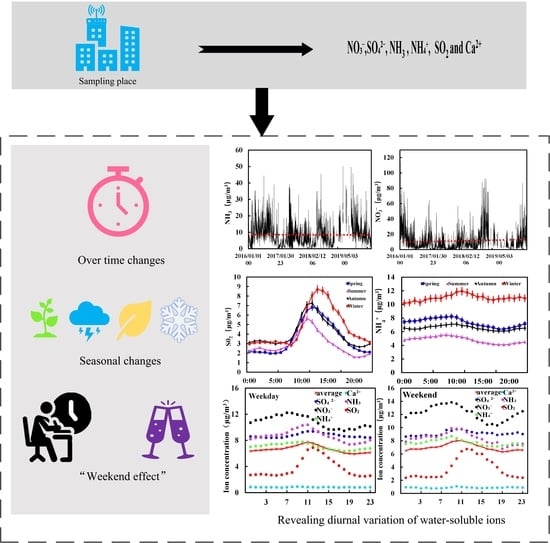
Analysis of the Diurnal Changes in the Water-Soluble Ion Concentration in Wuhan between 2016 and 2019
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Research Area
2.2. Sampling Site and Data Selection
2.3. Research Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration of Water-Soluble Ions over Time
3.2. Seasonal Changes in the Concentration of Water-Soluble Ions
3.3. “Weekend Effect” on the Changes in Water-Soluble Ion Concentration
3.4. Correlation Analysis between Water-Soluble Ions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- Sui, J.Y.; Gao, M.; Yan, H.L.; Yang, J.C.; Wang, Y.N. Analysis of the Relationship between Air Quality Characteristics and Meteorological Conditions in Yanqing Urban Area. Clim. Change Res. Lett. 2020, 9, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Communiqué on the State of Ecological Environment in China. 2017–2020. pp. 7–9. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/ (accessed on 4 July 2021).
- Suo, D.F.; Zeng, S.W. Research on the harm of airborne fine particulate matter PM2.5 to various human systems. Med. Inf. 2019, 32, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dominici, F.; Greenstone, M.; Sunstein, C.R. Particulate matter matters. Science 2014, 344, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; He, M.Q.; Wu, S.M.; Zhu, Y.H.; Wang, S.Q. Short-term effects of fine particulate matter and temperature on lung function among healthy college students in Wuhan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7777–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben, B.B.; Dunstone, N.J.; Halloran, P.R.; Andrews, T.; Bellouin, N. Aerosols implicated as a prime driver of twentieth-century North Atlantic climate variability. Nature 2012, 484, 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Cao, F.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhai, X.Y.; Fan, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Pollution source and health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in Changchun City in autumn of 2017. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 564–573. [Google Scholar]
- Shon, Z.-H.; Kim, K.-H.; Song, S.-K.; Kim, N.-J.; Lee, J.-B. Relationship between water-soluble ions in PM2.5 and their precursor gases in Seoul megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.C.; Wang, L.T.; Zhang, F.F.; Wei, F.; Ma, S.M.; Ma, X.; Yang, J. Characteristics of concentrations and water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 in Handan City, Hebei province, China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Shen, X.J.; Lin, W.L.; Yang, Y. Variability formation and acidity of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 in Beijing based on the semi-continuous observations. Atmos. Res. 2014, 145–146, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Sun, X.S.; Shi, A.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Yan, J.; Nie, T.; Yan, X.; Li, X. Secondary inorganic aerosols formation during haze episodes at an urban site in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 177, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Jian, Z.Y.; Peter, K.K.L.; Jimmy, C.H.F. Identification and spatiotemporal variations of dominant PM10 sources over Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, G.; Geravandi, S.; Alavi, N.; Idani, E.; Salmanzadeh, S.; Jamshidi, F.; Mohammad, J.M.; Ranjbarzadeh, A.; Alamdari, F.A.; Darabi, F.; et al. Association between cancer risk and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons’ exposure in the ambient air of Ahvaz, southwest of Iran. