Utilization of Global Precipitation Datasets in Data Limited Regions: A Case Study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Site Description
3. Datasets
3.1. Global Precipitation Dataset Products
3.1.1. Satellite Products
3.1.2. Reanalysis Products
3.1.3. Interpolated Products
3.2. Observed Precipitation and Streamflow Data
4. Methods
4.1. HBV-Light Model
4.2. Calibration of HBV-Light and Evaluation of Utility of GPDs in Data Limited Regions
4.3. Bias Correction of GPDs
4.3.1. Bias Correction with Quantile Mapping
4.3.2. Bias Correction GPDs with a Hydrological Model
4.3.3. Bias Correction of Monthly Data
5. Results
5.1. Mpanga Catchment
5.2. Kiburubutu Catchment
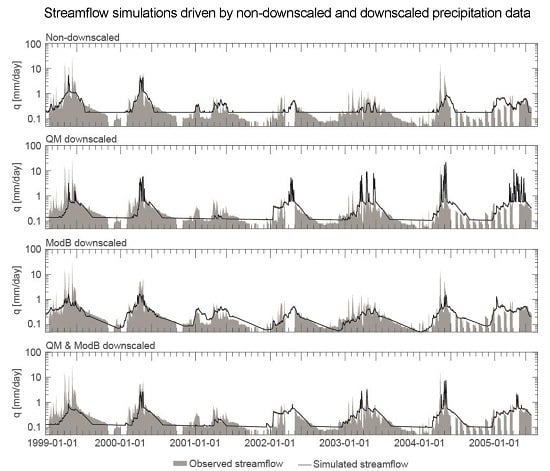
6. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
6.1. On the Potential for Using Non-Bias Corrected GPDs for Streamflow Modelling
6.2. On the Potential Limitations of Bias Correction with Rain Gauge Data in Data Limited Regions
6.3. On the Potential Utility of Considering Streamflow to Bias Correct GPDs
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sawunyama, T.; Hughes, D.A. Application of satellite-derived rainfall estimates to extend water resource simulation modelling in South Africa. Water SA 2008, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Barrios, S.; Bertinelli, L.; Strobl, E. Trends in Rainfall and Economic Growth in Africa: A Neglected Cause of the African Growth Tragedy. Rev. Econ. Stat. 2010, 92, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengoh, G.T.; Armah, F.A.; Onumah, E.E.; Odoi, J.O. Trends in Agriculturally-Relevant Rainfall Characteristics for Small-scale Agriculture in Northern Ghana. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyewa, Z.D.; Nakamura, K. Validation of TRMM Radar Rainfall Data over Major Climatic Regions in Africa. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashingia, F.; Mtalo, F.; Bruen, M. Validation of remotely sensed rainfall over major climatic regions in Northeast Tanzania. Phys. Chem. Earth 2014, 67–69, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Connor, S.; Ceccato, P. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates and Gridded Gauge Products over the Upper Blue Nile Region. In Nile River Basin; Melesse, A.M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 109–127. [Google Scholar]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M. Assessment of satellite rainfall products for streamflow simulation in medium watersheds of the Ethiopian highlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, V.; Lemann, T. Comparing CFSR and conventional weather data for discharge and soil loss modelling with SWAT in small catchments in the Ethiopian Highlands. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiemig, V.; Rojas, R.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Levizzani, V.; De Roo, A.; Thiemig, V.; Rojas, R.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Levizzani, V.; Roo, A. De Validation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products over Sparsely Gauged African River Basins. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1760–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauri, H.; Räsänen, T.A.; Kummu, M.; Lauri, H.; Räsänen, T.A.; Kummu, M. Using Reanalysis and Remotely Sensed Temperature and Precipitation Data for Hydrological Modeling in Monsoon Climate: Mekong River Case Study. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangi, A.; Khakbaz, B.; Jaw, T.C.; AghaKouchak, A.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. Hydrologic evaluation of satellite precipitation products over a mid-size basin. J. Hydrol. 2011, 397, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, K.J.; Bennett, M.E. Satellite precipitation products and hydrologic applications. Water Int. 2014, 39, 360–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ceccato, P.; Grover-Kopec, E.; Lemma, M.; Connor, S.J.; Ropelewski, C.F. Validation of satellite rainfall products over East Africa’s complex topography. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1503–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romilly, T.G.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall estimates over Ethiopian river basins. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, R.I.; Grimes, D.I.F.; Allan, R.P.; Greatrex, H.; Rojas, O.; Leo, O. Evaluation of satellite-based and model re-analysis rainfall estimates for Uganda. Meteorol. Appl. 2013, 20, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Körnich, H.; Holmgren, K. How well do reanalyses represent the southern African precipitation? Clim. Dyn. 2012, 40, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, C.; Kunstmann, H. The Hydrological Cycle in Three State-of-the-Art Reanalyses: Intercomparison and Performance Analysis. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 1397–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.-Y.Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, K.J.; Bennett, M.E. Using SWAT to model streamflow in two rivers basins with ground and satellite precipitation data 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2009, 45, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P.P. CMORPH: A Method that Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive Microwave and Infrared Data at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.D.; Jones, P.D. An improved method of constructing a database of monthly climate observations and associated high-resolution grids. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.-L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsouris, A.J.; Chen, D.; Lyon, S.W. Comparing global precipitation data sets in eastern Africa: A case study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2000–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacutt, L.A.; Herdies, D.L.; de Gonçalves, L.G.G.; Vila, D.A.; Andrade, M. Precipitation comparison for the CFSR, MERRA, TRMM3B42 and Combined Scheme datasets in Bolivia. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Elsaadani, M.; Haile, A.T. Climatology-Focused evaluation of CMORPH and TMPA satellite rainfall products over the Nile Basin. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2012, 51, 2105–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Wetterhall, F.; Seibert, J. Evaluation of different downscaling techniques for hydrological climate-change impact studies at the catchment scale. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 37, 2087–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, L.; Hao, Z.; Wang, J.; Shao, Q. Suitability of TRMM satellite rainfall in driving a distributed hydrological model in the source region of Yellow River. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, D.; Gao, B.; Jiao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Xu, T. Multiscale Hydrologic Applications of the Latest Satellite Precipitation Products in the Yangtze River Basin using a Distributed Hydrologic Model. J. Hydrometeorol. 2015, 16, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themeßl, J.M.; Gobiet, A.; Leuprecht, A. Empirical-downscaling and error correction of daily precipitation from regional climate models. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1530–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringard, J.; Seyler, F.; Linguet, L. A Quantile Mapping Bias Correction Method Based on Hydroclimatic Classification of the Guiana Shield. Sensors 2017, 17, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, S.W.; Koutsouris, A.; Scheibler, F.; Jarsjö, J.; Mbanguka, R.; Tumbo, M.; Robert, K.K.; Sharma, A.N.; van der Velde, Y. Interpreting characteristic drainage timescale variability across Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAGCOT Centre Ltd. Southern Agricultural Growth Investment Blueprint; SAGCOT Centre Ltd.: Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Tanzania Environmental Threats and Opportunities Assessment; United States Agency for International Development (USAID): Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Poméon, T.; Jackisch, D.; Diekkrüger, B. Evaluating the Performance of Remotely Sensed and Reanalysed Precipitation Data over West Africa using HBV light. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, T.G.; Rosen, P.A.; Caro, E.; Crippen, R.; Duren, R.; Hensley, S.; Kobrick, M.; Paller, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Roth, L.; et al. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberlin, P.; Philippon, N. The East African March—May Rainy Season: Associated Atmospheric Dynamics and Predictability over the 1968–97 Period. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 1002–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckenius, T. Interannual Variations of Tropical Precipitation Patterns. Mon. Weather Rev. 1981, 109, 1233–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, L.; Graham, N.E. Importance of the Indian Ocean for simulating rainfall anomalies over eastern and southern Africa. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, E.; Slingo, J.; Sperber, K.R. An Observational Study of the Relationship between Excessively Strong Short Rains in Coastal East Africa and Indian Ocean SST. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mölg, T.; Renold, M.; Vuille, M.; Cullen, N.J.; Stocker, T.F.; Kaser, G. Indian Ocean zonal mode activity in a multicentury integration of a coupled AOGCM consistent with climate proxy data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.J.; Gelaro, R.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Liu, E.; Bosilovich, M.G.; Schubert, S.D.; Takacs, L.; Kim, G.-K.; et al. MERRA: NASA’s Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3624–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Finger, P.; Meyer-Christoffer, A.; Rudolf, B.; Schamm, K.; Schneider, U.; Ziese, M. A description of the global land-surface precipitation data products of the Global Precipitation Climatology Centre with sample applications including centennial (trend) analysis from 1901–present. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2013, 5, 71–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Delaware (UDEL). Willmott, Matsuura and Collaborators’ Global Climate Resource Pages. Available online: climate.geog.udel.edu/~climate/ (accessed on 22 August 2016).
