Unprecedented Vessel-Icing Climatology Based on Spray-Icing Modelling and Reanalysis Data: A Risk-Based Decision-Making Input for Arctic Offshore Industries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Data
2.1. MINCOG Model Description, Study Assumption, and Data
2.2. Scope of the Study and Grid Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Icing Events and Their Rates in Some Regions of Interest
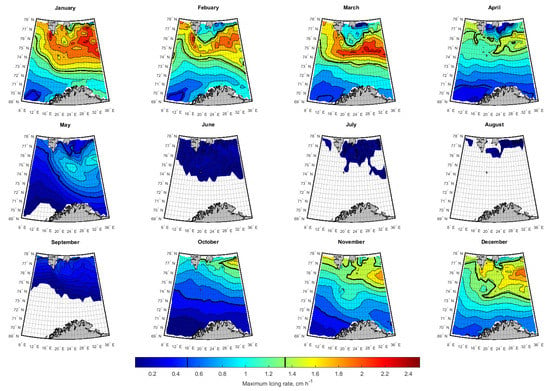
3.2. Spatial-Temporal Variation of Icing Rate and Frequency over the Arctic Norwegian Sea Areas
3.3. Historical Trend of Icing Rates and Frequencies over the Arctic Norwegian Sea Areas
4. Application in Risk-Based Decision-Making
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samuelsen, E.M.; Edvardsen, K.; Graversen, R.G. Modelled and observed sea-spray icing in Arctic-Norwegian waters. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 134, 54–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani-Sanij, A.R.; Dehghani, S.R.; Naterer, G.F.; Muzychka, Y.S. Sea spray icing phenomena on marine vessels and offshore structures: Review and formulation. Ocean Eng. 2017, 132, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, E.M. Prediction of ship icing in Arctic waters—Observations and modelling for application in operational weather forecasting. Ph.D. Thesis, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterton, M.; Cook, J.C. The Effects of Icing on Commercial Fishing Vessels; Worcester Polytechnic Institute: Worcester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 12494: Atmospheric Icing of Structures; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ryerson, C.C. Assessment of Superstructure Ice Protection as Applied to Offshore Oil Operations: Safety Problems, Hazards, Needs, and Potential Transfer Technologies; US Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Hanover, NH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.F.; Andreas, E.L. Sea Spray Icing of Drilling and Production Platforms; US Army Engineer Research and Development Centre: Hanover, NH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barabadi, A.; Garmabaki, A.H.S.; Zaki, R. Designing for performability: An icing risk index for Arctic offshore. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 124, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulyakhtin, A.; Tsarau, A. A time-dependent model of marine icing with application of computational fluid dynamics. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 104–105, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, M.; Barabady, J. On RAM performance of production facilities operating under the Barents Sea harsh environmental conditions. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2016, 7, 273–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryerson, C.C. Ice protection of offshore platforms. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2011, 65, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Khawaja, H.A.; Edvardsen, K. Review of marine icing and anti-/de-icing systems. J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2016, 15, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNV. DNV-OS-A201: Winterization for Cold Climate Operations; DNV: Høvik, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, G.W.K. A climatology of vessel icing for the subpolar North Atlantic Ocean. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 2495–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozowski, E.P.; Szilder, K.; Makkonen, L. Computer simulation of marine ice accretion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2000, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, E.M. Ship-icing prediction methods applied in operational weather forecasting. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertins, H. Icing on fishing vessels due to spray. Mar. Obs. 1968, 38, 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani-Sanij, A.R.; Dehghani, S.R.; Naterer, G.F.; Muzychka, Y.S. Marine icing phenomena on vessels and offshore structures: Prediction and analysis. Ocean Eng. 2017, 143, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.S.; Eik, K.J.; Teigen, S.H. Statistical Methods for Applying Icing Estimates in Offshore Design. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions (POACT15), Trondheim, Norway, 14–18 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Horjen, I. Numerical modeling of two-dimensional sea spray icing on vessel-mounted cylinders. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2013, 93, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horjen, I. Numerical Modelling of Time-dependent Marine Icing, Anti-icing and De-icing; Norges Tekniske Høgskole (NTH): Trondheim, Norway, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Forest, T.W.; Lozowski, E.P.; Gagnon, R.E. Estimating Marine Icing on Offshore Structures Using RIGICE04. In Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Atmospheric Icing of Structures, Montreal, QC, Canada, 12–16 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Overland, J.E. Prediction of vessel icing for near-freezing sea temperatures. Weather Forecast. 1990, 5, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigen, S.H.; Hansen, E.S.; Roth, J.C. Marine Icing Severity in the Barents Sea. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions (POAC15), Trondheim, Norway, 14–18 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Løset, S.; Vefsnmo, S.; Karas, J.; Kelly, M. Environmental Conditions in the Barents Sea in Regard to Icing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Technology for Polar Areas (Polartech), Trondheim, Norway, 15–17 June 1988; Volume 2, pp. 393–407. [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsen, E.M.; Løset, S.; Edvardsen, K. Marine icing observed on KV Nordkapp during a cold air outbreak with a developing polar low in the Barents Sea. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering Under Arctic Conditions (POAC15), Trondheim, Norway, 14–18 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Feit, D.M. Forecasting of superstructure icing for Alaskan waters. Natl. Weather Dig. Mar. 1987, 12, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Reistad, M.; Breivik, Ø.; Haakenstad, H.; Aarnes, O.J.; Furevik, B.R.; Bidlot, J.R. A high-resolution hindcast of wind and waves for the North Sea, the Norwegian Sea, and the Barents Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisenkov, Y.P.; Zablockiy, G.A.; Makshtas, A.P.; Migulin, A.I.; Panov, V.V. On the approximation of the spray-cloud dimensions. In Trudy Arkticeskogo; Romanova, L.I., Ed.; Antarkticheskii Nauchno-Issledovatelskii Institut; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1975; Volume 317, pp. 121–126. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Horjen, I.; Løset, S.; Vefsnmo, S. Icing Hazards on Supply Vessels and Stand-By Boats; Norwegian Hydrotechnical Laboratory: Trondheim, Norway, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Uppala, S.M.; KÅllberg, P.W.; Simmons, A.J.; Andrae, U.; Bechtold, V.D.C.; Fiorino, M.; Gibson, J.K.; Haseler, J.; Hernandez, A.; Kelly, G.A.; et al. The ERA-40 re-analysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2005, 131, 2961–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undén, P.; Rontu, L.; Järvinen, H.; Lynch, P.; Calvo-Sanchez, J.; Cats, G.; Cuxart, J.; Eerola, K.; Fortelius, C.; García-Moya, J. HIRLAM-5 Scientific Documentation; Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute: Norrköping, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Furevik, B.R.; Haakenstad, H. Near-surface marine wind profiles from rawinsonde and NORA10 hindcast. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Wamdi Group. The WAM Model—A Third Generation Ocean Wave Prediction Model. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1988, 18, 1775–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norwegian Petroleum Directorate. The Petroleum Resources on the Norwegian Continental Shelf; Norwegian Petroleum Directorate: Stavanger, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, A. Russian and Norwegian petroleum strategies in the Barents Sea. Arct. Rev. Law Politics 2010, 1, 225–248. [Google Scholar]
- Norwegian Petroleum Directorate. Factpages—Norwegian Petroleum Directorate. Available online: http://factpages.npd.no/factpages/ (accessed on 30 May 2018).
- Loeng, H.; Drinkwater, K. An overview of the ecosystems of the Barents and Norwegian Seas and their response to climate variability. Deep Sea Res. Part II: Topic. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 2478–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.L., Jr.; Stabeno, P.; Walters, G.; Sinclair, E.; Brodeur, R.D.; Napp, J.M.; Bond, N.A. Climate change and control of the southeastern Bering Sea pelagic ecosystem. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 5821–5853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgerson, S.G. Arctic meltdown—The economic and security implications of global warming. Foreign Aff. 2008, 78, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Z.; Perrie, W. Changes in ocean temperature in the Barents Sea in the twenty-first century. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 5901–5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, O.; Pavlov, V.; Gerland, S. The impact of winds and sea surface temperatures on the Barents Sea ice extent, a statistical approach. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 130, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overland, J.; Francis, J.A.; Hall, R.; Hanna, E.; Kim, S.-J.; Vihma, T. The melting Arctic and midlatitude weather patterns: Are they connected? J. Clim. 2015, 28, 7917–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, R.Y.; Kroese, D.P. Simulation and the Monte Carlo Method; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Naseri, M.; Emanuelsen, E.M. Anti-Icing Expected Heat Loss as a Risk Indicator for Arctic Offshore Logistics Operations. In Safety and Reliability—Safe Societies in a Challenging World; Haugen, S., Barros, A., Gulijk, C.V., Kongsvik, T., Vinnem, J.E., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1403–1410. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, W.N.; Hovelsrud, G.K.; Oort, B.E.H.; Key, J.R.; Kovacs, K.M.; Michel, C.; Haas, C.; Granskog, M.A.; Gerland, S.; Perovich, D.K.; et al. Arctic sea ice in transformation: A review of recent observed changes and impacts on biology and human activity. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzolato, L.; Howell, S.E.L.; Dawson, J.; Laliberté, F.; Copland, L. The influence of declining sea ice on shipping activity in the Canadian Arctic. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


















© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naseri, M.; Samuelsen, E.M. Unprecedented Vessel-Icing Climatology Based on Spray-Icing Modelling and Reanalysis Data: A Risk-Based Decision-Making Input for Arctic Offshore Industries. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040197
Naseri M, Samuelsen EM. Unprecedented Vessel-Icing Climatology Based on Spray-Icing Modelling and Reanalysis Data: A Risk-Based Decision-Making Input for Arctic Offshore Industries. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(4):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040197
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaseri, Masoud, and Eirik Mikal Samuelsen. 2019. "Unprecedented Vessel-Icing Climatology Based on Spray-Icing Modelling and Reanalysis Data: A Risk-Based Decision-Making Input for Arctic Offshore Industries" Atmosphere 10, no. 4: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040197
APA StyleNaseri, M., & Samuelsen, E. M. (2019). Unprecedented Vessel-Icing Climatology Based on Spray-Icing Modelling and Reanalysis Data: A Risk-Based Decision-Making Input for Arctic Offshore Industries. Atmosphere, 10(4), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040197