Effluent Water Reuse Possibilities in Northern Cyprus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Governance Systems in Natural Resource Management
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Water Balance Situation in the Country
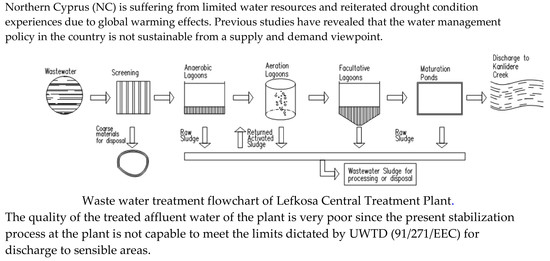
3.2. The Need for Wastewater Reuse in Northern Cyprus
3.3. Effluent Water Reuse Practices
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elkiran, G.; Turkman, F. Cisterns: How they can contribute against increasing trend of water shortage in TRNC? In Proceedings of the 6th National Hydrology Congress, Pamukkale University, Denizli, Turkey, 22–24 September 2010; pp. 793–803. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Levine, A.D. Wastewater reclamation, recycling and reuse: past, present, and future. Water Sci. Technol. 1996, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, E.; Auffarth, K.; Henze, M.; Ledin, A. Characteristics of grey wastewater. Urban Water 2002, 4, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mazumder, A.; Zhang, T.C.; Dai, C. The application of advanced materials on the water or wastewater treatment. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergil, M. The salination problem of the Guzelyurt aquifer, Cyprus. Water Resour. 2000, 34, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkiran, G.; Ergil, M. The assessment of a water budget of North Cyprus. J. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajenthira, A.; Siddiqi, A.; Anadon, L.D. A new case for promoting wastewater reuse in Saudi Arabia: Bringing energy into the water equation. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 102, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavioglu, Y. Personal Communication; Directive, H. A. T. Council Directive of 21 May 1991 Concerning Urban Waste Water Treatment (91/271/EEC); Ministry of Interior, Water Works Department: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Underground Water Treatment Plant (UWTP). Council of the European Community—Council directive concerning urban waste water treatment (91/271/EEC). Off. J. Eur. Un. 1991, 40–52. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/HTML/?uri=CELEX:31991L0271&from=EN (accessed on 28 October 2018).
- Angelakis, A.N.; Bontoux, L. Wastewater reclamation and reuse in Eureau countries. Water Policy 2001, 3, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Do Monte, M.M.; Bontoux, L.; Asano, T. The status of wastewater reuse practice in the Mediterranean basin: Need for guidelines. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2201–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkiran, G. Wastewater reuses possibilities in Northern Cyprus. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Civil and Environmental Engineering, Gemikonagi, Cyprus, 2008; pp. 56–71. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, B. Treatment technology and standards for agricultural wastewater reuse: A case study in Mexico. Irrig. Drain. J. Int. Com. Irrig. Drain. 2005, 54, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaiacovou, I. Case study-wastewater reuse in Limassol as an alternative water source. Desalination 2001, 138, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebhun, M. Desalination of reclaimed wastewater to prevent salinization of soils and groundwater. Desalination 2004, 160, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkiran, G.; Ergil, M. The water budget analysis of Girne region, North Cyprus. In Proceedings of the 6th International Congress on Advances in Civil Engineering, Bogazici University, Instanbul, Turkey, 6–8 October 2004; pp. 1238–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Muslu, T. Hotels in Northern Cyprus. Rep. No: 31.T.