Understanding Temporal Patterns and Determinants of Ground-Level Ozone
Abstract
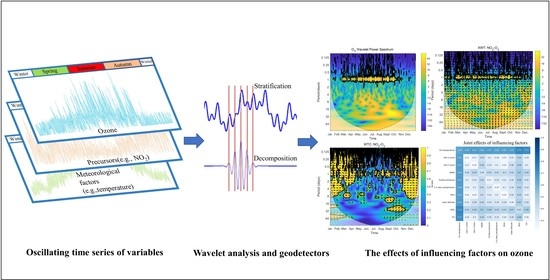
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.1.1. Ground Ozone and Its Precursors
2.1.2. ERA5 Land Meteorological Data
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Continuous Wavelets, Cross Wavelets, and Wavelet Coherence
- Continuous wavelet transform
- Cross wavelet
- Wavelet coherence
2.2.2. Geodetectors
- Factor detector
- Interactive detector
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Time–Frequency Characteristics of O3 and Its Influencing Factors
3.2. Correlation among Influencing Factors and Ozone
3.3. Stratified Heterogeneity of Ozone and Detection of Factor Effects
3.4. General Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bower, J.S.; Stevenson, K.J.; Broughton, G.F.J.; Lampert, J.E.; Sweeney, B.P.; Wilken, J. Assessing recent surface ozone concentrations in the U.K. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, P.; Cheng, E.; English, A.; Sun, F. China’s response to the air pollution shock. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Cheng, S. Projection of anthropogenic volatile organic compounds (VOCs) emissions in China for the period 2010–2020. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6863–6871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.Y.; Fu, K.; Klimont, Z.; Hao, J.M.; He, K.B.; Cofala, J.; Amann, M. NOx emissions in China: Historical trends and future perspectives. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9869–9897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, W.; Manning, W.J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Q. Ozone and ozone injury on plants in and around Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 191, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, W.W.; Neu, J.L.; Williams, J.E.; Bowman, K.W.; Worden, J.R.; Boersma, K.F. Rapid increases in tropospheric ozone production and export from China. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wei, S.; Luo, H.; Yue, C.; Grunder, O. A novel hybrid model for air quality index forecasting based on two-phase decomposition technique and modified extreme learning machine. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehelin, J.; Harris, N.R.P.; Appenzeller, C.; Eberhard, J. Ozone trends: A review. Rev. Geophys. 2001, 39, 231–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monks, P.S.; Archibald, A.T.; Colette, A.; Cooper, O.; Coyle, M.; Derwent, R.; Fowler, D.; Granier, C.; Law, K.S.; Mills, G.E.; et al. Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8889–8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Chen, D.; Zhuang, Y.; Gao, B.; Yang, L.; Li, M. Understanding the causal influence of major meteorological factors on ground ozone concentrations across China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, E.; Moiseenko, K.; Skorokhod, A.; Pankratova, N.V.; Belikov, I.; Belousov, V.; Elansky, N.F. Impact of VOCs and NOx on ozone formation in Moscow. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juráň, S.; Grace, J.; Urban, O. Temporal changes in ozone concentrations and their impact on vegetation. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Shi, B.; Qiu, R. Assessment of the characteristics and influencing factors of ozone in Fuzhou, China, using wavelet analysis. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 1898–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Kang, P.; Jaffe, D.A.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, K.; Zhou, M. Understanding the impact of meteorology on ozone in 334 cities of China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 248, 118221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Lichtfouse, E.; Rosenfeld, D.; et al. Large scale control of surface ozone by relative humidity observed during warm seasons in China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yin, L.; Ning, J. Artificial neural network model for ozone concentration estimation and Monte Carlo analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 184, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, F.; Shafiepour Motlagh, M.; Stohl, A.; Rashidi, Y.; Ehsani, A.H. Tropospheric ozone in Tehran, Iran, during the last 20 years. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 44, 3615–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingarzan, R. A review of surface ozone background levels and trends. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.I.V.; Martins, F.G.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M.; Pereira, M.C. Multiple linear regression and artificial neural networks based on principal components to predict ozone concentrations. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2007, 22, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Xia, Z.-G.; Wang, H.; Li, W. Temporal variations in surface ozone and its precursors and meteorological effects at an urban site in China. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 310–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Xu, X.; Wang, T.; Gao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Severe surface ozone pollution in China: A global perspective. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2018, 5, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zheng, B.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Fu, T.M.; Zhang, Q. Exploring 2016–2017 surface ozone pollution over China: Source contributions and meteorological influences. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 8339–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stafoggia, M.; Johansson, C.; Glantz, P.; Renzi, M.; Shtein, A.; de Hoogh, K.; Kloog, I.; Davoli, M.; Michelozzi, P.; Bellander, T. A random forest approach to estimate daily particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone at fine spatial resolution in Sweden. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, K.; Chen, L.; Ying, F.; White, S.J.; Jang, C.; Wu, X.; Gao, X.; Hong, S.; Shen, J.; Azzi, M.; et al. Meteorological and chemical impacts on ozone formation: A case study in Hangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 196, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Wang, T.J.; Huang, X.; Melas, D.; Zanis, P.