On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Mobile Monitoring
2.3. CFD Modeling
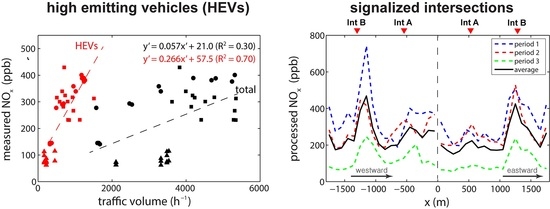
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Association with Traffic Composition
3.2. Association with Street-Canyon Ventilation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernard, S.M.; Samet, J.M.; Grambsch, A.; Ebi, K.L.; Romieu, I. The potential impacts of climate variability and change on air pollution-related health effects in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kwon, J.-W.; Jung, Y.-H.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.I.; Kim, H.-Y.; Seo, J.-H.; Kim, H.-B.; Kim, H.-C.; et al. Traffic-related air pollution is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halonen, J.I.; Blangiardo, M.; Toledano, M.B.; Fecht, D.; Gulliver, J.; Anderson, H.R.; Beevers, S.D.; Dajnak, D.; Kelly, F.J.; Tonne, C. Long-term exposure to traffic pollution and hospital admissions in London. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Diesel Engine Exhaust Carcinogenic; International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2012; Available online: http://www.iarc.fr/en/media-centre/pr/2012/pdfs/pr213_E.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Riddle, S.G.; Robert, M.A.; Jakober, C.A.; Hannigan, M.P.; Kleeman, M.J. Size-resolved source apportionment of airborne particle mass in a roadside environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6580–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Wu, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K.M. On-road emission factor distributions of individual diesel vehicles in and around Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yin, H.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K.M. On-road diesel vehicle emission factors for nitrogen oxides and black carbon in two Chinese cities. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallmann, T.R.; DeMartini, S.J.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Herndon, S.C.; Onasch, T.B.; Wood, E.C.; Harley, R.A. On-road measurement of gas and particle phase pollutant emission factors for individual heavy-duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8511–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Lipsky, E.M.; Saleh, R.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A. Characterizing the spatial variation of air pollutants and the contributions of high emitting vehicles in Pittsburgh, PA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14186–14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.F.; Rakowska, A.; Townsend, T.; Brimblecombe, P.; Chan, T.L.; Yam, Y.S.; Močnik, G.; Ning, Z. Evaluation of diesel fleet emissions and control policies from plume chasing measurements of on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, T.D.; Johnson, K.; Miller, J.W.; Maldonado, H.; Chernich, D. Emissions from heavy-duty vehicles under actual on-road driving conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4812–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maness, H.L.; Thurlow, M.E.; McDonald, B.C.; Harley, R.A. Estimates of CO2 traffic emissions from mobile concentration measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2087–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.D.; Johnson, K.C.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R., III. Emission rates of regulated pollutants from on-road heavy-duty diesel vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, C.; Jing, Q.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Dai, Y.; Huang, H.; Schipper, L.; et al. On-road emission characteristics of heavy-duty diesel vehicles in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5334–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Batterman, S. Air pollution and health risks due to vehicle traffic. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.-B.; Woo, S.H.; Bae, G.-N. NOx profile around a signalized intersection of busy roadway. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Kumar, P. Characterisation of nanoparticle emissions and exposure at traffic intersections through fast–response mobile and sequential measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Tao, L.; Miller, D.J.; Khan, M.A.; Zondlo, M.A. On-road ammonia emissions characterized by mobile, open-path measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3943–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beevers, S.D.; Kitwiroon, N.; Williams, M.L.; Carslaw, D.C. One way coupling of CMAQ and a road source dispersion model for fine scale air pollution predictions. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klompmaker, J.O.; Montagne, D.R.; Meliefste, K.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B. Spatial variation of ultrafine particles and black carbon in two cities: Results from a short-term measurement campaign. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Reis, S.; Lin, C.; Beverland, I.J.; Heal, M.R. Identifying drivers for the intra-urban spatial variability of airborne particulate matter components and their interrelationships. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghassoun, Y.; Ruths, M.; Löwner, M.-O.; Weber, S. Intra-urban variation of ultrafine particles as evaluated by process related land use and pollutant driven regression modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Ranasinghe, D.; Bunavage, K.; DeShazo, J.R.; Wu, L.; Seguel, R.; Winer, A.M.; Paulson, S.E. The effects of the built environment, traffic patterns, and micrometeorology on street level ultrafine particle concentrations at a block scale: Results from multiple urban sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittelson, D.B.; Watts, W.F.; Johnson, J.P. Nanoparticle emissions on Minnesota highways. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, E.P.; Khlystov, A.Y.; Kos, G.P.A.; Erisman, J.W. Variability of particulate matter concentrations along roads and motorways determined by a moving measurement unit. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, D.; Fruin, S.; Sax, T.; Fine, P.M.; Sioutas, C. Mobile platform measurements of ultrafine particles and associated pollutant concentrations on freeways and residential streets in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3597–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, G.S.W.; Thoma, E.D.; Baldauf, R.W. High-resolution mobile monitoring of carbon monoxide and ultrafine particle concentrations in a near-road environment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brantley, H.L.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Kimbrough, E.S.; Williams, R.W.; Mukerjee, S.; Neas, L.M. Mobile air monitoring data-processing strategies and effects on spatial air pollution trends. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2169–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, N.; Gilani, O.; Raja, S.; Batterman, S.; Ganguly, R.; Hopke, P.; Berrocal, V.; Robins, T.; Hoogterp, S. Factors affecting pollutant concentrations in the near-road environment. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Spengler, J.D.; Levy, J.I. Characterizing local traffic contributions to particulate air pollution in street canyons using mobile monitoring techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakowska, A.; Wong, K.C.; Townsend, T.; Chan, K.L.; Westerdahl, D.; Ng, S.; Močnik, G.; Drinovec, L.; Ning, Z. Impact of traffic volume and composition on the air quality and pedestrian exposure in urban street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Woo, D.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N. On-road measurements of ultrafine particles and associated air pollutants in a densely populated area of Seoul, Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, G.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Voliotis, A.; Tsakis, A.; Chasapidis, L.; Konstandopoulos, A.; Eleftheriadis, K. Concentration levels and source apportionment of ultrafine particles in road microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Fennell, P.; Britter, R. Measurements of particles in the 5–1000 nm range close to road level in an urban street canyon. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Seo, J.M.; Park, S.-B.; Baik, J.-J. Relationship between rooftop and on-road concentrations of traffic-related pollutants in a busy street canyon: Ambient wind effects. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oanh, N.T.K.; Martel, M.; Pongkiatkul, P.; Berkowicz, R. Determination of fleet hourly emission and on-road vehicle emission factor using integrated monitoring and modeling approach. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solazzo, E.; Vardoulakis, S.; Cai, X. A novel methodology for interpreting air quality measurements from urban streets using CFD modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5230–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Yang, C. Estimating urban roadside emissions with an atmospheric dispersion model based on in-field measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Sandberg, M.; Zhu, W.; Buccolieri, R.; Di Sabatino, S. City breathability in medium density urban-like geometries evaluated through the pollutant transport rate and the net escape velocity. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Wen, D.; Xiang, S.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Ultrafine-particle emission factors as a function of vehicle mode of operation for LDVs based on near-roadway monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Cui, G.X.