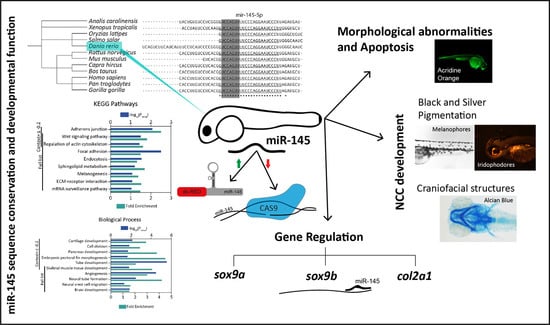
Conservation of Zebrafish MicroRNA-145 and Its Role during Neural Crest Cell Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish Care
2.2. In Silico Analysis of miR-145 Gene and Targets
2.3. MiR-145 Over- and Downregulation
2.4. Zebrafish DNA Extraction, Genotyping, and Characterization of the CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Mutation
2.5. RT-qPCR
2.6. Pigment Quantification
2.7. Alcian Blue staining
2.8. Acridine Orange Staining
2.9. Whole-Mount In Situ Hybridization (WISH)
2.10. Reporter Assays
3. Results
3.1. MiR-145 Is Conserved throughout Evolution
3.2. Expression Analysis of miR-145 during Zebrafish Development
3.3. Effects of miR-145 Over- and Downregulation on Neural Crest Derivatives
3.3.1. Effects on Pigmentation
3.3.2. Effects on Craniofacial Development
3.4. MiR-145 Over- and Downregulation Induces Apoptosis during Zebrafish Development
3.5. MiR-145 Overexpression Affects the Expression of NCC Marker Genes
3.6. The Expression of sox9b Can Be Regulated at the 3′UTR Level
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Theveneau, E.; Mayor, R. Neural crest delamination and migration: From epithelium-to-mesenchyme transition to collective cell migration. Dev. Biol. 2012, 366, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dupin, E.; Le Douarin, N.M. The neural crest, A multifaceted structure of the vertebrates. Birth. Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2014, 102, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega-Lopez, G.A.; Cerrizuela, S.; Tribulo, C.; Aybar, M.J. Neurocristopathies: New insights 150 years after the neural crest discovery. Dev. Biol. 2018, 444, S110–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.M.J.; Coux, G.; Armas, P.; Calcaterra, N. Insights into vertebrate head development: From cranial neural crest to the modelling of neurocristopathies. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2021, 65, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquinelli, A.E. Non-coding RNA: MicroRNAs and their targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal rela-tionship. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2012, 13, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Vidigal, J.A.; Ventura, A. The biological functions of miRNAs: Lessons from in vivo studies. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simões-Costa, M.; Bronner, M.E. Establishing neural crest identity: A gene regulatory recipe. Development 2015, 142, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bell, D.M.; Leung, K.K.H.; Wheatley, S.C.; Ng, L.J.; Zhou, S.; Ling, K.W.; Sham, M.H.; Koopman, P.; Tam, P.P.L.; Cheah, K.S.E. SOX9 directly regulates the type-II collagen gene. Nat. Genet. 1997, 16, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Miyamoto, M.M.; Cohn, M.J. Lamprey type II collagen and Sox9 reveal an ancient origin of the vertebrate collagenous skeleton. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3180–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, T.; Wirth, J.; Meyer, J.; Zabel, B.; Held, M.; Zimmer, J.; Pasantes, J.; Bricarelli, F.D.; Keutel, J.; Hustert, E.; et al. Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell 1994, 79, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.; Wali, N.; Sealy, I.M.; White, R.J.; Stemple, D.L.; Collins, J.E.; Busch-Nentwich, E.M. The gene regulatory basis of genetic compensation during neural crest induction. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hojo, H.; Ohba, S. Insights into Gene Regulatory Networks in Chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Dudek, K.A.; Murphy, C.L. Regulation of human chondrocyte function through direct inhi-bition of cartilage master regulator SOX9 by microRNA-145 (miRNA-145). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ying, D.; Dong, S. MicroRNA-145 Regulates Chondrogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Targeting Sox9. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakurta, S.G.; Budhiraja, G.; Subramanian, A. Growth factor and ultrasound-assisted bioreactor synergism for human mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis. J. Tissue Eng. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Pan, G.; Thomson, J.A.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-145 Regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and Represses Pluripotency in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell 2009, 137, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.-X.; Liu, Z.; Deng, F.; Wang, D.-D.; Li, X.-W.; Tian, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, J.