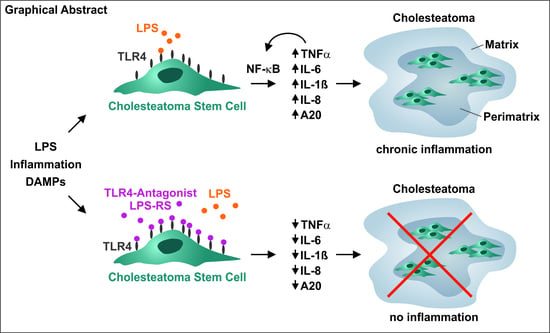
Stem Cell-Induced Inflammation in Cholesteatoma Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonist LPS-RS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement and Human Samples
2.2. Isolation and Culture of Cholesteatoma and Auditory Canal Skin Stem Cells
2.3. Haematoxylin and Eosin Staining of Cryostat Sections
2.4. Treatment of ME-CSCs and ACSCs with LPS, Heat-Killed Bacteria, TNFα, or LPS-RS
2.5. qPCR
2.6. Immunocytochemistry
2.7. Western Blot
3. Results
3.1. Successful Isolation of Sphere-Forming Stem Cells from Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Tissue and Auditory Canal Skin
3.2. Stem Cells Derived from Middle Ear Cholesteatoma Show Significantly Elevated Expression of TRL4 Compared to Auditory Canal Skin Stem Cells
3.3. Treatment of ME-CSCs with LPS Results in Significantly Enhanced Expression Levels of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators Compared to ACSCs
3.4. LPS-Dependent Pro-Inflammatory Gene Expression in ME-CSCs Is Mediated by an Enhanced Activity of NF-κB
3.5. ME-CSCs Show a TNFα-Mediated Feed-Forward-Loop of Pro-Inflammatory NF-κB Target Gene Expression
3.6. Functional Inactivation of TLR4 via a TLR4-Antagonist Blocks Pro-Inflammatory Signaling in ME-CSCs
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhutta, M.F.; Williamson, I.G.; Sudhoff, H.H. Cholesteatoma. BMJ 2011, 342, d1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberg, B.; Westin, T.; Tjellstrom, A.; Edstrom, S. Clinical characteristics of cholesteatoma. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1991, 12, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.L. Etiopathogenesis of acquired cholesteatoma: Prominent theories and recent advances in biomolecular research. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewska, E.; Wagner, M.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Ebmeyer, J.; Dazert, S.; Hildmann, H.; Sudhoff, H. Etiopathogenesis of cholesteatoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2004, 261, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, G.T.; Lee, K.H. Contemporary assessment and management of congenital cholesteatoma. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2009, 17, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhoff, H.; Tos, M. Pathogenesis of attic cholesteatoma: Clinical and immunohistochemical support for combination of retraction theory and proliferation theory. Am. J. Otol. 2000, 21, 786–792. [Google Scholar]
- Louw, L. Acquired cholesteatoma pathogenesis: Stepwise explanations. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2010, 124, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenda, S.A.; Aufdemorte, T.B. Localization of cytokines in cholesteatoma tissue. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1995, 112, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.S.; Lee, C.H.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, C.D. Interleukin-1α, Interleukin-1β and Interleukin-8 Gene Expression in Human Aural Cholesteatomas. Acta OtoLaryngol. 1996, 116, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peek, F.A.; Huisman, M.A.; Berckmans, R.J.; Sturk, A.; Van Loon, J.; Grote, J.J. Lipopolysaccharide concentration and bone resorption in cholesteatoma. Otol. Neurotol. 2003, 24, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sudhoff, H.; Liebehenz, Y.; Aschenbrenner, J.; Jung, J.; Hildmann, H.; Dazert, S. A Murine Model of Cholesteatoma-Induced Bone Resorption Using Autologous Dermal Implantation. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczkowski, J.; Sakowicz-Burkiewicz, M.; Izycka-Swieszewska, E.; Mikaszewski, B.; Pawelczyk, T. Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1alpha, interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in chronic otitis media with bone osteolysis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2011, 73, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Kariya, S.; Okano, M.; Fukushima, K.; Kataoka, Y.; Maeda, Y.; Nishizaki, K. Expression of toll-like receptors in chronic otitis media and cholesteatoma. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, Y.; Chen, Y.B.; Chen, S.J.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Xu, G.; Li, Z.H.; Huang, Q.H.; et al. TLR4 drives the pathogenesis of acquired cholesteatoma by promoting local inflammation and bone destruction. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Yin, T.; Ren, J.; Li, L.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, X.; Xie, D. Activation of the EGFR/Akt/NF-κB/cyclinD1 survival signaling pathway in human cholesteatoma epithelium. Eur. Arch. OtoRhinoLaryngol. 2014, 271, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.Y.; Yune, T.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Yeo, S.G.; Park, M.S. Expression of CYLD and NF-kappaB in human cholesteatoma epithelium. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 796315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, K.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB, inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraczek, M.; Rostkowska-Nadolska, B.; Kapral, M.; Szota, J.; Krecicki, T.; Mazurek, U. Microarray analysis of NF-kappaB-dependent genes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 22, 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.S.; Han, D.M.; Sy, C.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Fan, E.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, B. Differential expression of Toll-like receptor pathway genes in chronic rhinosinusitis with or without nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol. 2013, 133, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, J.; Wollner, S.; Schurmann, M.; Brotzmann, V.; Muller, J.; Greiner, J.F.; Goon, P.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C.; Sudhoff, H. Stem cells in middle ear cholesteatoma contribute to its pathogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, J.F.; Hauser, S.; Widera, D.; Muller, J.; Qunneis, F.; Zander, C.; Martin, I.; Mallah, J.; Schuetzmann, D.; Prante, C.; et al. Efficient animal-serum free 3D cultivation method for adult human neural crest-derived stem cell therapeutics. Eur. Cell Mater. 2011, 22, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Greiner, J.F.; Zeuner, M.; Brotzmann, V.; Schafermann, J.; Wieters, F.; Widera, D.; Sudhoff, H.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C. 1,8-Cineole potentiates IRF3-mediated antiviral response in human stem cells and in an ex vivo model of rhinosinusitis. Clin. Sci. Lond. 2016, 130, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricciardiello, F.; Cavaliere, M.; Mesolella, M.; Iengo, M. Notes on the microbiology of cholesteatoma: Clinical findings and treatment. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2009, 29, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mullarkey, M.; Rose, J.R.; Bristol, J.; Kawata, T.; Kimura, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Przetak, M.; Chow, J.; Gusovsky, F.; Christ, W.J.; et al. Inhibition of endotoxin response by e5564, a novel Toll-like receptor 4-directed endotoxin antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hauser, S.; Widera, D.; Qunneis, F.; Muller, J.; Zander, C.; Greiner, J.; Strauss, C.; Luningschror, P.; Heimann, P.; Schwarze, H.; et al. Isolation of novel multipotent neural crest-derived stem cells from adult human inferior turbinate. Stem Cells Dev. 2012, 21, 742–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastrana, E.; Silva-Vargas, V.; Doetsch, F. Eyes wide open: A critical review of sphere-formation as an assay for stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2011, 8, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.; Seonwoo, H.; Jang, K.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lim, H.J.; Lim, K.T.; Tian, C.; Chung, J.H.; Choung, Y.H. Latent progenitor cells as potential regulators for tympanic membrane regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, Y.; Toriyama, M.; Ogawa, H.; Kawakami, M. Cholesteatoma debris as an activator of human monocytes. Potentiation of the production of tumor necrosis factor. Acta Otolaryngol. 