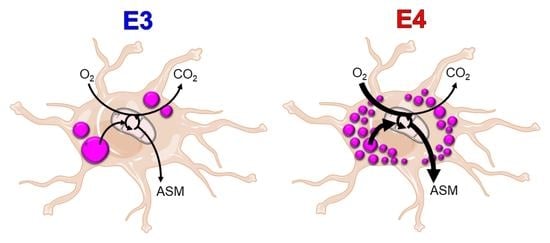
Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Western Blotting
2.3. Lipid Droplet Imaging
2.4. Fatty Acid Uptake Assay
2.5. Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay
2.6. Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. E4 Astrocytes Increased LD Count, Increased Cellular LD Volume, Decreased LD Size
3.2. E4 Astrocytes Take Up Less Palmitate
3.3. E4 Astrocytes Oxidize Less Exogenous Fatty Acids
3.4. E4 Astrocytes Are More Sensitive to CPT-1 Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregg, R.E.; Zech, L.A.; Schaefer, E.J.; Stark, D.; Wilson, D.; Brewer, H.B., Jr. Abnormal in vivo metabolism of apolipoprotein e4 in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 78, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein e and alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms, and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahley, R.W.; Weisgraber, K.H.; Huang, Y. Apolipoprotein e4: A causative factor and therapeutic target in neuropathology, including alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5644–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon, J.A.; Farmer, B.C.; Williams, H.C.; Johnson, L.A. Apoe and alzheimer’s disease: Neuroimaging of metabolic and cerebrovascular dysfunction. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.B.; Caselli, R.J.; Reiman, E.M.; Valla, J. Apoe and neuroenergetics: An emerging paradigm in alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yamada, K.; Liddelow, S.A.; Smith, S.T.; Zhao, L.; Luo, W.; Tsai, R.M.; Spina, S.; Grinberg, L.T.; Rojas, J.C.; et al. Apoe4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature 2017, 549, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiman, E.M.; Chen, K.; Alexander, G.E.; Caselli, R.J.; Bandy, D.; Osborne, D.; Saunders, A.M.; Hardy, J. Functional brain abnormalities in young adults at genetic risk for late-onset alzheimer’s dementia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshourbagy, N.A.; Liao, W.S.; Mahley, R.W.; Taylor, J.M. Apolipoprotein e mrna is abundant in the brain and adrenals, as well as in the liver, and is present in other peripheral tissues of rats and marmosets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitas, R.E.; Boyles, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Foss, D.; Mahley, R.W. Astrocytes synthesize apolipoprotein e and metabolize apolipoprotein e-containing lipoproteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1987, 917, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, D.M.; Herz, J.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein e and apolipoprotein e receptors: Normal biology and roles in alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Zhou, S.; Burgess, B.L.; Bernier, L.; McIsaac, S.A.; Chan, J.Y.; Tansley, G.H.; Cohn, J.S.; Hayden, M.R.; Wellington, C.L. Deficiency of abca1 impairs apolipoprotein e metabolism in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41197–41207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassine, H.N.; Feng, Q.; Chiang, J.; Petrosspour, L.M.; Fonteh, A.N.; Chui, H.C.; Harrington, M.G. Abca1-mediated cholesterol efflux capacity to cerebrospinal fluid is reduced in patients with mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmond, J.; Robbins, R.A.; Bergstrom, J.D.; Cole, R.A.; de Vellis, J. Capacity for substrate utilization in oxidative metabolism by neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes from developing brain in primary culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 1987, 18, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, D.; Haller, R.G.; Walton, M.E. Energy contribution of octanoate to intact rat brain metabolism measured by 13c nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 5928–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovatt, D.; Sonnewald, U.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Schousboe, A.; He, W.; Lin, J.H.C.; Han, X.; Takano, T.; Wang, S.; Sim, F.J.; et al. The transcriptome and metabolic gene signature of protoplasmic astrocytes in the adult murine cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernberg, J.N.; Bowman, C.E.; Wolfgang, M.J.; Scafidi, S. Developmental regulation and localization of carnitine palmitoyltransferases (cpts) in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panov, A.; Orynbayeva, Z.; Vavilin, V.; Lyakhovich, V. Fatty acids in energy metabolism of the central nervous system. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 472459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welte, M.A.; Gould, A.P. Lipid droplet functions beyond energy storage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1862, 1260–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, T.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Lipid droplets and cellular lipid metabolism. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahmer, N.; Farese, R.V.; Walther, T.C. Balancing the fat: Lipid droplets and human disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, P. Lipid droplet proteins and metabolic diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1968–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etschmaier, K.; Becker, T.; Eichmann, T.O.; Schweinzer, C.; Scholler, M.; Tam-Amersdorfer, C.; Poeckl, M.; Schuligoi, R.; Kober, A.; Chirackal Manavalan, A.P.; et al. Adipose triglyceride lipase affects triacylglycerol metabolism at brain barriers. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, N.B.; Murphy, D.D.; Grider, T.; Rueter, S.; Brasaemle, D.; Nussbaum, R.L. Lipid droplet binding and oligomerization properties of the parkinson’s disease protein alpha-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 6344–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, L.K.; Dufresne, M.; Joppe, S.E.; Petryszyn, S.; Aumont, A.; Calon, F.; Barnabe-Heider, F.; Furtos, A.; Parent, M.; Chaurand, P.; et al. Aberrant lipid metabolism in the forebrain niche suppresses adult neural stem cell proliferation in an animal model of alzheimer’s disease. Cell Stem Cell 2015, 17, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derk, J.; Bermudez Hernandez, K.; Rodriguez, M.; He, M.; Koh, H.; Abedini, A.; Li, H.; Fenyo, D.; Schmidt, A.M. Diaphanous 1 (diaph1) is highly expressed in the aged human medial temporal cortex and upregulated in myeloid cells during alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzheimer, A.; Stelzmann, R.A.; Schnitzlein, H.N.; Murtagh, F.R. An english translation of alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “uber eine eigenartige erkankung der hirnrinde”. Clin. Anat. 1995, 8, 429–431. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; MacKenzie, K.R.; Putluri, N.; Maletic-Savatic, M.; Bellen, H.J. The glia-neuron lactate shuttle and elevated ros promote lipid synthesis in neurons and lipid droplet accumulation in glia via apoe/d. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 719–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambini, M.D.; Pera, M.; Kanter, E.; Yang, H.; Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Holtzman, D.; Sulzer, D.; Area-Gomez, E.; Schon, E.A. Apoe4 upregulates the activity of mitochondria-associated er membranes. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Seo, J.; Gao, F.; Feldman, H.M.; Wen, H.L.; Penney, J.; Cam, H.P.; Gjoneska, E.; Raja, W.K.; Cheng, J.; et al. Apoe4 causes widespread molecular and cellular alterations associated with alzheimer’s disease phenotypes in human ipsc-derived brain cell types. Neuron 2018, 98, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Shimizu, Y.; Chan, J.; Wilkinson, A.; Ito, A.; Tontonoz, P.; Dullaghan, E.; Galea, L.A.; Pfeifer, T.; Wellington, C.L. Hormonal modulators of glial abca1 and apoe levels. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 3139–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Fu, Y.; Liu, C.C.; Shinohara, M.; Nielsen, H.M.; Dong, Q.; Kanekiyo, T.; Bu, G. Retinoic acid isomers facilitate apolipoprotein e production and lipidation in astrocytes through the retinoid x receptor/retinoic acid receptor pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 11282–11292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Trotter, J.; Zhang, J.; Peters, M.M.; Cheng, H.; Bao, J.; Han, X.; Weeber, E.J.; Bu, G. Neuronal lrp1 knockout in adult mice leads to impaired brain lipid metabolism and progressive, age-dependent synapse loss and neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 17068–17078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, M.; Fryer, J.D.; Sullivan, P.M.; Christopher, E.A.; Wahrle, S.E.; DeMattos, R.B.; O’Dell, M.A.; Fagan, A.M.; Lashuel, H.A.; Walz, T.; et al. Production and characterization of astrocyte-derived human apolipoprotein e isoforms from immortalized astrocytes and their interactions with amyloid-beta. Neurobiol. Dis. 2005, 19, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucken-Ardjomande Häsler, S.; Vallis, Y.; Jolin, H.E.; McKenzie, A.N.; McMahon, H.T. Graf1a is a brain-specific protein that promotes lipid droplet clustering and growth, and is enriched at lipid droplet junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 4602–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensaas, A.J.; Rustan, A.C.; Lovstedt, K.; Kull, B.; Wikstrom, S.; Drevon, C.A.; Hallen, S. Cell-based multiwell assays for the detection of substrate accumulation and oxidation. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huynh, F.K.; Green, M.F.; Koves, T.R.; Hirschey, M.D. Measurement of fatty acid oxidation rates in animal tissues and cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 542, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L. Human apoe isoforms differentially modulate brain glucose and ketone body metabolism: Implications for alzheimer’s disease risk reduction and early intervention. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 6665–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, J.T.; Ibrahimi, S.; Zhao, L. Human apoe isoforms differentially modulate glucose and amyloid metabolic pathways in female brain: Evidence of the mechanism of neuroprotection by apoe2 and implications for alzheimer’s disease prevention and early intervention. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 48, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.L.; Jahrling, J.B.; Zhang, W.; DeRosa, N.; Bakshi, V.; Romero, P.; Galvan, V.; Richardson, A. Rapamycin rescues vascular, metabolic and learning deficits in apolipoprotein e4 transgenic mice with pre-symptomatic alzheimer’s disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B.-C.; Shamay, A.; Argov-Argaman, N. Regulation of lipid droplet size in mammary epithelial cells by remodeling of membrane lipid composition—A potential mechanism. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.A.; Torres, E.R.S.; Impey, S.; Stevens, J.F.; Raber, J. Apolipoprotein e4 and insulin resistance interact to impair cognition and alter the epigenome and metabolome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinsinger, N.M.; Gachechiladze, M.A.; Rebeck, G.W. Apolipoprotein e genotype affects size of apoe complexes in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 75, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, D.R.; Zhou, H.; Atchison, K.; Warwick, H.K.; Atkinson, P.J.; Jefferson, J.; Xu, L.; Aschmies, S.; Kirksey, Y.; Hu, Y.; et al. Impact of apolipoprotein e (apoe) polymorphism on brain apoe levels. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 11445–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Z.; Lund, J.; Li, Y.; Knabenes, I.K.; Bakke, S.S.; Kase, E.T.; Lee, Y.K.; Kimmel, A.R.; Thoresen, G.H.; Rustan, A.C.; et al. Loss of perilipin 2 in cultured myotubes enhances lipolysis and redirects the metabolic energy balance from glucose oxidation towards fatty acid oxidation. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2147–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthivinayagam, S.; McIntosh, A.L.; Moon, K.C.; Atshaves, B.P. Plin2 inhibits cellular glucose uptake through interactions with snap23, a snare complex protein. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Tan, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Z. Reactive oxygen species induces lipid droplet accumulation in hepg2 cells by increasing perilipin 2 expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Suzuki, J.; Hirose, M.; Sato, S.; Imagawa, M.; Zenimaru, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Ikuyama, S.; Koizumi, T.; Konoshita, T.; et al. Cardiac overexpression of perilipin 2 induces dynamic steatosis: Prevention by hormone-sensitive lipase. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 313, E699–E709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.B.; Yu, K.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Tian, H.B.; Zhu, J.J.; Sun, Y.T.; Yao, D.W.; Xu, H.F.; Shi, H.P.; et al. Adipocyte differentiation-related protein promotes lipid accumulation in goat mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6954–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Sandoval, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Sanz, E.; Li, Z.; Hui, J.; Graham, B.H.; Quintana, A.; et al. Glial lipid droplets and ros induced by mitochondrial defects promote neurodegeneration. Cell 2015, 160, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, M.; Smith, J.D. Apolipoprotein e allele-specific antioxidant activity and effects on cytotoxicity by oxidative insults and beta-amyloid peptides. Nat. Genet. 