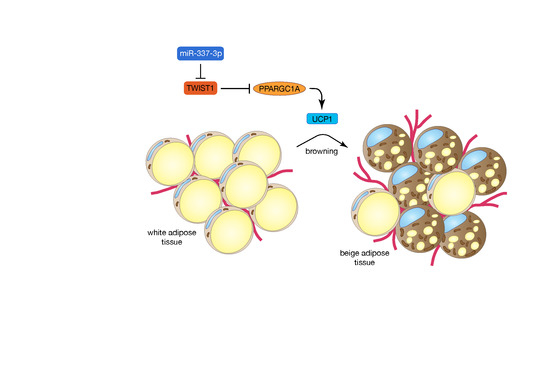
MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening of Brown Inducing miR Candidates
2.2. Quantitative RT-PCR
2.3. Western Blot Analysis
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Luciferase Assay
2.6. Immunofluorescence and Detection of Mitochondrial Activity
2.7. Mouse Adipose Tissue Isolation
2.8. Human Sample Collection
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. miR-337 is a Potential Regulator of Browning of Adipose Tissue
3.2. miR-337 Is Upregulated During Browning
3.3. miR-337 Targets Twist1, a Negative Feedback Regulator of Brown Fat Metabolism
3.4. Modulation of miR-337 Influences Twist1 and Modulates Mitochondrial Activity and Brown Fat Metabolism
3.5. miR-337/Twist1 Axis in Metabolic Syndrome Humans
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTB | (actin beta) |
| ATP | (adenosine triphosphate) |
| ATPB | (β-subunit of ATP synthase) |
| BAT | (brown adipose tissue) |
| Crls1 | (cardiolipin synthase 1) |
| Cs | (Citrate synthase) |
| GAPDH | (glyceraldehyde- 3 Phosphate dehydrogenase) |
| miR | (micro-RNA) |
| MetS | (Metabolic syndrome) |
| OXPHOS | (oxidative phosphorylation) |
| PPARGC1A | (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, gamma, co-activator alpha) |
| PPARD | (peroxisome proliferative activated receptor delta) |
| RT-PCR | (real-time polymerase chain reaction) |
| SAT | (subcutaneous adipose tissue) |
| TPS | (total protein stain) |
| Twist1 | (twist family basic helix–loop–helix transcription factor 1) |
| CP1 | (uncoupling protein1) |
| 3′UTR | (3′ untranslated region) |
| VAT | (visceral adipose tissue) |
| WAT | (white adipose tissue) |
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, P.L. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis. Model. Mech. 2009, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deepa, M.; Papita, M.; Nazir, A.; Anjana, R.M.; Ali, M.K.; Narayan, K.M.; Mohan, V. Lean people with dysglycemia have a worse metabolic profile than centrally obese people without dysglycemia. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2014, 16, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goossens, G.H.; Blaak, E.E. Adipose tissue dysfunction and impaired metabolic health in human obesity: A matter of oxygen. Front. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, J.C.; Converset, V.; Nolan, A.; Schmid, G.; Wang, S.; Heller, M.; Sennitt, M.V.; Hochstrasser, D.F.; Cawthorne, M.A. Effect of rosiglitazone on the differential expression of obesity and insulin resistance associated proteins in lep/lep mice. Proteomics 2003, 3, 1500–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerback, S. Human brown adipose tissue. Cell Metab. 2010, 11, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Bostrom, P.; Sparks, L.M.; Ye, L.; Choi, J.H.; Giang, A.H.; Khandekar, M.; Virtanen, K.A.; Nuutila, P.; Schaart, G.; et al. Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell 2012, 150, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, I.; Aprahamian, T.; Kikuchi, R.; Shimizu, A.; Papanicolaou, K.N.; MacLauchlan, S.; Maruyama, S.; Walsh, K. Vascular rarefaction mediates whitening of brown fat in obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Mitochondrial dysfunction in white adipose tissue. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Jiao, J.; Gao, G.; Prabhakar, B.S. Control of mitochondrial activity by miRNAs. J. Cell Biochem. 2012, 113, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreux, P.A.; Houtkooper, R.H.; Auwerx, J. Pharmacological approaches to restore mitochondrial function. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murri, M.; El Azzouzi, H. MicroRNAs as regulators of mitochondrial dysfunction and obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 315, H291–H302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, F.; Kong, X.; Di, W.; Liu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Lv, S.; Ding, G. MiR-27b-3p Inhibition Enhances Browning of Epididymal Fat in High-Fat Diet Induced Obese Mice. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, A.F.; Kaur, R.P.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, A.; Gupta, V.; Bansal, P. MicroRNA therapeutics: Discovering novel targets and developing specific therapy. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2016, 7, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Majo, F.; De Windt, L.J. RNA therapeutics for heart disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 155, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Fujimoto, M.; Lopes, A.; Wang, Y.X. Twist-1 is a PPARdelta-inducible, negative-feedback regulator of PGC-1alpha in brown fat metabolism. Cell 2009, 137, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uldry, M.; Yang, W.; St-Pierre, J.; Lin, J.; Seale, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. Complementary action of the PGC-1 coactivators in mitochondrial biogenesis and brown fat differentiation. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.Y.; Na, H.M.; Peng, G.; Pu, J.; Liu, P. Alteration of microRNA expression correlates to fatty acid-mediated insulin resistance in mouse myoblasts. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, K.I.; Middelbeek, R.J.; Townsend, K.L.; An, D.; Nygaard, E.B.; Hitchcox, K.M.; Markan, K.R.; Nakano, K.; Hirshman, M.F.; Tseng, Y.H.; et al. Brown adipose tissue regulates glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nairismägi, M.L.; Füchtbauer, A.; Labouriau, R.; Bramsen, J.B.; Füchtbauer, E.M. The proto-oncogene TWIST1 is regulated by microRNAs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Wang, H.; Ren, R.