BGN/TLR4/NF-κB Mediates Epigenetic Silencing of Immunosuppressive Siglec Ligands in Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
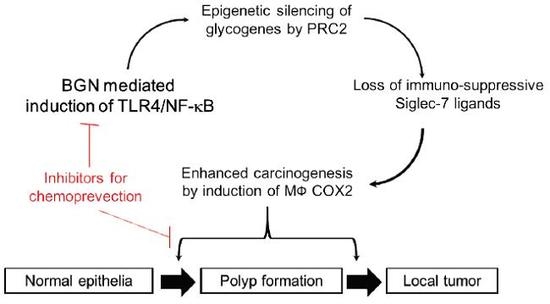
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures
2.2. Clinical Samples, Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.3. Immunoprecipitation and DNA Affinity Precipitation Assay (DAPA)
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis of Gene Expression
2.5. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
2.6. Administration of shRNA for BGN, p65, TLR2, and TLR4
2.7. Flow Cytometry and Recombinant Siglec Binding Assays
2.8. Reporter Constructs and Luciferase Assays
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TLR4 Silences Immunosuppressive Siglec Ligand Expression
3.2. Identification of BGN as a Potential TLR4 Ligand Involved in Suppression of Siglec Ligand in the Early Stage of Colon Cancer Carcinogenesis
3.3. Suppression of BGN Inactivates p65 and Decreases PRC2 Activity in Promoter Regions of SLC26A2 and ST6GalNAc6
3.4. Roles of TLR4 in Mediating NF-κB/BGN Loop for Epigenetic Silencing of SLC26A2 and ST6GalNAc6
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. Ca Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terzic, J.; Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Karin, M. Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtorf, A.; Conrad, A.; Holzmann, B.; Janssen, K.P. Cell-type specific MyD88 signaling is required for intestinal tumor initiation and progression to malignancy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1466770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, S.S.; Reis, C.A. Glycosylation in cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Ohmori, K.; Izawa, M.; Koike, T.; Kumamoto, K.; Furukawa, K.; Ando, T.; Kiso, M.; Yamaji, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; et al. Loss of disialyl Lewis(a), the ligand for lymphocyte inhibitory receptor sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin-7 (Siglec-7) associated with increased sialyl Lewis(a) expression on human colon cancers. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4498–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izawa, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Mitsuoka, C.; Kanamori, C.; Kanamori, A.; Ohmori, K.; Ishida, H.; Nakamura, S.; Kurata-Miura, K.; Sasaki, K.; et al. Expression of sialyl 6-sulfo Lewis X is inversely correlated with conventional sialyl Lewis X expression in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Yusa, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Kimura, N.; Izawa, M.; Kannagi, R. Epigenetic silencing of the sulfate transporter gene DTDST induces sialyl Lewisx expression and accelerates proliferation of colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4064–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, K.; Sakuma, K.; Kawamura, Y.I.; Izawa, M.; Ohmori, K.; Mitsuki, M.; Yamaji, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Saito, Y.; et al. Colonic epithelial cells express specific ligands for mucosal macrophage immunosuppressive receptors siglec-7 and -9. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4690–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benard, A.; Goossens-Beumer, I.J.; van Hoesel, A.Q.; Horati, H.; Putter, H.; Zeestraten, E.C.M.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Kuppen, P.J.K. Prognostic Value of Polycomb Proteins EZH2, BMI1 and SUZ12 and Histone Modification H3K27me3 in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Jones, R.S.; Zhang, Y. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in Polycomb-group silencing. Science 2002, 298, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.-C.; Chao, C.-C.; Wu, P.-H.; Chung, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-Y.; Suen, C.-S.; Hwang, M.-J.; Cai, B.-H.; Kannagi, R. Epigenetic silencing of the synthesis of immunosuppressive Siglec ligand glycans by NF-κB/EZH2/YY1 axis in early-stage colon cancers. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Yoon, B.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.Y. GENT2: An updated gene expression database for normal and tumor tissues. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–w560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broad Institute TCGA Genome Data Analysis Center. Analysis-ready Standardized TCGA Data From Broad GDAC Firehose 2016_01_28 Run. Broad Inst. MIT Harv. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannagi, R.; Kitahara, A.; Itai, S.; Zenita, K.; Shigeta, K.; Tachikawa, T.; Noda, A.; Hirano, H.; Abe, M.; Shin, S.; et al. Quantitative and qualitative characterization of human cancer-associated serum glycoprotein antigens expressing epitopes consisting of sialyl or sialyl-fucosyl type 1 chain. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 3856–3863. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka, C.; Sawada-Kasugai, M.; Ando-Furui, K.; Izawa, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Nakamura, S.; Ishida, H.; Kiso, M.; Kannagi, R. Identification of a major carbohydrate capping group of the L-selectin ligand on high endothelial venules in human lymph nodes as 6-sulfo sialyl Lewis X. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 11225–11233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohmori, K.; Fukui, F.; Kiso, M.; Imai, T.; Yoshie, O.; Hasegawa, H.; Matsushima, K.; Kannagi, R. Identification of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen as sialyl 6-sulfo Lewis X, a selectin ligand expressed on a subset of skin-homing helper memory T cells. Blood 2006, 107, 3197–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boehm, J.S.; Zhao, J.J.; Yao, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Firestein, R.; Dunn, I.F.; Sjostrom, S.K.; Garraway, L.A.; Weremowicz, S.; Richardson, A.L.; et al. Integrative genomic approaches identify IKBKE as a breast cancer oncogene. Cell 2007, 129, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erridge, C. Endogenous ligands of TLR2 and TLR4: Agonists or assistants? J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreth, K.; Frey, H.; Hubo, M.; Zeng-Brouwers, J.; Nastase, M.V.; Hsieh, L.T.; Haceni, R.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Iozzo, R.V.; Schaefer, L. Biglycan-triggered TLR-2- and TLR-4-signaling exacerbates the pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Matrix. Biol. 2014, 35, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, L.; Tredup, C.; Gubbiotti, M.A.; Iozzo, R.V. Proteoglycan neofunctions: Regulation of inflammation and autophagy in cancer biology. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Xu, T.; Xu, X.; Cui, Y.; Xing, X. Biglycan promotes the chemotherapy resistance of colon cancer by activating NF-kappaB signal transduction. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2018, 449, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Maeda, S.; Hikiba, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Hayakawa, Y.; Shibata, W.; Yanai, A.; Ogura, K.; Omata, M. Constitutive NF-kappaB activation in colorectal carcinoma plays a key role in angiogenesis, promoting tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2248–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiao, L.; Liu, X. Structural basis of histone H3K27 trimethylation by an active polycomb repressive complex 2. Science 2015, 350, aac4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.C.; Sundaram, C.; Reuter, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a therapeutic strategy. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (Bba)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2010, 1799, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsunaga, N.; Tsuchimori, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Ii, M. TAK-242 (resatorvid), a small-molecule inhibitor of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 signaling, binds selectively to TLR4 and interferes with interactions between TLR4 and its adaptor molecules. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 79, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laubli, H.; Pearce, O.M.; Schwarz, F.; Siddiqui, S.S.; Deng, L.; Stanczak, M.A.; Verhagen, A.; Secrest, P.; Lusk, C.; Schwartz, A.G.; et al. Engagement of myelomonocytic Siglecs by tumor-associated ligands modulates the innate immune response to cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2014, 111, 14211–14216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, T.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Peng, W.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, X.; Peng, Y.; Fu, X. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes M2 polarization of macrophages in the microenvironment of colorectal tumours via a TLR4-dependent mechanism. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Wang, F.S.; Jou, M.H.; Lee, K.C.; Chuang, J.H. Upregulation of TLRs and IL-6 as a marker in human colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 16, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proenca, M.A.; Biselli, J.M.; Succi, M.; Severino, F.E.; Berardinelli, G.N.; Caetano, A.; Reis, R.M.; Hughes, D.J.; Silva, A.E. Relationship between Fusobacterium nucleatum, inflammatory mediators and microRNAs in colorectal carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5351–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Zhang, G.; Song, G.; Shi, J.; Gong, L.; Mou, Y.; Han, Y. Integrated analysis of genes associated with poor prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25500–25512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.H.; Yu, J. Gut microbiota in colorectal cancer: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostic, A.D.; Chun, E.; Robertson, L.; Glickman, J.N.; Gallini, C.A.; Michaud, M.; Clancy, T.E.; Chung, D.C.; Lochhead, P.; Hold, G.L.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum potentiates intestinal tumorigenesis and modulates the tumor-immune microenvironment. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Cao, S.; Liu, S.; Yao, Z.; Sun, T.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Could gut microbiota serve as prognostic biomarker associated with colorectal cancer patients’ survival? A pilot study on relevant mechanism. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46158–46172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, F.-M.; Liu, H.-L. Fusobacterium nucleatum and colorectal cancer: A review. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 10, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Weng, W.; Peng, J.; Hong, L.; Yang, L.; Toiyama, Y.; Gao, R.; Liu, M.; Yin, M.; Pan, C.