Fine-Scale Columnar and Surface NOx Concentrations over South Korea: Comparison of Surface Monitors, TROPOMI, CMAQ and CAPSS Inventory
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
2.1. Surface Observations
2.2. TROPOMI
2.3. Model
2.4. CAPSS Emissions
2.5. Spatial and Vertical Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Base Model Performance
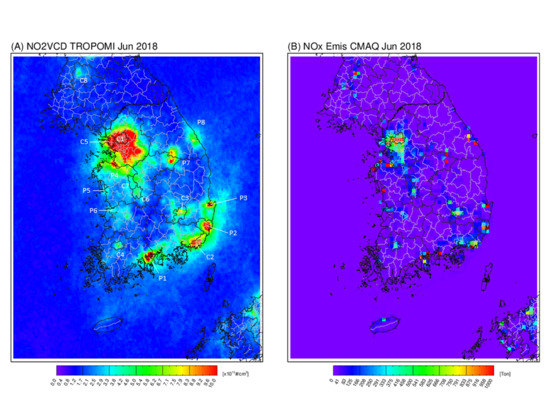
3.2. Spatial Distribution
3.3. Temporal Comparison
3.4. Point Sources
3.5. Nitric Oxide Comparison
3.6. Discussion on Uncertainties
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The current South Korean emission inventory, CAPSS 2016, represents the geographical distributions of the NOx emission sources over the country well. It shows good agreement (e.g., R = 0.96 for June 2018) with the TROPOMI NO2 column density distribution;
- (2)
- The model biases compared with the satellite and surface observations are generally consistent in their spatial patterns, showing overestimations over the SMA and major point sources and underestimations in other locations;
- (3)
- The modeled column densities overestimate all year, whereas the modeled surface concentrations mostly underestimate, especially during the cold season;
- (4)
- The diurnal variation agrees better in urban monitoring sites than in roadside monitoring sites. Prominent underestimations of daytime concentrations at roadside monitors are observed;
- (5)
- The modeled NO2:NOx ratio is higher than that of observations in all cases, and the largest differences are observed at roadside sites.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Georgoulias, A.K.; van der A, R.J.; Stammes, P.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J. Trends and trend reversal detection in 2 decades of tropospheric NO2 satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6269–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, R.V. Global inventory of nitrogen oxide emissions constrained by space-based observations of NO2 columns. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Richter, A.; De Smedt, I.; Lorente, A.; Beirle, S.; van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Zara, M.; Peters, E.; Van Roozendael, M.; et al. Improving algorithms and uncertainty estimates for satellite NO2 retrievals: results from the quality assurance for the essential climate variables (QA4ECV) project. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6651–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beirle, S.; Boersma, K.F.; Platt, U.; Lawrence, M.G.; Wagner, T. Megacity Emissions and Lifetimes of Nitrogen Oxides Probed from Space. Science 2011, 333, 1737–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leue, C.; Wenig, M.; Wagner, T.; Klimm, O.; Platt, U.; Jähne, B. Quantitative analysis of NOx emissions from Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment satellite image sequences. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 5493–5505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, L.; Tong, D.; Lee, P.; Kim, H.-C.; Chai, T. Assessment of NOx and O3 forecasting performances in the U.S. National Air Quality Forecasting Capability before and after the 2012 major emissions updates. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, T.; Kim, H.-C.; Lee, P.; Tong, D.; Pan, L.; Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; McQueen, J.; Tsidulko, M.; Stajner, I. Evaluation of the United States National Air Quality Forecast Capability experimental real-time predictions in 2010 using Air Quality System ozone and NO2 measurements. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1831–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boersma, K.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Bucsela, E.J.; Perring, A.E.; Dirksen, R.; van der A, R.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Park, R.J.; Wenig, M.O.; Bertram, T.H. Validation of OMI tropospheric NO2 observations during INTEX-B and application to constrain NOx emissions over the eastern United States and Mexico. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4480–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, D.Q.; Lamsal, L.; Pan, L.; Ding, C.; Kim, H.; Lee, P.; Chai, T.; Pickering, K.E.; Stajner, I. Long-term NOx trends over large cities in the United States during the great recession: Comparison of satellite retrievals, ground observations, and emission inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Pan, L.; Chen, W.; Lamsal, L.; Lee, P.; Tang, Y.; Kim, H.; Kondragunta, S.; Stajner, I. Impact of the 2008 Global Recession on air quality over the United States: Implications for surface ozone levels from changes in NOx emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 9280–9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; de Foy, B.; Lamsal, L.N.; Streets, D.G.; Lu, Z.; Pickering, K.E.; Krotkov, N.A. The observed response of Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) NO2 columns to NOx emission controls on power plants in the United States: 2005–2011. