Size-Segregated Chemical Compositions of HULISs in Ambient Aerosols Collected during the Winter Season in Songdo, South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Aerosol Sampling
2.2. Preparation of HULISs from Size-Segregated Aerosols
2.3. FT–ICR MS Analysis and Data Processing for Elemental Composition Assignments
2.4. Air Mass Backward Trajectory Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
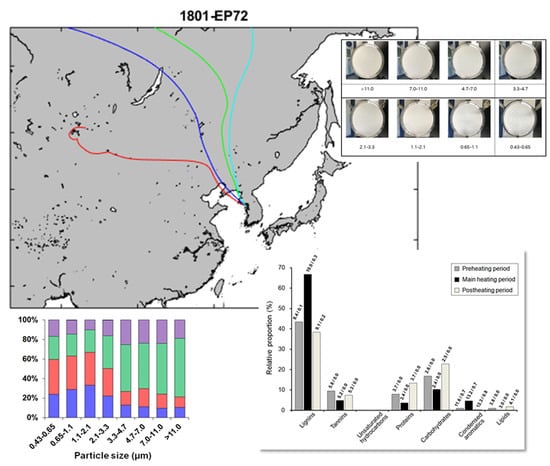
3.1. Size-Segregated Sampling of Ambient Aerosols during the Winter Season in Songdo, South Korea
3.2. UHR FT–ICR MS Profiles of HULISs in Size-Segregated Aerosols
3.3. Seasonal Characteristics of Ambient Size-Resolved HULIS Samples
3.4. Implications of Size-Dependent Chemical Compositions and Their Source Origins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohara, T.; Akimoto, H.; Kurokawa, J.; Horii, N.; Yamaji, K.; Yan, X.; Hayasaka, T. An Asian emission inventory of anthropogenic emission sources for the period 1980–2020. Atmos Chem Phys 2007, 7, 4419–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monks, P.S.; Granier, C.; Fuzzi, S.; Stohl, A.; Williams, M.L.; Akimoto, H.; Amann, M.; Baklanov, A.; Baltensperger, U.; Bey, I.; et al. Atmospheric composition change—Global and regional air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5268–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemistry of secondary organic aerosol: Formation and evolution of low-volatility organics in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3593–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poschl, U. Atmospheric aerosols: Composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallquist, M.; Wenger, J.C.; Baltensperger, U.; Rudich, Y.; Simpson, D.; Claeys, M.; Dommen, J.; Donahue, N.M.; George, C.; Goldstein, A.H.; et al. The formation, properties and impact of secondary organic aerosol: Current and emerging issues. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5155–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervens, B.; Turpin, B.J.; Weber, R.J. Secondary organic aerosol formation in cloud droplets and aqueous particles (aqSOA): A review of laboratory, field and model studies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11069–11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, J.A.; Alexis, N.; Barnes, C.; Bernstein, I.L.; Bernstein, J.A.; Nel, A.; Peden, D.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Tarlo, S.M.; Williams, P.B. Health effects of air pollution. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H. Environmental carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Photochemistry and phototoxicity. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2002, 20, 149–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.H.; He, Q.; Male, T.L.; Brune, W.H.; Rudich, Y.; Pardo, M. Exposure of lung epithelial cells to photochemically aged secondary organic aerosol shows increased toxic effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, E.R.; Rudich, Y. Atmospheric HULIS: How humic-like are they? A comprehensive and critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 729–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- 1Han, H.; Kim, G. Significant seasonal change in optical properties by atmospheric humic-like substances (HULIS) in water-soluble organic carbon aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ikemori, F.; Higo, H.; Asakawa, D.; Mochida, M. Chemical Structural Characteristics of HULIS and Other Fractionated Organic Matter in Urban Aerosols: Results from Mass Spectral and FT-IR Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Rincon, A.G.; Kalberer, M.; Yu, J.Z. Elemental composition of HULIS in the Pearl River Delta Region, China: Results inferred from positive and negative electrospray high resolution mass spectrometric data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7454–7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Xiang, P.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Ma, Y.; He, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, J.; Querol, X. Chemical characterization of humic-like substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 573, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Qiao, T.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Xiu, G.; Yu, J.Z. Temporal variations and source apportionment of Hulis-C in PM2.5 in urban Shanghai. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wan, X.; Gao, S.; Fu, P.; Yin, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, G.; Kang, S.; Ram, K.; Cong, Z. Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) in Aerosols of Central Tibetan Plateau (Nam Co, 4730 m asl): Abundance, Light Absorption Properties, and Sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7203–7211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Mo, Y.; Ding, P.; Li, J.; Shen, C.; Zhang, G. Dual carbon isotopes ((14)C and (13)C) and optical properties of WSOC and HULIS-C during winter in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Biswas, J.; Guttikunda, S.; Roychowdhury, S.; Nayak, M. An investigation of potential regional and local source regions affecting fine particulate matter concentrations in Delhi, India. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Tan, H.