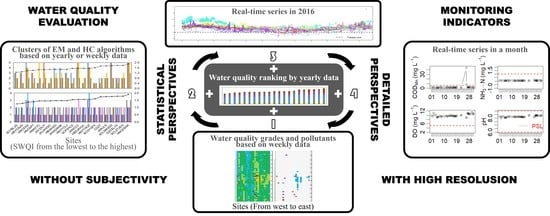
Water Quality Evaluation of the Yangtze River in China Using Machine Learning Techniques and Data Monitoring on Different Time Scales
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Monitoring Sites
2.2. Monitoring Methods and Data Sources
2.3. Water Quality Indices and Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Water Quality of SWQI and Grades
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
Coefficient of Variation
Clustering Analyses
Correlation Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Water Quality Indices and SWQI Ranking of Sites in the YRB
3.2. Water Quality Grades and Main Pollutants of the YRB Sites
3.3. Clustering Analysis of Water Quality at the YRB Sites
3.3.1. Clustering Algorithms vs Single Indices Based on Yearly Monitoring Data
3.3.2. Pollution Characteristics Using EM Clustering for Yearly and Weekly Monitoring Data
3.3.3. Temporal Distribution Characteristics Using HC Clustering and Weekly Monitoring Data
3.4. Real-Time Series Analyses of the YRB Sites
3.5. Temporal Correlation Analyses between Different Sites
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitation of SWQI and Yearly Data for Water Quality Evaluation
4.2. The Application of Multiple Classifications and Correlations for Water Quality Evaluation
4.3. Necessity of Real-time Monitoring for Water Quality Interpretation
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CODMn | permanganate index for chemical oxygen demand |
| CV | coefficient of variation |
| DO | dissolved oxygen |
| EM | expectation-maximization clustering |
| HC | hierarchical clustering |
| NH3-N | ammonia nitrogen |
| PSL | polluted standard limit |
| YRB | Yangtze River Basin |
References
- Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, C.; Lu, Y.; He, G.; Giesy, J.P. Determination of water environment standards based on water quality criteria in China: Limitations and feasibilities. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 57, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Environmental Protection Administration and General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; No. GB3838-2002; State Environmental Protection Administration and General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine: Beijing, China, 2002. Available online: http://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/standards/water_environment/quality_standard/200710/W020061027509896672057.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. U.S. Clean Water Act Action Plan, 2009; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- Minister of Ministry of Environmental Protection, The People’s Republic of China. 2016 Report on the State of the Environment in China. Available online: http://english.mee.gov.cn/Resources/Reports/soe/ReportSOE/201709/P020170929573904364594.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Editorial Committee of Changjiang & Southwest Rivers Water Resources Bulletin 2016. Available online: http://www.cjw.gov.cn/UploadFiles/zwzc/2017/8/201708281625181596.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Wong, H.; Hu, B.Q. Application of interval clustering approach to water quality evaluation. J. Hydrol. 2013, 491, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srdjevic, B. Linking analytic hierarchy process and social choice methods to support group decision-making in water management. Decis. Support Syst. 2007, 42, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Duque, W.; Ferre-Huguet, N.; Domingo, J.L.; Schuhmacher, M. Assessing water quality in rivers with fuzzy inference systems: A case study. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y. Studies on the Evaluation System for Surface Water Quality Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, P.; Yang, W. Environment Assessment and Protection; The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press: Zhengzhou, China, 2012; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; He, B.; Zhu, X.; Zou, R.; Zhu, Y. Three-dimensional hydrodynamic and water quality model for TMDL development of Lake Fuxian, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behmel, S.; Damour, M.; Ludwig, R.; Rodriguez, M.J. Water quality monitoring strategies-A review and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 1312–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Wu, W.; Yao, Y.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Bi, J.; Yao, R. Coupling watershed environmental model with optimizing method to provide least cost alternatives in environmental planning and management. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2015, 24, 539–546. [Google Scholar]
- Eggimann, S.; Mutzner, L.; Wani, O.; Schneider, M.Y.; Spuhler, D.; de Vitry, M.M.; Beutler, P.; Maurer, M. The Potential of Knowing More: A Review of Data-Driven Urban Water Management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2538–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, U.; Sànchez-Marrè, M.; Ceccaroni, L.; R-Roda, I.; Poch, M. Artificial intelligence and environmental decision support systems. Appl. Intell. 2000, 13, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chini, C.M.; Stillwell, A.S. The state of us urban water: data and the energy-water nexus. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1796–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.M.P.; Hallett, S.H.; Jude, S. Leveraging big data tools and technologies: addressing the challenges of the water quality sector. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, N.S.V.; Falk, A.K.V.; Borup, M.; Madsen, H.; Mikkelsen, P.S. Model predictive control of urban drainage systems: A review and perspective towards smart real-time water management. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 279–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rauch, W.; Urich, C.; Bach, P.M.; Rogers, B.C.; de Haan, F.J.; Brown, R.R.; Mair, M.; McCarthy, D.T.; Kleidorfer, M.; Sitzenfrei, R.; et al. Modelling transitions in urban water systems. Water Res. 2017, 126, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, Y.H.; Fu, D.F.; Minh, H.D.