Quantification of the Culture Stability of Stem Cell Fractions from Oral-Derived, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Preparations: A Significant Step toward the Clinical Translation of Cell Therapies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
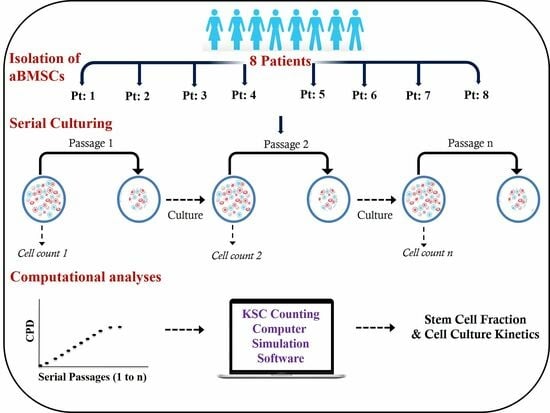
2.1. Isolation of Human aBMSC-Containing Preparations
2.2. Characterization of Human aBMSC-Containing Preparations
2.3. Serial Cell Culture
2.4. KSC Counting Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Isolation, Characterization, and Serial Cell Culture of Human aBMSC Strains
3.2. KSC Counting Analysis of the SCF of Human aBMSC Preparations
3.3. KSC Counting Analysis of the SCF Half-Life of Human aBMSC Preparations during Serial Cell Culture
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gjerde, C.; Mustafa, K.; Hellem, S.; Rojewski, M.; Gjengedal, H.; Yassin, M.A.; Feng, X.; Skaale, S.; Berge, T.; Rosen, A.; et al. Cell therapy induced regeneration of severely atrophied mandibular bone in a clinical trial. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šponer, P.; Kučera, T.; Brtková, J.; Urban, K.; Kočí, Z.; Měřička, P.; Bezrouk, A.; Konrádová, Š.; Filipová, A.; Filip, S. Comparative study on the application of mesenchymal stromal cells combined with tricalcium phosphate scaffold into femoral bone defects. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, J.F.; Villarón, E.M.; Pescador, D.; da Casa, C.; Gómez, V.; Redondo, A.M.; López-Villar, O.; López-Parra, M.; Muntión, S.; Sánchez-Guijo, F. Autologous mesenchymal stromal cells embedded in tricalcium phosphate for posterolateral spinal fusion: Results of a prospective phase I/II clinical trial with long-term follow-up. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Monjaraz, B.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Ledesma-Martínez, E.; Aguiñiga-Sánchez, I.; Sosa-Hernández, N.A.; Mendoza-Núñez, V.M. Dental pulp mesenchymal stem cells as a treatment for periodontal disease in older adults. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 8890873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Barrena, E.; Padilla-Eguiluz, N.; Rosset, P.; Gebhard, F.; Hernigou, P.; Baldini, N.; Rouard, H.; Sensebé, L.; Gonzalo-Daganzo, R.-M.; Giordano, R.; et al. Early efficacy evaluation of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) combined to biomaterials to treat long bone non-unions. Injury 2020, 51 (Suppl. 1), S63–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galipeau, J.; Krampera, M. The challenge of defining mesenchymal stromal cell potency assays and their potential use as release criteria. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketterl, N.; Brachtl, G.; Schuh, C.; Bieback, K.; Schallmoser, K.; Reinisch, A.; Strunk, D. A robust potency assay highlights significant donor variation of human mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell immune modulatory capacity and extended radio-resistance. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.; Webster, A.; Genever, P. Nomenclature and heterogeneity: Consequences for the use of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. Regen. Med. 2019, 14, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennerfeldt, D.A.; Van Vliet, K.J. Concise review: When colonies are not clones: Evidence and implications of intracolony heterogeneity in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinney, D.G. Functional heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cells: Implications for cell therapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 2806–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.; Tarle, S.; Osibin, W.; Kinfu, Y.; Kaigler, D. Standardization and safety of alveolar bone–derived stem cell isolation. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherley, J.L. A Kinetic Stem Cell Counting Analysis of the Specific Effects of Cell Culture Medium Growth Factors on Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Life 2023, 13, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.A.; Eiro, N.; Fraile, M.; Gonzalez, L.O.; Saá, J.; Garcia-Portabella, P.; Vega, B.; Schneider, J.; Vizoso, F.J. Functional heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cells from natural niches to culture conditions: Implications for further clinical uses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherley, J.L.; Daley, M.P.; Dutton, R.A. Validation of Kinetic Stem Cell (KSC) counting algorithms for rapid quantification of human hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cell Ther. Transpl. 