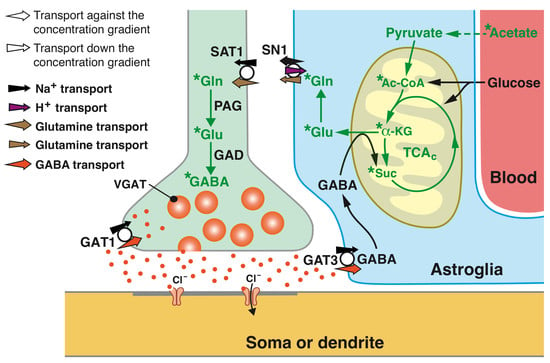
Slc38a1 Conveys Astroglia-Derived Glutamine into GABAergic Interneurons for Neurotransmitter GABA Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Handling
2.2. Labeling Experiments with 14C- and 13C-Labeled Acetate
2.3. Preparation and Incubation of In Vitro Hippocampal Slices
2.4. Immunoperoxidase Processing and Analyses of Rat Brain Slices
3. Results
4. Discussion
Slc38a1 Furnishes GABAergic Neurons with Glutamine to Synthesize Neurotransmitter GABA De Novo
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, H.; Gan, J.; Jonas, P. Interneurons. Fast-spiking, parvalbumin(+) GABAergic interneurons: From cellular design to microcircuit function. Science 2014, 345, 1255263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.; Chiu, C.S.; Sokolova, I.; Lester, H.A.; Mody, I. GABA transporter-1 (GAT1)-deficient mice: Differential tonic activation of GABAA versus GABAB receptors in the hippocampus. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 90, 2690–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowley, N.M.; Madsen, K.K.; Schousboe, A.; Steve, W.H. Glutamate and GABA synthesis, release, transport and metabolism as targets for seizure control. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soghomonian, J.J.; Martin, D.L. Two isoforms of glutamate decarboxylase: Why? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1998, 19, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.A.; Curley, A.A.; Glausier, J.R.; Volk, D.W. Cortical parvalbumin interneurons and cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Mucke, L. Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 2012, 148, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Reimer, R.J.; Krizaj, D.; Barber, R.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Copenhagen, D.R.; Edwards, R.H. Molecular analysis of System N suggests novel physiological roles in nitrogen metabolism and synaptic transmission. Cell 1999, 99, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Krizaj, D.; Larsen, P.; Reimer, R.J.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Copenhagen, D.R.; Kavanaugh, M.P.; Edwards, R.H. Coupled and uncoupled proton movement regulates amino acid transport by System N. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 7041–7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todd, A.C.; Marx, M.C.; Hulme, S.R.; Broer, S.; Billups, B. SNAT3-mediated glutamine transport in perisynaptic astrocytes in situ is regulated by intracellular sodium. Glia 2017, 65, 900–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Schmitz, D.; Reimer, R.J.; Larsson, P.; Gray, A.T.; Nicoll, R.; Kavanaugh, M.; Edwards, R.H. Glutamine uptake by neurons: Interaction of protons with system a transporters. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solbu, T.T.; Bjorkmo, M.; Berghuis, P.; Harkany, T.; Chaudhry, F.A. SAT1, a glutamine transporter, is preferentially expressed in GABAergic neurons. Front. Neuroanat. 2010, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qureshi, T.; Sorensen, C.; Berghuis, P.; Jensen, V.; Dobszay, M.B.; Farkas, T.; Dalen, K.T.; Guo, C.; Hassel, B.; Utheim, T.P.; et al. The glutamine transporter Slc38a1 regulates GABAergic neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 5166–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassel, B.; Brathe, A. Neuronal pyruvate carboxylation supports formation of transmitter glutamate. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassel, B.; Paulsen, R.E.; Johnsen, A.; Fonnum, F. Selective inhibition of glial cell metabolism in vivo by fluorocitrate. Brain Res. 1992, 576, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordengen, K.; Morland, C.; Slusher, B.S.; Gundersen, V. Dendritic localization and exocytosis of NAAG in the rat hippocampus. Cereb. Cortex 2020, 30, 1422–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, V.; Fonnum, F.; Ottersen, O.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J. Redistribution of neuroactive amino acids in hippocampus and striatum during hypoglycemia: A quantitative immunogold study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gammelsaeter, R.; Froyland, M.; Aragon, C.; Danbolt, N.C.; Fortin, D.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Davanger, S.; Gundersen, V. Glycine, GABA and their transporters in pancreatic islets of Langerhans: Evidence for a paracrine transmitter interplay. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3749–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jenstad, M.; Quazi, A.Z.; Zilberter, M.; Haglerod, C.; Berghuis, P.; Saddique, N.; Goiny, M.; Buntup, D.; Davanger, S.; Finn-Mogens, S.H.; et al. System A transporter SAT2 mediates replenishment of dendritic glutamate pools controlling retrograde signaling by glutamate. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ottersen, O.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J. Glutamate-and GABA-containing neurons in the mouse and rat brain as demonstrated with a new immunocytochemical technique. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 229, 374–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benno, R.H.; Tucker, L.W.; Joh, T.H.; Reis, D.J. Quantitative immunocytochemistry of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain. I. Development of a computer assisted method using the peroxidase-antiperoxidase technique. Brain Res. 1982, 246, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassel, B.; Bachelard, H.; Jones, P.; Fonnum, F.; Sonnewald, U. Trafficking of amino acids between neurons and glia in vivo. Effects of inhibition of glial metabolism by fluoroacetate. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1997, 17, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Hernandez, A.; Bell, K.P.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine synthetase: Glial localization in brain. Science 1977, 195, 1356–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, V.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Bjaalie, J.G.; Fonnum, F.; Ottersen, O.P.; Storm-Mathisen, J. Synaptic vesicular localization and exocytosis of L-aspartate in excitatory nerve terminals: A quantitative immunogold analysis in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 6059–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halasy, K.; Buhl, E.H.; Lorinczi, Z.; Tamas, G.; Somogyi, P. Synaptic target selectivity and input of GABAergic basket and bistratified interneurons in the CA1 area of the rat hippocampus. Hippocampus 1996, 6, 306–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamori, K.; Ross, B.D. Kinetics of glial glutamine efflux and the mechanism of neuronal uptake studied in vivo in mildly hyperammonemic rat brain. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 1103–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, M.N.; Jones-Davis, D.M.; Mathews, G.C. Glutamine uptake by System A transporters maintains neurotransmitter GABA synthesis and inhibitory synaptic transmission. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storm-Mathisen, J.; Ottersen, O.P.; Fu-long, T.; Gundersen, V.; Laake, J.H.; Nordbø, G. Metabolism and transport of amino acids studied by immunocytochemistry. Med. Biol. 1986, 64, 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Battaglioli, G.; Martin, D.L. Stimulation of synaptosomal gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis by glutamate and glutamine. J. Neurochem. 1990, 54, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holten, A.T.; Gundersen, V. Glutamine as a precursor for transmitter glutamate, aspartate and GABA in the cerebellum: A role for phosphate-activated glutaminase. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schousboe, A.; Westergaard, N.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Larsson, O.M.; Bakken, I.J.; Sonnewald, U. Trafficking between glia and neurons of TCA cycle intermediates and related metabolites. Glia 1997, 21, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, C.; Hare, N.; Bubb, W.A.; McEwan, S.R.; Broer, A.; McQuillan, J.A.; Balcar, V.J.; Conigrave, A.D.; Broer, S. Inhibition of glutamine transport depletes glutamate and GABA neurotransmitter pools: Further evidence for metabolic compartmentation. J. Neurochem. 2003, 85, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gliddon, C.M.; Shao, Z.; LeMaistre, J.L.; Anderson, C.M. Cellular distribution of the neutral amino acid transporter subtype ASCT2 in mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Lehre, K.P.; Van Lookeren Campagne, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Danbolt, N.C.; Storm-Mathisen, J. Glutamate transporters in glial plasma membranes: Highly differentiated localizations revealed by quantitative ultrastructural immunocytochemistry. Neuron 1995, 14, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norenberg, M.D.; Martinez-Hernandez, A. Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res. 1979, 161, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laake, J.H.; Takumi, Y.; Eidet, J.; Torgner, I.A.; Roberg, B.; Kvamme, E.; Ottersen, O.P. Postembedding immunogold labelling reveals subcellular localization and pathway-specific enrichment of phosphate activated glutaminase in rat cerebellum. Neuroscience 1999, 88, 1137–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, J.; Darmon, M.; Conjard, A.; Chuhma, N.; Ropert, N.; Thoby-Brisson, M.; Foutz, A.S.; Parrot, S.; Miller, G.M.; Jorisch, R.; et al. Mice lacking brain/kidney phosphate-activated glutaminase have impaired glutamatergic synaptic transmission, altered breathing, disorganized goal-directed behavior and die shortly after birth. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, F.A.; Boulland, J.L.; Jenstad, M.; Bredahl, M.K.; Edwards, R.H. Pharmacology of neurotransmitter transport into secretory vesicles. In Pharmacology of Neurotransmitter Release; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 77–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kam, K.; Nicoll, R. Excitatory synaptic transmission persists independently of the glutamate-glutamine cycle. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 9192–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulsen, R.E.; Odden, E.; Fonnum, F. Importance of glutamine for gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in rat neostriatum in vivo. J. Neurochem. 1988, 13, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglioli, G.; Martin, D.L. GABA synthesis in brain slices is dependent on glutamine produced in astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 1991, 16, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.L.; Rimvall, K. Regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid synthesis in the brain. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnewald, U.; Westergaard, N.; Schousboe, A.; Svendsen, J.S.; Unsgard, G.; Petersen, S.B. Direct demonstration by [13C]NMR spectroscopy that glutamine from astrocytes is a precursor for GABA synthesis in neurons. Neurochem. Int. 1993, 22, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.L.; Carlson, G.C.; Coulter, D.A. Dynamic regulation of synaptic GABA release by the glutamate-glutamine cycle in hippocampal area CA1. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 8537–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortinski, P.I.; Dong, J.; Mungenast, A.; Yue, C.; Takano, H.; Watson, D.J.; Haydon, P.G.; Coulter, D.A. Selective induction of astrocytic gliosis generates deficits in neuronal inhibition. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haeberle, J.; Shahbeck, N.; Ibrahim, K.; Schmitt, B.; Scheer, I.; O’Gorman, R.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Ben-Omran, T. Glutamine supplementation in a child with inherited GS deficiency improves the clinical status and partially corrects the peripheral and central amino acid imbalance. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2012, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nissen-Meyer, L.S.; Chaudhry, F.A. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the system N glutamine transporter SN1 (Slc38a3) and regulates its membrane trafficking and degradation. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cubelos, B.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, I.M.; Gimenez, C.; Zafra, F. Amino acid transporter SNAT5 localizes to glial cells in the rat brain. Glia 2005, 49, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdani, E.H.; Gudbrandsen, M.; Bjorkmo, M.; Chaudhry, F.A. The system N transporter SN2 doubles as a transmitter precursor furnisher and a potential regulator of NMDA receptors. Glia 2012, 60, 1671–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoqui, H.; Zhu, H.; Yao, D.; Ming, H.; Erickson, J.D. Cloning and functional identification of a neuronal glutamine transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4049–4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulland, J.L.; Osen, K.K.; Levy, L.M.; Danbolt, N.C.; Edwards, R.H.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Chaudhry, F.A. Cell-specific expression of the glutamine transporter SN1 suggests differences in dependence on the glutamine cycle. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1615–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulland, J.L.; Rafiki, A.; Levy, L.M.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Chaudhry, F.A. Highly differential expression of SN1, a bidirectional glutamine transporter, in astroglia and endothelium in the developing rat brain. Glia 2003, 41, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzsaki, G.; Kaila, K.; Raichle, M. Inhibition and brain work. Neuron 2007, 56, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freund, T.F. Interneuron diversity series: Rhytm and mood in perisomatic inhibition. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossart, R.; Bernard, C.; Ben-Ari, Y. Multiple facets of GABAergic neurons and synapses: Multiple fates of GABA signalling in epilepsies. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maya Vetencourt, J.F.; Sale, A.; Viegi, A.; Baroncelli, L.; De, P.R.; O’Leary, O.F.; Castren, E.; Maffei, L. The antidepressant fluoxetine restores plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 2008, 320, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, B.E.; Lee, C.J. GABA as a rising gliotransmitter. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buntup, D.; Skare, O.; Solbu, T.T.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Thangnipon, W. Beta-amyloid 25-35 peptide reduces the expression of glutamine transporter SAT1 in cultured cortical neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qureshi, T.; Bjørkmo, M.; Nordengen, K.; Gundersen, V.; Utheim, T.P.; Watne, L.O.; Storm-Mathisen, J.; Hassel, B.; Chaudhry, F.A. Slc38a1 Conveys Astroglia-Derived Glutamine into GABAergic Interneurons for Neurotransmitter GABA Synthesis. Cells 2020, 9, 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071686
Qureshi T, Bjørkmo M, Nordengen K, Gundersen V, Utheim TP, Watne LO, Storm-Mathisen J, Hassel B, Chaudhry FA. Slc38a1 Conveys Astroglia-Derived Glutamine into GABAergic Interneurons for Neurotransmitter GABA Synthesis. Cells. 2020; 9(7):1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071686
Chicago/Turabian StyleQureshi, Tayyaba, Mona Bjørkmo, Kaja Nordengen, Vidar Gundersen, Tor Paaske Utheim, Leiv Otto Watne, Jon Storm-Mathisen, Bjørnar Hassel, and Farrukh Abbas Chaudhry. 2020. "Slc38a1 Conveys Astroglia-Derived Glutamine into GABAergic Interneurons for Neurotransmitter GABA Synthesis" Cells 9, no. 7: 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071686
APA StyleQureshi, T., Bjørkmo, M., Nordengen, K., Gundersen, V., Utheim, T. P., Watne, L. O., Storm-Mathisen, J., Hassel, B., & Chaudhry, F. A. (2020). Slc38a1 Conveys Astroglia-Derived Glutamine into GABAergic Interneurons for Neurotransmitter GABA Synthesis. Cells, 9(7), 1686. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071686