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Zevenbergen, C.; Pathirana, A. Urban surface water quality, flood water quality and human health impacts in Chinese cities. What do we know? Water 2018, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, D.K.; Ahmadisharaf, E.; Padmanabhan, G.; Imen, S.; Mohamoud, Y.M. Watershed models for development and implementation of total maximum daily loads. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2019, 24, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.M.; Klein, C.; Funfrocken, E.; Kautenburger, R.; Beck, H.P. Real-time monitoring of water quality to identify pollution pathways in small and middle scale rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.P.; Zhang, F.; Kung, H.T.; Ghulam, A.; Trumbo, A.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Ren, Y.; Jing, Y.Q. Evaluation and estimation of surface water quality in an arid region based on EEM-PARAFAC and 3D fluorescence spectral index: A case study of the Ebinur Lake Watershed, China. Catena 2017, 155, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.; Bealing, D. Organic pollution: Biochemical oxygen demand and ammonia. In Handbook of Ecotoxicology; Calow, P., Ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxfod, UK, 2009; p. 69. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. 1993. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/15669.html (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Latif, U.; Dickert, F.L. Chemical oxygen demand. In Environmental Analysis by Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: Applications; Moretto, L.M., Kalcher, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 719–728. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Escher, B.I.; Fenner, K.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Johnson, C.A.; von Gunten, U.; Wehrli, B. The challenge of micropollutants in aquatic systems. Science 2006, 313, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghabozorgi, S.; Seyed Shirkhorshidi, A.; Ying Wah, T. Time-series clustering–A decade review. Inform. Syst. 2015, 53, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtagh, F.; Downs, G.; Contreras, P. Hierarchical clustering of massive, high dimensional data sets by exploiting ultrametric embedding. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 2008, 30, 707–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F. Hierarchical Clustering of Observations and Features in High-Dimensional Data. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Han, F.; Liu, H. Challenges of big data analysis. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2014, 1, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, C.B.; Batzoglou, S. What is the expectation maximization algorithm? Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Editorial Committee of Encyclopedia of Rivers and Lakes in China. Section of Changjiang River Basin (Vol.One). In Encyclopedia of rivers and lakes in China; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2010; p. 510. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wikipedia. Yangtze. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yangtze (accessed on 30 August 2018).
- Xinhua. China Releases Yangtze Environmental Protection Plan. Available online: http://english.mep.gov.cn/News_service/media_news/201707/t20170724_418374.shtml (accessed on 30 August 2018).
- Xinhua. China Battles Chemical Pollution along Yangtze. Available online: http://english.mep.gov.cn/News_service/media_news/201610/t20161011_365297.shtml (accessed on 30 August 2018).
- Cheng, L.; Opperman, J.J.; Tickner, D.; Speed, R.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D. Managing the three gorges dam to implement environmental flows in the Yangtze River. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Weekly Reports on Automatic Monitoring Data of National Water Quality; China National Environmental Monitoring Centre: Beijing, China, 2016; Available online: http://www.cnemc.cn/sssj/szzdjczb/ (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. The Publishing System of Real-Time Automatic Monitoring Data of National Surface Water Quality; China National Environmental Monitoring Centre: Beijing, China, 2016; Available online: http://58.68.130.147/# (accessed on 3 December 2017).
- General Office of Ministry of Environmental Protection. Ministry of Environmental Protection, the People’s Republic of China (MEP General Office [2017] No. 51), Beijing. 2017. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgt/201706/W020170615563179786247.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Ji, X.; Sun, Z.; Chen, Y. Method study on sequence of city surface water environmental quality. Environ. Monit. Chin. 2016, 32, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- General Office of Ministry of Environmental Protection. Ministry of Environmental Protection, the People’s Republic of China (MEP General Office [2011] No. 22), Beijing. 2011. Available online: http://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgt/201104/W020110401583735386081.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2018).
- Brown, C.E. Coefficient of variation. In Applied Multivariate Statistics in Geohydrology and Related Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 155–157. [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh, F.; Legendre, P. Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J. Classif. 2014, 31, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charrad, M.; Ghazzali, N.; Boiteau, V.e.; Niknafs, A. NbClust: An R package for determining the relevant number of clusters in a data set. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 61, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrucca, L.; Fop, M.; Murphy, T.B.; Raftery, A.E. Mclust 5: Clustering, classification and density estimation using gaussian finite mixture models. R J. 2016, 8, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Statistics. China Social Statistical Yearbook 2017; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2017; p. 433.