2022, 6, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, R.; Abdi, F.; Minnetyan, L.; Sherley, J.L.; Asymmetrex, L. A Computational Simulation Technology for Specific Counting of Perinatal and Postnatal Human Tissue Stem Cells for Transplantation Medicine. OBM Transplant. 2020, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Vigen, M.; Putnam, A.J.; Cao, C.; Tarlé, S.A.; Guinn, T.; Kaigler, D. Phenotypic, trophic, and regenerative properties of mesenchymal stem cells from different osseous tissues. Cell Tissue Res. 2022, 388, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, T.S.; Giacoppo, S.; Diomede, F.; Ballerini, P.; Paolantonio, M.; Marchisio, M.; Piattelli, A.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E.; Trubiani, O. The secretome of periodontal ligament stem cells from MS patients protects against EAE. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Ren, J.-L.; Xu, F.; Chen, F.-M.; Li, A. Exosomes secreted by stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth contribute to functional recovery after traumatic brain injury by shifting microglia M1/M2 polarization in rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, F.; Zhang, D.; Fang, T.; Lu, C.; Wang, B.; Ding, X.; Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pi, W.; Xu, H.; et al. Exosomes from Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Biodegradable Chitin Conduits Promote Rat Sciatic Nerve Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 2546367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, Y.; Hata, M.; Matsukawa, R.; Aoyagi, A.; Omi, M.; Mizutani, M.; Naruse, K.; Ozawa, S.; Honda, M.; Matsubara, T.; et al. Efficacy of extracellular vesicles from dental pulp stem cells for bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defects. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Dental stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as promising therapeutic agents in the treatment of diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajestan, M.N.; Rajan, A.; Edwards, S.P.; Aronovich, S.; Cevidanes, L.H.S.; Polymeri, A.; Travan, S.; Kaigler, D. Stem cell therapy for reconstruction of alveolar cleft and trauma defects in adults: A randomized controlled, clinical trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, T.; Yamato, M.; Washio, K.; Yoshida, T.; Tsumanuma, Y.; Yamada, A.; Onizuka, S.; Izumi, Y.; Ando, T.; Okano, T.; et al. Periodontal regeneration with autologous periodontal ligament-derived cell sheets - A safety and efficacy study in ten patients. Regen Ther. 2018, 9, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza, G.; Urrejola, D.; Saint Jean, N.; Inostroza, C.; López, V.; Khoury, M.; Brizuela, C. Personalized cell therapy for pulpitis using autologous dental pulp stem cells and leukocyte platelet-rich fibrin: A case report. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanikawa, D.; Pinheiro, C.C.; Almeida, M.C.A.; Oliveira, C.R.; Coudry, R.D.A.; Rocha, D.L.; Bueno, D.F. Deciduous dental pulp stem cells for maxillary alveolar reconstruction in cleft lip and palate patients. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 6234167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, N.; Fierravanti, L.; Núñez, J.; Vignoletti, F.; González-Zamora, M.; Santamaría, S.; Suárez-Sancho, S.; Fernández-Santos, M.E.; Figuero, E.; Herrera, D.; et al. Periodontal regeneration using a xenogeneic bone substitute seeded with autologous periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A 12-month quasi-randomized controlled pilot clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, M.; Fukuyama, F.; Iohara, K. Pulp regenerative cell therapy for mature molars: A report of 2 cases. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Song, T.; Ding, G.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shi, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Functional tooth restoration by allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell-based bio-root regeneration in swine. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyota, A.; Shinagawa, R.; Mano, M.; Tokioka, K.; Suda, N. Regeneration in Experimental Alveolar Bone Defect Using Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Transplant. 