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Poupkou, A. Enhanced surface ozone during the heat wave of 2013 in Yangtze River Delta region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 603–604, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, D.; Cheng, N.; Yang, L.; Li, R. Understanding long-term variations of meteorological influences on ground ozone concentrations in Beijing during 2006–2016. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, F.; Gao, B. Influential factors detection for surface water quality with geographical detectors in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2018, 32, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleanthous, S.; Vrekoussis, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kalabokas, P.; Lelieveld, J. On the temporal and spatial variation of ozone in Cyprus. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Tie, X.; Gao, W.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Q. Measurement and model analyses of the ozone variation during 2006 to 2015 and its response to emission change in megacity Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 9017–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Fan, S.; Guo, H.; Gao, B.; Sun, J.; Chen, L. Assessing the impact of local meteorological variables on surface ozone in Hong Kong during 2000–2015 using quantile and multiple line regression models. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 144, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mandal, T.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Shukla, D.K.; Singh, S. Relationships of surface ozone with its precursors, particulate matter and meteorology over Delhi. J. Atmos. Chem. 2017, 74, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Li, R.; Xu, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Meng, F.; Cheng, B.; Ma, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; He, B.; et al. Ground ozone variations at an urban and a rural station in Beijing from 2006 to 2017: Trend, meteorological influences and formation regimes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Middey, A.; Rao, P.S. Prediction and examination of seasonal variation of ozone with meteorological parameter through artificial neural network at Neeri, Nagpur, India. Urban Clim. 2017, 20, 148–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Bakheit, C.S.; Al-Alawi, S.M. Principal component and multiple regression analysis in modelling of ground-level ozone and factors affecting its concentrations. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2005, 20, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, K.L.; Wang, T. On the local and regional influence on ground-level ozone concentrations in Hong Kong. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, P.; Hurd, H.L.; Lund, R.B. Periodic correlation in stratospheric ozone data. J. Time Ser. Anal. 1994, 15, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yin, L.; Fan, Y.; Song, L.; Ji, T.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Zheng, W. Temporal evolution characteristics of PM2.5 concentration based on continuous wavelet transform. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Velázquez, D.; Reyes-Ramírez, I. A wavelet analysis of multiday extreme ozone and its precursors in Mexico city during 2015–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Fang, C.; Qiu, J.; Wang, J. Analysis of ozone pollution characteristics and influencing factors in northeast economic cooperation region, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Yammahi, A.; Aung, Z. A study of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) periodicity over the United Arab Emirates using wavelet analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Karimian, H.; Li, M.; Fan, Q.; Xu, Z. Spatio-temporal variation of ozone pollution risk and its influencing factors in China based on geodetector and geospatial models. Chemosphere 2022, 302, 134843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; NixiaCiren; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; GesangDeji; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal variations of surface ozone and its influencing factors across Tibet: A geodetector-based study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Song, H.; Wang, T.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Miao, C.; Zhao, H. Effects of meteorological conditions and anthropogenic precursors on ground-level ozone concentrations in Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-b.; Li, J.-x.; Liang, L.-w. Spatio-temporal evolution of ozone pollution and its influencing factors in the Teijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Qian, Y.; Wang, H.; Fu, J.; Wu, J. Analysis of the spatial and temporal patterns of ground-level ozone concentrations in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao greater bay area and the contribution of influencing factors. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haagen-Smit, A.J.; Bradley, C.E.; Fox, M.M. Ozone formation in photochemical oxidation of organic substances. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1953, 45, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, L.; Yang, D.-y.; Liu, Y.-b. Quantifying the spatial heterogeneity influences of natural and socioeconomic factors and their interactions on air pollution using the geographical detector method: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 692–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; O’Brien, T.; Streets, D.G.; Patel, M. Relationship of ground-level ozone with synoptic weather conditions in Chicago. Urban Clim. 2016, 17, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Y. Study on ENSO time-frequency characteristics in recent 50 years and its correlation with typhoon in the South China Sea. J. Guangdong Ocean Univ. 2018, 38, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlin. Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Cheng, B. Application of cross wavelet transformation to analysis on regional climate variations. J. Appl. Meteor. Sci. 2008, 19, 479–487. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Zhang, T.-L.; Fu, B.-J. A measure of spatial stratified heterogeneity. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical detectors-based health risk assessment and its application in the neural tube defects study of the Heshun region, China. Int. J. Geog. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Su, H.; Shao, M.; Zeng, L.; Zhong, L.; Xiang, Y.; Chang, C.; Chou, C.K.C.; Wahner, A. Regional ozone pollution and key controlling factors of photochemical ozone production in Pearl River Delta during summer time. Sci. China Chem. 2010, 53, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yao, G.; Guo, J.; Bai, K. Distinct spatiotemporal variation patterns of surface ozone in China due to diverse influential factors. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J.; Mar, K.A.; Ojha, N.; Butler, T.M. The influence of temperature on ozone production under varying NOx conditions—A modelling study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 11601–11615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stathopoulou, E.; Mihalakakou, G.; Santamouris, M.; Bagiorgas, H.S. On the impact of temperature on tropospheric ozone concentration levels in urban environments. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 117, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninneman, M.; Jaffe, D. Observed relationship between ozone and temperature for urban nonattainment areas in the United States. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinosian, J.R. Ozone-precursor relationships from EKMA diagrams. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 880–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomer, B.J.; Stehr, J.W.; Piety, C.A.; Salawitch, R.J.; Dickerson, R.R. Observed relationships of ozone air pollution with temperature and emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L09803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkinson, R. Atmospheric chemistry of VOCs and NOx. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2063–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J. Heterogeneous chemistry and tropospheric ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2131–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, D.; Amann, M.; Anderson, R.; Ashmore, M.; Cox, P.; Depledge, M.; Derwent, D.; Grennfelt, P.; Hewitt, N.; Hov, O. Ground-Level Ozone in the 21st Century: Future Trends, Impacts and Policy Implications; The Royal Society: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Pan, Z.; Liu, D.; Guo, X. Exploring the regional differences of ecosystem health and its driving factors in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Bian, H.; Feng, Y.; Liu, A.; Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Zhang, X. Analysis of the relationship between O3, NO and NO2 in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Meng, W. Influence of summer local circulation on ozone transport in downwind areas of Beijing. China Environ. Sci. Chin. Ed. 2009, 29, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Observation-Based Analysis of Causes and Sources of Ambient Air Ozone Pollution in Beijing. Ph.D. Thesis, Shan Dong University, Jinan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, W.; Bi, J. Spatiotemporal distributions of surface ozone levels in China from 2005 to 2017: A machine learning approach. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wild, O.; Chen, X.; Wu, Q.; Gao, M.; Chen, H.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z. Health impacts of long-term ozone exposure in China over 2013–2017. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, K.J.; Ye, W.-F.; Arora, M.; Nagendra, S.M.S. Ozone pollution in Chinese cities: Assessment of seasonal variation, health effects and economic burden. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Index | 2 m Temperature | 10 m U-Wind Component | 10 m V-Wind Component | Net Surface solar Radiation | Surface Pressure | 2 m Dewpoint Temperature | RHU * | Solar Altitude | NO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q statistic | 0.64 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.41 |
| p value | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Variable | 2 m Temperature | 10 m U-Wind Component | 10 m V-Wind Component | Net Surface Solar Radiation | Surface Pressure | 2 m Dewpoint Temperature | RHU * | Solar Altitude | NO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 m temperature | 0.64 | ||||||||
| 10 m U-wind component | 0.66 | 0.22 | |||||||
| 10 m V-wind component | 0.67 | 0.27 | 0.23 | ||||||
| Net surface solar radiation | 0.66 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.36 | |||||
| Surface pressure | 0.67 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.42 | 0.27 | ||||
| 2 m dewpoint temperature | 0.66 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.25 | |||
| RHU | 0.66 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.22 | ||
| Solar altitude | 0.67 | 0.31 | 0.38 | 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.29 | |
| NO2 | 0.74 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.45 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Dong, J.; Guo, J.; Cai, P.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Song, X. Understanding Temporal Patterns and Determinants of Ground-Level Ozone. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030604
Wang J, Dong J, Guo J, Cai P, Li R, Zhang X, Xu Q, Song X. Understanding Temporal Patterns and Determinants of Ground-Level Ozone. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(3):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030604
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junshun, Jin Dong, Jingxian Guo, Panli Cai, Runkui Li, Xiaoping Zhang, Qun Xu, and Xianfeng Song. 2023. "Understanding Temporal Patterns and Determinants of Ground-Level Ozone" Atmosphere 14, no. 3: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030604
APA StyleWang, J., Dong, J., Guo, J., Cai, P., Li, R., Zhang, X., Xu, Q., & Song, X. (2023). Understanding Temporal Patterns and Determinants of Ground-Level Ozone. Atmosphere, 14(3), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14030604