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Visser, A.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Ganzeveld, L.N.; Krol, M.C. European NOx emissions in WRF-Chem derived from OMI: impacts on summertime surface ozone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11821–11841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huijnen, V.; Eskes, H.J.; Poupkou, A.; Elbern, H.; Boersma, K.F.; Foret, G.; Sofiev, M.; Valdebenito, A.; Flemming, J.; Stein, O.; et al. Comparison of OMI NO2 tropospheric columns with an ensemble of global and European regional air quality models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3273–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curier, R.L.; Kranenburg, R.; Segers, A.J.S.; Timmermans, R.M.A.; Schaap, M. Synergistic use of OMI NO2 tropospheric columns and LOTOS–EUROS to evaluate the NOx emission trends across Europe. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 149, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Foy, B.; Wilkins, J.L.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Duncan, B.N. Model evaluation of methods for estimating surface emissions and chemical lifetimes from satellite data. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Beirle, S.; Zhang, Q.; Dörner, S.; He, K.; Wagner, T. NOx lifetimes and emissions of cities and power plants in polluted background estimated by satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5283–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Beirle, S.; Zhang, Q.; van der A, R.J.; Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; He, K. NOx emission trends over Chinese cities estimated from OMI observations during 2005 to 2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9261–9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, K.; Sekiya, T.; Fu, D.; Bowman, K.W.; Kulawik, S.S.; Sudo, K.; Walker, T.; Kanaya, Y.; Takigawa, M.; Ogochi, K.; et al. Balance of Emission and Dynamical Controls on Ozone During the Korea-United States Air Quality Campaign From Multiconstituent Satellite Data Assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 387–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mijling, B.; van der A, R.J.; Zhang, Q. Regional nitrogen oxides emission trends in East Asia observed from space. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 12003–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Lee, C.S.; Zhang, R.; Chen, L. Spatial and temporal evaluation of long term trend (2005–2014) of OMI retrieved NO2 and SO2 concentrations in Henan Province, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 154, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijling, B.; van der A, R.J. Using daily satellite observations to estimate emissions of short-lived air pollutants on a mesoscopic scale. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; van der A, R.J.; Eskes, H.; Ding, J.; Mijling, B. Evaluation of modeling NO2 concentrations driven by satellite-derived and bottom-up emission inventories using in situ measurements over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Klimont, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Martin, R.V.; Zheng, B.; Heyes, C.; Cofala, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, K. Comparison and evaluation of anthropogenic emissions of SO2 and NOx over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 3433–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, Z.; Henze, D.K.; Capps, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Keller, M. Monthly top-down NOx emissions for China (2005–2012): A hybrid inversion method and trend analysis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4600–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Duncan, B.N.; Yoshida, Y.; Krotkov, N.A.; Pickering, K.E.; Streets, D.G.; Lu, Z.U.S. NO2 trends (2005–2013): EPA Air Quality System (AQS) data versus improved observations from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI). Atmos. Environ. 2015, 110, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, D.; Zhao, X.; McLinden, C.A.; Boersma, F.; Bourassa, A.; Dammers, E.; Degenstein, D.; Eskes, H.; Fehr, L.; Fioletov, V.; et al. High-Resolution Mapping of Nitrogen Dioxide With TROPOMI: First Results and Validation Over the Canadian Oil Sands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wu, Z. Marinello Spatial Variation of NO2 and Its Impact Factors in China: An Application of Sentinel-5P Products. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, C.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, B.-U.; Kim, S. Surface ozone response to satellite-constrained NOx emission adjustments and its implications. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 113469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Kwon, S.; Kim, B.-U.; Kim, S. Review of Shandong Peninsular Emissions Change and South Korean Air Quality. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 34, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-U.; Bae, C.