MicroRNA-29a Suppresses CD36 to Ameliorate High Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in Mice
Abstract
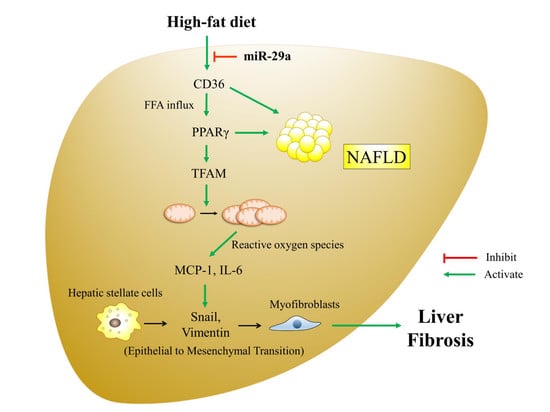
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Construction and Breeding of the miR-29a Transgenic Mouse Colony
2.3. Animal Model and Experimental Protocol
2.4. Open-Field Test
2.5. Histological Analysis
2.6. Real-Time RT-PCR
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.9. DNA Isolation and Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number Quantification
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overexpression of miR-29a Significantly Reduces Weight Gain, Fat Accumulation in Adipose Tissue, and Liver Weight in the Context of Chronic HFD
3.2. Overexpression of miR-29a Reduces Hepatocellular Steatosis and Fibrosis in the Context of Chronic HFD
3.3. Overexpression of miR-29a Represses Hepatic Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Inflammation in the Context of Chronic HFD
3.4. Overexpression of miR-29a Modulates HFD-Caused Perturbation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis in the Liver
3.5. miR-29a Inhibits the Expression of Fatty Acid Translocase CD36 by Targeting 3’ UTR
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rinella, M.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. Jama 2015, 313, 2263–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomba, R.; Abraham, M.; Unalp, A.; Wilson, L.; Lavine, J.; Doo, E.; Bass, N.M. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis clinical research, association between diabetes, family history of diabetes, and risk of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.D.; Stengel, J.; Asike, M.I.; Torres, D.M.; Shaw, J.; Contreras, M.; Landt, C.L.; Harrison, S.A. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: A prospective study. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, M.; Zatterale, F.; Naderi, J.; Parrillo, L.; Formisano, P.; Raciti, G.A.; Beguinot, F.; Miele, C. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, e2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, K.; Teratani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sato, H.; Narimatsu, K.; Okada, Y.; Kurihara, C.; Irie, R.; Yokoyama, H.; et al. Free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells: Mechanism of liver fibrosis aggravation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernacka, A.; Dobaczewski, M.; Frangogiannis, N.G. TGF-beta signaling in fibrosis. Growth Factors 2011, 29, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, L.; Laviolette, M.; Rodrigue-Way, A.; Sow, B.; Brochu, M.; Caron, V.; Tremblay, A. The CD36-PPARgamma pathway in metabolic disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, e1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, W.; Yang, P.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; et al. Cluster of differentiation 36 deficiency aggravates macrophage infiltration and hepatic inflammation by upregulating monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression of hepatocytes through histone deacetylase 2-dependent pathway. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2017, 27, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.G.; Tran, J.L.; Erion, D.M.; Vera, N.B.; Febbraio, M.; Weiss, E.J. Hepatocyte-Specific disruption of CD36 attenuates fatty liver and improves insulin sensitivity in HFD-fed mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begriche, K.; Massart, J.; Robin, M.A.; Bonnet, F.; Fromenty, B. Mitochondrial adaptations and dysfunctions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.K.; Rao, M.S. Lipid metabolism and liver inflammation. II. Fatty liver disease and fatty acid oxidation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006, 290, G852–G858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipsen, D.H.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic lipid accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3313–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Z.; Liang, S.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; He, F.; Shalapour, S.; Lin, X.J.; Wong, J.; Ding, S.; Seki, E.; Schnabl, B.; et al. New mitochondrial DNA synthesis enables NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2018, 560, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, J.P.; Simtchouk, S.; Schindler, S.M.; Villanueva, E.B.; Gill, N.E.; Walker, D.G.; Wolthers, K.R.; Klegeris, A. Mitochondrial transcription factor A (Tfam) is a pro-inflammatory extracellular signaling molecule recognized by brain microglia. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 60, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.J.; Factora, T.D.; Dey, S.; Kota, J. A systematic review of miR-29 in cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2019, 12, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. Micrornas: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 2001, 107, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.; Chu, D.C.; Maxwell, A.; Oakley, F.; Zhu, N.L.; Tsukamoto, H.; Mann, D.A. MeCP2 controls an epigenetic pathway that promotes myofibroblast transdifferentiation and fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation by microRNA-29b. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, S.; Hashemi, M.; Ande, S.R.; Yeganeh, B.; Xiao, W.; Eshraghi, M.; Bus, C.J.; Kadkhoda, K.; Wiechec, E.; Halayko, A.J.; et al. Apoptosis and cancer: Mutations within caspase genes. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 46, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Wang, F.S.; Yang, Y.L.; Tiao, M.M.; Chuang, J.H.; Huang, Y.H. Microarray study of pathway analysis expression profile associated with microrna-29a with regard to murine cholestatic liver injuries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiao, M.M.; Wang, F.S.; Huang, L.T.; Chuang, J.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Huang, Y.H. MicroRNA-29a protects against acute liver injury in a mouse model of obstructive jaundice via inhibition of the extrinsic apoptosis pathway. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Yu-Hsieh, H.; Huang, C.C.; Shin-Mu, V.T.; Tai, M.H.; Chen, C.L.; Chuang, J.H. Liver hepcidin and stainable iron expression in biliary atresia. Pediatr. Res. 2006, 59, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Shih, H.H.; Tiao, M.M.; Huang, C.C.; Kuo, K.C.; Huang, F.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Chuang, J.H. Toll-like receptor 7 agonist induces hypoplasia of the biliary system in a neonatal mouse model. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.L.; Huang, F.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, M.H.; Wang, F.S. MicroRNA-29a mitigation of endoplasmic reticulum and autophagy aberrance counteracts in obstructive jaundice-induced fibrosis in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, F.S. The Role of miR-29a in the regulation, function, and signaling of liver fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, F.S. MicroRNA-29a is a key regulon that regulates BRD4 and mitigates liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.L.; Kuo, H.C.; Wang, F.S.; Huang, Y.H. MicroRNA-29a Disrupts DNMT3b to ameliorate diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, e1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Wang, F.S.; Li, S.C.; Tiao, M.M.; Huang, Y.H. MicroRNA-29a alleviates bile duct ligation exacerbation of hepatic fibrosis in mice through epigenetic control of methyltransferases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Menini, S.; Ricci, C.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Scipioni, A.; Salvi, L.; Cordone, S.; Delucchi, F.; Serino, M.; Federici, M.; et al. Galectin-3 ablation protects mice from diet-induced NASH: A major scavenging role for galectin-3 in liver. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Murata, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Okazaki, K. Reversible human TGF-beta signal shifting between tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis: Implications of smad phospho-isoforms for hepatic epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, A.P.; Khoury-Hanold, W.; Staron, M.; Tal, M.C.; Pineda, C.M.; Lang, S.M.; Bestwick, M.; Duguay, B.A.; Raimundo, N.; MacDuff, D.A.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA stress primes the antiviral innate immune response. Nature 2015, 520, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corona, J.C.; Duchen, M.R. PPARgamma as a therapeutic target to rescue mitochondrial function in neurological disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: The good, the bad and the future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.C.; Horton, J.D.; Hobbs, H.H. Human fatty liver disease: Old questions and new insights. Science 2011, 332, 1519–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.W.; Kuo, H.M.; Huang, H.T.; Chang, A.Y.; Weng, S.W.; Tai, M.H.; Chuang, J.H.; Chen, I.Y.; Huang, S.C.; Lin, T.K.; et al. Biphasic response of mitochondrial biogenesis to oxidative stress in visceral fat of diet-induced obesity mice. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2014, 20, 2572–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, J.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; van Grunsven, L.A. The miRFIB-Score: A serological miRNA-based scoring algorithm for the diagnosis of significant liver fibrosis. Cells 2019, 8, e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rector, R.S.; Thyfault, J.P.; Uptergrove, G.M.; Morris, E.M.; Naples, S.P.; Borengasser, S.J.; Mikus, C.R.; Laye, M.J.; Laughlin, M.H.; Booth, F.W.