupta, I.; Haroutunian, V.; et al. Integrative transcriptome analyses of the aging brain implicate altered splicing in Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nik, S.; Bowman, T.V. Bowman, Splicing and neurodegeneration: Insights and mechanisms. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2019, 10, e1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lareau, L.F.; Brooks, A.N.; Soergel, D.A.; Meng, Q.; Brenner, S.E. The coupling of alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 623, 190–211. [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Pai, A.A.; Gilad, Y.; Pritchard, J.K. Noisy Splicing Drives mRNA Isoform Diversity in Human Cells. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.T.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zheng, X.H.; Xie, T.H.; Wang, W.; Zou, J.; Li, Y.; Li, H.-Y.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Interferon-γ induces retinal pigment epithelial cell Ferroptosis by a JAK1-2/STAT1/SLC7A11 signaling pathway in Age-related Macular Degeneration. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 1968–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Lin, H.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, F.; Shi, J.; Yang, T.; Shi, X.; Guo, H.; Tan, X.; et al. The inhibitory effect of IFN-γ on protease HTRA1 expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, R.; Gunay-Aygun, M. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome Overview. In GeneReviews(®); Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Daich Varela, M.; Duignan, E.S.; De Silva, S.R.; Ba-Abbad, R.; Fujinami-Yokokawa, Y.; Leo, S.; Fujinami, K.; Mahroo, O.A.; Robson, A.G.; Webster, A.R.; et al. CERKL-Associated Retinal Dystrophy: Genetics, Phenotype, and Natural History. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2023, 7, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtel, J.; Eisenberger, T.; Gliem, M.; Müller, P.L.; Herrmann, P.; Betz, C.; Zahnleiter, D.; Neuhaus, C.; Lenzner, S.; Holz, F.G.; et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of 251 consecutive patients with macular and cone/cone-rod dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auslender, N.; Sharon, D.; Abbasi, A.H.; Garzozi, H.J.; Banin, E.; Ben-Yosef, T. A common founder mutation of CERKL underlies autosomal recessive retinal degeneration with early macular involvement among Yemenite Jews. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5431–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, E.; Bost-Usinger, L.; Burnside, B. Characterization of a novel C-kinesin (KIFC3) abundantly expressed in vertebrate retina and RPE. Exp. Eye Res. 1999, 69, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Gioia, S.A.; Farinelli, P.; Letteboer, S.J.; Arsenijevic, Y.; Sharon, D.; Roepman, R.; Rivolta, C. Interactome analysis reveals that FAM161A, deficient in recessive retinitis pigmentosa, is a component of the Golgi-centrosomal network. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3359–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltanás, F.C.; Berciano, M.T.; Santos, E.; Lafarga, M. The Childhood-Onset Neurodegeneration with Cerebellar Atrophy (CONDCA) Disease Caused by AGTPBP1 Gene Mutations: The Purkinje Cell Degeneration Mouse as an Animal Model for the Study of this Human Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, H.; Mannarino, M.; Pacis, A.S.; Ragoussis, J.; Rabau, O.; Ouellet, J.A.; Haglund, L. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis of Cells from Degenerating and Non-Degenerating Intervertebral Discs from the Same Individual Reveals New Biomarkers for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.H.; Shaver, A.; Sheehan, J.H.; Mallal, S.; Stone, J.H.; Pillai, S.; Bastarache, L.; Riebau, D.; Allard-Chamard, H.; Stone, W.M.; et al. IgG4-related disease: Association with a rare gene variant expressed in cytotoxic T cells. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuźma-Kozakiewicz, M.; Chudy, A.; Gajewska, B.; Dziewulska, D.; Usarek, E.; Barańczyk-Kuźma, A. Kinesin expression in the central nervous system of humans and transgenic hSOD1G93A mice with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 12, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goo, B.S.; Mun, D.J.; Kim, S.; Nhung, T.T.M.; Lee, S.B.; Woo, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Suh, B.K.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.-E.; et al. Schizophrenia-associated Mitotic Arrest Deficient-1 (MAD1) regulates the polarity of migrating neurons in the developing neocortex. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furney, S.J.; Simmons, A.; Breen, G.; Pedroso, I.; Lunnon, K.; Proitsi, P.; Hodges, A.; Powell, J.; Wahlund, L.-O.; Kloszewska, I.; et al. Genome-wide association with MRI atrophy measures as a quantitative trait locus for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey, C.A.B.; Larsen, L.J.; Tümer, Z.; Brøndum-Nielsen, K.; Grønskov, K.; Hjortshøj, T.D.; Møller, L.B. BBS Proteins affect Ciliogenesis and Are Essential for Hedgehog Signaling, but Not for Formation of iPSC-Derived RPE-65 Expressing RPE-like Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xue, K.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C. RORA Overexpression Alleviates Nasal Mucosal Injury and Enhances Red Blood Cell Immune Adhesion Function in a Mouse Model of Allergic Rhinitis via Inactivation of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 180, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Qiu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, W.; Gu, C.; Li, G.; Zhu, Y. Silencing of cZNF292 circular RNA suppresses human glioma tube formation via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63449–63455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeAngelis, M.M.; Owen, L.A.; Morrison, M.A.; Morgan, D.J.; Li, M.; Shakoor, A.; Vitale, A.; Iyengar, S.; Stambolian, D.; Kim, I.K.; et al. Genetics of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R45–R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Owen, L.A.; Lillvis, J.H.; Zhang, S.X.; Kim, I.K.; DeAngelis, M.M. AMD Genomics: Non-Coding RNAs as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berber, P.; Grassmann, F.; Kiel, C.; Weber, B.H.F. An Eye on Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The Role of MicroRNAs in Disease Pathology. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2017, 21, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, C.; Rezende, F.A.; Miloudi, K.; Wilson, A.; Tétreault, N.; Hardy, P.; SanGiovanni, J.P.; De Guire, V.; Sapieha, P. MicroRNA signatures in vitreous humour and plasma of patients with exudative AMD. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19171–19184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, G.L.; Platania, C.B.M.