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Increases Proliferation of Colorectal Cancer Cells and Tumor Development in Mice by Activating Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling to Nuclear Factor-kappaB, and Up-regulating Expression of MicroRNA-21. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, X.; Gu, X.; Ma, T. Knockdown of biglycan expression by RNA interference inhibits the proliferation and invasion of, and induces apoptosis in, the HCT116 colon cancer cell line. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7538–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, G.B.; Grimm, T.; Sers, C.; Riemer, P.; Elmasry, M.; Kirchner, T.; Stief, C.G.; Karl, A.; Horst, D. Prognostic value and association with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and molecular subtypes of the proteoglycan biglycan in advanced bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zang, M.D.; Wang, H.X.; Li, J.F.; Su, L.P.; Yan, M.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.M.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhu, Z.G. Biglycan stimulates VEGF expression in endothelial cells by activating the TLR signaling pathway. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1473–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobsen, F.; Kraft, J.; Schroeder, C.; Hube-Magg, C.; Kluth, M.; Lang, D.S.; Simon, R.; Sauter, G.; Izbicki, J.R.; Clauditz, T.S.; et al. Up-regulation of Biglycan is Associated with Poor Prognosis and PTEN Deletion in Patients with Prostate Cancer. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Ma, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, H.; Song, C.; Gong, Y.; Xing, X. Up-regulated biglycan expression correlates with the malignancy in human colorectal cancers. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 12, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Duan, Y.T.; Li, J.F.; Su, L.P.; Yan, M.; Zhu, Z.G.; Liu, B.Y.; Yang, Q.M. Biglycan enhances gastric cancer invasion by activating FAK signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.S.; Zeng, T.T.; Xie, X.; Guan, X.Y. High expression of biglycan is associated with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Tai, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yang, N.; Jiang, J. Expression and significance of biglycan in endometrial cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2014, 289, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungefroren, H.; Lenschow, W.; Chen, W.B.; Faendrich, F.; Kalthoff, H. Regulation of biglycan gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta requires MKK6-p38 mitogen-activated protein Kinase signaling downstream of Smad signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11041–11049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doe, M.R.; Ascano, J.M.; Kaur, M.; Cole, M.D. Myc posttranscriptionally induces HIF1 protein and target gene expression in normal and cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.B.; Lenschow, W.; Tiede, K.; Fischer, J.W.; Kalthoff, H.; Ungefroren, H. Smad4/DPC4-dependent regulation of biglycan gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta in pancreatic tumor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36118–36128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaefer, L.; Babelova, A.; Kiss, E.; Hausser, H.J.; Baliova, M.; Krzyzankova, M.; Marsche, G.; Young, M.F.; Mihalik, D.; Gotte, M.; et al. The matrix component biglycan is proinflammatory and signals through Toll-like receptors 4 and 2 in macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, S.; Hughey, J.J.; Lee, T.K.; Lipniacki, T.; Quake, S.R.; Covert, M.W. Single-cell NF-kappaB dynamics reveal digital activation and analogue information processing. Nature 2010, 466, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, F.; Zambrano, S.; Agresti, A. NF-kappaB, the Importance of Being Dynamic: Role and Insights in Cancer. Biomedicines 2018, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, A.; Levchenko, A.; Scott, M.L.; Baltimore, D. The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: Temporal control and selective gene activation. Science 2002, 298, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shembade, N.; Harhaj, E.W. Regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by the A20 deubiquitinase. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.-C.; Cai, B.-H.; Suen, C.-S.; Lee, H.-Y.; Hwang, M.-J.; Liu, F.-T.; Kannagi, R. BGN/TLR4/NF-κB Mediates Epigenetic Silencing of Immunosuppressive Siglec Ligands in Colon Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020397
Huang H-C, Cai B-H, Suen C-S, Lee H-Y, Hwang M-J, Liu F-T, Kannagi R. BGN/TLR4/NF-κB Mediates Epigenetic Silencing of Immunosuppressive Siglec Ligands in Colon Cancer Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(2):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020397
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hsiang-Chi, Bi-He Cai, Ching-Shu Suen, Hsueh-Yi Lee, Ming-Jing Hwang, Fu-Tong Liu, and Reiji Kannagi. 2020. "BGN/TLR4/NF-κB Mediates Epigenetic Silencing of Immunosuppressive Siglec Ligands in Colon Cancer Cells" Cells 9, no. 2: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020397
APA StyleHuang, H. -C., Cai, B. -H., Suen, C. -S., Lee, H. -Y., Hwang, M. -J., Liu, F. -T., & Kannagi, R. (2020). BGN/TLR4/NF-κB Mediates Epigenetic Silencing of Immunosuppressive Siglec Ligands in Colon Cancer Cells. Cells, 9(2), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020397