-H. MiR-145: A potential biomarker of cancer migration and invasion. Am. J. Transl. Res 2019, 11, 6739–6753. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.-C.; Tsai, L.-L.; Wang, M.-L.; Yu, C.-H.; Lo, W.-L.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chiou, G.-Y.; Chou, M.-Y.; Chiou, S.-H. MiR145 targets the SOX9/ADAM17 axis to inhibit tumor-initiating cells and IL-6-mediated paracrine effects in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3425–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, I.W.Y.; Singh, S.; Turcotte, R.; Ghert, M. The epigenetic regulation of SOX9 by miR-145 in human chondrosarcoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.B.; Rathod, S.S.; Karthik, S.; Kaur, N.; Muzumdar, D.; Shiras, A.S. MiR-145 functions as a tumor-suppressive RNA by targeting Sox9 and adducin 3 in human glioma cells. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panza, A.; Votino, C.; Gentile, A.; Valvano, M.R.; Colangelo, T.; Pancione, M.; Micale, L.; Merla, G.; Andriulli, A.; Sabatino, L.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ-mediated induction of microRNA-145 opposes tumor phenotype in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2014, 1843, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y. The effects of lncRNA MALAT1 on proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer through regulating SOX9. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, M.; et al. circPTN sponges miR-145-5p/miR-330-5p to promote proliferation and stemness in glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Yang, Q. Long Non-Coding RNA LINC01089 Enhances the Development of Gastric Cancer by Sponging miR-145-5p to Mediate SOX9 Expression. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9213–9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynoodt, P.; Speeckaert, R.; De Wever, O.; Chevolet, I.; Brochez, L.; Lambert, J.; Van Gele, M. miR-145 overexpression suppresses the migration and invasion of metastatic melanoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Carter, A.D.; Childs, S.J. miR-145 directs intestinal maturation in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17793–17798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Childs, S.J. The smooth muscle microRNA miR-145 regulates gut epithelial development via a paracrine mechanism. Dev. Biol. 2012, 367, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gays, D.; Hess, C.; Camporeale, A.; Ala, U.; Provero, P.; Mosimann, C.; Santoro, M.M. An exclusive cellular and molecular network governs intestinal smooth muscle cell differentiation in vertebrates. Development 2017, 144, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-W.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Wu, S.-Y.; Liu, W.; Lin, C.-R.; Wu, J.-L. MiR-145 mediates zebrafish hepatic outgrowth through progranulin a signaling. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Gupta, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Mitra, S.; Chawla, B.; Khursheed, M.A.; Ramachandran, R. Oct4 mediates Müller glia reprogramming and cell cycle exit during retina regeneration in zebrafish. Life Sci. Alliance 2019, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Gupta, S.; Chaudhary, M.; Mitra, S.; Chawla, B.; Khursheed, M.A.; Saran, N.K.; Ramachandran, R. Biphasic Role of Tgf-β Signaling during Müller Glia Reprogramming and Retinal Regeneration in Zebrafish. iScience 2020, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiner, A.M. MicroRNAs and the neural crest: From induction to differentiation. Mech. Dev. 2018, 154, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Dutta, S.; Pal, R. Dysregulation of Wnt-Signaling and a Candidate Set of miRNAs Underlie the Effect of Metformin on Neural Crest Cell Development. Stem Cells 2015, 34, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Yu, Y.; Qiao, J. Decreased expression of microRNA-145 promotes the biological functions of fibroblasts in hypertrophic scar tissues by upregulating the expression of transcription factor SOX-9. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 3450–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westerfield, M. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish Danio (Brachydanio) Rerio, 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Ballard, W.W.; Kimmel, S.R.; Ullmann, B.; Schilling, T.F. Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 253–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Lopez, R. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howe, K.L.; Achuthan, P.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Flicek, P. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D884–D891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimson, A.; Farh, K.K.H.; Johnston, W.K.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Lim, L.P.; Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA Targeting Specificity in Mammals: Determinants beyond Seed Pairing. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Sherlock, G. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbon, S.; Douglass, E.; Good, B.M.; Unni, D.R.; Harris, N.L.; Mungall, C.J.; Basu, S.; Elser, J. The Gene Ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D325–D334. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Ebert, D.; Huang, X.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER version 14: More genomes, a new PANTHER GO-slim and improvements in enrichment analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D419–D426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuker, M.; Stiegler, P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981, 9, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, J.N.; Steenberg, C.D.; Bois, J.S.; Wolfe, B.R.; Pierce, M.B.; Khan, A.R.; Pierce, N.A. NUPACK: Analysis and design of nucleic acid systems. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy, A.A.; Domingues, I.; Nogueira, A.J.A.; Kummrow, F. Ecotoxicological effects, water quality standards and risk assessment for the anti-diabetic metformin. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raney, B.J.; Dreszer, T.R.; Barber, G.P.; Clawson, H.; Fujita, P.A.; Wang, T.; Kent, W.J. Track data hubs enable visualization of user-defined genome-wide annotations on the UCSC Genome Browser. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Mateos, M.A.; Vejnar, C.E.; Beaudoin, J.D.; Fernandez, J.P.; Mis, E.K.; Khokha, M.K.; Giraldez, A.J. CRISPRscan: Designing highly efficient sgRNAs for CRISPR/Cas9 targeting in vivo. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varshney, G.K.; Pei, W.; LaFave, M.; Idol, J.; Xu, L.; Gallardo, V.; Carrington, B.; Bishop, K.; Jones, M.; Li, M.; et al. High-throughput gene targeting and phenotyping in zebrafish using CRISPR/Cas9. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1030–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, M.F. Stem-Loop RT-qPCR for miRNAs. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2011, 95, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Dodd, A.; Lai, D.; McNabb, W.; Love, D.R. Validation of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Reference Genes for Quantitative Real-time RT-PCR Normalization. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experi-ments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stirling, D.; Suleyman, O.; Gil, E.; Elks, P.M.; Torraca, V.; Noursadeghi, M.; Tomlinson, G.S. Analysis tools to quantify dissemination of pathology in zebrafish larvae. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiner, A.M.; Scampoli, N.L.; Steeman, T.J.; Dooley, C.M.; Busch-Nentwich, E.M.; Kelsh, R.; Calcaterra, N.B. Dicer1 is required for pigment cell and craniofacial development in zebrafish. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2019, 1862, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.M.J.; Sdrigotti, M.A.; Kelsh, R.N.; Calcaterra, N.B. Deciphering the cellular and molecular roles of cellular nucleic acid binding protein during cranial neural crest development. Dev. Growth Differ. 2011, 53, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thisse, C.; Thisse, B. High-resolution in situ hybridization to whole-mount zebrafish embryos. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 3, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, W.; Xu, T. microRNA-145 regulates the RLR signaling pathway in miiuy croaker after poly(I:C) stimulation via targeting MDA5. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 68, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ason, B.; Darnell, D.K.; Wittbrodt, J.; Berezikov, E.; Kloosterman, W.P.; Antin, P.; Plasterk, R.H.A. Differences in vertebrate microRNA expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14385–14389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kelsh, R.N.; Brand, M.; Jiang, Y.J.; Heisenberg, C.P.; Lin, S.; Haffter, P.; Odenthal, J.; Mullins, M.C.; Van Eeden, F.J.; Furutani-Seiki, M.; et al. Zebrafish pigmentation mutations and the processes of neural crest development. Development 1996, 123, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petratou, K.; Subkhankulova, T.; Lister, J.A.; Rocco, A.; Schwetlick, H.; Kelsh, R.N. A systems biology approach uncovers the core gene regulatory network governing iridophore fate choice from the neural crest. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.L.; Hatta, K.; Riggleman, B.; Postlethwait, J.H. Expression of a type II collagen gene in the zebrafish embryonic axis. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, K.R.; Sheehy, N.T.; White, M.P.; Berry, E.C.; Morton, S.U.; Muth, A.N.; Lee, T.; Miano, J.M.; Ivey, K.N.; Srivastava, D. miR-145 and miR-143 Regulate Smooth Muscle Cell Fate Decisions. Nature 2009, 460, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muñoz, W.A.; Trainor, P.A. Neural crest cell evolution: How and when did a neural crest cell become a neural crest cell. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 111, 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dynoodt, P.; Mestdagh, P.; Van Peer, G.; Vandesompele, J.; Goossens, K.; Peelman, L.J.; Geusens, B.; Speeckaert, R.M.; Lambert, J.; Van Gele, M.J. Identification of miR-145 as a Key Regulator of the Pigmentary Process. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, H.; Yu, P.; Wang, W.Z.; Niu, Y.Y.; Li, X. The reduced lncRNA NKILA inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of chondrocytes via miR-145/SP1/NF-κB signaling in human osteoarthritis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 535–548. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Ren, S.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y. LncRNA MALAT1/MiR-145 Adjusts IL-1β-Induced Chondrocytes Viability and Cartilage Matrix Degradation by Regulating ADAMTS5 in Human Osteoarthritis. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Liu, Z.; Tao, B.; Fan, S.; Pu, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, D.; Xia, H.; Xu, L. miR-145 attenuates cardiac fibrosis through the AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway by directly targeting SOX9 in fibroblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Ying, D. The microRNA expression profiles of mouse mesenchymal stem cell during chondrogenic differentiation. BMB Rep. 2011, 44, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barritt, L.C.; Miller, J.M.; Scheetz, L.R.; Gardner, K.; Pierce, M.L.; Soukup, G.A.; Rocha-Sanchez, S.M. Conditional deletion of the human ortholog gene Dicer1 in Pax2-Cre expression domain impairs orofacial development. Indian J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 18, 310–319. [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel, C.B.; Miller, C.T.; Moens, C.B. Specification and Morphogenesis of the Zebrafish Larval Head Skeleton. Dev. Biol. 2001, 233, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wada, N.; Javidan, Y.; Nelson, S.; Carney, T.J.; Kelsh, R.; Schilling, T.F. Hedgehog signaling is required for cranial neural crest morphogenesis and chondrogenesis at the midline in the zebrafish skull. Development 2005, 132, 3977–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eberhart, J.K.; Swartz, M.E.; Crump, J.G.; Kimmel, C.B. Early Hedgehog signaling from neural to oral epithelium organizes anterior craniofacial development. Development 2006, 133, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wu, L.; Pei, M.; Zhang, Y. YTHDF2, a protein repressed by miR-145, regulates proliferation, apoptosis, and migration in ovarian cancer cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, K.; Ma, L.; Zhang, H. MicroRNA-145 overexpression inhibits neuroblastoma tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo. Bioengineered 2020, 11, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Steeman, T.J.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Sánchez, L.E.; Calcaterra, N.B.; Weiner, A.M.J. Conservation of Zebrafish MicroRNA-145 and Its Role during Neural Crest Cell Development. Genes 2021, 12, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071023
Steeman TJ, Rubiolo JA, Sánchez LE, Calcaterra NB, Weiner AMJ. Conservation of Zebrafish MicroRNA-145 and Its Role during Neural Crest Cell Development. Genes. 2021; 12(7):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSteeman, Tomás J., Juan A. Rubiolo, Laura E. Sánchez, Nora B. Calcaterra, and Andrea M. J. Weiner. 2021. "Conservation of Zebrafish MicroRNA-145 and Its Role during Neural Crest Cell Development" Genes 12, no. 7: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071023
APA StyleSteeman, T. J., Rubiolo, J. A., Sánchez, L. E., Calcaterra, N. B., & Weiner, A. M. J. (2021). Conservation of Zebrafish MicroRNA-145 and Its Role during Neural Crest Cell Development. Genes, 12(7), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12071023