1996, 14, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, H.; Hu, Z.; Hu, H.; Shi, P. The relationship between cerebral glucose metabolism and age: Report of a large brain pet data set. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, B.; Grady, C.L.; Schlageter, N.L.; Duara, R.; Rapoport, S.I. Intercorrelations of regional cerebral glucose metabolic rates in alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1987, 407, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, M.K.; Langhi, L.G.P.; Cordeiro, I.; Brito, J.M.; Batista, C.M.d.C.; Mattson, M.P.; de Mello Coelho, V. Lipid-laden cells differentially distributed in the aging brain are functionally active and correspond to distinct phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, N.; Weisgraber, K.H. Understanding the association of apolipoprotein e4 with alzheimer disease: Clues from its structure. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6027–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chouinard-Watkins, R.; Plourde, M. Fatty acid metabolism in carriers of apolipoprotein e epsilon 4 allele: Is it contributing to higher risk of cognitive decline and coronary heart disease? Nutrients 2014, 6, 4452–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, R.P. Role of phosphatidylcholine-dha in preventing apoe4-associated alzheimer’s disease. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, A.J.; Bayer, J.L.; Baker, L.D.; Cholerton, B.; VanFossen, B.; Trittschuh, E.; Rissman, R.A.; Donohue, M.C.; Moghadam, S.H.; Plymate, S.R.; et al. Differential effects of meal challenges on cognition, metabolism, and biomarkers for apolipoprotein e varepsilon4 carriers and adults with mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 48, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, H.N.; Croteau, E.; Rawat, V.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Rapoport, S.I.; Cunnane, S.C.; Umhau, J.C. Dha brain uptake and apoe4 status: A pet study with [1-(11)c]-dha. Alzheimer Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, A.; Turunen, H.; Ngandu, T.; Peltonen, M.; Levalahti, E.; Helisalmi, S.; Antikainen, R.; Backman, L.; Hanninen, T.; Jula, A.; et al. Effect of the apolipoprotein e genotype on cognitive change during a multidomain lifestyle intervention: A subgroup analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Johnson, L.A.; Torres-Perez, E.; Garcia, A.E.; Perez-Diaz, S.; Raber, J.; Maeda, N. Metabolic shifts toward fatty-acid usage and increased thermogenesis are associated with impaired adipogenesis in mice expressing human apoe4. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouinard-Watkins, R.; Rioux-Perreault, C.; Fortier, M.; Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Zhang, Y.; Lawrence, P.; Vohl, M.C.; Perron, P.; Lorrain, D.; Brenna, J.T.; et al. Disturbance in uniformly 13c-labelled dha metabolism in elderly human subjects carrying the apoe epsilon4 allele. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuriel, T.; Angulo, S.L.; Khan, U.; Ashok, A.; Chen, Q.; Figueroa, H.Y.; Emrani, S.; Liu, L.; Herman, M.; Barrett, G.; et al. Neuronal hyperactivity due to loss of inhibitory tone in apoe4 mice lacking alzheimer’s disease-like pathology. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farmer, B.C.; Kluemper, J.; Johnson, L.A. Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation. Cells 2019, 8, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020182
Farmer BC, Kluemper J, Johnson LA. Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation. Cells. 2019; 8(2):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020182
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarmer, Brandon C., Jude Kluemper, and Lance A. Johnson. 2019. "Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation" Cells 8, no. 2: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020182
APA StyleFarmer, B. C., Kluemper, J., & Johnson, L. A. (2019). Apolipoprotein E4 Alters Astrocyte Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Droplet Formation. Cells, 8(2), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020182