Ç.B.75/01-335; Ministry of Tourism and Environment, Tourism Planning Division: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Elkiran, G.; Ergil, M. Integrated water resources planning and management of North Cyprus. In Where Waters Meet: Auckland 28 November–2 December 2005: NZHS-IAH-NZSSS Auckland Conference 2005; New Zealand Hydrological Society: Wellington, New Zealand, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alberti, L.; La Licata, I.; Cantone, M. Saltwater intrusion and freshwater storage in sand sediments along the coastline: Hydrogeological investigations and groundwater modeling of Nauru Island. Water 2017, 9, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Bontoux, L.; Lazarova, V. Challenges and prospective for water recycling and reuse in EU countries. Water Sci. Technol. Water Supply 2003, 3, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Grasby, S.E.; Osadetz, K.G. Relation between climate variability and groundwater levels in the upper carbonate aquifer, southern Manitoba, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2004, 290, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkiran, G. Implementations of Integrated Water Resources Planning and Management: The Case of North Cyprus; Lambert Academic Publishing: Riga, Latvia, 2010; ISBN 978-3-8383-7902-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rist, S.; Chidambaranathan, M.; Escobar, C.; Wiesmann, U.; Zimmermann, A. Moving from sustainable management to sustainable governance of natural resources: The role of social learning processes in rural India, Bolivia and Mali. J. Rural Stud. 2007, 23, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.J.; Coleman, K.J. The multidimensionality of trust: Applications in collaborative natural resource management. Soc. Nat. Res. 2015, 28, 117–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withanachchi, S.S.; Ghambashidze, G.; Kunchulia, I.; Urushadze, T.; Ploeger, A. A paradigm shift in water quality governance in a transitional context: A critical study about the empowerment of local governance in Georgia. Water 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkiran, G.; Ergil, M. Integrated water resources planning and management of North Cyprus: Case study on water supply and demand including drought conditions. In Proceedings of the Conference on Water Observation and Information System for Decision Support BALWOIS, Ohrid, Macedonia, 23–26 May 2006; MagnaSken: Skopje, Macedonia, 2008; Available online: www.balwois.org (accessed on 15 February 2007).
- Elkiran, G.; Ongul, Z. Implications of excessive water withdrawals to the environment of Northern Cyprus. Water Environ. J. 2009, 23, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaravli, M. Groundwater Resources of Northern Cyprus. Rep. No: 118/98; Department of Geology and Mining, Ministry of Interior: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brissaud, F. Criteria for water recycling and reuse in the Mediterranean countries. Desalination 2008, 218, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixio, D.; Thoeye, C.; De Koning, J.; Joksimovic, D.; Savic, D.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. Wastewater reuse in Europe. Desalination 2006, 187, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madungwe, E.; Sakuringwa, S. Greywater reuse: A strategy for water demand management in Harare? Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A B C 2007, 32, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, F.; Kalavrouziotis, I.; Alarcón, J.J.; Koukoulakis, P.; Asano, T. Use of treated municipal wastewater in irrigated agriculture—Review of some practices in Spain and Greece. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oznel, N. Answers of the Questions Related to Treatment Plant in Haspolat; Document; Lefkoşa Turkish Municipality, Sewage Division: Lefkosa, Cyprus, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Celiker, T.E. Laboratory Results of LCTP; Lefkosa Turkish Municipality, Sewage Division: Lefkosa, Cyprus, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Oznel, N. The New LCTP and the Consequences. Rep. No: 82/76/A; Lefkosa Turkish Municipality, Sewage Division: Lefkosa, Cyprus, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fatta, D.; Anayiotou, S. MEDAWARE project for wastewater reuse in the Mediterranean countries: An innovative compact biological wastewater treatment system for promoting wastewater reclamation in Cyprus. Desalination 2007, 211, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Northern Cyprus | Resource | Volume | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Springs | 0.3 × 106 m3 | 0.3% | |