2021, 30, 0963689720975391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Moraissi, E.; Oginni, F.; Holkom, M.; Mohamed, A.; Al-Sharani, H. Tissue-engineered bone using mesenchymal stem cells versus conventional bone grafts in the regeneration of maxillary alveolar bone: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, G.; A Ankrum, J.; Olson, S.D.; Nolta, J.A. Improved MSC Minimal Criteria to Maximize Patient Safety: A Call to Embrace Tissue Factor and Hemocompatibility Assessment of MSC Products. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2022, 11, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantri, S.; Reinisch, A.; Dejene, B.T.; Lyell, D.J.; DiGiusto, D.L.; Agarwal-Hashmi, R.; Majeti, R.; Weinberg, K.I.; Porteus, M.H. CD34 expression does not correlate with immunophenotypic stem cell or progenitor content in human cord blood products. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5357–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, T.H.; Longaker, M.T.; Chan, C.K.F. A Revised Perspective of Skeletal Stem Cell Biology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potten, C.S.; Morris, R.J. Epithelial stem cells in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 1988, 10 (Suppl. 10), 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potten, C.S.; Loeffler, M. Stem Cells and Cellular Pedigrees—A Conceptual Introduction; Stem Cells Academic: London, UK, 1997; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Purton, L.E.; Scadden, D.T. Limiting factors in murine hematopoietic stem cell assays. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, S.P.; Eppert, K.; Lechman, E.R.; Doedens, M.; Dick, J.E. Comparison of human cord blood engraftment between immunocompromised mouse strains. Blood 2010, 116, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| P | Sex | Age | CD73 | CD90 | CD105 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 90 | 99.66 | 98.39 | 98.96 |
| 2 | M | 56 | 99.81 | 99.86 | 99.38 |
| 3 | F | 78 | 99.92 | 99.80 | 99.29 |
| 4 | F | 62 | 99.77 | 99.80 | 99.10 |
| 5 | M | 61 | 99.62 | 99.84 | 99.80 |
| 6 | F | 49 | 99.92 | 99.94 | 99.91 |
| 7 | F | 25 | 99.54 | 99.65 | 99.73 |
| 8 | M | 43 | 99.94 | 99.95 | 99.86 |
| Patient | Simulation Quality Score (SQS) | Stem Cell Fraction (SCF) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | p-Value | 95% CI | Mean ± SD | p-Value | 95% CI | |
| 1 | 0.07 | <0.0001 | 0.05–0.09 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | <0.0001 | 0.05–0.08 |
| 2 | 0.18 | <0.0001 | 0.13–0.22 | 0.30 ± 0.22 | 0.0018 | 0.15–0.46 |
| 3 | 0.07 | <0.0001 | 0.05–0.09 | 0.26 ± 0.13 | 0.0001 | 0.17–0.35 |
| 4 | 0.13 | <0.0001 | 0.12–0.13 | 0.77 ± 0.26 | <0.0001 | 0.58–0.95 |
| 5 | 0.46 | <0.0001 | 0.43–0.49 | 0.37 ± 0.15 | <0.0001 | 0.26–0.48 |
| 6 | 0.22 | <0.0001 | 0.20–0.24 | 0.22 ± 0.10 | <0.0001 | 0.15–0.29 |
| 7 | 0.09 | <0.0001 | 0.08–0.09 | 0.30 ± 0.16 | 0.0002 | 0.18–0.41 |
| 8 | 0.03 | <0.0001 | 0.02–0.04 | 0.56 ± 0.18 | <0.0001 | 0.43–0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chopra, H.; Cao, C.; Sommer, C.; Dahlkemper, A.; Sugai, J.; Sherley, J.L.; Kaigler, D. Quantification of the Culture Stability of Stem Cell Fractions from Oral-Derived, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Preparations: A Significant Step toward the Clinical Translation of Cell Therapies. Cells 2023, 12, 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232703
Chopra H, Cao C, Sommer C, Dahlkemper A, Sugai J, Sherley JL, Kaigler D. Quantification of the Culture Stability of Stem Cell Fractions from Oral-Derived, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Preparations: A Significant Step toward the Clinical Translation of Cell Therapies. Cells. 2023; 12(23):2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232703
Chicago/Turabian StyleChopra, Hitesh, Chen Cao, Celia Sommer, Alex Dahlkemper, James Sugai, James L. Sherley, and Darnell Kaigler. 2023. "Quantification of the Culture Stability of Stem Cell Fractions from Oral-Derived, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Preparations: A Significant Step toward the Clinical Translation of Cell Therapies" Cells 12, no. 23: 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232703
APA StyleChopra, H., Cao, C., Sommer, C., Dahlkemper, A., Sugai, J., Sherley, J. L., & Kaigler, D. (2023). Quantification of the Culture Stability of Stem Cell Fractions from Oral-Derived, Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Preparations: A Significant Step toward the Clinical Translation of Cell Therapies. Cells, 12(23), 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12232703