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.C.; Yu, X.G.; Ding, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, R.F.; Hou, S.Y.; Hou, X.H. Diurnal changes and source analysis of chemical components in PM2.5 in winter in Jiangbei New Area, Nanjing. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 529–536. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Li, L.; Song, L.M.; Wang, F.; Zhao, H.H.; Wu, W.C.; Tang, Q.; Pan, C.; Chen, H. Characteristics and source analysis of the chemical components of PM2.5 in Jiashan in winter. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 754–764. [Google Scholar]
- Duong, H.H.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Nguyen, X.T.N.; To Thin, H. Commuter exposures to in-transit PM in an urban city dominated by motorcycle: A case study in Vietnam. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101351. [Google Scholar]
- Dao, D.; Zhu, H.X.; Tan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.J.; Teng, E.J.; Lv, Y.B.; Li, G.G. Changes of water-soluble ions in PM2.5 in Beijing and surrounding key cities during APEC in 2014. Environ. Chem. 2015, 34, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Hu, S.X.; Huang, Z.; Tian, J.J. Characteristics of water-soluble ions in atmospheric PM2.5 Wuhan in spring. China Environ. Monit. 2017, 33, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Wuhan Municipal Ecological Environment Bureau. Wuhan City Ecological Environment Status Bulletin. 2017–2020. pp. 1–13. Available online: http://hbj.wuhan.gov.cn/fbjd_19/xxgkml/zwgk/hjjc/hjzkgb/ (accessed on 21 July 2021).
- Chen, Y.; Yun, L.; Luo, Y.; Niu, Y.B.; Peng, X.; He, L.Y.; Huang, X.F. Characteristics of gas-particle partitioning of gaseous nitric acid and particle nitrate in Shenzhen in winter. China Environ. Sci. 2021, 41, 4036–4042. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Graedel, T.E.; Kleiner, B.; Warner, J.L. Sunday and Workday Variations in Photochemical Air Pollutants in New Jersey and New York. Science 1974, 186, 1037–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.W.; Feng, Y.C.; Ren, L.; Lu, X.Q.; Zhong, Y.Q.; Han, X.Y.; Ning, P. Mass Concentration, Chemical Composition, and Source Characteristics of PM2.5 in a Plateau Slope City in Southwest China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.H.; Le, T.T.; Norimichi, T.; To Thin, H. Comparative study on water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 from two distinct climate regions and air quality. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Prodip, A.; Kaushar, A.; Dinesh, K.T.; Safai, P.D.; Sachin, G.U.; Thara, P.; Rajeevan, M. Characterization of atmospheric trace gases and water soluble inorganic chemical ions of PM1 and PM2.5 at Indira Gandhi International Airport, New Delhi during 2017–2018 winter. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138800. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Brink, H.M.; Kruisz, C.; Kos, G.P.A.; Berner, A. Composition/size of the light-scattering aerosol in the Netherlands. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 3955–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewnick, F.; Schwab, J.J.; Hogrefe, O.; Peters, S.; Husain, L.; Diamond, D.; Weber, R.; Demerjian, K.L. Intercomparison and evaluation of four semi-continuous PM2.5 sulfate instruments. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3335–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xiao, H.Y.; Wu, P.; Xiao, H.W.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zheng, N.J. Composition characteristics and source analysis of PM2.5 water-soluble ions in Guiyang in autumn. Environ. Chem. 2019, 38, 548–555. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Yin, S.J.; Guo, S.F. Seasonal pollution characteristics and source analysis of water-soluble ions in atmospheric PM2.5 in Taiyuan City. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 3120–3130. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; Zhang, J.K.; Dong, G.M.; Deng, J.L.; Liu, Z.R.; Wang, Y.S. Characterization of Water-soluble Inorganic Ions in Atmospheric PM2.5 in Chengdu during the Later Stage of the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 5616–5623. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L. Seasonal Disparity in the Effect of Meteorological Conditions on Air Quality in China Based on Artificial Intelligence. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunea, D.; Iordache, V.; Frasin, L.N.; Neago, A. Monitoring Rainwater Properties and Outdoor Particulate Matter in a Former Steel Manufacturing City in Romania. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Xiang, F.; Shen, Q.F.; Xia, W.Y.; Wan, P.J.; Qiu, F. Research on the characteristics and influencing factors of ozone pollution in Yunnan Province in 2019. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.L.; Zhou, W.Q.; Han, L.J. Human activities and urban air pollution in Chinese mega city: An insight of ozone weekend effect in Beijing. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 110, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.X.; Wu, L.; Fang, X.Z.; Yang, Z.W.; Li, F.H.; Mao, H.J. Analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions of atmospheric particulate matter in the road environment of Tianjin. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 4133–4141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.S.; Li, Y.T.; Dong, X.; Sun, R.W.; Sun, N.D.; Pan, L.B. Analysis of "weekend effect" of air pollutants in Beijing urban area. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2015, 32, 843–850. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ju, X.T.; Zhang, L.J.; Wan, Y.J.; Liu, S.Q. Effects of different fertilization methods on soil ammonia volatilization and nitrous oxide emissions. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 19, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.Y.; Guo, X.P.; Lin, L.; Shen, G.X. Research on the influence of NH3 emissions from agricultural sources at home and abroad on the formation of PM2.5. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.G.; Wang, B.G.; Yang, J.; Zhong, S.F. Research on the source and emission factors of ammonia in urban sewage plants. Environ. Chem. 2012, 31, 708–713. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.T.; Cheng, J.X.; Cheng, S.G. Seasonal Variations and Correlation Analysis of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.W.; Wang, Z.W.; Chen, N.; Cheng, H.R.; Yuan, C. Monitoring of atmospheric ammonia-ammonium gas/particle conversion before and after the Military Games in Wuhan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 43, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Q.J.; Cheng, F.Y.; Chen, M. Experimental Study on the Chemical Characterization of Atmospheric Aerosols in Wuhan, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Ion | Season | 8:00 | 9:00 | 10:00 | 11:00 | 12:00 | 13:00 | 14:00 | 15:00 | 16:00 | 17:00 | 18:00 | 19:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ | Spring | 9.29 | 9.42 | 9.39 | 9.22 | 8.95 | 8.72 | 8.39 | 8.09 | 7.86 | 7.59 | 7.20 | 7.01 |
