Topography and Data Mining Based Methods for Improving Satellite Precipitation in Mountainous Areas of China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
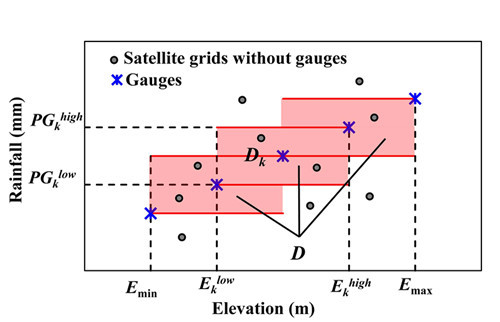
2.1. The Gauge-Elevation-Consistency (GEC) Rule for Assessment

2.2. The Location-Elevation-TMPA (LET) Correlation for Improvement
3. Case Study and Results
3.1. Data

| Region | Area (103 km2) | Mean Elevation a(m) | Peak Elevation (m) | Gauges Information | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauges Numbers | Gauges Altitudes (m) | Mean Annual Rainfall (2001–2012) (mm) | ||||
| Himalaya | 1054.7 | 4592 | 8848 | 33 | 2328–4900 | 467 |
| Kunlun | 786.7 | 2897 | 7576 | 15 | 887–3504 | 102 |
| Tianshan | 392.2 | 1712 | 7125 | 19 | 35–2458 | 180 |
| Qilian | 337.6 | 2954 | 5820 | 23 | 1139–3367 | 230 |
| Qinling | 129.5 | 921 | 3747 | 13 | 249–2065 | 770 |
| Taihang | 223.2 | 1012 | 3059 | 22 | 63–2208 | 498 |
| Changbai | 631.9 | 334 | 2667 | 48 | 4–775 | 663 |
| Wuyi | 366.2 | 386 | 2154 | 43 | 3–1654 | 1589 |
3.2. Assessment the Uncertainty of Satellite Precipitation
3.2.1. Grid Cells with Gauges
| Region | Altitude of Gauges (m) | Gauge (mm) | 3B43 (mm) | Bias (%) | RMSD (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher Mountains | Himalaya | 2328–4900 | 453 | 667 | 47.2 | 272 |
| Kunlun | 887–3504 | 106 | 131 | 23.6 | 76 | |
| Tianshan | 35–2458 | 175 | 200 | 14.3 | 54 | |
| Qilian | 1139–3367 | 233 | 264 | 13.3 | 65 | |
| Lower Mountains | Qinling | 249–2065 | 776 | 791 | 1.9 | 46 |
| Taihang | 63–2208 | 502 | 542 | 8.0 | 49 | |
| Changbai | 4–775 | 674 | 757 | 12.3 | 103 | |
| Wuyi | 3–1654 | 1560 | 1654 | 6.0 | 161 | |
| Average | -- | 560 | 626 | 15.8 | 103 | |

3.2.2. Grid Cells without Gauges

| Region | CR in the Whole Region | CR in the Hillside Face to Vapor Transportation | CR in the Hillside Back to Vapor Transportation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauged Grids | Ungauged Grids | Gauged Grids | Ungauged Grids | Gauged Grids | Ungauged Grids | ||
| Higher Mountains | Himalaya | 51.5 | 57.4 | 100.0 | 84.7 | 42.9 | 47.7 |
| Kunlun | 57.1 | 60.0 | 57.1 | 60.0 | -- | -- | |
| Tianshan | 57.9 | 63.5 | 55.6 | 74.4 | 60.0 | 53.4 | |
| Qilian | 65.2 | 58.7 | 50.0 | 51.4 | 88.9 | 69.5 | |
| Lower Mountains | Qinling | 92.3 | 75.0 | 100.0 | 73.1 | 87.5 | 77.6 |
| Taihang | 63.6 | 64.6 | 42.9 | 55.0 | 73.3 | 68.2 | |
| Changbai | 60.4 | 67.0 | 58.1 | 67.0 | 64.7 | 67.5 | |
| Wuyi | 51.2 | 33.8 | 50.0 | 36.4 | 51.9 | 32.5 | |
| Average | 62.4 | 60.4 | 64.2 | 62.8 | 67.0 | 59.5 | |
3.3. Improvement the Robust of Satellite Precipitation
3.3.1. Testing Calibration and Cross Validation
3.3.2. Final Calibration and Correction of TMPA