- Shrestha, S.; Kazama, F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2007, 22, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Dong, L.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Ni, G.H.; Feng, S.X. Effect of reservoir’s initial impoundment and climatic conditions on the dissolved oxygen in downstream reaches: A case study on Xiangjiaba and Xiluodu Reservoirs. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 2575–2586. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lin, P.F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Chen, C. Treatment technologies and mechanisms for three odorants at trace level: IPMP, IBMP, and TCA. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.K. The expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1996, 13, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Quality Criteria for Water 1986; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Aquatic Life Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Ammonia -Freshwater 2013; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Gerhardt, A. Review of impact of heavy metals on stream invertebrates with special emphasis on acid conditions. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 1993, 66, 289–314. [Google Scholar]
- Altenburger, R.; Ait-Aissa, S.; Antczak, P.; Backhaus, T.; Barcelo, D.; Seiler, T.B.; Brion, F.; Busch, W.; Chipman, K.; de Alda, M.L.; et al. Future water quality monitoring-Adapting tools to deal with mixtures of pollutants in water resource management. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, B.; Berg, M.; Yao, Z.P.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, D.; Pfluger, A. How polluted is the Yangtze River? Water quality downstream from the Three Gorges Dam. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 402, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| No | Site Code | Site Name Cronym | River Name | Province Name | Reaches of the YRB | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SC1 | SCPZHLD | Yangtze River | Sichuan | Upper | 101.66° E | 26.59° N |
| 2 | SC2 | SCLSMJDQ | Minjiang River | Sichuan | Upper | 103.76° E | 29.51° N |
| 3 | SC3 | SCYBLJG | Minjiang River | Sichuan | Upper | 104.43° E | 28.78° N |
| 4 | SC4 | SCLZTJEQ | Tuojiang River | Sichuan | Upper | 105.45° E | 28.90° N |
| 5 | GZ1 | GZCSLYX | Chishui River | Guizhou | Upper | 105.74° E | 28.61° N |
| 6 | CQ1 | CQZT | Yangtze River | Chongqing | Upper | 105.85° E | 29.02° N |
| 7 | SC5 | SCGYQFX | Jialing River | Sichuan | Upper | 105.88° E | 32.67° N |
| 8 | HB1 | HBYCNJG | Yangtze River | Hubei | TGD | 111.27° E | 30.76° N |
| 9 | HB2 | HBDJKHJL | Danjiangkou Reservoir | Hubei | Middle | 111.50° E | 32.57° N |
| 10 | HeN1 | HNNYTC | Danjiangkou Reservoir | Henan | Middle | 111.71° E | 32.67° N |
| 11 | HuN1 | HNCDPT | Yuan River | Hunan | Middle | 112.13° E | 28.92° N |
| 12 | HuN2 | HNCDSHK | Lishui River | Hunan | Middle | 112.13° E | 29.47° N |
| 13 | HuN3 | HNYYWJZ | Zishui River | Hunan | Middle | 112.63° E | 28.80° N |
| 14 | HuN4 | HNCSXG | Xiangjiang River | Hunan | Middle | 112.84° E | 28.34° N |
| 15 | HuN5 | HNYYCLJ | Yangtze River | Hunan | Middle | 113.23° E | 29.54° N |
| 16 | HB3 | HBWHZG | Han River | Hubei | Middle | 114.22° E | 30.58° N |
| 17 | JX1 | JXJJHXSC | Yangtze River | Jiangxi | Middle | 115.75° E | 29.81° N |
| 18 | JX2 | JXNCCC | Gan River | Jiangxi | Middle | 116.08° E | 28.77° N |
| 19 | AH1 | AHAQWHK | Yangtze River | Anhui | Lower | 117.03° E | 30.50° N |
| 20 | JS1 | JSNJLS | Yangtze River | Jiangsu | Lower | 118.52° E | 31.89° N |
| 21 | JS2 | JSYZSJY | Jiajiang River | Jiangsu | Lower | 119.65° E | 32.35° N |
| Levels | I | II | III * | IV | V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indices (units) | ||||||
| pH | 6–9 | |||||
| DO (mg L−1) ≥ | 7.5 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| CODMn (mg L−1) ≤ | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 15 | |
| NH3-N (mg L−1) ≤ | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | |
| Methods | Cluster Class Name | Input Data * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yearly Means | CWQI (i) | Ratio of Unpolluted Weeks | CV (i)s | Weekly Means | |||
| EM | EM_Y | EM_Class_Y | Yes (4) | ||||
| EM_R | EM_Class_R | Yes (4) | Yes | ||||
| EM_CV | EM_Class_CVR | Yes | Yes (4) | ||||
| HC | HC_Y | HC_Class_Y | Yes (4) | ||||
| HC_pH | HC_Class_pH | Yes (1 − pH) | |||||
| HC_DO | HC_Class_DO | Yes (1 − DO) | |||||
| HC_COD | HC_Class_COD | Yes (1 − CODMn) | |||||
| HC_NH | HC_Class_NH | Yes (1 − NH3-N) | |||||
| Site Code | Yearly Means | CVs of Weekly Means | Maximums of Weekly Means | Minimums of Weekly Means | Polluted Standard Limits (PSL) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | DO | CODMn | NH3-N | pH | DO | CODMn | NH3-N | pH | CODMn | NH3-N | pH | DO | pH | DO | CODMn | NH3-N | |