| Summer | 6.26 | 6.49 | 6.63 | 6.70 | 6.41 | 5.85 | 5.58 | 5.31 | 5.11 | 4.93 | 4.73 | 4.54 | |
| Autumn | 6.69 | 6.96 | 7.29 | 7.39 | 7.28 | 6.97 | 6.63 | 6.34 | 6.19 | 5.95 | 5.88 | 5.68 | |
| Winter | 7.98 | 8.18 | 8.72 | 9.30 | 9.19 | 9.25 | 8.84 | 8.76 | 8.34 | 8.34 | 8.04 | 8.05 | |
| Ca2+ | Spring | 0.77 | 0.78 | 0.81 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.68 |
| Summer | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.63 | |
| Autumn | 1.18 | 1.29 | 1.33 | 1.29 | 1.35 | 1.23 | 1.36 | 1.40 | 1.35 | 1.16 | 1.23 | 1.33 | |
| Winter | 0.66 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.71 | |
| NO3− | Spring | 22.29 | 21.56 | 20.28 | 19.10 | 18.28 | 17.46 | 17.09 | 16.04 | 15.65 | 15.22 | 14.25 | 14.09 |
| Summer | 5.98 | 5.68 | 5.39 | 5.07 | 4.42 | 3.91 | 3.49 | 3.24 | 3.03 | 3.12 | 3.03 | 3.13 | |
| Autumn | 11.47 | 11.39 | 11.16 | 10.76 | 10.45 | 10.09 | 9.59 | 8.76 | 8.80 | 8.74 | 8.73 | 8.86 | |
| Winter | 19.28 | 19.32 | 19.87 | 20.51 | 19.79 | 19.63 | 18.50 | 18.41 | 17.96 | 18.61 | 18.21 | 19.29 | |
| SO42− | Spring | 10.08 | 10.00 | 10.17 | 9.96 | 9.96 | 9.90 | 9.66 | 9.53 | 9.52 | 9.29 | 9.18 | 9.04 |
| Summer | 8.15 | 8.26 | 8.61 | 8.68 | 8.97 | 8.50 | 8.39 | 8.31 | 8.19 | 7.96 | 7.84 | 7.82 | |
| Autumn | 8.35 | 8.42 | 8.53 | 8.55 | 8.67 | 8.43 | 8.39 | 8.54 | 8.53 | 8.29 | 8.27 | 8.22 | |
| Winter | 9.52 | 9.72 | 10.24 | 10.76 | 10.07 | 10.43 | 9.96 | 10.03 | 9.87 | 10.00 | 9.50 | 9.64 | |
| SO2 | Spring | 3.17 | 4.40 | 5.46 | 6.50 | 6.82 | 6.66 | 6.01 | 5.56 | 4.98 | 4.30 | 3.63 | 2.88 |
| Summer | 3.01 | 4.00 | 4.77 | 5.66 | 5.30 | 4.42 | 3.91 | 3.26 | 2.92 | 2.55 | 2.20 | 1.90 | |
| Autumn | 3.45 | 4.54 | 6.05 | 7.09 | 7.26 | 6.48 | 5.68 | 5.12 | 4.76 | 4.09 | 3.49 | 3.00 | |
| Winter | 2.81 | 3.43 | 4.78 | 6.84 | 8.06 | 8.70 | 8.56 | 8.11 | 6.76 | 6.27 | 5.37 | 4.20 | |
| NH3 | Spring | 11.23 | 11.57 | 11.51 | 11.29 | 10.62 | 10.42 | 9.90 | 9.85 | 9.57 | 9.41 | 9.07 | 9.01 |
| Summer | 14.00 | 14.64 | 14.78 | 14.81 | 14.01 | 12.87 | 12.61 | 12.02 | 11.61 | 11.14 | 10.53 | 9.66 | |
| Autumn | 8.68 | 9.04 | 9.52 | 9.75 | 9.08 | 8.94 | 8.31 | 7.83 | 7.47 | 7.31 | 7.51 | 6.57 | |
| Winter | 4.33 | 4.54 | 4.85 | 5.05 | 4.81 | 4.65 | 4.24 | 4.18 | 4.04 | 3.86 | 3.64 | 3.67 |
| Ion | Season | 20:00 | 21:00 | 22:00 | 23:00 | 0:00 | 1:00 | 2:00 | 3:00 | 4:00 | 5:00 | 6:00 | 7:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ | Spring | 7.05 | 7.29 | 7.59 | 7.83 | 8.06 | 8.22 | 8.32 | 8.34 | 8.46 | 8.64 | 8.71 | 8.87 |
| Summer | 4.54 | 4.66 | 4.83 | 5.02 | 5.26 | 5.46 | 5.63 | 5.67 | 5.70 | 5.71 | 5.75 | 6.03 | |
| Autumn | 5.67 | 5.82 | 5.89 | 5.97 | 6.11 | 6.07 | 6.07 | 6.07 | 6.17 | 6.22 | 6.32 | 6.43 | |
| Winter | 7.98 | 7.99 | 7.88 | 7.67 | 7.41 | 7.65 | 7.62 | 7.67 | 7.69 | 7.94 | 7.80 | 7.96 | |
| Ca2+ | Spring | 0.68 | 0.71 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.66 | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.64 |
| Summer | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 0.72 | 0.80 | |