| Dams | 20.0 × 106 m3 | 20.4% | |
| Groundwater | 74.1 × 106 m3 | 75.5% | |
| Desalination | 3.7 × 106 m3 | 3.8% | |
| Total water volume | 98.1 × 106 m3 | 100% |
| Aquifers | Safe Yield (million m3) | Withdrawals (million m3) | Situation (million m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guzelyurt | 37 | 57 | −20 (deficit) |
| Yesilirmak | 7.5 | 7.5 | - |
| Girne Mountains | 11.5 | 11.5 | - |
| East Mesaria | 2 | 8.5 | −6.5 (deficit) |
| South East Mesaria | 2.5 | 2.5 | - |
| Central Mesaria | 0.5 | 0.5 | - |
| Yesilkoy | 1.6 | 3 | −1.4 (deficit) |
| Girne Coast | 5 | 5 | - |
| Karpaz | 1.8 | 1.8 | - |
| Akdeniz-Korucam | 2.7 | 2.7 | - |
| Others (spread) | 2 | 2 | - |
| Total | 74.1 | 103 | −28.9 (deficit) |
| Sector | Resource | Volume | Percentage | Overall (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Springs | 0.1 × 106 m3 | 0% | |
| Dams | 3.4 × 106 m3 | 3% | ||
| Groundwater | 96.8 × 106 m3 | 97% | ||
| Total | 100.3 × 106 m3 | 100% | 71% | |
| Domestic | Springs | 0.2 × 106 m3 | 1% | |
| Desalination | 3.7 × 106 m3 | 9% | ||
| Groundwater | 36.6 × 106 m3 | 90% | ||
| Total | 40.5 × 106 m3 | 100% | 29% | |
| Total water demand | 140.8 × 106 m3 | 100% |
| Sector | Unit | Volume | Percentage | Overall (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation | 60.8 × 106 m3 | 61% | |
| Losses | 39.5 × 106 m3 | 39% | ||
| Total | 100.3 × 106 m3 | 100% | 71% | |
| Domestic | Household | 29 × 106 m3 | 72% | |
| Institutions | 1.7 × 106 m3 | 4% | ||
| Losses | 9.8 × 106 m3 | 24% | ||
| Total | 40.5 × 106 m3 | 100% | 29% | |
| Total water demand | 140.8 × 106 m3 | 100% |
| City/Town | Completion (%) |
|---|---|
| Girne | 50 |
| Iskele | 40 |
| Mehmetcik | 15 |
| Beyarmudu | 25 |
| Lapta | 100 |
| Y. Bogazici | 25 |
| Lefkosa | 60 |
| Parameters | Inlet Water | Outlet Water | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 476 | 30 | 94 |
| COD (mg/L) | 998 | 147 | 85 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 385 | 42 | 90 |
| TP (mg/L) | 18 | 12.8 | 71 |
| TKN (mg/L) | 120 | N/A | N/A |
| Parameters | Outlet Water |
|---|---|
| Conductivity micromhos/cm (25 °C) | 3160 |
| F (mg/L) | 0.009 |
| Cl (mg/L) | 540 |
| NO2 (mg/L) | <0.05 |
| Br (mg/L) | 1.40 |
| NO3 (mg/L) | 0.3 |
| PO4 (mg/L) | 38.6 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 80 |
| HCO3 | 586 |
| Li (mg/L) | <0.001 |
| Na (mg/L) | 371 |
| NH4 (mg/L) | 120 |
| K (mg/L) | 32.2 |
| Fecal coliforms count/100 mL | >2000 |
| Mg (mg/L) | 63.7 |
| Ca (mg/L) | 106.4 |
| Parameters | Maximum Value | Minimum Percentage of Reduction (1) |
|---|---|---|
| Requirement for normal area | ||
| BOD5 | 25 mg/L O2 | 70% to 90% |
| COD | 125 mg/L O2 | 75% |
| TSS | 35 mg/L (WTPs with more than 10,000 PE) 60 mg/L (WTPs with 2000 till 10,000 PE) | 90% (for WTPs with more than 10,000 PE) (2) 70% (for WTPs with 2000 till 10,000 PE) (2) |
| Additional requirements for sensitive areas | ||
| Total P | 2 mg/L P (WTPs with 10,000 till 100,000 PE) 1 mg/L P (WTPs with more than 100,000 PE) | 80% |
| Total N (3) | 15 mg/L N (WTPs with 10,000 till 100,000 PE) (4) 10 mg/L N (WTPs with more than 100,000 PE) (3) | 70% to 80% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkiran, G.; Aslanova, F.; Hiziroglu, S. Effluent Water Reuse Possibilities in Northern Cyprus. Water 2019, 11, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020191
Elkiran G, Aslanova F, Hiziroglu S. Effluent Water Reuse Possibilities in Northern Cyprus. Water. 2019; 11(2):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020191
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkiran, Gozen, Fidan Aslanova, and Salim Hiziroglu. 2019. "Effluent Water Reuse Possibilities in Northern Cyprus" Water 11, no. 2: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020191
APA StyleElkiran, G., Aslanova, F., & Hiziroglu, S. (2019). Effluent Water Reuse Possibilities in Northern Cyprus. Water, 11(2), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020191