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Wolters, M.A.; Qin, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Large-scale transport of PM2.5 in the lower troposphere during winter cold surges in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havers, N.; Burba, P.; Lambert, J.; Klockow, D. Spectroscopic characterization of humic-like substances in airborne particulate matter. J. Atmos. Chem. 1998, 29, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, B.; Kiss, G.; Ganszky, I.; Gelencser, A.; Krivacsy, Z. Isolation of water-soluble organic matter from atmospheric aerosol. Talanta 2001, 55, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Yu, J.Z.; Engling, G.; Kalberer, M. Organosulfates in humic-like substance fraction isolated from aerosols at seven locations in East Asia: A study by ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 13118–13127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, Y.K.; Pack, S.P.; Jung, J.Y.; Jang, K.S. Chemical characterization of dissolved organic matter in moist acidic tussock tundra soil using ultra-high resolution 15T FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2017, 22, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Ryu, J.; Jeon, S.; Seo, J.; Yang, Y.H.; Pack, S.P.; Choung, S.; Jang, K.S. In-depth compositional analysis of water-soluble and -insoluble organic substances in fine (PM2.5) airborne particles using ultra-high-resolution 15T FT-ICR MS and GCxGC-TOFMS. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoleni, L.R.; Ehrmann, B.M.; Shen, X.; Marshall, A.G.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Water-soluble atmospheric organic matter in fog: Exact masses and chemical formula identification by ultrahigh-resolution fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3690–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kramer, R.W.; Hatcher, P.G. Graphical method for analysis of ultrahigh-resolution broadband mass spectra of natural organic matter, the van Krevelen diagram. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5336–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hockaday, W.C.; Grannas, A.M.; Kim, S.; Hatcher, P.G. Direct molecular evidence for the degradation and mobility of black carbon in soils from ultrahigh-resolution mass spectral analysis of dissolved organic matter from a fire-impacted forest soil. Org. Geochem. 2006, 37, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, B.P.; Dittmar, T. From mass to structure: An aromaticity index for high-resolution mass data of natural organic matter. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, N.; Davis, C.E.; Blackbird, S.; Daniels, L.R.; Preece, C.; Woodward, M.; Mahaffey, C. Seasonal and spatial variability in the optical characteristics of DOM in a temperate shelf sea. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczuk, P.; Tilstone, G.H.; Zablocka, M.; Röttgers, R.; Thomas, R. Composition of dissolved organic matter along an Atlantic Meridional Transect from fluorescence spectroscopy and Parallel Factor Analysis. Mar. Chem. 2013, 157, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yue, D.; Hu, M.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guo, S.; Wehner, B.; Nowak, A.; Achtert, P.; Wiedensohler, A.; Jung, J.; et al. Characteristics of aerosol size distributions and new particle formation in the summer in Beijing. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D00G12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Miura, K.; Kawata, R.; Furutani, H.; Uematsu, M.; Omori, Y. Number-size distribution of aerosol particles and new particle formation events in tropical and subtropical Pacific Oceans. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kindi, S.S.; Pope, F.D.; Beddows, D.C.; Bloss, W.J.; Harrison, R.M. Size-dependent chemical ageing of oleic acid aerosol under dry and humidified conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 15561–15579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.N.; Dunn, M.J.; VanReken, T.M.; Iida, K.; Stolzenburg, M.R.; McMurry, P.H.; Huey, L.G. Chemical composition of atmospheric nanoparticles formed from nucleation in Tecamac, Mexico: Evidence for an important role for organic species in nanoparticle growth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Erdakos, G.B.; Asher, W.E.; Pankow, J.F. Modeling the formation of secondary organic aerosol (SOA). 2. The predicted effects of relative humidity on aerosol formation in the alpha-pinene-, beta-pinene-, sabinene-, delta 3-carene-, and cyclohexene-ozone systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, L.A.P.; Macias, E.S.; White, W.H. Aerosol composition as a function of haze and humidity levels in the Southwestern U.S. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 28, 3679–3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Kourtchev, I.; Pant, P.; Keyte, I.J.; O’Connor, I.P.; Wenger, J.C.; Pope, F.D.; Harrison, R.M.; Kalberer, M. Molecular composition of organic aerosols at urban background and road tunnel sites using ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry. Faraday Discuss. 2016, 189, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, K.M.; Louchouarn, P.; Griffin, R.J. Lignin-derived phenols in Houston aerosols: Implications for natural background sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8268–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Sokhi, R.; van Grieken, R. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Source attribution, emission factors and regulation. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2895–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.F.; Fang, G.C.; Chen, J.C.; Wu, Y.S. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Asia: A review from 1999 to 2004. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 142, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Liang, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M.; Shi, Q. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in ambient aerosols from Beijing: Characterization of low volatile PAHs by positive-ion atmospheric pressure photoionization (APPI) coupled with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4716–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petters, M.D.; Prenni, A.J.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; DeMott, P.J.; Matsunaga, A.; Lim, Y.B.; Ziemann, P.J. Chemical aging and the hydrophobic-to-hydrophilic conversion of carbonaceous aerosol. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L24806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denjean, C.; Formenti, P.; Picquet-Varrault, B.; Camredon, M.; Pangui, E.; Zapf, P.; Katrib, Y.; Giorio, C.; Tapparo, A.; Temime-Roussel, B.; et al. Aging of secondary organic aerosol generated from the ozonolysis of α-pinene: Effects of ozone, light and temperature. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 883–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C. Evidence of an increasing NO2/NOX emissions ratio from road traffic emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4793–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Tuomi, T.; Aarnio, P.; Pirjola, L.; Mäkelä, T.; Hillamo, R.; Jantunen, M. Emissions of fine particles, NOx, andCO from on-road vehicles in Finland. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6696–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.D.; Kim, J.S. The Status of the Atmospheric Environment and Air Quality Management Measures of the Port. of Incheon; The Incheon Institute: Incheon, Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, S.L.; MacMillan, A.C.; Drozd, G.T.; Goldstein, A.H.; Chu, R.K.; Pasa-Tolic, L.; Shaw, J.B.; Tolic, N.; Lin, P.; Laskin, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Organosulfur Compounds in Biodiesel and Diesel Fuel Secondary Organic Aerosol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Surratt, J.D.; Lin, Y.H.; Bapat, J.; Kamens, R.M. Effect of relative humidity on SOA formation from isoprene/NO photooxidation: Enhancement of 2-methylglyceric acid and its corresponding oligoesters under dry conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6411–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuelsson, E.U.; Watne, A.K.; Lutz, A.; Ljungstrom, E.; Hallquist, M. Influence of humidity, temperature, and radicals on the formation and thermal properties of secondary organic aerosol (SOA) from ozonolysis of beta-pinene. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 10346–10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepri, L.; Bubba, M.D.; Masi, F.; Udisti, R.; Cini, R. Particle size distribution of organic compounds in aqueous aerosols collected from above sewage aeration tanks. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, C.E.; Gerde, P.; Hanberg, A.; Jernstrom, B.; Johansson, C.; Kyrklund, T.; Rannug, A.; Tornqvist, M.; Victorin, K.; Westerholm, R. Cancer risk assessment, indicators, and guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the ambient air. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 451–488. [Google Scholar]
- Hauser, R.; Calafat, A.M. Phthalates and human health. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 6, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, S.; Masai, E.; Kamimura, N.; Takahashi, K.; Anderson, R.C.; Faisal, P.A. Phthalates impact human health: Epidemiological evidences and plausible mechanism of action. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 360–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Jie, J.; Li, X.; Dong, X.; Miao, Z.; Shen, M.; Bu, Q. Spatial, seasonal and particle size dependent variations of PAH contamination in indoor dust and the corresponding human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 653, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksionzek, K.B.; Lechtenfeld, O.J.; McCallister, S.L.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Geuer, J.K.; Geibert, W.; Koch, B.P. Dissolved organic sulfur in the ocean: Biogeochemistry of a petagram inventory. Science 2016, 354, 456–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, K.-S.; Choi, A.Y.; Choi, M.; Kang, H.; Kim, T.-W.; Park, K.-T. Size-Segregated Chemical Compositions of HULISs in Ambient Aerosols Collected during the Winter Season in Songdo, South Korea. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040226
Jang K-S, Choi AY, Choi M, Kang H, Kim T-W, Park K-T. Size-Segregated Chemical Compositions of HULISs in Ambient Aerosols Collected during the Winter Season in Songdo, South Korea. Atmosphere. 2019; 10(4):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040226
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, Kyoung-Soon, A Young Choi, Mira Choi, Hyunju Kang, Tae-Wook Kim, and Ki-Tae Park. 2019. "Size-Segregated Chemical Compositions of HULISs in Ambient Aerosols Collected during the Winter Season in Songdo, South Korea" Atmosphere 10, no. 4: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040226
APA StyleJang, K. -S., Choi, A. Y., Choi, M., Kang, H., Kim, T. -W., & Park, K. -T. (2019). Size-Segregated Chemical Compositions of HULISs in Ambient Aerosols Collected during the Winter Season in Songdo, South Korea. Atmosphere, 10(4), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos10040226