| Autumn | 1.35 | 1.33 | 1.24 | 1.27 | 1.44 | 1.24 | 1.25 | 1.13 | 1.21 | 1.17 | 1.10 | 1.18 | |
| Winter | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.61 | |
| NO3− | Spring | 14.40 | 15.77 | 17.30 | 18.18 | 18.94 | 19.60 | 20.29 | 20.42 | 20.75 | 21.55 | 21.81 | 21.90 |
| Summer | 3.35 | 3.57 | 3.92 | 4.29 | 4.50 | 4.82 | 5.21 | 5.41 | 5.75 | 5.91 | 6.02 | 6.11 | |
| Autumn | 8.86 | 9.46 | 9.68 | 9.72 | 9.88 | 9.94 | 9.89 | 10.05 | 10.26 | 10.62 | 10.89 | 11.12 | |
| Winter | 18.97 | 19.23 | 19.02 | 18.14 | 17.96 | 18.72 | 18.27 | 18.53 | 18.23 | 19.37 | 18.80 | 19.68 | |
| SO42− | Spring | 9.16 | 9.13 | 9.26 | 9.28 | 9.50 | 9.54 | 9.38 | 9.31 | 9.32 | 9.35 | 9.42 | 9.55 |
| Summer | 7.74 | 7.87 | 7.90 | 7.72 | 8.03 | 8.02 | 7.95 | 7.84 | 7.71 | 7.60 | 7.62 | 7.90 | |
| Autumn | 8.18 | 8.17 | 8.17 | 8.11 | 8.11 | 7.95 | 7.90 | 7.84 | 7.95 | 7.90 | 7.96 | 8.08 | |
| Winter | 9.55 | 9.67 | 9.36 | 9.22 | 8.79 | 8.93 | 8.95 | 9.12 | 9.19 | 9.21 | 9.05 | 9.23 | |
| SO2 | Spring | 2.54 | 2.28 | 2.12 | 2.10 | 2.15 | 2.13 | 2.10 | 2.08 | 1.96 | 1.98 | 2.07 | 2.42 |
| Summer | 1.59 | 1.59 | 1.68 | 1.92 | 2.23 | 2.41 | 2.58 | 2.35 | 2.29 | 2.25 | 2.43 | 2.65 | |
| Autumn | 2.79 | 2.65 | 2.72 | 2.97 | 3.11 | 3.26 | 3.30 | 3.23 | 3.13 | 2.96 | 3.07 | 3.15 | |
| Winter | 3.86 | 3.64 | 3.43 | 3.15 | 2.96 | 3.08 | 3.11 | 3.14 | 3.09 | 3.23 | 3.08 | 3.06 | |
| NH3 | Spring | 9.02 | 9.15 | 9.30 | 9.53 | 9.64 | 9.82 | 9.94 | 9.93 | 10.18 | 10.33 | 10.30 | 10.62 |
| Summer | 9.80 | 9.98 | 10.38 | 11.02 | 11.33 | 11.85 | 12.22 | 12.64 | 12.49 | 12.52 | 12.42 | 13.26 | |
| Autumn | 6.71 | 6.98 | 7.02 | 7.20 | 7.59 | 7.64 | 7.71 | 7.74 | 7.88 | 7.92 | 8.09 | 8.13 | |
| Winter | 3.78 | 3.87 | 3.75 | 3.95 | 3.91 | 4.18 | 4.16 | 4.26 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 4.34 | 4.30 |
| Ca2⁺ (μg/m3) | SO42− (μg/m3) | NH₃ (μg/m3) | NO3− (μg/m3) | SO₂ (μg/m3) | NH4+ (μg/m3) | Average (μg/m3) | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekday | 0.827 | 8.743 | 8.684 | 10.823 | 3.804 | 7.040 | 6.654 | 3.369 |
| Weekend | 0.880 | 9.115 | 8.352 | 12.195 | 3.823 | 7.725 | 7.015 | 3.682 |
| Rate | −6.07% | −4.08% | 3.97% | −11.25% | −0.48% | −8.87% | −5.15% | / |
| Weekend Effect Index | 6.46% | 4.24% | −3.82% | 12.67% | 4.86% | 9.73% | 5.43% | / |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; He, C.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, N.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, X. Analysis of the Diurnal Changes in the Water-Soluble Ion Concentration in Wuhan between 2016 and 2019. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040582
Sun Y, Zhao J, He C, Zhang Z, Chen N, Hu J, Liu H, Wang X. Analysis of the Diurnal Changes in the Water-Soluble Ion Concentration in Wuhan between 2016 and 2019. Atmosphere. 2022; 13(4):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040582
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yingying, Jinhui Zhao, Chao He, Zhouxiang Zhang, Nan Chen, Jiaqi Hu, Huanhuan Liu, and Xinlei Wang. 2022. "Analysis of the Diurnal Changes in the Water-Soluble Ion Concentration in Wuhan between 2016 and 2019" Atmosphere 13, no. 4: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040582
APA StyleSun, Y., Zhao, J., He, C., Zhang, Z., Chen, N., Hu, J., Liu, H., & Wang, X. (2022). Analysis of the Diurnal Changes in the Water-Soluble Ion Concentration in Wuhan between 2016 and 2019. Atmosphere, 13(4), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13040582