| SC1 | 8.04 | 9.07 | 1.8 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 1.81 | 8.52 | 4.3 | 2.25 | 7.47 | 7.09 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| SC2 | 7.40 | 8.08 | 2.9 | 0.46 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.33 | 0.55 | 7.85 | 4.9 | 1.87 | 6.78 | 6.39 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| SC3 | 7.31 | 8.63 | 2.0 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 8.01 | 3.3 | 0.28 | 6.63 | 6.57 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| SC4 | 7.83 | 7.49 | 3.3 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 8.32 | 5.5 | 0.30 | 7.50 | 5.33 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| GZ1 | 8.05 | 8.54 | 2.5 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.64 | 0.75 | 8.91 | 6.8 | 1.10 | 7.29 | 4.59 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| CQ1 | 7.84 | 7.45 | 2.4 | 0.25 | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 8.62 | 6.5 | 0.56 | 6.86 | 5.21 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| SC5 | 8.31 | 9.03 | 1.8 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.55 | 0.86 | 8.62 | 8.3 | 0.49 | 7.94 | 6.92 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HB1 | 7.50 | 8.49 | 1.9 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.29 | 1.16 | 8.09 | 3.6 | 0.73 | 6.40 | 6.75 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HB2 | 7.95 | 8.61 | 2.1 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.30 | 8.42 | 3.3 | 0.38 | 6.89 | 6.47 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HeN1 | 7.94 | 9.12 | 2.1 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.48 | 8.66 | 2.8 | 0.20 | 7.18 | 7.39 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HuN1 | 7.63 | 10.0 | 1.9 | 0.26 | 0.04 | 0.26 | 0.57 | 1.50 | 8.39 | 4.9 | 2.88 | 7.12 | 6.04 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HuN2 | 7.89 | 8.40 | 1.6 | 0.58 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.47 | 9.12 | 2.6 | 2.27 | 7.10 | 6.18 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HuN3 | 7.12 | 6.22 | 1.9 | 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.37 | 1.02 | 8.29 | 4.1 | 2.09 | 6.12 | 2.69 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HuN4 | 7.10 | 6.16 | 2.0 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.55 | 7.77 | 3.8 | 0.46 | 6.21 | 3.82 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HuN5 | 7.64 | 7.75 | 2.0 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 8.34 | 2.9 | 0.36 | 6.77 | 6.15 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| HB3 | 7.61 | 8.51 | 2.4 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.44 | 8.55 | 4.6 | 0.44 | 6.91 | 4.08 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| JX1 | 7.52 | 7.99 | 2.7 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.39 | 7.81 | 4.9 | 0.26 | 7.33 | 5.47 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| JX2 | 6.88 | 7.83 | 3.0 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 8.78 | 5.1 | 0.67 | 6.01 | 5.99 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| AH1 | 7.47 | 7.74 | 2.5 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 7.76 | 3.3 | 0.52 | 7.11 | 5.64 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| JS1 | 7.91 | 7.80 | 2.5 | 0.23 | 0.03 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.41 | 8.61 | 5.8 | 0.76 | 7.43 | 4.75 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
| JS2 | 7.32 | 7.99 | 2.7 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.69 | 7.67 | 5.2 | 0.95 | 7.01 | 4.34 | 6–9 | 5 | 6 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di, Z.; Chang, M.; Guo, P. Water Quality Evaluation of the Yangtze River in China Using Machine Learning Techniques and Data Monitoring on Different Time Scales. Water 2019, 11, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020339
Di Z, Chang M, Guo P. Water Quality Evaluation of the Yangtze River in China Using Machine Learning Techniques and Data Monitoring on Different Time Scales. Water. 2019; 11(2):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020339
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi, Zhenzhen, Miao Chang, and Peikun Guo. 2019. "Water Quality Evaluation of the Yangtze River in China Using Machine Learning Techniques and Data Monitoring on Different Time Scales" Water 11, no. 2: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020339
APA StyleDi, Z., Chang, M., & Guo, P. (2019). Water Quality Evaluation of the Yangtze River in China Using Machine Learning Techniques and Data Monitoring on Different Time Scales. Water, 11(2), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11020339