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S.; Ragusa, M.; Barbagallo, C.; Di Pietro, C.; Purrello, M.; Reibaldi, M.; Avitabile, T.; et al. Retinal and Circulating miRNAs in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An In vivo Animal and Human Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwińska, Z.; Sobuś, A.; Łuczkowska, K.; Grabowicz, A.; Mozolewska-Piotrowska, K.; Safranow, K.; Kawa, M.P.; Machaliński, B.; Machalińska, A. The Interplay Between Systemic Inflammatory Factors and MicroRNAs in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.M.; Zhao, Y.; Clement, C.; Neumann, D.M.; Lukiw, W.J. HSV-1 infection of human brain cells induces miRNA-146a and Alzheimer-type inflammatory signaling. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1500–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, J. MicroRNAs and their therapeutic potential for human diseases: Aberrant microRNA expression in Alzheimer’s disease brains. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 114, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Rau, C.S.; Jeng, S.F.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Wu, C.J.; Lu, T.-H.; Lu, C.-H.; Chang, W.-N. Identification of the potential target genes of microRNA-146a induced by PMA treatment in human microvascular endothelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1119–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nashine, S.; Cohen, P.; Chwa, M.; Lu, S.; Nesburn, A.B.; Kuppermann, B.D.; Kenney, M.C. Humanin G (HNG) protects age-related macular degeneration (AMD) transmitochondrial ARPE-19 cybrids from mitochondrial and cellular damage. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minasyan, L.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Hinton, D.R.; Kannan, R. Protective Mechanisms of the Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide Humanin in Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in RPE Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 1675230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Bakshi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Goddard, M.E.; Wray, N.R.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Integration of summary data from GWAS and eQTL studies predicts complex trait gene targets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, M. Linking GWAS to gene regulation. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguet, F.; Brown, A.A.; Castel, S.E.; Davis, J.R.; He, Y.; Jo, B.; Chiang, C. Genetic effects on gene expression across human tissues. Nature 2017, 550, 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zauhar, R.J.; Grazal, C.; Curcio, C.A.; DeAngelis, M.M.; Stambolian, D. RNA expression in human retina. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R68–R74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, P.N.; Guida, E.; Chu, D.T.; Vu, H.T.; Guymer, R.H. The ε2 and ε4 alleles of the apolipoprotein gene are associated with age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, O.; Lavalette, S.; Hu, S.J.; Housset, M.; Raoul, W.; Eandi, C.; Sahel, J.-A.; Sullivan, P.M.; Guillonneau, X.; Sennlaub, F. APOE Isoforms Control Pathogenic Subretinal Inflammation in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13568–13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Hoffmann, T.J.; Melles, R.B.; Sakoda, L.C.; Kvale, M.N.; Banda, Y.; Schaefer, C.; Risch, N.; Jorgenson, E. Differences in the Genetic Susceptibility to Age-Related Macular Degeneration Clinical Subtypes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 4290–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrer, L.A.; Cupples, L.A.; Haines, J.L.; Hyman, B.; Kukull, W.A.; Mayeux, R.; Myers, R.H.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Risch, N.; van Duijn, C.M. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 1997, 278, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Normal | |||||