- Xue, X.; Hong, Y.; Limaye, A.S.; Gourley, J.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Khan, S.I.; Dorji, C.; Chen, S. Statistical and hydrological evaluation of TRMM-based Multi-satellite Precipitation Analysis over the Wangchu Basin of Bhutan: Are the latest satellite precipitation products 3B42V7 ready for use in ungauged basins? J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Yoo, S.; Joyce, R.; Yarosh, Y. Bias-Corrected CMORPH: A 13-Year Analysis of High-Resolution Global Precipitation. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2011, Vienna, Austria, 3–8 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dee, D.P.; Balmaseda, M.; Balsamo, G.; Engelen, R.; Simmons, A.J.; Thépaut, J.N. Toward a consistent reanalysis of the climate system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Chen, M.; Yang, S.; Yatagai, A.; Hayasaka, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Liu, C. A Gauge-Based Analysis of Daily Precipitation over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, I.; Jones, P.D.D.; Osborn, T.J.J.; Lister, D.H.H. Updated high-resolution grids of monthly climatic observations—The CRU TS3.10 Dataset. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, T.C.; Vose, R.S. An Overview of the Global Historical Climatology Network Temperature Database. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2837–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, T.C.; Karl, T.R.; Jamason, P.F.; Knight, R.; Easterling, D.R. First difference method: Maximizing station density for the calculation of long-term global temperature change. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 25967–25974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legates, D.R.; Willmott, C.J. Mean seasonal and spatial variability in gauge-corrected, global precipitation. Int. J. Climatol. 1990, 10, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Robeson, S.M. Climatologically aided interpolation (CAI) of terrestrial air temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 1995, 15, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Rowe, C.M.; Philpot, W.D. Small-scale climate maps—A sensitivity analysis of some common assumptions associated with grid-point interpolation and contouring. Am. Cartogr. 1985, 12, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, D. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM National Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–29 August 1968; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 1968; pp. 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Lindström, G.; Johansson, B.; Persson, M.; Gardelin, M.; Bergström, S. Development and test of the distributed HBV-96 hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 1997, 201, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, S. Development and Application of a Conceptual Runoff Model for Scandinavian Catchments; SMHI: Norrköping, Sweden, 1976.
- Seibert, J.; Vis, M.J.P. Teaching hydrological modeling with a user-friendly catchment-runoff-model software package. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3315–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoche, M.; Fischer, C.; Pohl, E.; Krause, P.; Merz, R. Combined uncertainty of hydrological model complexity and satellite-based forcing data evaluated in two data-scarce semi-arid catchments in Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2049–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J. Estimation of Parameter Uncertainty in the HBV Model. Nord. Hydrol. 1997, 28, 247–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Samani, Z.A. Reference Crop Evapotranspiration from Temperature. Appl. Eng. Agric. 1985, 1, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, J. Multi-criteria calibration of a conceptual runoff model using a genetic algorithm. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagg, M.; Woodhead, T.; Rijks, D.A. Evaporation in East Africa. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Bull. 1970, 15, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjemah, I.C.; Walraevens, K. Hydrogeological mapping and estimation of potential evapotranspiration and recharge rate of Quaternary sand aquifers in Dar-es-Salaam, Tanzania. Int. J. Geomat. Geosci. 2015, 6, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar]
- Maidment, D.R. Handbook of Hydrology, 1st ed.; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yan, D.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L. Effect of calibration data series length on performance and optimal parameters of hydrological model. Water Sci. Eng. 2010, 3, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusli, S.R.; Yudianto, D.; Liu, J. Effects of temporal variability on HBV model calibration. Water Sci. Eng. 2015, 8, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.J.D. An efficient method for finding the minimum of a function of several variables without calculating derivatives. Comput. J. 1964, 7, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobler, A.; Ahrens, B. Precipitation by a regional climate model and bias correction in Europe and South Asia. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piani, C.; Haerter, J.O.; Coppola, E. Statistical bias correction of daily precipitation in regional climate models over Europe. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndomba, P.M. Validation of PSIAC Model for Sediment Yields Estimation in Ungauged Catchments of Tanzania. Int. J. Geosci. 2013, 4, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W. Catchments as simple dynamical systems: Catchment characterization, rainfall-runoff modeling, and doing hydrology backward. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrugt, J.A.; ter Braak, C.J.F.; Clark, M.P.; Hyman, J.M.; Robinson, B.A. Treatment of input uncertainty in hydrologic modeling: Doing hydrology backward with Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavetski, D.; Kuczera, G.; Franks, S.W. Bayesian analysis of input uncertainty in hydrological modeling: 2. Application. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawdy, D.R.; Bergmann, J.M. Effect of rainfall variability on streamflow simulation. Water Resour. Res. 1969, 5, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, K.K.; Hogue, T.S.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Gupta, H.V.; Wagener, T. Intercomparison of Rain Gauge, Radar, and Satellite-Based Precipitation Estimates with Emphasis on Hydrologic Forecasting. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D. Bias Correction, Quantile Mapping, and Downscaling: Revisiting the Inflation Issue. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 2137–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maraun, D. Reply to “Comment on ‘Bias Correction, Quantile Mapping, and Downscaling: Revisiting the Inflation Issue’”. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1821–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maurer, E.P.; Ficklin, D.L.; Wang, W. Technical Note: The impact of spatial scale in downscaling of climate model output for hydrologic impact studies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2015, 12, 10893–10920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duethmann, D.; Zimmer, J.; Gafurov, A.; Güntner, A.; Kriegel, D.; Merz, B.; Vorogushyn, S. Evaluation of areal precipitation estimates based on downscaled reanalysis and station data by hydrological modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2415–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brath, A.; Montanari, A.; Toth, E. Analysis of the effects of different scenarios of historical data availability on the calibration of a spatially-distributed hydrological model. J. Hydrol. 2004, 291, 232–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Bárdossy, A.; Zehe, E.; He, Y. Comparison of conceptual model performance using different representations of spatial variability. J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K. A manifesto for the equifinality thesis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, A.; Babel, M.S.; Maskey, S. Analysis of future precipitation in the Koshi river basin, Nepal. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, R.; Bayabil, H.; Fares, A. Analysis of Potential Future Climate and Climate Extremes in the Brazos Headwaters Basin, Texas. Water 2016, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemig, V.; Rojas, R.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; De Roo, A. Hydrological evaluation of satellite-based rainfall estimates over the Volta and Baro-Akobo Basin. J. Hydrol. 2013, 499, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Product | Type | Spatial Resolution | Spatial Coverage | Temporal Coverage | Temporal Resolution | n * | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMORPH | Satellite | 0.25° × 0.25° | 60 N–60 S | 1998–present | 0.5 h | 9;4 | [20] |
| TRMMv7 | Satellite | 0.25° × 0.25° | 50 N–50 S | 1998–present | 3 h | 9;4 | [41] |
| CFSR | Reanalysis | 0.50° × 0.50° | 90 N–90 S | 1979–present | 6 h | 7;4 | [22] |
| ERA-i | Reanalysis | 0.75° × 0.75° | 90 N–90 S | 1979–present | 6 h | 4;2 | [42] |
| MERRA | Reanalysis | 0.67° × 0.50° | 90 N–90 S | 1979–present | 1 h | 6;2 | [43] |
| CRU | Interpolated | 0.50° × 0.50° | 90 N–90 S | 1901–2014 | Monthly | 4;2 | [21] |
| GPCC | Interpolated | 0.50° × 0.50° | 90 N–90 S | 1900–2013 | Monthly | 4;2 | [44] |
| UDEL | Interpolated | 0.50° × 0.50° | 90 N–90 S | 1900–2014 | Monthly | 4;2 | [45] |
| Parameter | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|
| FC | 100 | 1000 |
| LP | 0 | 1 |
| β | 1 | 5 |
| PERC | 0 | 6 |
| UZL | 0 | 70 |
| K0 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| K1 | 0.01 | 0.2 |
| K2 | 5E-07 | 0.1 |
| MAXBAS | 1 | 2.5 |
| PCORR * | 0.6 | 2 |
| Mpanga Catchment | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | Reff,log | R2 | Ve | RMSE | Reff,log | R2 | Ve | RMSE | ||||
| CFSR | Non- | bias corrected | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.96 | 0.28 | ModB | bias corrected | 0.43 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 0.26 |
| ERAi | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.96 | 0.23 | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.96 | 0.23 | ||||