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.S. Large eddy simulation of wind field and pollutant dispersion in downtown Macao. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2849–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Nguyen, M.T.; Steffens, J.T.; Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhang, K.M. Modeling multi-scale aerosol dynamics and micro-environmental air quality near a large highway intersection using the CTAG model. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J.; Ryu, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Urban air quality simulation in a high-rise building area using a CFD model coupled with mesoscale meteorological and chemistry-transport models. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Chambliss, S.; Isakov, V. Spatial resolution requirements for traffic-related air pollutant exposure evaluations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.-H.; Kwak, K.-H.; Bae, G.-N.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.H.; Yook, S.-J.; Jeon, S.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.-B. Overestimation of on-road air quality surveying data measured with a mobile laboratory caused by exhaust plumes of a vehicle ahead in dense traffic areas. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-J.; Baik, J.-J. A numerical study of the effects of ambient wind direction on flow and dispersion in urban street canyons using the RNG k–ε turbulence model. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.-J.; Kwak, K.-H.; Park, S.-B.; Ryu, Y.-H. Effects of building roof greening on air quality in street canyons. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J. Diurnal variation of NOx and ozone exchange between a street canyon and the overlying air. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Seo, J.; Bae, G.-N.; Lee, J.Y. A multivariate receptor modeling study of air-borne particulate PAHs: Regional contributions in a roadside environment. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Patel, M.; Kinney, P.; Chrillrud, S.; Zhang, K.M. Modeling spatial variations of black carbon particles in an urban highway-building environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, J.-J.; Park, S.-B.; Kim, J.-J. Urban flow and dispersion simulation using a CFD model coupled to a mesoscale model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Kordowski, K.; Kuttler, W. Variability of particle number concentration and particle size dynamics in an urban street canyon under different meteorological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Monitoring Period | Time of Day | Number of Trips | Wind Speed a (m s−1) | Predominant Wind Direction a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 04:21 to 09:00 LT | 13 | 1.4 | ENE (parallel) |
| 2 | 17:13 to 23:00 LT | 13 | 1.7 | WSW (parallel) |
| 3 | 23:02 to 04:00 LT | 13 | 2.0 | WNW (diagonal) |
| Pollutant | Instrument | Flow Rate (L min−1) | Time Resolution (s) | Delay Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx | AC32M, Environmental S.A. | 1 | 5 | 19 |
| BC | AE42, Magee Scientific | 5 | 30 | 28 |
| pPAH | PAS2000, EcoChem Analytics | 2 | 6 | 13 |
| PN | CPC model 5.403, GRIMM | 1.5 | 1 | 18 |
| Pollutant | Private Car | Taxi | RV/SUV | Truck | Van | Bus | Motorcycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 0.08 |
| BC | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.05 |
| pPAH | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.32 | 0.07 |
| PN | 0.42 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.16 |
| Pollutant | Measured Concentration | Converted Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Btw Int | Int A | Int B | Btw Int | Int A | Int B | |
| NOx (ppb) | 214 | 226 (6) | 265 (24) | 212 | 227 (7) | 333 (57) |
| BC (μg m−3) | 6.98 | 6.57 (–6) | 7.34 (5) | – | – | – |
| pPAH (ng m−3) | 151 | 167 (11) | 189 (25) | 157 | 198 (26) | 225 (43) |
| PN (× 104 cm−3) | 4.32 | 4.30 (–1) | 4.68 (8) | – | – | – |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwak, K.-H.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N.; Ma, Y.-I.; Sunwoo, Y.; Baik, J.-J. On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092
Kwak K-H, Woo SH, Kim KH, Lee S-B, Bae G-N, Ma Y-I, Sunwoo Y, Baik J-J. On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(3):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwak, Kyung-Hwan, Sung Ho Woo, Kyung Hwan Kim, Seung-Bok Lee, Gwi-Nam Bae, Young-Il Ma, Young Sunwoo, and Jong-Jin Baik. 2018. "On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling" Atmosphere 9, no. 3: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092
APA StyleKwak, K. -H., Woo, S. H., Kim, K. H., Lee, S. -B., Bae, G. -N., Ma, Y. -I., Sunwoo, Y., & Baik, J. -J. (2018). On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere, 9(3), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092