| Group | N | Avg. RIN | Age (Range) | Males | Females |
| Macular RPE/Choroid (All Samples) | 12 | 6.66 | 74.0 (60–94) | 9 | 3 |
| Macular RPE/Choroid (Outliers Removed) | 9 | 6.93 | 74.2 (60–94) | 7 | 2 |
| Macular Retina (All Samples) | 12 | 6.65 | 74.0 (60–94) | 9 | 3 |
| Macular Retina (Outliers Removed) | 10 | 6.76 | 74.4 (60–94) | 8 | 2 |
| Intermediate AMD | |||||
| Group | N | Avg. RIN | Age (Range) | Males | Females |
| Macular RPE/Choroid (All Samples) | 10 | 6.70 | 76.0 (60–87) | 6 | 4 |
| Macular RPE/Choroid (Outliers Removed) | 9 | 6.76 | 75.0 (60–87) | 7 | 2 |
| Macular Retina (All Samples) | 10 | 6.89 | 76.0 (60–87) | 6 | 4 |
| Macular Retina (Outliers Removed) | 9 | 6.91 | 75.0 (60–87) | 6 | 3 |
| Neovascular AMD | |||||
| Group | N | Avg. RIN | Age (Range) | Males | Females |
| Macular RPE/Choroid (All Samples) | 5 | 7.06 | 83.4 (74–94) | 2 | 3 |
| Macular RPE/Choroid (Outliers Removed) | 5 | 7.06 | 83.4 (74–94) | 2 | 3 |
| Macular Retina (All Samples) | 5 | 6.70 | 83.4 (74–94) | 2 | 3 |
| Macular Retina (Outliers Removed) | 5 | 6.70 | 83.4 (74–94) | 2 | 3 |
| Normal Macular RPE/Choroid vs. Normal Macular Retina | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Associated Loci | Padj-Value DEG | Fold Change DEG | RPE/Retina DEG | AMD Associated Loci | Padj-Value DEG | Fold Change DEG | RPE/Retina DEG |
| ABCA1 | 1.39 × 10−83 | +13.86 | RPE | LRP6 | 1.68 × 10−19 | +2.71 | RPE |
| ABCA7 | 6.44 × 10−13 | −6.37 | Retina | ME3 | 2.88 × 10−4 | +1.69 | RPE |
| ABHD2 | 3.86 × 10−21 | +4.30 | RPE | MMP19 | 1.86 × 10−31 | +5.40 | RPE |
| ACAA2 | 1.23 × 10−16 | +2.54 | RPE | MMP9 | 4.07 × 10−5 | +5.72 | RPE |
| ADAM19 | 9.01 × 10−23 | −3.42 | Retina | MYO1E | 3.14 × 10−79 | +9.18 | RPE |
| ADAMTS9-AS1 | 2.85 × 10−24 | +11.73 | RPE | NLRP2 | 1.66 × 10−3 | −4.16 | Retina |
| ADAMTS9-AS2 | 1.16 × 10−46 | +16.65 | RPE | NPLOC4 | 3.47 × 10−16 | +1.78 | RPE |
| AFF1 | 1.21 × 10−3 | +1.28 | Retina | OCA2 | 2.00 × 10−71 | +64.02 | RPE |
| ARHGAP21 | 8.32 × 10−7 | −1.53 | Retina | PCOLCE | 4.88 × 10−85 | +24.56 | RPE |
| B3GALTL | 1.50 × 10−4 | −1.36 | Retina | PDGFB | 7.41 × 10−63 | +14.29 | RPE |
| C10orf88 | 6.79 × 10−35 | −2.16 | Retina | PELI3 | 8.96 × 10−22 | −2.51 | Retina |
| C2 | 1.71 × 10−21 | +17.82 | RPE | PILRA | 1.01 × 10−6 | +3.70 | RPE |
| C3 | 3.73 × 10−24 | +16.82 | RPE | PKP2 | 1.04 × 10−62 | +6.14 | RPE |
| C4A | 2.28 × 10−19 | +19.68 | RPE | PLA2G4A | 6.81 × 10−33 | +6.86 | RPE |
| C5 | 1.47 × 10−9 | +2.24 | RPE | RAD51B | 7.50 × 10−5 | +1.63 | RPE |
| C9 | 6.47 × 10−31 | +14.42 | RPE | RASIP1 | 1.34 × 10−94 | +14.43 | RPE |
| CCT3 | 6.66 × 10−6 | −1.52 | Retina | RDH5 | 4.47 × 10−34 | +22.82 | RPE |
| CD46 | 1.07 × 10−9 | +2.02 | RPE | RGS13 | 1.40 × 10−7 | +9.17 | RPE |
| CD55 | 8.99 × 10−22 | +2.98 | RPE | RLBP1 | 1.63 × 10−9 | +4.80 | RPE |
| CD63 | 3.07 × 10−65 | +4.95 | RPE | ROBO1 | 2.80 × 10−7 | +1.72 | RPE |
| CDH7 | 2.73 × 10−231 | −83.36 | Retina | RORA | 1.19 × 10−30 | −4.95 | Retina |
| CDH9 | 2.36 × 10−17 | −31.33 | Retina | RORB | 3.68 × 10−23 | −3.03 | Retina |
| CETP | 1.97 × 10−35 | +146.22 | RPE | RP1L1 | 1.20 × 10−24 | −37.69 | Retina |
| CFB | 7.13 × 10−26 | +29.72 | RPE | RRAS | 4.74 × 10−55 | +8.90 | RPE |
| CFH | 4.79 × 10−179 | +62.53 | RPE | SERPINA1 | 1.23 × 10−13 | +14.19 | RPE |