1990, 110, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Asano, K.; Kanai, K.; Suzaki, H. Suppressive activity of vitamin D3 on matrix metalloproteinase production from cholesteatoma keratinocytes in vitro. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilmore, T.D. Introduction to NF-kappaB: Players, pathways, perspectives. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6680–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, F.; Lenardo, M.J. The nuclear signaling of NF-kappaB: Current knowledge, new insights, and future perspectives. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mori, N.; Prager, D. Transactivation of the interleukin-1alpha promoter by human T-cell leukemia virus type I and type II Tax proteins. Blood 1996, 87, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiscott, J.; Marois, J.; Garoufalis, J.; D’Addario, M.; Roulston, A.; Kwan, I.; Pepin, N.; Lacoste, J.; Nguyen, H.; Bensi, G.; et al. Characterization of a functional NF-kappa B site in the human interleukin 1 beta promoter: Evidence for a positive autoregulatory loop. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 6231–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greiner, J.F.; Muller, J.; Zeuner, M.T.; Hauser, S.; Seidel, T.; Klenke, C.; Grunwald, L.M.; Schomann, T.; Widera, D.; Sudhoff, H.; et al. 1,8-Cineol inhibits nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB p65 and NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2866–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Libermann, T.A.; Baltimore, D. Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1990, 10, 2327–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenke, C.; Janowski, S.; Borck, D.; Widera, D.; Ebmeyer, J.; Kalinowski, J.; Leichtle, A.; Hofestadt, R.; Upile, T.; Kaltschmidt, C.; et al. Identification of novel cholesteatoma-related gene expression signatures using full-genome microarrays. PloS ONE 2012, 7, e52718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herlaar, E.; Brown, Z. p38 MAPK signalling cascades in inflammatory disease. Mol. Med. Today 1999, 5, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekalski, J.; Zuk, P.J.; Kochanczyk, M.; Junkin, M.; Kellogg, R.; Tay, S.; Lipniacki, T. Spontaneous NF-kappaB activation by autocrine TNFalpha signaling: A computational analysis. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e78887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwamborn, J.; Lindecke, A.; Elvers, M.; Horejschi, V.; Kerick, M.; Rafigh, M.; Pfeiffer, J.; Prüllage, M.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C. Microarray analysis of tumor necrosis factor α induced gene expression in U373 human glioblastoma cells. BMC Genomics 2003, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Du, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, N.; She, F.; Chen, Y. TNF-alpha promotes gallbladder cancer cell growth and invasion through autocrine mechanisms. Int J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proksch, E.; Folster-Holst, R.; Jensen, J.M. Skin barrier function, epidermal proliferation and differentiation in eczema. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2006, 43, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspari, A.A. Innate and adaptive immunity and the pathophysiology of psoriasis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 54, S67–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barochia, A.; Solomon, S.; Cui, X.; Natanson, C.; Eichacker, P.Q. Eritoran tetrasodium (E5564) treatment for sepsis: Review of preclinical and clinical studies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Park, B.S.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, J.; Oh, S.C.; Enkhbayar, P.; Matsushima, N.; Lee, H.; Yoo, O.J.; et al. Crystal structure of the TLR4-MD-2 complex with bound endotoxin antagonist Eritoran. Cell 2007, 130, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visintin, A.; Halmen, K.A.; Latz, E.; Monks, B.G.; Golenbock, D.T. Pharmacological inhibition of endotoxin responses is achieved by targeting the TLR4 coreceptor, MD-2. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 6465–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, J.E.; Park, Z.Y.; Kim, N.D.; Lee, J.Y. Sulforaphane inhibits the engagement of LPS with TLR4/MD2 complex by preferential binding to Cys133 in MD2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savov, J.D.; Brass, D.M.; Lawson, B.L.; McElvania-Tekippe, E.; Walker, J.K.; Schwartz, D.A. Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist (E5564) prevents the chronic airway response to inhaled lipopolysaccharide. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2005, 289, L329–L337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, T.; Tsujimoto, T.; Kawaratani, H.; Fukui, H. Therapeutic approach to regulate innate immune response by Toll-like receptor 4 antagonist E5564 in rats with D-galactosamine-induced acute severe liver injury. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opal, S.M.; Scannon, P.J.; Vincent, J.L.; White, M.; Carroll, S.F.; Palardy, J.E.; Parejo, N.A.; Pribble, J.P.; Lemke, J.H. Relationship between plasma levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS-binding protein in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opal, S.M.; Laterre, P.F.; Francois, B.; LaRosa, S.P.; Angus, D.C.; Mira, J.P.; Wittebole, X.; Dugernier, T.; Perrotin, D.; Tidswell, M.; et al. Effect of eritoran, an antagonist of MD2-TLR4, on mortality in patients with severe sepsis: The ACCESS randomized trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saber, A.; Strand, S.P.; Ulfendahl, M. Use of the biodegradable polymer chitosan as a vehicle for applying drugs to the inner ear. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 39, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Size of Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| A20 | TACCCTTGGTGACCCTGAAG CCTTGGACGGGGATTTCTAT | 175 |
| GAPDH | CTGCACCACCAACTGCTTAG GTCTTCTGGGTGGCAGTGAT | 108 |
| IL-18 | GCAAGGATTGTCTCCCAGT CGATCTGGAAGGTCTGAGGT | 125 |
| IL-1α | TGCCTGAGATACCCAAACC GCCAAGCACACCCAGTAGTC | 145 |
| IL-1β | TGTACCTGTCCTGCGTGTTGAAAG CTGGGCAGACTCAAATTCCAGCTT | 149 |
| IL-6 | GCAAAGAGGCACTGGCAGAAAACA TTCTGCAGGAACTGGATCAGGACT | 226 |
| IL-8 | TCTCTTGGCAGCCTTCCTGATTTC AGTTTTCCTTGGGGTCCAGACAGA | 227 |
| IκBα | AGACCTGGCCTTCCTCAACT GTCTCGGAGCTCAGGATCAC | 127 |
| TLR2 | AGATGCCTCCCTCTTACCCATGTT AAGACTTTGGCCAGTGCTTGCT | 186 |
| TLR4 | CACAGACTTGCGGGTTCTACATCA TGGACTTCTAAACCAGCCAGACCT | 192 |
| TNFR1 | AGGGGACAGGGAGAAGAGAGGTT TTCTGAAGCGGTGAAGG | 181 |
| TNFR2 | TCACCTCCAGCTCCACCTAT AGGCTCTGTGGCTTGTGG | 175 |
| TNFα | AAGCCCTGGTATGAGCCCATCTAT AGGGCAATGATCCCAAAGTAGACC | 137 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schürmann, M.; Greiner, J.F.W.; Volland-Thurn, V.; Oppel, F.; Kaltschmidt, C.; Sudhoff, H.; Kaltschmidt, B. Stem Cell-Induced Inflammation in Cholesteatoma Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonist LPS-RS. Cells 2020, 9, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010199
Schürmann M, Greiner JFW, Volland-Thurn V, Oppel F, Kaltschmidt C, Sudhoff H, Kaltschmidt B. Stem Cell-Induced Inflammation in Cholesteatoma Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonist LPS-RS. Cells. 2020; 9(1):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010199
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchürmann, Matthias, Johannes F. W. Greiner, Verena Volland-Thurn, Felix Oppel, Christian Kaltschmidt, Holger Sudhoff, and Barbara Kaltschmidt. 2020. "Stem Cell-Induced Inflammation in Cholesteatoma Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonist LPS-RS" Cells 9, no. 1: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010199
APA StyleSchürmann, M., Greiner, J. F. W., Volland-Thurn, V., Oppel, F., Kaltschmidt, C., Sudhoff, H., & Kaltschmidt, B. (2020). Stem Cell-Induced Inflammation in Cholesteatoma Is Inhibited by the TLR4 Antagonist LPS-RS. Cells, 9(1), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010199