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, W. Reduced expression of Twist 1 is protective against insulin resistance of adipocytes and involves mitochondrial dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrian, A.D. A tale with a Twist: A developmental gene with potential relevance for metabolic dysfunction and inflammation in adipose tissue. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2012, 3, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Brown adipose tissue: Function and physiological significance. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 277–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheele, C.; Nielsen, S. Metabolic regulation and the anti-obesity perspectives of human brown fat. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuster, A.; Patlas, M.; Pinthus, J.H.; Mourtzakis, M. The clinical importance of visceral adiposity: A critical review of methods for visceral adipose tissue analysis. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sam, S. Differential effect of subcutaneous abdominal and visceral adipose tissue on cardiometabolic risk. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, F.; Tong, N. The association of visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneous adipose tissue with metabolic risk factors in a large population of Chinese adults. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2016, 85, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verboven, K.; Wouters, K.; Gaens, K.; Hansen, D.; Bijnen, M.; Wetzels, S.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Goossens, G.H. Abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipocyte size, lipolysis and inflammation relate to insulin resistance in male obese humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C. Mitochondria: Dynamic organelles in disease, aging, and development. Cell 2006, 125, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phielix, E.; Mensink, M. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and skeletal muscle metabolic function. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustarsic, E.G.; Ma, T.; Lynes, M.D.; Larsen, M.; Karavaeva, I.; Havelund, J.F.; Nielsen, C.H.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Moreno-Torres, M.; Lundh, M.; et al. Cardiolipin Synthesis in Brown and Beige Fat Mitochondria Is Essential for Systemic Energy Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 159–174.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.; Zheng, S.; Garcia-Ruiz, D.; Hou, D.; Wei, Z.; Liao, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, X.; Zen, K.; et al. Fasting induces a subcutaneous-to-visceral fat switch mediated by microRNA-149-3p and suppression of PRDM16. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Sui, W.; Zhang, M.; Dong, M.; Lim, S.; Seki, T.; Guo, Z.; Fischer, C.; Lu, H. Switching harmful visceral fat to beneficial energy combustion improves metabolic dysfunctions. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e89044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Gene Name | Gene ID | Sequence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primers for Mus Musculus | |||
| L7 | NM_011291 | Forward | GAAGCTCATCTATGAGAAGGC |
| Reverse | AAGACGAAGGAGCTGCAGAAC | ||
| Twist1 | NM_011658 | Forward | CAGGCCGGAGACCTAGATG |
| Reverse | CCACGCCCTGATTCTTGTG | ||
| Cs | NM_026444 | Forward | TAAGGAGCAGGCCAGAATTAAG |
| Reverse | CCGAAGTCTCATACACAAGTCC | ||
| Crls1 | NM_001024385 | Forward | GCTCTTGATCCACTTGCTGATA |
| Reverse | GTAAGTGAGTGGGACTGGAATAAG | ||
| Ucp1 | NM_009463 | Forward | GGGAGAGAAACACCTGCCTCT |
| Reverse | GGGAGAGAAACACCTGCCTCT | ||
| Cox8b | NM_007751 | Forward | TTGGGGCCAAGGAAGGAGTG |
| Reverse | GAGATCCCCACAGCCTGCTC | ||
| miR-337-3p | TCAGCTCCTATATGATGCCTTT | ||
| Primers for Humans | |||
| TWIST1 | NM_000474 | Forward | GCTCAGCTACGCCTTCTC |
| Reverse | TGTCCATTTTCTCCTTCTCTGG | ||
| CS | NM_004077 | Forward | GGCCATTGACTCTAACCTGG |
| Reverse | CACTTACATTGCCACCCTCA | ||
| CRLS1 | NM_019095 | Forward | ATGACGAGAATTGGCTTGGC |
| Reverse | TTTGATTGGCCCAGTTTCGA | ||
| UCP1 | NM_021833 | Forward | CGGAATCAAACCTCGCTACA |
| Reverse | TGACACTTCTCATCAGATTGGG | ||
| TCF21 | NM_003206 | Forward | CAGATCCTGGCTAACGACAA |
| Reverse | CGGTCACCACTTCTTTCAGG | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vonhögen, I.G.C.; el Azzouzi, H.; Olieslagers, S.; Vasilevich, A.; de Boer, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; da Costa Martins, P.A.; de Windt, L.J.; Murri, M. MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1. Cells 2020, 9, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041056
Vonhögen IGC, el Azzouzi H, Olieslagers S, Vasilevich A, de Boer J, Tinahones FJ, da Costa Martins PA, de Windt LJ, Murri M. MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1. Cells. 2020; 9(4):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041056
Chicago/Turabian StyleVonhögen, Indira G.C., Hamid el Azzouzi, Servé Olieslagers, Aliaksei Vasilevich, Jan de Boer, Francisco J. Tinahones, Paula A. da Costa Martins, Leon J. de Windt, and Mora Murri. 2020. "MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1" Cells 9, no. 4: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041056
APA StyleVonhögen, I. G. C., el Azzouzi, H., Olieslagers, S., Vasilevich, A., de Boer, J., Tinahones, F. J., da Costa Martins, P. A., de Windt, L. J., & Murri, M. (2020). MiR-337-3p Promotes Adipocyte Browning by Inhibiting TWIST1. Cells, 9(4), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9041056