| CFHR3 | 1.56 × 10−16 | +44.62 | RPE | SKIV2L | 1.72 × 10−14 | +1.63 | RPE |
| CFI | 1.44 × 10−12 | +3.51 | RPE | SLC16A8 | 6.76 × 10−54 | +54.98 | RPE |
| CLUL1 | 8.25 × 10−19 | −19.87 | Retina | SMAD3 | 8.24 × 10−96 | +8.51 | RPE |
| CNN2 | 6.84 × 10−60 | +8.02 | RPE | SPEF2 | 3.60 × 10−25 | −2.98 | Retina |
| COL5A1 | 7.78 × 10−32 | +7.65 | RPE | SRPK2 | 2.29 × 10−39 | −1.77 | Retina |
| COL8A1 | 3.09 × 10−106 | +90.43 | RPE | STON1 | 6.39 × 10−3 | +1.81 | RPE |
| CSK | 3.38 × 10−2 | +1.45 | Retina | STON1-GTF2A1L | 4.51 × 10−2 | +1.54 | RPE |
| CYP24A1 | 1.12 × 10−4 | −5.64 | Retina | SYN3 | 1.16 × 10−74 | −17.08 | Retina |
| DDR1 | 6.88 × 10−5 | −1.77 | Retina | TGFB1 | 1.76 × 10−11 | +2.32 | RPE |
| EXOC3L2 | 9.79 × 10−72 | +139.24 | RPE | TGFBR1 | 9.59 × 10−24 | +3.73 | RPE |
| FILIP1L | 2.63 × 10−46 | +3.68 | RPE | TIMP3 | 3.04 × 10−129 | +54.19 | RPE |
| FLT1 | 2.33 × 10−14 | +3.15 | RPE | TMEM97 | 3.66 × 10−12 | −3.67 | Retina |
| HERC2 | 2.52 × 10−4 | −1.24 | Retina | TNF | 4.30 × 10−8 | +24.29 | RPE |
| HLA-DQB1 | 8.10 × 10−11 | +15.72 | RPE | TNFRSF10A | 3.57 × 10−58 | +17.43 | RPE |
| HTRA1 | 1.17 × 10−2 | −1.52 | Retina | TRPM1 | 1.20 × 10−12 | +2.88 | RPE |
| IER3 | 5.43 × 10−17 | +14.33 | RPE | TRPM3 | 3.97 × 10−40 | +7.24 | RPE |
| IGFBP7 | 2.05 × 10−279 | +31.68 | RPE | TSPAN10 | 2.60 × 10−80 | +67.02 | RPE |
| IL6 | 3.58 × 10−9 | +41.87 | RPE | TYR | 7.34 × 10−127 | +794.49 | RPE |
| ITGA7 | 1.66 × 10−32 | +3.61 | RPE | UNC93B1 | 1.38 × 10−47 | +25.51 | RPE |
| KMT2E | 2.51 × 10−11 | −1.47 | Retina | VDR | 1.29 × 10−7 | +4.98 | RPE |
| LBP | 1.86 × 10−11 | +214.07 | RPE | VTN | 8.35 × 10−7 | −4.78 | Retina |
| LIPC | 2.41 × 10−15 | +13.30 | RPE | ZNF385B | 4.83 × 10−43 | −17.67 | Retina |
| Normal Macular RPE/Choroid vs. Normal Macular Retina | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| AMD Associated Loci | Padj-Value DSG | Fold Change DSG | RPE/Retina DSG |
| ABHD2 | 1.16 × 10−14 | −2.79 | Retina |
| ADAM19 | 1.05 × 10−2 | +2.80 | RPE |
| AFF1 | 5.95 × 10−251 | −6.74 | Retina |
| ARHGAP21 | 1.06 × 10−78 | −4.96 | Retina |
| C2 | 3.65 × 10−205 | −27.63 | Retina |
| CCT3 | 2.48 × 10−3 | +2.21 | RPE |
| CD55 | 4.79 × 10−24 | +2.43 | RPE |
| CD63 | 5.40 × 10−99 | −4.77 | Retina |
| CLUL1 | 3.02 × 10−283 | +35.49 | RPE |
| FILIP1L | 1.98 × 10−04 | −2.85 | Retina |
| FLT1 | 6.22 × 10−38 | −16.98 | Retina |
| GTF2A1L | 2.04 × 10−3 | +3.79 | RPE |
| MMP9 | 1.10 × 10−12 | +2.78 | RPE |
| PCOLCE | 1.30 × 10−9 | +2.73 | RPE |
| PILRA | 3.93 × 10−65 | −3.64 | Retina |
| RDH5 | 5.27 × 10−94 | −3.49 | Retina |
| RLBP1 | 1.00 × 10−320 | −14.86 | Retina |
| RORA | 2.48 × 10−296 | +12.15 | RPE |
| SPEF2 | 4.69 × 10−8 | +3.05 | RPE |
| SRPK2 | 1.25 × 10−24 | +2.81 | RPE |
| STON1-GTF2A1L | 7.62 × 10−82 | −4.98 | Retina |
| TGFB1 | 1.00 × 10−320 | +8.69 | RPE |
| TRPM1 | 1.00 × 10−320 | −2.11 | Retina |
| TRPM3 | 1.00 × 10−320 | −38.06 | Retina |
| TSPAN10 | 1.00 × 10−320 | −24.20 | Retina |
| ZBTB38 | 4.97 × 10−113 | +8.88 | RPE |
| Macular RPE/Choroid: AMD Associated Loci (DEGs) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate AMD vs. Normal | Neovascular AMD vs. Normal | Intermediate AMD vs. Neovascular AMD | ||||||
| Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-value | Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value | Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value |
| CDH7 | −3.3 | 0.0128 | ABCA7 * | +3.4 | 0.0018 | ABCA7 * | −3.2 | 0.0032 |