| Region | Mean of Gauges (mm) | Mean of gauged grids (mm) | Bias (%) | RMSD (mm) | CR of Gauged Grids (%) | CR of Ungauged Grids (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Himalaya | 453 | 422 | −6.8 | 92 | 84.8 | 78.2 |
| Kunlun | 106 | 76 | −28.2 | 49 | 64.3 | 63.7 |
| Tianshan | 175 | 171 | −2.2 | 31 | 84.2 | 66.7 |
| Qilian | 233 | 235 | 1.0 | 26 | 82.6 | 60.4 |
| Qinling | 776 | 777 | 0.2 | 27 | 76.9 | 71.6 |
| Taihang | 502 | 503 | 0.3 | 19 | 72.7 | 77.0 |
| Changbai | 674 | 674 | 0.0 | 44 | 75.0 | 55.1 |
| Wuyi | 1560 | 1561 | 0.0 | 89 | 72.1 | 41.1 |
| Average | 560 | 552 | −4.5 | 47 | 76.6 | 64.2 |


4. Discussion
4.1. The Sensitive of CR to l of Rainfall-Elevation Mask
| Region | l = 2 | l = 3 | l = 4 | l = 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher Mountains | Himalaya | 42.0 | 57.4 | 61.4 | 62.8 |
| Kunlun | 31.9 | 60.0 | 69.4 | 75.9 | |
| Tianshan | 29.8 | 63.5 | 75.1 | 83.0 | |
| Qilian | 36.9 | 58.7 | 71.0 | 77.8 | |
| Lower Mountains | Qinling | 40.5 | 75.0 | 89.7 | 94.0 |
| Taihang | 44.0 | 64.6 | 82.5 | 85.9 | |
| Changbai | 38.2 | 67.0 | 79.8 | 84.0 | |
| Wuyi | 12.9 | 33.8 | 44.0 | 53.6 | |
| Average | 34.5 | 60.0 | 71.6 | 77.1 | |
4.2. The Suitability of LET for Monthly Precipitation of TMPA 3B43 (V7)
| Time Scale | Original | Corrected | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | CV(RMSD) (%) | R2 | CV(RMSD) (%) | |
| Every July | 0.55 | 72.9 | 0.73 | 57.1 |
| Every month | 0.53 | 124.9 | 0.61 | 109.2 |

4.3. The Effectivity for the of TMPA 3B42RT (V7)
4.3.1. Effective for Assessment
| Region | Mean of Gauge (mm) | Mean of Gauged Grids (mm) | Bias (%) | RMSD (mm) | CR of Gauged Grids (%) | CR of Ungauged Grids (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Himalaya | 453 | 1457 | 221.6 | 1050 | 0.0 | 1.9 |
| Kunlun | 106 | 360 | 239.6 | 332 | 14.3 | 44.0 |
| Tianshan | 175 | 771 | 340.6 | 660 | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| Qilian | 233 | 454 | 94.8 | 276 | 30.4 | 47.8 |
| Qinling | 776 | 835 | 7.6 | 81 | 76.9 | 58.6 |
| Taihang | 502 | 653 | 30.1 | 162 | 22.7 | 16.5 |
| Changbai | 674 | 676 | 0.3 | 104 | 77.1 | 67.3 |
| Wuyi | 1560 | 1562 | 0.1 | 313 | 34.9 | 22.5 |
| Average | 560 | 846 | 116.8 | 372 | 32.0 | 32.6 |

4.3.2. Effective for Correction
| Region | Mean of Gauges (mm) | Mean of Gauged Grids (mm) | Bias (%) | RMSD (mm) | CR of Gauged Grids (%) | CR of Ungauged Grids (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Himalaya | 453 | 454 | 0.2 | 95 | 87.9 | 76.1 |
| Kunlun | 106 | 117 | 10.8 | 35 | 64.3 | 78.8 |
| Tianshan | 175 | 290 | 65.2 | 130 | 42.1 | 46.8 |
| Qilian | 233 | 231 | −0.6 | 38 | 78.3 | 61.1 |
| Qinling | 776 | 770 | −0.8 | 41 | 100.0 | 62.1 |
| Taihang | 502 | 496 | −1.2 | 30 | 86.4 | 71.8 |
| Changbai | 674 | 656 | −2.7 | 60 | 83.3 | 50.5 |
| Wuyi | 1560 | 1544 | −1.0 | 143 | 74.4 | 54.3 |
| Average | 560 | 570 | 8.7 | 72 | 77.1 | 62.7 |

