Scaling Reduction in Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membrane during Membrane Distillation
Abstract
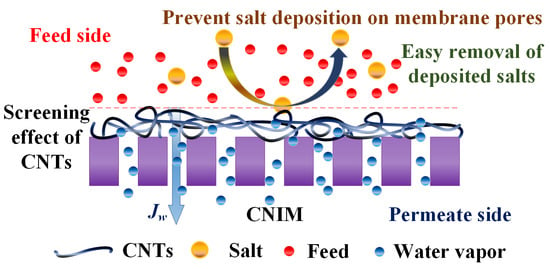
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.3. DCMD Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Membranes
3.2. Effect of Temperature and Feed Flowrate on the Water Vapor Flux
3.3. Membrane Scaling
3.4. Deposition of Salts on the Membranes
3.5. Membrane Regeneration and Stability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Warsinger, D.M.; Swaminathana, J.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Lienhard V, J.H. Scaling and fouling in membrane distillation for desalination applications: A review. Desalination 2015, 356, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humplik, T.; Lee, J.; O’Hern, S.C.; Fellman, B.A.; Baig, M.A.; Hassan, S.F.; Atieh, M.A.; Rahman, F.; Laoui, T.; Karnik, R.; et al. Nanostructured materials for water desalination. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 292001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Ragunath, S. Emerging membrane technologies for water and energy sustainability: Future prospects, constraints and challenges. Energies 2018, 11, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillén-Burrieza, E.; Blanco, J.; Zaragoza, J.; CésarAlarcón, D.; Palenzuela, P.; Ibarra, M.; Gernjak, W. Experimental analysis of an air gap membrane distillation solar desalination pilot system. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, S.; Hoang, M.; Zarzo, D.; Olewniak, F.; Campos, E.; Bolto, B.; Barron, O. Desalination techniques—A review of the opportunities for desalination in agriculture. Desalination 2015, 364, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.-X.; Yan, L.-J. Application of alternative energy integration technology in seawater desalination. Desalination 2009, 249, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ragunath, S.; Mitra, S. Effect of module configuration on the overall mass recovery in membrane distillation. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 95, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charcosset, C. A review of membrane processes and renewable energies for desalination. Desalination 2009, 245, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qtaishat, M.R.; Banat, F. Desalination by solar powered membrane distillation systems. Desalination 2013, 308, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffour, N.; Missimer, T.M.; Amy, G.L. Technical review and evaluation of the economics of water desalination: current and future challenges for better water supply sustainability. Desalination 2013, 309, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gude, V.G.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Deng, S. Renewable and sustainable approaches for desalination. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.N.; Fane, A.G.; Winston Ho, W.S.; Matsuura, T. Advanced Membrane Technology and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W.; Hilal, N.; Leo, C.P. A review on the applicability of integrated/hybrid membrane processes in water treatment and desalination plants. Desalination 2015, 363, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K. Handbook of Industrial Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Soldenhoff, K.; McCulloch, J.; Manis, A.; Macintosh, P. Nanofiltration in Metal. and Acid Recovery; Elsevier Advanced Technology: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 459–477. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shammiri, M.; Safar, M.; Al-Dawas, M. Evaluation of two different antiscalants in real operation at the Doha research plant. Desalination 2000, 128, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chae, S.-R.; Drews, A.; Kraume, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Yang, F. Recent advances in membrane bioreactors (MBRs): membrane fouling and membrane material. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1489–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Fouling in direct contact membrane distillation process. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Watanabe, Y. The effect of shear rate on controlling the concentration polarization and membrane fouling. Desalination 2000, 131, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosen, M.F.A.; SablanI, S.S.; Al-Hinai, H.; Al-Obeidani, S.; Al-belushi, R.; Jackson, D. Fouling of reverse osmosis and ultrafiltration membranes: a critical review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2261–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, E.; Curcio, E.; Ji, X.; Profio, G.D.; Sulaiman, A.O.; Fontananova, E.; Drioli, E. Membrane distillation operated at high seawater concentration factors: Role of the membrane on CaCO3 scaling in presence of humic acid. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 346, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñate, B.; García-Rodríguez, L. Current trends and future prospects in the design of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology. Desalination 2012, 284, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorgun, M.; Balcioglu, I.A.; Saygin, O. Performance comparison of ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis on whey treatment. Desalination 2008, 229, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C. Distillation vs. membrane filtration: overview of process evolutions in seawater desalination. Desalination 2002, 143, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimkhani, A.; Zhang, W.; Marhaba, T. Ceramic membrane defouling (cleaning) by air Nano Bubbles. Chemosphere 2016, 146, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Huang, H. Ultrasonic assisted direct contact membrane distillation hybrid process for membrane scaling mitigation. Desalination 2015, 375, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthukumaran, S.; Kentish, S.E.; Stevens, G.W.; Ashokkumar, M. Application of ultrasound in membrane separation processes: a review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2006, 22, 155–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humoud, M.S.; Intrchom, W.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Reduction of scaling in microwave induced membrane distillation on a carbon nanotube immobilized membrane. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Intrchom, W.; Humoud, M.; Mitra, S. Microwave-induced desalination via direct contact membrane distillation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coday, B.D.; Xu, P.; Beaudry, E.G.; Herron, J.; Lampi, K.; Hancock, N.T.; Cath, T.Y. The sweet spot of forward osmosis: Treatment of produced water, drilling wastewater, and other complex and difficult liquid streams. Desalination 2014, 333, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Warsinger, D.M.; Lienhard, V.J.H.; Duke, M.C.; Matsuura, T.; Samhaber, W.M. Wetting phenomena in membrane distillation: mechanisms, reversal, and prevention. Water Res. 2018, 139, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istirokhatun, T.; Dewi, M.N.; Ilma, H.I.; Susanto, H. Separation of antiscalants from reverse osmosis concentrates using nanofiltration. Desalination 2018, 429, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adham, S.; Hussain, A.; Matar, J.M.; Dores, R.; Janson, A. Application of membrane distillation for desalting brines from thermal desalination plants. Desalination 2013, 314, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Sirkar, K.K.; Gilron, J. Effects of antiscalants to mitigate membrane scaling by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M. Polyphosphates used for membrane scaling inhibition during water desalination by membrane distillation. Desalination 2012, 285, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Enhanced desalination using carboxylated carbon nanotube immobilized membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 120, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Roy, S.; Bhadra, M. Nanocarbon Immobilized Membranes. United States Patent US20170333848A1, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gethard, K.O.; Khow, S.; Mitra, S. Water desalination using carbon-nanotube-enhanced membrane distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 3, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragunath, S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Carbon nanotube immobilized membrane with controlled nanotube incorporation via phase inversion polymerization for membrane distillation based desalination. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bhadra, M.; Mitra, S. Enhanced desalination via functionalized carbon nanotube immobilized membrane in direct contact membrane distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 136, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, O.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Enhanced membrane distillation of organic solvents from their aqueous mixtures using a carbon nanotube immobilized membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 568, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Petrova, R.S.; Mitra, S. Effect of carbon nanotube (CNT) functionalization in epoxy-CNT composites. Nanotechnology reviews. 2018, 6, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. A bilayered structure comprised of functionalized carbon nanotubes for desalination by membrane distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 19507–19513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, M.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Flux enhancement in direct contact membrane distillation by implementing carbon nanotube immobilized PTFE membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 161, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intrchom, W.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Immobilized Membrane for Low Temperature Ammonia Removal via Membrane Distillation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Sahle-Demessie, E.; Varughese, E.; Shi, H. Polypropylene–MWCNT composite degradation, and release, detection and toxicity of MWCNTs during accelerated environmental aging. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1876–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Macedonio, F.; Drioli, E.; Aljlil, S.; Alharbi, O.A. Experimental and theoretical evaluation of temperature polarization phenomenon in direct contact membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2013, 91, 1966–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, L.M.; Ludovic, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Duke, M.C.; Gomez, J.; Gray, S. Advances in membrane distillation for water desalination and purification applications. Water 2013, 5, 94–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antony, A.; Low, J.H.; Gray, S.; Childress, A.E.; Le-Clech, P.; Leslie, G. Scale formation and control in high pressure membrane water treatment systems: a review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 383, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzotzi, C.; Pahiadaki, T.; Yiantsios, S.G.; Karabelas, A.J.; Andritsos, N. A study of CaCO3 scale formation and inhibition in RO and NF membrane processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 296, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drak, A.; Glucina, K.; Busch, M.; Hasson, D.; Laîne, J.-M.; Semiat, R. Laboratory technique for predicting the scaling propensity of RO feed waters. Desalination 2000, 132, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, R.; Merta, J.; Rosenholm, J.B. The calcite/water interface: I. Surface charge in indifferent electrolyte media and the influence of low-molecular-weight polyelectrolyte. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takizawa, Y.; Glucina, K.; Busch, M.; Hasson, D.; Laîne, J.-M.; Semiat, R. Effective Antiscaling Performance of Reverse-Osmosis Membranes Made of Carbon Nanotubes and Polyamide Nanocomposites. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6047–6055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloede, M.; Melin, T. Physical aspects of Membr. scaling. Desalination 2008, 224, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, S.; Al-Deffeeri, N.S. Impacts of different antiscalant dosing rates and their thermal performance in Multi Stage Flash (MSF) distiller in Kuwait. Desalination 2010, 250, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Control of protein (BSA) fouling in RO system by antiscalants. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, S.; Lin, C.-J.; Chen, D. Inorganic fouling of pressure-driven membrane processes—A critical review. Desalination 2010, 250, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, J.A.; Childress, A.E. Assessing short-range membrane–colloid interactions using surface energetics. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 203, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, A.; Sanciolo, P.; Vasiljevic, T.; Weeks, M.; Schroën, K.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Fouling of dairy components on hydrophobic polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membranes for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 442, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’souza, N.; Mawson, A. Membrane cleaning in the dairy industry: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakkthivel, P.; Vasudevan, T. Acrylic acid-diphenylamine sulphonic acid copolymer threshold inhibitor for sulphate and carbonate scales in cooling water systems. Desalination 2006, 197, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Salt | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | CNIM | PP-AS | CNIM-AS | |
| CaSO4 | 66 | 36 | 40 | 30.8 |
| CaCO3 | 53 | 37 | 25 | 27 |
| BaSO4 | 51 | 24 | 17 | 22 |
| Salt | Amount of Salt Deposited on the Membrane Surface (mg) | % Weight Decrease | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | PP-AS | ||
| CaSO4 | 12.4 | 8.9 | 28.2 |
| CaCO3 | 22.6 | 16.8 | 25.7 |
| BaSO4 | 6.8 | 5.3 | 22.1 |
| CNIM | CNIM-AS | ||
| CaSO4 | 8.6 | 6.4 | 25.6 |
| CaCO3 | 10.5 | 7.9 | 24.8 |
| BaSO4 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 21.2 |
| Membrane | 1st Day Flux (kg/m2∙h) | 2nd Day Flux (kg/m2∙h) | Flux Regenerated (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 39.4 | 33.5 | 85.0 |
| PP-AS | 44.4 | 39.4 | 88.7 |
| CNIM | 47.6 | 45.2 | 95.0 |
| CNIM-AS | 52.0 | 50.2 | 96.5 |
| Salt | Amount of Salt Remained on the Membrane Surface after Washing (mg) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaSO4 | PP | PP-AS | CNIM | CNIM-AS |
| 5.5 | 4.2 | 2.3 | 1.9 | |
| Removal (%) | 55.6 | 52.8 | 73.3 | 70.3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Humoud, M.S.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S. Scaling Reduction in Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membrane during Membrane Distillation. Water 2019, 11, 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122588
Humoud MS, Roy S, Mitra S. Scaling Reduction in Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membrane during Membrane Distillation. Water. 2019; 11(12):2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122588
Chicago/Turabian StyleHumoud, Madihah Saud, Sagar Roy, and Somenath Mitra. 2019. "Scaling Reduction in Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membrane during Membrane Distillation" Water 11, no. 12: 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122588
APA StyleHumoud, M. S., Roy, S., & Mitra, S. (2019). Scaling Reduction in Carbon Nanotube-Immobilized Membrane during Membrane Distillation. Water, 11(12), 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122588