| CLUL1 * | +15.3 | 1.5 × 10−9 | CLUL1 * | −8.5 | 6.6 × 10−6 | |||
| FLT1 | −1.9 | 0.0081 | RP1L1 * | −7.0 | 0.0001 | |||
| RASIP1 | −1.6 | 0.0246 | SPEF2 * | −1.5 | 0.0165 | |||
| RORα * | +1.9 | 0.0043 | TNFRSF10B | +1.7 | 0.0183 | |||
| RP1L1 * | +13.3 | 5.30 × 10−8 | TRPM1 | +1.7 | 0.0410 | |||
| VTN * | +3.3 | 0.0206 | ZNF385B * | −4.8 | 7.8 × 10−8 | |||
| ZNF385B * | +4.3 | 4.3 × 10−7 | ||||||
| Macular RPE/Choroid: AMD Associated Loci (DSGs) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate AMD vs. Normal | Neovascular AMD vs. Normal | Intermediate AMD vs. Neovascular AMD | ||||||
| Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value | Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value | Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value |
| C2 | −5.0 | 0.000131 | ABCA7 | −2.0 | 4.9 × 10−12 | ABHD2 * | −2.4 | 1.9 × 10−12 |
| CFB * | +3.9 | 3.4 × 10−321 | ABHD2 * | +3.9 | 1.5 × 10−7 | CFB | +2.3 | 3.2 × 10−121 |
| CLUL1 | −2.1 | 0.0460 | AFF1 | −2.0 | 7.7 × 10−23 | CHD9 | +2.2 | 3.4 × 10−15 |
| FLT1 | +2.2 | 8.35 × 10−7 | CFB * | +2.6 | 6.2 × 10−321 | CLUL1 | +11.3 | 5.1 × 10−59 |
| CLUL1 | −13.5 | 1.2 × 10−124 | RORα | +2.1 | 7.7 × 10−10 | |||
| RORα | −2.0 | 1.6 × 10−14 | SPEF2 | +2.3 | 0.0192 | |||
| Macular Retina: AMD Associated Loci (DSGs) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intermediate AMD vs. Normal | Neovascular AMD vs. Normal | Intermediate AMD vs. Neovascular AMD | ||||||
| Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value | Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value | Gene Name | Fold Change | Padj-Value |
| ACAD10 | −2.2 | 2.1 × 10−7 | ARHGAP21 | −2.1 | 1.7 × 10−44 | ADAM19 | +2.1 | 6.3 × 10−9 |
| CCT3 * | +2.7 | 6.1 × 10−15 | C3 * | +2.2 | 0.0169 | ARHGAP21 | +2.2 | 4.82 × 10−35 |
| CHD9 * | +2.4 | 7.4 × 10−41 | CLUL1 * | +2.6 | 8.2 × 10−139 | COL4A3 | +2.1 | 9.0 × 10−35 |
| HERC2 | −2.7 | 1.6 × 10−15 | HERC2 | +2.0 | 2.6 × 10−11 | |||
| LRP2 | −2.1 | 3.8 × 10−63 | LRP2 | +2.4 | 1.4 × 10−180 | |||
| ME3 * | +2.6 | 0.0347 | SKIV2L | +2.1 | 2 × 10−22 | |||
| ROBO1 | −2.1 | 1.2 × 10−20 | SMAD3 * | −2.4 | 5.2 × 10−7 | |||
| SMAD3 * | +2.4 | 2.4 × 10−8 | SPEF2 * | −2.1 | 9.8 × 10−5 | |||
| SPEF2 * | +2.4 | 1.4 × 10−12 | TRPM1 | +2.3 | 1.4 × 10−15 | |||
| TRPM1 | −2.8 | 2.7 × 10−16 | ZNF385B * | −2.7 | 5.4 × 10−6 | |||
| ZNF385B * | +2.9 | 6.1 × 10−10 | ||||||
| Validated Genes Across DEGs, DSGs, and a Bulk RNASeq Dataset | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macular RPE/Choroid: Intermediate AMD vs. Normal | ||||||||
| Discovery DEG | Discovery DSG | Validation Bulk RNA Seq | ||||||
| Gene Name | Location hg19 | Log FC | Adjusted p-value | Splice Coordinates hg19 | Log FC | Adjusted p-value | Log FC | Adjusted p-value |
| STAT1 * | 2q32.3 | +0.45 | 0.0486 | chr2:191829088-191829424 | −0.41 | 6.2 × 10−43 | +0.84 | 2.8 × 10−3 |
| Macular RPE/Choroid: Neovascular AMD vs. Normal | ||||||||
| Discovery DEG | Discovery DSG | Validation Bulk RNA Seq | ||||||
| Gene Name | Location hg19 | Log FC | Adjusted p-value | Splice Coordinates hg19 | Log FC | Adjusted p-value | Log FC | Adjusted p-value |
| AGTPBP1 | 9q21.33 | +0.42 | 2.1 × 10−8 | chr9:88168784-88169184 | +0.40 | 6.3 × 10−61 | +0.39 | 6.7 × 10−3 |
| BBS5 | 2q31.1 | +0.21 | 0.0018 | chr2:170374704-170374880 | +0.55 | 5.9 × 10−17 | −0.42 | 4.7 × 10−3 |
| CERKL | 2q31.3 | +0.43 | 0.0012 | chr2:182403824-182403984 | +0.38 | 0.012 | +0.76 | 1.2 × 10−4 |
| FGFBP2 | 4p15.32 | +0.58 | 3.7 × 10−5 | chr4:15970850-15970932 | +0.91 | 9.6 × 10−203 | +0.78 | 1.3 × 10−3 |