| MERRA | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.94 | 0.29 | 0.61 | 0.58 | 0.99 | 0.22 | ||||
| CMORPH | 0.41 | 0.32 | 0.95 | 0.27 | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.95 | 0.27 | ||||
| TRMMv7 | 0.45 | 0.36 | 1.00 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.42 | 0.99 | 0.24 | ||||
| Ensemble | 0.55 | 0.49 | 0.97 | 0.23 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.99 | 0.23 | ||||
| Rain gauge | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.94 | 0.36 | 0.47 | 0.34 | 0.97 | 0.25 | ||||
| CRU * | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.98 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.96 | 0.29 | ||||
| GPCC * | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.99 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.97 | 0.29 | ||||
| UDEL * | 0.35 | 0.25 | 0.99 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.37 | 0.99 | 0.25 | ||||
| CFSR | QM | bias corrected | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.96 | 0.33 | QM + ModB | bias corrected | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.98 | 0.23 |
| ERAi | 0.18 | 0.16 | 0.91 | 0.35 | 0.54 | 0.41 | 0.98 | 0.23 | ||||
| MERRA | 0.05 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 0.52 | 0.45 | 0.98 | 0.23 | ||||
| CMORPH | 0.35 | 0.22 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 0.51 | 0.40 | 0.98 | 0.23 | ||||
| TRMMv7 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.91 | 0.35 | 0.51 | 0.42 | 0.98 | 0.24 | ||||
| Ensemble | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.91 | 0.35 | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.98 | 0.24 | ||||
| GPCC * | DP | bias corrected | 0.34 | 0.19 | 0.99 | 0.29 | DP + ModB | bias corrected | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.97 | 0.28 |
| CRU * | 0.36 | 0.24 | 0.97 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.27 | 0.95 | 0.28 | ||||
| UDEL * | 0.46 | 0.32 | 0.96 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 1.00 | 0.24 | ||||

| Kiburubutu Catchment | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP | Reff,log | R2 | Vol. Err. | RMSE | Reff,log | R2 | Vol. Err. | RMSE | ||||
| CFSR | Non- | bias corrected | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.78 | 0.26 | ModB | bias corrected | 0.41 | 0.01 | 0.74 | 0.25 |
| ERAi | 0.63 | 0.26 | 0.78 | 0.18 | 0.66 | 0.24 | 0.73 | 0.18 | ||||
| MERRA | 0.47 | 0.25 | 0.86 | 0.20 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 0.72 | 0.18 | ||||
| CMORPH | 0.56 | 0.08 | 0.79 | 0.23 | 0.62 | 0.10 | 0.68 | 0.20 | ||||
| TRMMv7 | 0.55 | 0.07 | 0.87 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 0.70 | 0.20 | ||||
| Ensemble | 0.63 | 0.19 | 0.80 | 0.19 | 0.67 | 0.22 | 0.73 | 0.19 | ||||
| Rain gauge | 0.52 | 0.25 | 0.96 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 0.21 | 0.78 | 0.20 | ||||
| CRU * | 0.42 | 0.09 | 0.97 | 0.29 | 0.57 | 0.12 | 0.70 | 0.21 | ||||
| GPCC * | 0.38 | 0.14 | 0.79 | 0.24 | 0.59 | 0.14 | 0.69 | 0.21 | ||||
| UDEL * | 0.47 | 0.12 | 0.86 | 0.23 | 0.64 | 0.16 | 0.71 | 0.19 | ||||
| CFSR | QM | bias corrected | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.92 | 0.27 | QM + ModB | bias corrected | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.71 | 0.20 |
| ERAi | 0.49 | 0.14 | 0.91 | 0.27 | 0.59 | 0.20 | 0.79 | 0.20 | ||||
| MERRA | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.96 | 0.29 | 0.53 | 0.12 | 0.75 | 0.21 | ||||
| CMORPH | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.92 | 0.27 | 0.51 | 0.08 | 0.74 | 0.22 | ||||
| TRMMv7 | 0.45 | 0.04 | 0.98 | 0.29 | 0.52 | 0.04 | 0.77 | 0.23 | ||||
| Ensemble | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.91 | 0.29 | 0.56 | 0.06 | 0.83 | 0.23 | ||||
| GPCC * | DP | bias corrected | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.96 | 0.24 | DP + ModB | bias corrected | 0.59 | 0.12 | 0.82 | 0.22 |
| CRU * | 0.51 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 0.18 | 0.83 | 0.21 | ||||
| UDEL * | 0.56 | 0.24 | 0.99 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 0.82 | 0.19 | ||||

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koutsouris, A.J.; Seibert, J.; Lyon, S.W. Utilization of Global Precipitation Datasets in Data Limited Regions: A Case Study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120246
Koutsouris AJ, Seibert J, Lyon SW. Utilization of Global Precipitation Datasets in Data Limited Regions: A Case Study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(12):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120246
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoutsouris, Alexander J., Jan Seibert, and Steve W. Lyon. 2017. "Utilization of Global Precipitation Datasets in Data Limited Regions: A Case Study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania" Atmosphere 8, no. 12: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120246
APA StyleKoutsouris, A. J., Seibert, J., & Lyon, S. W. (2017). Utilization of Global Precipitation Datasets in Data Limited Regions: A Case Study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Atmosphere, 8(12), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120246