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction precedes insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis and contributes to the natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in an obese rodent model. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grattagliano, I.; de Bari, O.; Bernardo, T.C.; Oliveira, P.J.; Wang, D.Q.; Portincasa, P. Role of mitochondria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—From origin to propagation. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, C.; Auwerx, J. PGC-1alpha, SIRT1 and AMPK, an energy sensing network that controls energy expenditure. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2009, 20, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliaki, C.; Szendroedi, J.; Kaul, K.; Jelenik, T.; Nowotny, P.; Jankowiak, F.; Herder, C.; Carstensen, M.; Krausch, M.; Knoefel, W.T.; et al. Adaptation of hepatic mitochondrial function in humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver is lost in steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaung, W.W.; Wu, R.; Ji, Y.; Dong, W.; Wang, P. Mitochondrial transcription factor A is a proinflammatory mediator in hemorrhagic shock. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, S.; Wei, L.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; Chen, Y.; et al. CD36 plays a negative role in the regulation of lipophagy in hepatocytes through an AMPK-dependent pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Park, K.W.; Cho, S. Inhibition of the CD36 receptor reduces visceral fat accumulation and improves insulin resistance in obese mice carrying the BDNF-Val66Met variant. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 13338–13348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokoi, H.; Yanagita, M. Targeting the fatty acid transport protein CD36, a class B scavenger receptor, in the treatment of renal disease. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.L.; Lin, S.H.; Chuang, L.Y.; Guh, J.Y.; Liao, T.N.; Lee, T.C.; Chang, W.T.; Chang, F.R.; Hung, M.Y.; Chiang, T.A.; et al. CD36 is a novel and potential anti-fibrogenic target in albumin-induced renal proximal tubule fibrosis. J. Cell Biochem. 2007, 101, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawelke, N.; Vasel, M.; Sens, C.; Au, A.; Dooley, S.; Nakchbandi, I.A. Fibronectin protects from excessive liver fibrosis by modulating the availability of and responsiveness of stellate cells to active TGF-beta. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Lee, P.H.; Hsu, Y.C.; Lei, C.C.; Ko, J.Y.; Chuang, P.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Wang, S.Y.; Wu, S.L.; Chen, Y.S.; et al. MicroRNA-29a promotion of nephrin acetylation ameliorates hyperglycemia-induced podocyte dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Wang, F.S.; Yang, Y.L.; Chuang, Y.T.; Huang, Y.H. MicroRNA-29a mitigation of toll-like receptor 2 and 4 signaling and alleviation of obstructive jaundice-induced fibrosis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.R.; Xu, G.T.; Lv, L.X.; Yang, C.Q. The ratio of transforming growth factor-beta1/bone morphogenetic protein-7 in the progression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition contributes to rat liver fibrosis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.S.; Syn, W.K.; Karaca, G.F.; Omenetti, A.; Moylan, C.A.; Witek, R.P.; Agboola, K.M.; Jung, Y.; Michelotti, G.A.; Diehl, A.M. Leptin promotes the myofibroblastic phenotype in hepatic stellate cells by activating the hedgehog pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 36551–36560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Dedhar, S.; Kalluri, R.; Thompson, E.W. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in signaling, development, and disease. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, F.-S.; Yang, Y.-L.; Huang, Y.-H. MicroRNA-29a Suppresses CD36 to Ameliorate High Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Cells 2019, 8, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101298
Lin H-Y, Wang F-S, Yang Y-L, Huang Y-H. MicroRNA-29a Suppresses CD36 to Ameliorate High Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101298
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Hung-Yu, Feng-Sheng Wang, Ya-Ling Yang, and Ying-Hsien Huang. 2019. "MicroRNA-29a Suppresses CD36 to Ameliorate High Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in Mice" Cells 8, no. 10: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101298
APA StyleLin, H. -Y., Wang, F. -S., Yang, Y. -L., & Huang, Y. -H. (2019). MicroRNA-29a Suppresses CD36 to Ameliorate High Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Cells, 8(10), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101298