| KIFC3 | 16q21 | +0.19 | 0.0117 | chr16:57880252-57880440 | +0.73 | 5.8 × 10−8 | −0.59 | 2.0 × 10−4 |
| RORA * | 15q22.2 | +0.27 | 0.0043 | chr15:61333304-61333332 | −0.30 | 1.6 × 10−14 | +0.32 | 8.4 × 10−3 |
| ZNF292 * | 6q14.3 | +0.18 | 0.0054 | chr6:87864912-87865080 | ×0.32 | 2.9 × 10−16 | +0.33 | 6.9 × 10−3 |
| Macular RPE/Choroid | Macular Retina | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNP | Location | #Hets | Normal | Intermediate AMD | Neovascular AMD | Normal | Intermediate AMD | Neovascular AMD |
| CFH rs1061147 | chr1:196654324 | 18 | 7/7 | 5/6 | 3/4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| CFH rs1061170 | chr1:196659237 | 18 | 1/7 | 2/6 | 0/4 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| CFH rs35292876 | chr1:196706642 | 1 | 0/0 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| CFH rs121913059 | chr1:196716375 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| PLA2G4A rs2285714 | chr4:110638810 | 15 | 0/1 | 0/3 | 0/0 | 0/3 | 0/1 | 0/1 |
| CFI rs141853578 | chr4:110685820 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| C2 rs9332739 | chr6:31903804 | 4 | 0/2 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| CFB rs641153 | chr6:31914180 | 6 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| ARMS2 rs10490924 | chr10:124214448 | 7 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| APOE rs429358 | chr19:45411941 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| C3 rs147859257 | chr19:6718146 | 0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| C3 rs2230199 | chr19:6718387 | 6 | 2/2 | 2/3 | 0/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 0/0 |
| Individuals with Significant ASE (p < 0.05) | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shwani, T.; Zhang, C.; Owen, L.A.; Shakoor, A.; Vitale, A.T.; Lillvis, J.H.; Barr, J.L.; Cromwell, P.; Finley, R.; Husami, N.; et al. Patterns of Gene Expression, Splicing, and Allele-Specific Expression Vary among Macular Tissues and Clinical Stages of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cells 2023, 12, 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232668
Shwani T, Zhang C, Owen LA, Shakoor A, Vitale AT, Lillvis JH, Barr JL, Cromwell P, Finley R, Husami N, et al. Patterns of Gene Expression, Splicing, and Allele-Specific Expression Vary among Macular Tissues and Clinical Stages of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cells. 2023; 12(23):2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232668
Chicago/Turabian StyleShwani, Treefa, Charles Zhang, Leah A. Owen, Akbar Shakoor, Albert T. Vitale, John H. Lillvis, Julie L. Barr, Parker Cromwell, Robert Finley, Nadine Husami, and et al. 2023. "Patterns of Gene Expression, Splicing, and Allele-Specific Expression Vary among Macular Tissues and Clinical Stages of Age-Related Macular Degeneration" Cells 12, no. 23: 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232668
APA StyleShwani, T., Zhang, C., Owen, L. A., Shakoor, A., Vitale, A. T., Lillvis, J. H., Barr, J. L., Cromwell, P., Finley, R., Husami, N., Au, E., Zavala, R. A., Graves, E. C., Zhang, S. X., Farkas, M. H., Ammar, D. A., Allison, K. M., Tawfik, A., Sherva, R. M., ... DeAngelis, M. M. (2023). Patterns of Gene Expression, Splicing, and Allele-Specific Expression Vary among Macular Tissues and Clinical Stages of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cells, 12(23), 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232668