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, E.; Kim, S. Spatially and chemically resolved source apportionment analysis: Case study of high particulate matter event. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 162, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.M.; Lee, S.; Chang, L.S.; Song, C.H. A comparison study between CMAQ-simulated and OMI-retrieved NO2 columns over East Asia for evaluation of NOx emission fluxes of INTEX-B, CAPSS, and REAS inventories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1913–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, K.M.; Lee, C.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Song, C.H. A comparison study between model-predicted and OMI-retrieved tropospheric NO2 columns over the Korean peninsula. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2962–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, Y.P.; Morino, Y.; Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T. Verification of NOx emission inventory over South Korea using sectoral activity data and satellite observation of NO2 vertical column densities. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.C. Detection of Strong NOx Emissions from Fine-scale Reconstruction of the OMI Tropospheric NO2 Product. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Saide, P.E.; Lamsal, L.N.; de Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Woo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Gao, M.; Carmichael, G.; et al. A top-down assessment using OMI NO2 suggests an underestimate in the NOx emissions inventory in Seoul, South Korea, during KORUS-AQ. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1801–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.W.; Lee, J.H.; Woo, J.W.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, S.H. Comparison of PM2.5 Chemical Components over East Asia Simulated by the WRF-Chem and WRF/CMAQ Models: On the Models’ Prediction Inconsistency. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, K.-H.; Park, C. Long-term trend of NO2 in major urban areas of Korea and possible consequences for health. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, H.; Muto, T.; Itahashi, S.; Kurokawa, J.; Uno, I. Turnaround of Tropospheric Nitrogen Dioxide Pollution Trends in China, Japan, and South Korea. Sola 2016, 12, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shon, Z.-H.; Kim, K.-H. Impact of emission control strategy on NO2 in urban areas of Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, D.; Sanchez, D.; Wang, M.; Seco, R.; Blake, D.; Meinardi, S.; Barletta, B.; Hughes, S.; Jung, J.; et al. The Controlling Factors of Photochemical Ozone Production in Seoul, South Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Lee, Y.-M.; Jang, K.-W.; Yoo, C.; Kang, K.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jung, S.-W.; Park, J.-M.; Lee, S.-B.; Han, J.-S.; et al. Korean National Emissions Inventory System and 2007 Air Pollutant Emissions. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 5, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elizabeth, C.E. Technical Assistance Document for the Chemiluminescence Measurement of Nitrogen Dioxide. EPA, 1975. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/ttnamti1/archive/files/ambient/criteria/reldocs/4-75-003.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Steinbacher, M.; Zellweger, C.; Schwarzenbach, B.; Bugmann, S.; Buchmann, B.; Ordóñez, C.; Prevot, A.S.H.; Hueglin, C. Nitrogen oxide measurements at rural sites in Switzerland: Bias of conventional measurement techniques. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D11307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Eskes, H.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Veefkind, J.P. TROPOMI ATBD of the total and Tropospheric NO2 Data Products. Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management, 2019. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/documents/247904/2476257/Sentinel-5P-TROPOMI-ATBD-NO2-data-products (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Eskes, H.; van Geffen, J.; Boersma, K.F.; Eichmann, K.-U.; Apituley, A.; Pedergnana, M.; Sneep, M.; Veefkind, P.J.; Loyola, D. Sentinel-5 precursor/TROPOMI Level 2 Product User Manual Nitrogen Dioxide. Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management, 2019. Available online: https://sentinel.esa.int/documents/247904/2474726/Sentinel-5P-Level-2-Product-User-Manual-Nitrogen-Dioxide (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B. A time-split nonhydrostatic atmospheric model for weather research and forecasting applications. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 3465–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the Governing Equations, Computational Algorithms, and Other Components of the Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) Modeling System. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, T.L.; Pleim, J.E. The Meteorology-Chemistry Interface Processor (MCIP) for the CMAQ modeling system: updates through MCIPv3.4.1. Geosci. Model Dev. 2010, 3, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, W.P.L. The SAPRC-99 Chemical Mechanism and Updated VOC Reactivity Scales. University of California Riverside, 2003. Available online: http://www.cert.ucr.edu/~carter/reactdat.htm (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Jang, Y.; Lee, Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Woo, J.-H. Improvement China Point Source for Improving Bottom-Up Emission Inventory. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- NCEP NCEP FNL Operational Model Global Tropospheric Analyses, Continuing From July 1999; Research Data Archive, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory: Boulder, CO, USA, 2000; Available online: https://doi.org/10.5065/D6M043C6 (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Hong, S.-Y.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S.-H. A Revised Approach to Ice Microphysical Processes for the Bulk Parameterization of Clouds and Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain–Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an Advanced Land Surface–Hydrology Model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hertel, O.; Berkowicz, R.; Christensen, J.; Hov, Ø. Test of two numerical schemes for use in atmospheric transport-chemistry models. Atmos. Environ. Part A. Gen. Top. 1993, 27, 2591–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, F.S. Models-3 Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model aerosol component 1. Model description. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamartino, R.J. Nonnegative, Conserved Scalar Transport Using Grid-Cell-centered, Spectrally Constrained Blackman Cubics for Applications on a Variable-Thickness Mesh. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louis, J.-F. A parametric model of vertical eddy fluxes in the atmosphere. Bound-Lay. Meteorol. 1979, 17, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.S.; Brost, R.A.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; Madronich, S.; Middleton, P.; Stockwell, W.R.; Walcek, C.J. A three-dimensional Eulerian acid deposition model: Physical concepts and formulation. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 14681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Lee, P.; Judd, L.; Pan, L.; Lefer, B. OMI NO2 column densities over North American urban cities: the effect of satellite footprint resolution. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.-M.; Chai, T.; Ngan, F.; Pan, L.; Lee, P. A Conservative Downscaling of Satellite-Detected Chemical Compositions: NO2 Column Densities of OMI, GOME-2, and CMAQ. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valin, L.C.; Russell, A.R.; Hudman, R.C.; Cohen, R.C. Effects of model resolution on the interpretation of satellite NO2 observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11647–11655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Foy, B.; Krotkov, N.A.; Bei, N.; Herndon, S.C.; Huey, L.G.; Martínez, A.-P.; Ruiz-Suárez, L.G.; Wood, E.C.; Zavala, M.; Molina, L.T. Hit from both sides: tracking industrial and volcanic plumes in Mexico City with surface measurements and OMI SO2 retrievals during the MILAGRO field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 9599–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.R.; Valin, L.C.; Bucsela, E.J.; Wenig, M.O.; Cohen, R.C. Space-based Constraints on Spatial and Temporal Patterns of NOx Emissions in California, 2005−2008. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3608–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroidis, I.; Chaloulakou, A. Long-term trends of primary and secondary NO2 production in the Athens area. Variation of the NO2/NOx ratio. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6872–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, R.J.; Dubé, W.P.; Aikin, K.C.; Eilerman, S.J.; Neuman, J.A.; Peischl, J.; Ryerson, T.B.; Brown, S.S. On-road measurements of vehicle NO2 /NOx emission ratios in Denver, Colorado, USA. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.G.; Khalek, I.; McDonald, J.D.; van Erp, A.M. The Advanced Collaborative Emissions Study (ACES) of 2007- and 2010-Emissions Compliant Heavy-Duty Diesel Engines: Characterization of Emissions and Health Effects. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, A.A.; Nguyen, N.T.; Presto, A.A.; Gordon, T.D.; Lipsky, E.M.; Karve, M.; Gutierrez, A.; Robertson, W.H.; Zhang, M.; Brandow, C.; et al. Gas- and particle-phase primary emissions from in-use, on-road gasoline and diesel vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond-Bryant, J.; Chris Owen, R.; Graham, S.; Snyder, M.; McDow, S.; Oakes, M.; Kimbrough, S. Estimation of on-road NO2 concentrations, NO2/NOX ratios, and related roadway gradients from near-road monitoring data. Air Qual. Atmos. Heal. 2017, 10, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbrough, S.; Chris Owen, R.; Snyder, M.; Richmond-Bryant, J. NO to NO2 conversion rate analysis and implications for dispersion model chemistry methods using Las Vegas, Nevada near-road field measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.P.; Lee, G. Trend of Air Quality in Seoul: Policy and Science. Aerosol. Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dickerson, R.R.; Anderson, D.C.; Ren, X. On the use of data from commercial NOx analyzers for air pollution studies. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; de Foy, B.; Griffin, D.; McLinden, C.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Krotkov, N.A.; Eskes, H. Enhanced Capabilities of TROPOMI NO2: Estimating NOX from North American Cities and Power Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12594–12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.C.; Loughner, C.P.; Diskin, G.; Weinheimer, A.; Canty, T.P.; Salawitch, R.J.; Worden, H.M.; Fried, A.; Mikoviny, T.; Wisthaler, A.; et al. Measured and modeled CO and NOy in DISCOVER-AQ: An evaluation of emissions and chemistry over the eastern US. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 96, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canty, T.P.; Hembeck, L.; Vinciguerra, T.P.; Anderson, D.C.; Goldberg, D.L.; Carpenter, S.F.; Allen, D.J.; Loughner, C.P.; Salawitch, R.J.; Dickerson, R.R. Ozone and NOx chemistry in the eastern US: evaluation of CMAQ/CB05 with satellite (OMI) data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 10965–10982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kota, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Schade, G.W.; Ying, Q. Evaluation of on-road vehicle CO and NOx National Emission Inventories using an urban-scale source-oriented air quality model. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 85, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; McDonald, B.C.; Worden, H.; Worden, J.R.; Miyazaki, K.; Qu, Z.; Henze, D.K.; Jones, D.B.A.; Arellano, A.F.; Fischer, E.V.; et al. Unexpected slowdown of US pollutant emission reduction in the past decade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5099–5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Travis, K.R.; Jacob, D.J.; Fisher, J.A.; Kim, P.S.; Marais, E.A.; Zhu, L.; Yu, K.; Miller, C.C.; Yantosca, R.M.; Sulprizio, M.P.; et al. Why do models overestimate surface ozone in the Southeast United States? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13561–13577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Model | Configuration | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| WRF v3.3 | Initial field Microphysics Cumulus scheme LSM scheme PBL scheme | FNL [52] WSM3 [53] Kain-Fritsch [54] NOAH [55] YSU [56] |
| CMAQ v4.7.1 | Chemical mechanism Chemical solver Aerosol module Advection scheme Horizontal diffusion Vertical diffusion Cloud scheme | SAPRC99 [49] EBI [57] AERO5 [58] YAMO [59] Multiscale [60] Eddy [60] RADM [61] |
| Source Classification Code | CAPSS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2010 | 2013 | 2016 | |
| Combustion in energy industries | 156,304 | 153,441 | 177,219 | 145,445 |
| Nonindustrial combustion plants | 82,396 | 96,480 | 88,769 | 85,824 |
| Combustion in manufacturing industries | 155,053 | 164,942 | 178,034 | 175,332 |
| Production processes | 48,725 | 49,022 | 55,151 | 55,932 |
| Road transport | 495,084 | 382,226 | 335,721 | 452,995 |
| Other mobile sources and machinery | 237,101 | 208,878 | 246,027 | 309,986 |
| Waste treatment and disposal | 13,097 | 6,062 | 9,529 | 13,570 |
| Other sources and sinks | 163 | 158 | 165 | 167 |
| Combustion total | 393,753 | 414,863 | 444,022 | 406,601 |
| Mobile total | 732,185 | 591,104 | 581,748 | 762,981 |
| Total | 1,187,923 | 1,061,210 | 1,090,614 | 1,239,251 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.C.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, B.-U.; Lee, P. Fine-Scale Columnar and Surface NOx Concentrations over South Korea: Comparison of Surface Monitors, TROPOMI, CMAQ and CAPSS Inventory. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010101
Kim HC, Kim S, Lee S-H, Kim B-U, Lee P. Fine-Scale Columnar and Surface NOx Concentrations over South Korea: Comparison of Surface Monitors, TROPOMI, CMAQ and CAPSS Inventory. Atmosphere. 2020; 11(1):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010101
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun Cheol, Soontae Kim, Sang-Hyun Lee, Byeong-Uk Kim, and Pius Lee. 2020. "Fine-Scale Columnar and Surface NOx Concentrations over South Korea: Comparison of Surface Monitors, TROPOMI, CMAQ and CAPSS Inventory" Atmosphere 11, no. 1: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010101
APA StyleKim, H. C., Kim, S., Lee, S. -H., Kim, B. -U., & Lee, P. (2020). Fine-Scale Columnar and Surface NOx Concentrations over South Korea: Comparison of Surface Monitors, TROPOMI, CMAQ and CAPSS Inventory. Atmosphere, 11(1), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos11010101