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
| Region | Relationships for 3B42RT | Relationships for 3B43 |
|---|---|---|
| Himalaya | ||
| Kunlun | ||
| Tianshan | ||
| Qilian | ||
| Qinling | ||
| Taihang | ||
| Changbai | ||
| Wuyi |
References
- Nespor, V.; Sevruk, B. Estimation of wind-induced error of rainfall gauge measurements using a numerical simulation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, F.; Hantel, M. Correction of daily rain gauge measurements in the Baltic Sea drainage basin. Nord. Hydrol. 1999, 30, 191–208. [Google Scholar]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Nasrollahi, N.; Habib, E. Accounting for Uncertainties of the TRMM Satellite Estimates. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Morrissey, M.M.; Bolvin, D.T.; Curtis, S.; Joyce, R.; McGavock, B.; Susskind, J. Global precipitation at one-degree daily resolution from multisatellite observations. J. Hydrometeorol. 2001, 2, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.L.; Gao, X.; Gupta, H.V.; Imam, B.; Braithwaite, D. Evaluation of PERSIANN system satellite-based estimates of tropical rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A method that produces global precipitation estimates from passive microwave and infrared data at high spatial and temporal resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Global precipitation map using satellite-borne microwave radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Nelkin, E.J.; Bowman, K.P.; Hong, Y.; Stocker, E.F.; et al. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J. The TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA). Chapter 1. In Satellite Rainfall Applications for Surface Hydrology; ISBN 978-90-481-2914-0. Springer Netherlands: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, F.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Flood prediction in the future: Recognizing hydrologic issues in anticipation of the Global Precipitation Measurement mission. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W11301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Adler, R.; Huffman, G. Evaluation of the potential of NASA multi-satellite precipitation analysis in global landslide hazard assessment. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L22402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T. TRMM and Other Data Precipitation Data Set Documentation; NASA Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2014; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.L.; Moradkhani, H.; Sorooshian, S. Uncertainty quantification of satellite precipitation estimation and Monte Carlo assessment of the error propagation into hydrologic response. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W08421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.I.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Khattak, M.U.K.; Yong, B.; Vergara, H.J. Evaluation of three high-resolution satellite precipitation estimates: Potential for monsoon monitoring over Pakistan. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 54, 670–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, D.; Li, Z.; Mishra, A.K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H. Multi-scale evaluation of six high-resolution satellite monthly rainfall estimates over a humid region in China with dense rain gauges. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 1272–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Choudhury, B.J.; Garcia, M. Multitemporal analysis of TRMM-based satellite precipitation products for land data assimilation applications. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 1165–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Hong, Y. Multi-scale evaluation of high-resolution multi-sensor blended global precipitation products over the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2013, 500, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, M.J.M.; Bastiaanssen, W.G. Local calibration of remotely sensed rainfall from the TRMM satellite for different periods and spatial scales in the Indus Basin. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 2603–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Yu, J. A high spatiotemporal gauge-satellite merged precipitation analysis over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 3063–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, A.M.; Roe, G.H.; Hallet, B.; Montgomery, D.R.; Finnegan, N.J.; Putkonen, J. Spatial patterns of precipitation and topography in the Himalaya. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 2006, 398, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gebregiorgis, A.S.; Hossain, F. Understanding the dependence of satellite rainfall uncertainty on topography and climate for hydrologic model simulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookhagen, B.; Burbank, D.W. Topography, relief, and TRMM-derived rainfall variations along the Himalaya. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L08405. [Google Scholar]
- Hirpa, F.A.; Gebremichael, M.; Hopson, T. Evaluation of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over very complex terrain in Ethiopia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Luo, Y. Quality Assessment of the TRMM Precipitation Data in Mid Tianshan Mountains. Arid Land Geogr. 2013, 36, 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, G.F.; Pu, T.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, X.B.; Liang, F. The Accuracy of TRMM Precipitation Data in Hengduan Mountainous Region, China. Sci. Geogr. Sinca 2013, 33, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Colella, M.; Chen, X. An assessment of the biases of satellite rainfall estimates over the Tibetan Plateau and correction methods based on topographic analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 301–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.F.; Thompson, S.E. Bias adjustment of satellite rainfall data through stochastic modeling: Methods development and application to Nepal. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 60, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsdon, C.; McClatchey, J.; Unwin, D.J. Spatial variations in the average rainfall–altitude relationship in Great Britain: An approach using geographically weighted regression. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derin, Y.; Yilmaz, K.K. Evaluation of multiple satellite-based precipitation products over complex topography. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1498–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Xiong, A.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P. Performance of high-resolution satellite precipitation products over China. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D02114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, M.L.M.; Rohrer, M.; Huggel, C.; Santos Villar, D.; Silvestre, E.; Huffman, G.J. Evaluation of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) performance in the central Andes region and its dependency on spatial and temporal resolution. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2649–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Mehran, A.; Norouzi, H.; Behrangi, A. Systematic and random error components in satellite precipitation data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L09406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Liu, D.; Gourley, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Huffman, G.J.; Ren, L.; Hong, Y. Global view of real-time TRMM Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis: Implication to its successor Global Precipitation Measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.Y.; Pradhanang, S.M.; Lakhankar, T.; Jha, A.K. Evaluating Satellite Products for Precipitation Estimation in Mountain Regions: A Case Study for Nepal. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4107–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Y.; Mischke, S.; Zhang, C.J.; Gao, D.; Fan, R. Ostracod distribution and habitat relationships in the Kunlun Mountains, northern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2013, 313, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.P.; Zheng, D.W.; Zheng, W.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, W.T.; Yu, J.X. Controls on decadal erosion rates in Qilian Shan: Re-evaluation and new insights into landscape evolution in north-east Tibet. Geomorphology 2014, 223, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.B.; Liu, X.H.; Qin, D.H.; Chen, T.; Wang, W.Z.; Wu, G.J.; Sun, W.Z.; An, W.L.; Zeng, X.M. Tree-ring delta δ18O evidence for the drought history of eastern Tianshan Mountains, northwest China since 1700 AD. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3336–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.F.; Liu, Y. Climatic response of Chinese pine and PDSI variability in the middle Taihang Mountains, north China since 1873. Trees 2013, 27, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.J.; Tan, L.C.; Cheng, H.; An, Z.S.; Edwards, R.L.; Kelly, M.J.; Kong, X.G.; Wang, X.F. The variation of summer monsoon precipitation in central China since the last deglaciation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 291, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.L.; Wallin1, D.O.; Hao, Z.Q. Rates and patterns of landscape change between 1972 and 1988 in the Changbai Mountain area of China and North Korea. Landsc. Ecol. 1997, 12, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, P.; Peng, P.A.; Gleixner, G.; Zheng, Z.; Pang, Z.H.; Ding, Z.L. Empirical relationship between leaf wax n-alkane delta D and altitude in the Wuyi, Shennongjia and Tianshan Mountains, China: Implications for paleoaltimetry. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 301, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Shen, Y.J.; Sun, A.; Hong, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Yang, Y.T.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Drought and flood monitoring for a large karst plateau in Southwest China using extended GRACE data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.X.; Chen, Z.Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Shi, R.H. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates over the Chinese Mainland. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11649–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Su, F.; Yang, D.; Hao, Z. Evaluation ofsatellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Chen, B.; Hong, Y.; Gourley, J.J.; Li, Z. Impact of Missing Passive Microwave Sensors on Multi-Satellite Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 668–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Hong, Y.; Cao, Q.; Gourley, J.J.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Yong, B.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, Y.; Hardy, J.; et al. Similarity and difference of the two successive V6 and V7 TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis performance over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 13060–13074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Ren, L.L.; Hong, Y.; Wang, J.H.; Gourley, J.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Chen, X.; Wang, W. Hydrologic evaluation of Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis standard precipitation products in basins beyond its inclined latitude band: A case study in Laohahe basin, China. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W07542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, T.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zheng, H. Topography and Data Mining Based Methods for Improving Satellite Precipitation in Mountainous Areas of China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 983-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6080983
Xia T, Wang Z-J, Zheng H. Topography and Data Mining Based Methods for Improving Satellite Precipitation in Mountainous Areas of China. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(8):983-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6080983
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Ting, Zhong-Jing Wang, and Hang Zheng. 2015. "Topography and Data Mining Based Methods for Improving Satellite Precipitation in Mountainous Areas of China" Atmosphere 6, no. 8: 983-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6080983
APA StyleXia, T., Wang, Z. -J., & Zheng, H. (2015). Topography and Data Mining Based Methods for Improving Satellite Precipitation in Mountainous Areas of China. Atmosphere, 6(8), 983-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6080983